Theoretic Vs Documented Risk
Whenever discussing HIV risk, it is important to differentiate between a theoretic and documented risk. A documented risk is based on the actual number of cases to which HIV can be directly attributed to an act of oral sex. And, when looking through that lens, the risk of infection by oral sex is actually extremely low. Not zero, perhaps, but edging close to it.
In fact, according to a study from the University of California San Francisco’s Centers for AIDS Prevention Studies, the probability of HIV infection through unprotected oral sex was statistically zero, although the researchers went so far as to add that “we can not rule out the possibility that the probability of infection is indeed greater than zero.”
For an individual perspective, there are numerous factors and situations that can increase personal risk, sometimes considerably. By understanding and identifying these factors, you can make better, more informed choices about the sexual health of you and your partner.
Can Someone Get Hiv Through Oral Sex
If a person who is infected with HIV gives a partner oral sex, can the partner become infected with HIV? Dan
Yes. Although rare, it is possible to transmit HIV through giving and receiving oral sex.
When someone with HIV gives oral sex, the virus can go from small cuts or sores in the mouth into the uninfected persons body through the urethra , vagina, or anus. When someone with HIV receives oral sex, the virus can enter the other persons body when semen or vaginal fluids get into the mouth.
If either partner also has another STD , it increases the chance of HIV infection even more.
Placing a protective barrier between the mouth and genitals can lower the chances of HIV infection both when giving and receiving oral sex. Guys should always wear a latex condom . Girls should put a dental dam or plastic food wrapping as a barrier over the genitals.
Date reviewed: January 2015
*Names have been changed to protect user privacy.
Note: All information on KidsHealth is for educational purposes only. For specific medical advice, diagnoses, and treatment, consult your doctor.
What You Can Do
Not having sex is a 100% effective way to make sure you dont get or transmit HIV through sex. If youre sexually active, you can lower your risk by choosing sexual activities that carry a lower risk for HIV than anal sex. You can also do other things to reduce your risk, including taking medicine to prevent or treat HIV and using condomsthe right way, every time. Condoms and medicine to prevent or treat HIV are highly effective at preventing HIV if used correctly. But the medicines are much less effective if you dont take them daily as prescribed, and condoms can sometimes break or come off during anal sex. Using a water-based or silicone lubricant can help prevent condoms from breaking or slipping.
Talking openly and frequently with your partner about sex can help you make decisions that decrease your risk of getting or transmitting HIV. Learn more about how to get the conversation started.
Conversation Starters
Certain things about your sex and injection partners can put you at increased risk for getting or transmitting HIV. Explore Estimate the HIV Risk to learn more.
Explore other resources from CDC:
Also Check: Does Cookie Johnson Have Aids
How You Become Infected
There is HIV virus in body fluids like vaginal secretions and semen. If those fluids are present, they can enter the bloodstream of someone who doesn’t have HIV through an opening such as a mouth sore or a genital ulcer.
Your chances are higher of getting HIV if you:
- Have sores in your mouth, vagina, or penis
- Have another sexually transmitted disease
How To Reduce The Risk
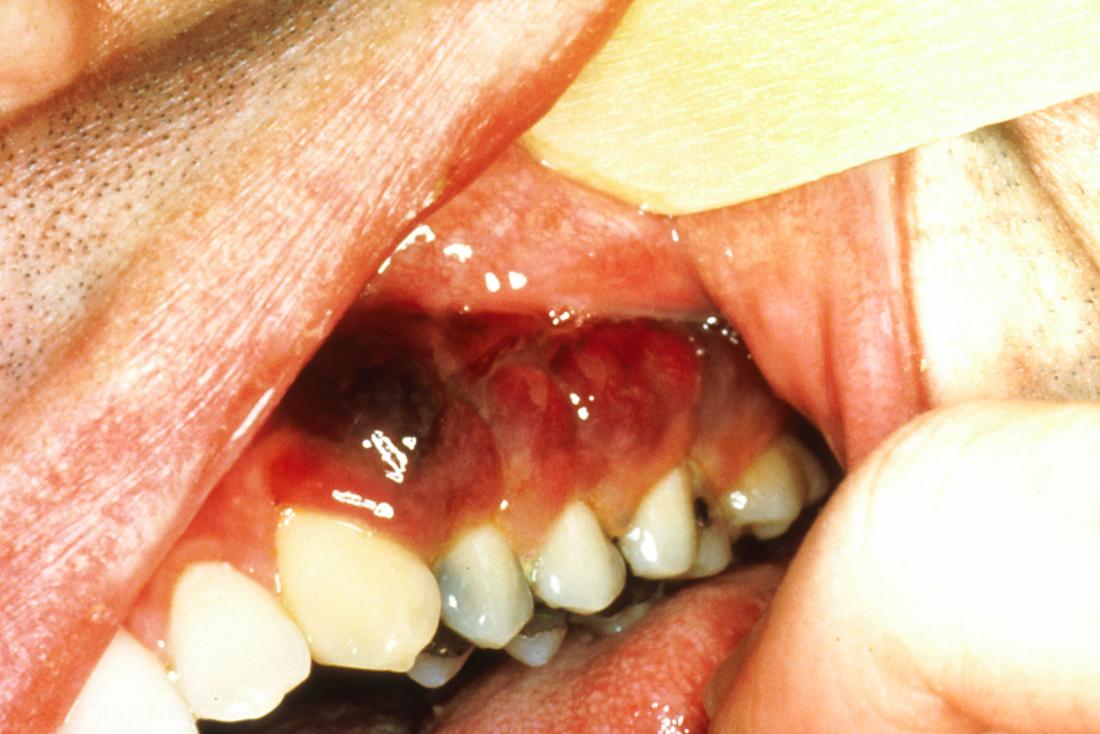
Although the risk of HIV passing to another person through oral sex is low, people can take steps to reduce it further.
For example, people with HIV can avoid ejaculating in the mouth of their sexual partner. They can do this by using a condom or withdrawing the penis before ejaculation.
A dental dam is another option. This is a small latex or silicone sheet that a person places over the vagina, anus, or mouth during sex.
Flossing or brushing the teeth can cause the gums to bleed, so it might also help to avoid this right before sexual activity.
People without HIV can take additional steps to avoid transmission, including:
- taking pre-exposure prophylaxis medication beforehand
- using condoms or dental dams correctly during all sexual activities
- avoiding lubricants with an oil base, such as Vaseline or baby oil
- taking post-exposure prophylaxis within a couple of days after the sexual contact
- getting regular sexual health checkups
People with HIV should take antiretroviral medication exactly as their doctor recommends.
In the early stages of HIV, people might experience:
- a fever
- rashes that are not itchy
- aching muscles
- swollen glands, or lymph nodes
- oral sores
Recommended Reading: Does Nba Youngboy Have An Std
Ways Hiv Cannot Be Spread
HIV is not spread by:
- Air or water
- Mosquitoes, ticks or other insects
- Saliva, tears, or sweat that is not mixed with the blood of a person with HIV
- Shaking hands hugging sharing toilets sharing dishes, silverware, or drinking glasses or engaging in closed-mouth or social kissing with a person with HIV
- Drinking fountains
Can I Get Hiv From Vaginal Sex
Yes. In general vaginal sex is not as risky anal sex, but is still a high-risk behavior for HIV infection.
Yes. In general, vaginal sex is not as risky anal sex but is still a high-risk behavior for HIV infection. It is possible for either partner to become infected this way. This risk depends on many factors, including whether the partners are using condoms, whether the partner with HIV is using antiretroviral therapy consistently and correctly and whether the partner who is HIV-negative is using pre-exposure prophylaxis consistently and correctly. Condoms and HIV medicines can greatly lower the risk of transmitting HIV.
In women, HIV can be directly absorbed through the mucous membranes that line the vagina and cervix. The lining of the vagina can also sometimes tear and possibly allow HIV to enter the body.
In men, HIV can enter the body through the urethra or through small cuts or open sores on the penis. Men who are not circumcised are at greater risk of HIV infection through vaginal sex than are circumcised men.
Risk for HIV infection increases if you or a partner also has a sexually transmitted disease . See also Is there a connection between HIV and other sexually transmitted infections?
Many barrier methods that women use to prevent pregnancy do not protect them against HIV or other STDs because they still allow infected semen to come in contact with the lining of the vagina.
Oral or hormonal contraceptives do not protect women against HIV or other STDs.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Aids From Dried Blood
How Can You Reduce The Risks
The most effective ways to prevent HIV being passed on are HIV treatment and PrEP.
There are several other ways to reduce the risk of HIV transmission from oral sex. Naturally, some will be more acceptable than others to different individuals, so you must make your own decisions about the level of risk you find acceptable. If you would like to discuss these issues, ask to see a health adviser, or other health professional, at your HIV treatment centre or sexual health clinic. Many of the strategies below will also provide protection against other sexually transmitted infections:
If you are living with HIV, taking HIV treatment as prescribed, so that you maintain an undetectable viral load is the most effective way of preventing HIV being passed on.
If you are HIV negative and are concerned that you may be vulnerable to acquiring HIV, you may want to consider taking pre-exposure prophylaxis .
If I Already Have Hiv Can I Get Another Kind Of Hiv
Yes. This is called HIV superinfection. The new strain of HIV can replace the original strain or remain along with the original strain. The effects of superinfection differ from person to person. For some people, superinfection may cause them to get sicker faster because they become infected with a new strain of the virus that is resistant to the medicines they are currently taking to treat their original HIV infection. Research suggests that the kind of superinfection where a person becomes infected with a new strain of HIV that is hard to treat is rare, less than 4%.
You May Like: Does Nba Youngboy Have Hiv
How Do You Give A Woman Oral Sex
Before you begin giving a woman oral sex, she may enjoy it if you spend some time kissing and touching her upper thighs and the area around her vagina first, to help her get aroused.
The whole genital area is sensitive, but for most women the clitoris is the most sensitive part. Gently part the outer lips of the vagina and look for the vaginal opening, and the hooded clitoris just above it.
Start off softly, using a relaxed tongue to make slow movements and work up to faster movements with a firmer tongue. You can experiment moving your tongue in different ways and try different rhythms taking cues from your partner to find out what she enjoys most.
Oral Sex And Hiv Acquisition
Oral sex is not likely to transmit HIV under most circumstances. Many large studies have shown that a person living with HIV who takes HIV drugs and has an undetectable viral load cannot transmit the virus to their sexual partners. This includes any kind of sex, including oral sex and sex without using condoms or barriers. This reality is known in the HIV community as Undetectable Equals Untransmittable, or U=U.
When a person living with HIV is not on treatment, oral sex is still a low-risk activity for HIV. If a person is not taking HIV drugs and/or has a detectable viral load, that low chance of transmission is greater if one of the partners has bleeding gums, mouth ulcers, gum disease, genital sores, and other sexually transmitted infections or diseases .
A number of studies have tried to figure out the exact level of HIV transmission risk that oral sex poses, but this is not easy to do. When HIV is transmitted, it is difficult to tell if oral sex or another activity that poses more risk was responsible.
The chances of HIV being passed from one person to another depend on the type of contact. HIV is most easily spread or transmitted through unprotected anal sex, unprotected vaginal sex, and sharing injection drug equipment that has not been cleaned. Unprotected sex means sex in which no condoms, other barriers, or HIV treatment-as-prevention methods are used.
For HIV transmission to be possible:
Don’t Miss: Hiv Causes Hair Loss
No 3 Having Anal Sex : 1 In 909
The insertive partner is less likely than the receptive partner to get the infection from an HIV-positive partner. However, bodily fluids carrying the virus can enter the insertive persons body through the urethra or any cuts or sores on the penis.
- Reduce the risk. If the insertive partner uses a condom, that can cut the risk of HIV transmission by an average of 63 percent, according to the CDC. You can help lessen the chance that the condom will slip or break by using water- or silicone-based lubricants. In addition, be aware that condoms dont fully protect against certain sexually transmitted diseases that can be contracted through skin-to-skin contact, like syphilis and herpes.
No 4 Having Vaginal Sex : 1 In 1250

Most women who get HIV are infected through vaginal sex. In such cases, an HIV-positive man transmits the virus to his female partner through preseminal fluid or ejaculate, which allows HIV to pass through the linings of the vagina and cervix.
- Reduce the risk. In theory, withdrawal practiced as a safety measure may help reduce a womans risk of contracting HIV from an HIV-positive partner, but because the virus can be found in preseminal fluids, the method may not be effective. Using condoms, however, can help lower the odds of transmitting HIV by 80 percent or more, according to the World Health Organization.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have Herpes
When Is Oral Sex More Risky
If you are living with HIV, there is a higher risk of passing on HIV through someone performing oral sex on you, if you are not taking treatment and if you also have an untreated sexually transmitted infection. If you don’t have HIV and you are performing oral sex on someone who does have HIV, you are at more risk of acquiring HIV if you have cuts, sores or abrasions in your mouth or on your gums. There is also more risk if you have an infection in your throat or mouth which is causing inflammation.
effectiveness
How well something works . See also ‘efficacy’.
For men, having a high viral load in the blood may also mean that viral load is high in the semen. Factors like untreated sexually transmitted infections can cause viral load in semen to increase.
For women, the levels of HIV in vaginal fluid vary. They are likely to be highest around the time of menstruation , when HIV-bearing cells shed from the cervix are most likely to be found in vaginal fluid, along with blood. Oral sex will therefore be more risky around the time of menstruation.
How Can You Prevent Getting Or Transmitting Hiv Through Sex
There are several ways to prevent getting or transmitting HIV through anal or vaginal sex.
If you are HIV-negative, you can use HIV prevention medicine known as pre-exposure prophylaxis or post-exposure prophylaxis to protect yourself. You can also use other HIV prevention methods, below.
If you have HIV, the most important thing you can do to prevent transmission and stay healthy is to take your HIV medicine , every day, exactly as prescribed. People living with HIV who take HIV medicine daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners. Read more about Treatment as Prevention. There also are other options to choose from, below.
Read Also: Hiv From Dried Blood
Can I Get Hiv From Injecting Drugs
Yes. If you share injection drug equipment with someone who has HIV, your risk is high.
Risk also depends on whether the person who has HIV is using antiretroviral therapy consistently and correctly, and whether the person who is HIV-negative is using preexposure prophylaxis consistently and correctly.
Sharing drug equipment can also be a risk for spreading HIV. Infected blood can get into drug solutions by
- Using blood-contaminated syringes to prepare drugs.
- Reusing water.
- Reusing bottle caps, spoons, or other containers to dissolve drugs in water and to heat drug solutions.
- Reusing small pieces of cotton or cigarette filters to filter out particles that could block the needle.
Street sellers of syringes may repackage used syringes and sell them as sterile syringes. For this reason, people who continue to inject drugs should get syringes from reliable sources of sterile syringes, such as pharmacies or needle-exchange programs.
It is important to know that sharing a needle or syringe for any use, including skin popping and injecting steroids, hormones, or silicone, can put you at risk for HIV and other blood-borne infections.
For more information, see If I use drugs, how can I prevent getting HIV?
Very Rare Ways Hiv Is Spread:
- Oral sexputting the mouth on the penis , vagina , or anus . In general, theres little to no risk of getting HIV from oral sex. But transmission of HIV, though extremely rare, is theoretically possible if an HIV-positive man ejaculates in his partners mouth during oral sex. To learn more about how to lower your risk, see CDCs Oral Sex and HIV Risk.
- Receiving blood transfusions, blood products, or organ/tissue transplants that are contaminated with HIV. This was more common in the early years of HIV, but now the risk is extremely small because of rigorous testing of the US blood supply and donated organs and tissues.
- Eating food that has been pre-chewed by an HIV-infected person. The contamination occurs when infected blood from a caregivers mouth mixes with food while chewing. The only known cases are among infants.
- Being bitten by a person with HIV. Each of the very small number of documented cases has involved severe trauma with extensive tissue damage and the presence of blood. There is no risk of transmission if the skin is not broken.
- Contact between broken skin, wounds, or mucous membranes and HIV-infected blood or blood-contaminated body fluids.
- Deep, open-mouth kissing if both partners have sores or bleeding gums and blood from the HIV-positive partner gets into the bloodstream of the HIV-negative partner. HIV is not spread through saliva.
For more information about HIV transmission, visit CDCs HIV Transmission.
Also Check: Can Hiv Lay Dormant
Should I Have Oral Sex
Talking to your partner about protection before you start having oral sex will help make things easier. This may feel embarrassing but taking responsibility for protecting yourself and your partner is an important part of having sex. If you find it too awkward to talk about then you may not be ready to have oral sex just yet.
You should never give or receive oral sex just because you feel forced into it. Dont be pressured into any sex act by comments like it doesnt mean weve had real sex youll still be a virgin, or if you dont want sex at least go down on me, or its not as risky as having intercourse. If one of you isnt comfortable with the decision it can ruin the whole experience. Oral sex should be fun for both of you.
Our article Am I ready for sex? will help you work out what is right for you.