Trends In Hiv Transmission In The United States
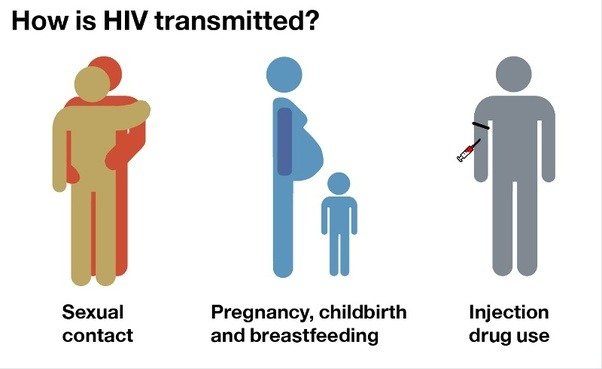
HIV is most commonly transmitted by sexual contact and the sharing of contaminated needles by injection drug users . By the end of 2000, an estimated 900,000 Americans were living with HIV. Approximately 40,000 new cases of active AIDS disease are diagnosed annually . Historically, HIV has been most prevalent among men who have sex with men whereas most new HIV infections are reported among men who have sex with men and among injection drug users . Recently, however, the proportion of HIV cases acquired through heterosexual contact has increased and almost equals the proportion of cases attributable to injection drug use . The proportion of all AIDS cases reported among women has tripled since the mid-1980s, primarily as a result of heterosexual exposure and secondarily through injection drug use . Minority groups are the most heavily affected by HIV associated with drug injection, and Blacks and Hispanics now account for an estimated 70 percent of all new AIDS cases .
What Is The Connection Between Hiv And Substance Use
Substance use is the use of drugs and alcohol and includes the misuse of prescription drugs and over-the-counter medicines. Substance use is related to HIV in the following ways:
- Use of alcohol and recreational drugs can lead to risky behaviors that increase the chances of getting HIV or passing it on to others . Recreational drugs include injection and non-injection drugs, such as opioids , methamphetamine , crack cocaine, and inhalants . Some prescription drugs and over-the-counter medicines contain stimulants that when used inappropriately can also lead to risky behaviors.
- Substance use can harm the health of a person with HIV. Specifically, drug and alcohol use can weaken the immune system and damage the liver.
What Are The Uk Guidelines On Alcohol
New UK guidelines on alcohol were published in 2016. The UK Chief Medical Officers recommendation is that people should not regularly drink more than 14 units of alcohol a week. This applies to both men and women.
A unit of alcohol is around:
- a third of a pint of beer, lager or cider
- half a standard glass of wine
- a single measure of spirits
- a small glass of sherry or port .
It is also recommended that you spread your alcohol intake over the week rather than saving up your units for one session often called binge drinking but also try to have some alcohol-free days each week.
Binge drinking can lead to poor co-ordination, vomiting, exaggerated emotional reactions and loss of memory. It can also lead to heart problems, alcohol poisoning and unconsciousness.
A good tool to help you calculate how many units of alcohol there are in your drinks is: www.drinkaware.co.uk/understand-your-drinking/unit-calculator
Alcohol can contain a lot of calories so if you are trying to lose weight then youll need to take into account how much you are drinking.
Drinking alcohol during pregnancy can harm the unborn baby, so women who are pregnant or planning to become so, are advised to avoid alcohol.
Also Check: What Race Has The Highest Hiv Rate
Can You Catch Hiv From Drinking Another Persons Blood
If you simply touch the blood of a person living with HIV with your hands, there is no chance of transmitting the virus, as HIV is not passed through skin contact. However, if the blood is put into an open wound , then there is risk of HIV transmission.
But lets talk about blood drinking, because that is the question at hand.
In theory, you can acquire HIV by drinking an HIV positive persons blood. But we dont know what the actual risk is we have no reliable studies or documented cases in reputable medical literature of a person getting HIV by drinking blood. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention does not include drinking blood in its rundown of the HIV acquisition odds from various events. But as we stated earlier, there is a theoretical risk if the blood of a person who 1) is living with HIV and 2) has a detectable HIV viral load comes into contact with another persons mucous membraneand there are plenty of mucous membranes along the digestive tract.
While there is that theoretical chance that you can get HIV from drinking an HIV-positive persons blood if youre HIV negative, its impossible to get it by drinking your own blood. If you are HIV negative, you cannot give yourself HIV. If you are living with HIV, you already have the virus and cannot change that status. Nobody can give any STI to themselves thats why you are actually your safest sex partner.
Characteristics Of Participants Using Antiretrovirals Compared To Those Not On Antiretrovirals

There were 87 participants who were not on antiretrovirals at the beginning of the study. These participants were significantly younger , with higher percentage of women , and had significantly higher CD4+ cell counts than those who were on ART. The mean viral load of those not on ART was 98,758.5±178,576. There were no significant differences in drug and alcohol use between the two groups. Three hundred and twenty-five person-years of follow-up were completed for individuals on ART and 175 person-years for participants not on ART.
Read Also: Can Someone Who Is Hiv Positive But Undetectable Transmit
Getting Treatment For Alcohol Use
Substance and alcohol use are directly correlated with the increased risk of contracting HIV and the decreased effectiveness of HIV treatment. People who use alcohol while undergoing HIV treatment are much more likely to experience a number of complications, including increased infections and liver damage.
Getting treatment for alcohol use and addiction is imperative for individuals who are also HIV positive. There are several treatment options available for overcoming an alcohol addiction, many of which can be administered alongside HIV treatment.
Many people find great success through formal treatment programs such as inpatient alcohol rehab treatment. Inpatient programs require individuals to participate in residential treatment for several weeks or months. Many programs provide customized plans of recovery for each patient.
To learn more about how alcohol use affects people with HIV, contact a treatment specialist today.
Contact Vertava Health Now
Can I Get Hiv By Drinking Out Of The Same Glass As An Infected Person
Absolutely not. There is no risk whatsoever in using a glass, a cup, a plate, a spoon or any other everyday household object that a person living with HIV has used.
For HIV to be transmitted, the virus has to be present in a body fluid which then enters another person’s bloodstream. However HIV is not present in infectious quantities in saliva. Just as there is no risk in kissing a person with HIV, there is no risk in using an object that has had contact with their saliva.
While we’re on the subject of ways you can’t get HIV, it’s also impossible to acquire the infection from a toilet seat, from a swimming pool, through mosquito bites, by donating blood, or through contact with saliva, tears, sweat, feces or urine.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Treatment For Hiv Aids
Which Bodily Fluids Carry Hiv
So, how is HIV transmitted? HIV is spread through only a select number of bodily fluids: sexual fluids , breast milk, and blood. HIV is transmitted by the passage of the virus from one person to another by having the virus come in contact with the blood of another, Gersh says.
The virus can get into the body through any opening of the skin or mucous membranes, including the rectum or vagina. It can also be transmitted through direct blood-to-blood cuts or wounds, or by sharing injection needles.
HIV can only be transmitted sexually if the person living with HIV has a detectable viral loadthat is, the amount of HIV in a persons bloodstream is high enough to show up within a type of blood test known as an HIV viral load test. The higher a persons viral load, the more likely it is that another person may contract HIV from them during sex if other forms of protection arent used.
The point being: Because blood is one of the fluids that carries HIV, its important to discuss transmission in the context of blood play.
Help With Alcohol Problems
Alcohol dependency is common in people living with HIV in the UK and heavy drinking may affect your immune system and slow down recovery from infections.
If you are concerned about your alcohol use, speak to a member of your healthcare team. There are also lots of organisations who can give you advice and support.
Alcohol Concern, one of the UKs largest alcohol charities, can be contacted via www.alcoholconcern.org.uk, or phone Drinkline on 0300 123 1110.
The website Drinkaware provides a list of support services that may be helpful.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Current Transmission Rate Of Hiv
Drugs And Alcohol: Interactions With Your Hiv Meds
HIV medications can be hard on your body. When you are taking these medications, it is important that your liver works as well as possible. The liver is responsible for getting rid of waste products from the medications.
When you are HIV positive, your body may react differently to alcohol and drugs. Many people find that it takes longer to recover from using pot, alcohol, or other recreational drugs than it did before they had HIV.
Remember that having HIV means a major change has taken place in your body. You may choose to use alcohol and drugs in moderation, but be sure to respect your body. Pay attention to what and how much you eat, drink, smoke, and take into your body.
Certain HIV medications can boost the level of recreational drugs in your system in unexpected and potentially dangerous ways. For example, amphetamines can be present at 3 to 22 times their normal levels in the bloodstream when mixed with an HIV drug called ritonavir . That’s because ritonavir affects the body’s ability to break down these other drugs.
If you are going to take a recreational drug while you are on HIV medication, it is better to start with a very low amount of the recreational drug and allow time to see how it affects you before increasing the amount. Keep in mind that recreational drugs aren’t regulated, so you never know exactly how much you are getting.
Does Alcohol Use Impact Hiv
Research has shown that the effects of alcohol are more significant in people who have HIV compared to those who dont. This means that even regular alcohol use can have a significant impact on the health of someone with HIV. This is true even in those individuals whose virus has been suppressed through treatment.
Unfortunately, alcohol use among individuals with HIV is high. In fact, some studies have shown that people who are HIV positive are twice as likely to participate in heavy drinking than those who are not.
Ways in which alcohol can negatively impact a person with HIV include:
- increase the risk of hepatic injury
- increase the possibility of side effects experienced from medication
- change the way in which medication acts in the body
- reduce the likelihood that someone will practice safe sex
- increase the risk of liver damage
Additionally, alcohol is known to weaken a persons immune system. This is especially harmful to people with HIV, since the virus itself significantly impacts a persons immune system. By further weakening the immune system, alcohol use raises an individuals risk of infection as well as increases the likelihood of damage done by the virus itself.
Whats more, people who are HIV positive and use alcohol are less likely to have positive results when taking antiretroviral medications. In fact, someone who uses alcohol is two to four times less likely to experience improvement from ART.
Don’t Miss: Can You Catch Hiv Twice
Study Design Settings And Participants
A cross-sectional study was conducted among 132 HIV infected individuals who received antiretroviral therapy at the ART clinic of the Sukraraj Tropical and Infectious Disease Hospital a national-level government health care facility for infectious disease control in Kathmandu, Nepal. The STIDH is one of the largest ART clinics in Nepal that provides HIV counseling, testing, nutritional supports, antiretroviral medicines, medical care, opportunistic infection treatment and medicine services. HIV-infected individuals aged 18 years and older were eligible participants of the study. All the participants were randomly selected. We developed a list of 1447 ART receiving clients. The first list was developed using a simple random sampling technique that included 132 clients the second list was developed when we were not able to interview the clients from the first list. We calculated sample size using a conservative formula with 50% prevalence, 95% confidence level, 10% margin of error and 30% no-response, resulting in a total sample estimation of 132 HIV infected individuals. The study was conducted between September and December 2014 and the response rate was 100%.
Drugs Alcohol And Safer Sex
Many drugs, including alcohol and methamphetamine, may affect your ability to make decisions.
Even if you take your HIV medications regularly and practice safer sex when you’re not high, when you’re under the influence of methamphetamine or other drugs you may be willing to take more risks. For example, you might not use a condom or take your HIV medications.
Alcohol also can affect the decisions you make about safer sex. For example, if you have too much to drink, you may not remember where you put the condoms, and decide simply not to use them. These are decisions you probably would not make if you were sober.
These actions put your partner at risk for HIV and put you at risk for other sexually transmitted diseases or for pregnancy.
Remember to take your HIV medications every day, and to keep condoms handy in places where you might have sex. Also, try to limit the amount of drugs you use or alcohol you drink if you know you are going to have sex.
You May Like: Is Hiv And Herpes The Same Thing
Effect Of Alcohol Use On Hiv Viral Load
Our findings indicated that HIV viral load in participants reporting frequent alcohol use at any time point of the study had a higher mean HIV viral load independent of ART, compared to those who abstained or did not use alcohol frequently. However, when participants were divided into those receiving ART and those not on ART for subset analyses, those without ART who used alcohol frequently did not have significantly increased viral load as compared to those who were not frequent alcohol users. On the other hand, frequent alcohol users who were on ART had a significantly higher viral load across all time points than those who were either moderate alcohol drinkers or abstainers. Only a relatively low percentage of those on ART had attained viral load control over time, which is consistent with previous literature with similar populations. Samet et al.31 found that less than half of at-risk drinkers adhered to ART regimens, and others32 found that only 24% of those on ART in a population of drug users and only 14% of heavy alcohol users within this population were able to achieve controlled viral load. These results suggest that the mechanism for diminished HIV viral control in frequent alcohol drinkers is mediated by reduced adherence to ART, and not a direct result of alcohol abuse on viral load.
Is It Safe To Drink Alcohol If You Have Hiv
In the past 35 years, HIV infection has transformed from an illness that was almost invariably fatal to a chronic disease that can be managed. HIV medications have made it possible to control the HIV, which has led to dramatically increased survival and longer lives for people with HIV.
While scientists continue the search for a cure, research is also being conducted to understand how people with HIV can achieve maintain health as they age, and to identify barriers to successful self-management.
One such barrier is the use of alcohol.
Alcohol is the most widely abused substance in the United States, and estimates as high as 50 percent of people with HIV in the U.S. have histories of alcohol problems. Alcohol use has been associated with new infections, increased hospitalizations, causing inflammation that increases the amount of HIV in the body, and progression to illicit drug use.
Gender also plays a major role in the overall impact of alcohol consumption. Men and women process alcohol differently, with women naturally absorbing more alcohol and having slower alcohol metabolism regardless of the amount they drink. Women with HIV are a group that is at particularly high risk for health complications related to alcohol use, as a smaller quantity of alcohol can interfere with HIV treatment compared to men. Furthermore, alcohol has been linked to liver dysfunction, cardiovascular disease, and interference with HIV medications.
Don’t Miss: What Diseases Are Associated With Hiv Infection
Relative Risk For Decline Of Cd4 200 Cells/l By Alcohol Use
The effect of frequent alcohol use on the rate of decline of CD4+ cell count to < 200 cells/l over 30 months was assessed in 130 participants who had a baseline CD4+ cell count > 200 cells/l. Moderate alcohol use, classified as any reported use of one alcoholic drink daily or less in the past 6 months, did not significantly increase the rate of decline of CD4+ cells compared to abstainers. Frequent alcohol use over time, classified as two or more alcoholic drinks daily however, nearly tripled the risk of a decline of CD4+ cell count to 200 cells/l compared to moderate alcohol use and alcohol abstention after controlling for baseline CD4+ cell count and HIV viral load, ART as a time-dependent variable, years since self-reported HIV diagnosis, age, and gender . Both baseline CD4+ cell count and HIV viral load were significantly related to CD4+ cell count decline in this model. A comparison of frequent alcohol users to abstainers also showed a significant risk of decline of CD4+ cell count, although to a lesser extent .
The effect of frequent alcohol use on the rate of decline of CD4+ cell count to 200 cells/l over 30 months was assessed in 130 participants who had a baseline CD4+ cell count > 200 cells/l. Frequent alcohol use over time significantly increased the decline of CD4+ cell count to 200 cells/l. From Cox analysis we calculated an HR=2.91: 95% CI: 1.236.85, p=0.015.