The Devil Is In The Details
An analysis of the details of this study gives us a glimpse into why there’s still a life expectancy gap between HIV-negative and HIV-positive people — as well as who appears to do better or worse than this average. While the life expectancy gap wasn’t much affected by gender, it was affected by race — African Americans had lower life expectancy, for instance — and it was lower for people who inject drugs. Importantly, people who initiated HIV treatment with a higher CD4 count narrowed the life expectancy gap from eight to five years. The study authors concluded that “timely initiation” of HIV treatment should further narrow the overall gap. Ditto for smoking cessation cigarette use is about twice as common among people with HIV, which obviously lowers life expectancy.
Of course, there are plenty of other reasons why life expectancy for people with HIV remains lower, on average, than for the general public. Many of those reasons become clear when we take a glimpse at the HIV care continuum.
Despite recommendations for near-universal HIV testing and treatment for all people with HIV in the U.S., many Americans living with HIV don’t know their status many are diagnosed late and less than half are engaged in medical care — only 37% of the HIV-positive population currently receives ART. Some populations of people fare even worse — African Americans, for example, as well as immigrants and people who use drugs.
How Do I Talk With People About Having Hiv
It might feel scary to admit that you have HIV, but talking about things can really ease your mind. You could lean on a close, non-judgmental friend or family member whom you trust to keep the conversation private. Counselors and support groups can also be sources of comfort and they can help you figure out how to talk with others about your HIV. Be careful about who you tell your status to people with HIV sometimes deal with unfair discrimination.
Theres no one right way to talk to your partners about having HIV, but here are some basic tips that might help:
Try to stay calm and remember that youre not the only one dealing with this. Millions of people have HIV, and plenty of them are in relationships. Try to go into the conversation with a calm, positive attitude. Having HIV is a health issue, and it doesnt mean anything about you as a person.
Know your HIV and AIDS facts. There are a lot of myths about HIV out there, so read up on the facts and be ready to answer your partners questions. Check out HIV.gov. Let your partner know there are medications that can help you live for a long time and avoid passing HIV to them. Safer sex like condoms and PrEP can also help protect your partner.
Its really important to also tell your past partners that you have HIV, so they can get tested, too. A lot of health departments have programs that let your partners know they were exposed to HIV without giving them your name unless you want them to.
Gains And Losses In Life Years
Factors that influence life expectancy are either static or dynamic .
Static factors, like race or sexual orientation, influence life expectancy because they are ones people are often unable to escape. For example, high levels of poverty in Black communities combined with a lack of access to health care and high levels of HIV stigma take back many of the gains seen in White communities.
Dynamic factors, by comparison, have a strong cause-and-effect relation to survival times. For instance, treatment adherence is directly related to disease progression. The less adherence is maintained, the greater the risk of drug resistance and treatment failure. With each failure, a person loses more and more treatment options.
When looking at both static and dynamic risk factors, we can begin to identify where an individual can gain or lose life-years without even knowing it. Among them:
Don’t Miss: Does Hiv Make Your Hair Fall Out
Calculating Life Expectancy With Hiv Or Aids
Recent research shows that a young person with HIV or AIDS could potentially live almost as long as anyone else in the general population. But this is only the case if they have routine access to health care and respond well to modern antiretroviral treatments . So a 20-year-old who starts on ARTs today, for example, might eventually live to be 67.
Keep in mind though, since there is no known cure, HIV life expectancy varies greatly from one individual to the next based on many things. This includes early detection plus, gender and lifestyle choices such as alcohol, tobacco, or drug use.
Over the past two decades, HIV life expectancy has drastically risen. What was once considered a terminal illness is now a medically manageable condition at any age. Those who abuse intravenous drugs or possess a preexisting immune disorder, however, do not fare as well.
In light of huge disparities in access to health care and ARTs, the CDC regularly publishes reports on obstacles to HIV and AIDS treatment. By 2016, it was estimated that 1.1 million people in the U.S., aged 13 or older, had HIV .
How Can I Live A Healthier Life With Hiv
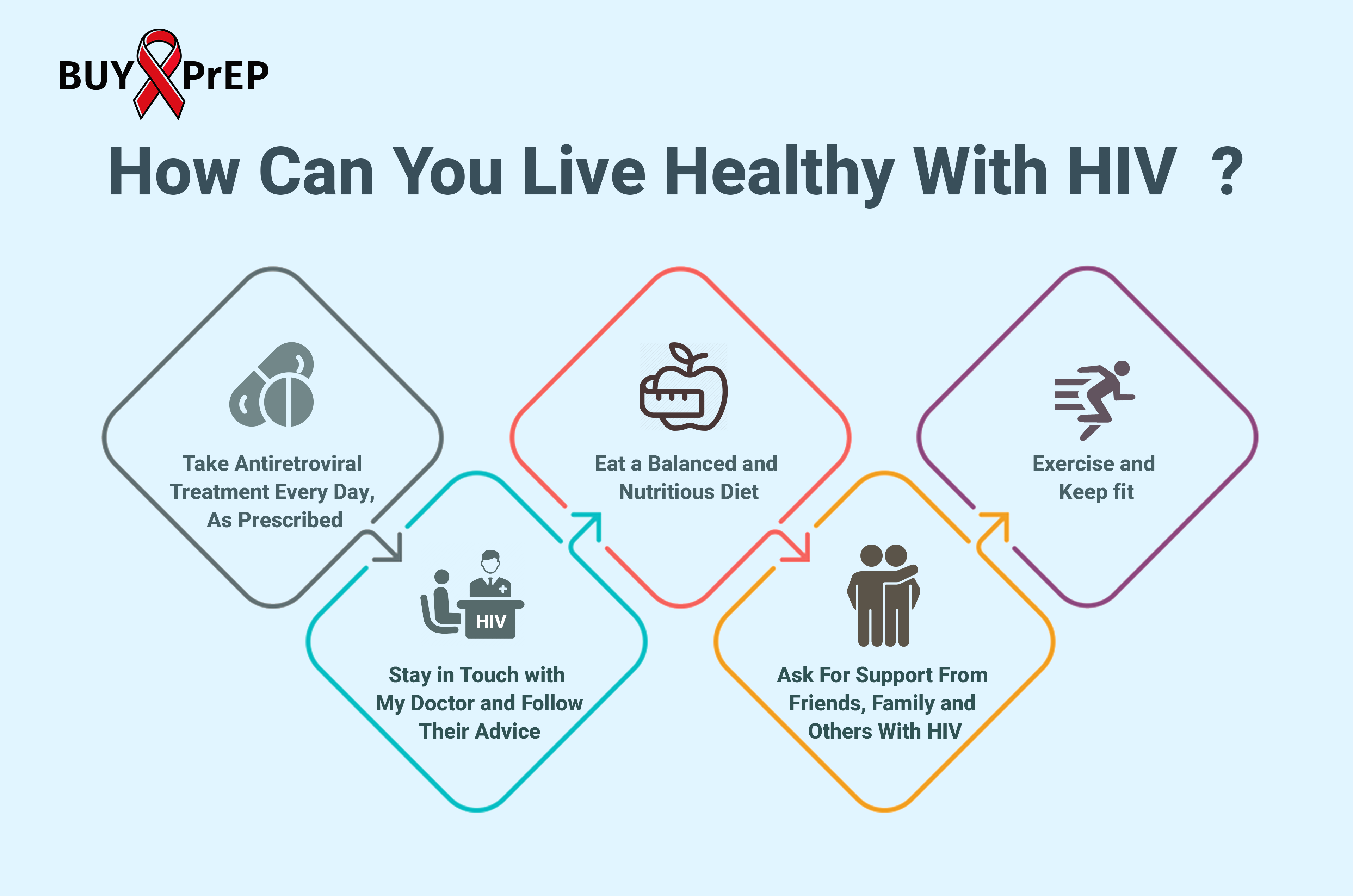
IIf you have HIV, you can help yourself by:
- Getting medical care as soon as you find out that you have HIV. You should find a health care provider who has experience in treating HIV/AIDS.
- Making sure to take your medicines regularly
- Keeping up with your regular medical and dental care
- Managing stress and getting support, such as from support groups, therapists, and social service organizations
- Learning as much as you can about HIV/AIDS and its treatments
- Trying to live a healthy lifestyle, including
- Eating healthy foods.This can give your body the energy it needs to fight HIV and other infections. It can also help you manage HIV symptoms and medicine side effects. It may also improve absorption of your HIV medicines.
- Exercising regularly. This can strengthen your body and immune system. It may also reduce the risk of depression.
- Getting enough sleep. Sleep is important for your physical strength and mental health.
- Not smoking. People with HIV who smoke have a higher risk of developing conditions such as certain cancers and infections. Smoking can also interfere with your medicines.
It is also important to reduce the risk of spreading HIV to other people. You should tell your sex partners that you have HIV and always use latex condoms. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
Recommended Reading: Does Cookie Have Hiv
Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis
- HIV medicine is recommended for all people with HIV, regardless of how long theyve had the virus or how healthy they are.
- Talk to your health care provider about any medical conditions you may have or any other medicines you are taking.
- Let your health care provider know if you or your partner is pregnant or thinking about getting pregnant. They will determine the right type of HIV medicine that can help prevent transmitting HIV to your baby.
What if I delay treatment?
- HIV will continue to harm your immune system.
- This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infections.
- This will put you at higher risk for transmitting HIV to your sexual and injection partners.
What are the benefits of taking my HIV medicine every day as prescribed?
Sex With A Partner That Is Hiv+
Condoms should be used during all sex acts, whether it be oral, anal or vaginal intercourse. Condoms uses correctly and consistently form very good protection against infection with HIV and most other sexually transmitted diseases.
When using condoms, check the expiration date. Condoms kept in a cool and dark place can be used for 4 years after the manufacturing date. Never use oils, creams or Vaseline for extra lubrication when using condoms. Use a water or silicon based lubricant such as KY-Jelly or other brand.
There has been no evidence of spread of HIV infection through saliva. Kissing, including tongue/deep kissing is safe. However, if there are bleeding gum irritations in the mouth deep kissing should be avoided.
Recommended Reading: Hiv Causes Hair Loss
You Cant Avoid Other Hiv
Myth. People with HIV can get infections like pneumonia, tuberculosis, candidiasis, cytomegalovirus, and toxoplasmosis. The best way to cut the risk is to take HIV medications. People with advanced HIV infection can prevent some of these infections with specific drugs in addition to antiretroviral therapy. You can lessen exposure to some germs by avoiding undercooked meat, litter boxes, and contaminated water.
Health Issues And Aging With Hiv
People aging with HIV share many of the same health concerns as the general population aged 50 and older: multiple chronic diseases or conditions, the use of multiple medications, changes in physical and cognitive abilities, and increased vulnerability to stressors. In addition, while effective HIV treatment has decreased the likelihood of AIDS-defining illnesses among people aging with HIV, many HIV-associated non-AIDS conditions occur frequently in older persons with HIV, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, renal disease, and cancer. These conditions are likely related to a number of interacting factors, including chronic inflammation caused by HIV. Researchers are working to better understand what causes chronic inflammation, even when people are being treated with ART.
HIV and its treatment can also have effects on the brain. Researchers estimate that between 25 and 50% of people with HIV have HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder , a spectrum of cognitive, motor, and/or mood disorders categorized into three levels: asymptomatic, mild, and HIV-associated dementia. Researchers are studying how HIV and its treatment affect the brain, including the effects on older people living with HIV.
HIV Long-Term Survivors Awareness Day
Read Also: How Long Does Aids Take To Show
Taking Care Of Yourself When Living With Hiv
FAST FACTS
Starting antiretroviral treatment as soon as possible, and sustaining it as part of your everyday routine, is the best way of ensuring that your immune system stays strong.
Exercising regularly, eating well, getting enough rest and quality sleep are all vital to maintaining your health.
Your mental wellbeing is just as important as your physical health. Talking about your concerns with family, friends or a support group can really help.
Having HIV doesnt have to stop you living a healthy life in the way that you choose to do. With the right treatment and care, you can expect to live as long as someone who doesnt have HIV. Find out how you can look after yourself and stay healthy.
What Will Happen If I Skip My Arv For 2 Days
Missing doses of HIV medicines can reduce their usefulness and increase the possibility of developing drug resistance, which makes certain HIV drugs lose their effectiveness. If you realize you have missed a dose, go ahead and take the medication as soon as you can, then take the next dose at your usual scheduled time.
Recommended Reading: Oraquick At Walgreens
When Someone You Know Has Hiv
When someone in your family tests positive for HIV, you may feel a range of emotions. Among fear, confusion, regret and love for the person afflicted, you may also feel afraid for your own personal well-being and may have questions about just how contagious HIV may be. Rest assured that people with HIV can live at home and maintain a normal social life. Since the virus is not spread by casual household contact, family members, roommates, and visitors are not at risk of becoming infected.
The following information is provided to clarify what should and should not be done in living with someone with HIV. You will see that most of it is just good hygiene practices.
Hand washing is an effective way to prevent the spread of any germs. Wash hands with soap and water before preparing food, before eating, and after using the toilet. This is to protect both the infected and uninfected family members remember that a person living with HIV may have a weak immune system and therefore may be more likely to catch any type of infection from another person. They, too, are vulnerable.
Personal Articles such as toothbrushes, razors and razor blades should not be shared among household members. These may become soiled with blood and could spread germs that may cause many illnesses.
Wash dishes in hot soapy water. No special precautions are necessary. There is no need to wash separately the dishes used by the infected person.
Aids Or Hiv Life Expectancy Without Medication

How long can you live with HIV or AIDS if you chose not to treat with ART combinations or other prescription drugs? In the absence of such therapy, a patient should expect to see a notable decrease in life expectancy.
In countries where health care and ARTs arent readily accessible, HIV rates are above 20 percent. Shorter HIV life expectancy in these regions, combined with a high incidence of AIDS in younger age groups, boosts their overall mortality rate.
Population studies proved that AIDS patients who did not take HIV medications survived for roughly three years. Once they developed a dangerous opportunistic illness, life expectancy with AIDS decreased to one year or less.
Thats why HIV and AIDS remain a serious threat to public health, and why early detection is absolutely critical to long-term survival.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take For Hiv To Show
Ongoing Stigma And Discrimination
Dr Neilsen says that Queenslanders who are HIV positive, like Nathan, can face ongoing stigma and discrimination, even if theyre taking medication that means they are not at risk of transmitting HIV to others.
Unfortunately, the stigma and discrimination still persist, he says. In recent years, I’ve still seen patients newly diagnosed with HIV experience awful discrimination. We still see rejection by family, rejection by their lovers and so on, at a time when that is really unjustified. It’s appalling. In that respect, HIV still has the potential to destroy relationships and cause major damage to people’s self-esteem.
Dr Neilsen finds this frustrating, particularly because modern treatments mean that people with HIV who are taking ART and have undetectable HIV viral loads in their blood results, are extremely unlikely to transmit the virus to others.
These days people are unlikely to get HIV from someone on HIV treatment, he says. The modes of transmission are well known, and people do not get HIV through normal social contact. If someone has a friend, family member or partner who is infected with HIV, they should be supportive and encourage them to seek treatment. People should be respecting and looking after each other as though they were not infected with HIV.
He thinks a lot of this discrimination comes from a lack of understanding in the community about what HIV actually is.
Treatment Reduces The Amount Of Hiv In The Blood
- The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load.
- Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will help keep your viral load low and your CD4 cell count high.
- HIV medicine can make the viral load very low . Viral suppression is defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood.
- HIV medicine can make the viral load so low that a test cant detect it .
- If your viral load goes down after starting HIV treatment, that means treatment is working. Continue to take your medicine as prescribed.
- If you skip your medications, even now and then, you are giving HIV the chance to multiply rapidly. This could weaken your immune system, and you could become sick.
- Getting and keeping an undetectable viral load is the best way to stay healthy and protect others.
Also Check: Does Nba Youngboy Have Herpies
What About Travel And Vaccines
You should be up to date on routine vaccines, no matter where you are going. If you are planning a trip outside the United States, you may need to get vaccinated against diseases that are present in other parts of the world, such as cholera or yellow fever.
If you have HIV, talk to your health care provider about any vaccines you may need before you travel. He or she will know which ones are safe for you. Keep in mind: most travel vaccines can be given safely to people with HIV and others with weakened immune systems. However, they may be less effective than in people with strong immune systems, and may not provide full protection. Your doctor may recommend blood tests to confirm that a vaccine was effective, or recommend additional precautions to keep you safe.
Some travel vaccines are LAVs and many people with weakened immune systems should not take them. However, depending on the circumstances, the benefits of protection may outweigh the risks. Talk to your health care provider about what is recommended for you.
How Long Can You Live With Hiv Very
Roz Woodward for Photodisc via Thinkstock
Just this past week, I met John , a 50-year-old long-term survivor with HIV, in our clinic in Denver, Colorado. He was on a well-tolerated treatment regimen, had an undetectable viral load and normal CD4 count. He asked me about new studies on HIV treatments, and about both his projected quality and quantity of life.
I told him that, on average, life expectancy for people living with HIV — provided they get tested, find their way into a care center, initiate antiretroviral treatment and continue taking that treatment regularly — is similar to people who don’t have HIV infection.
He gave me a suspicious look. “Are you sure?” he asked.
Read Also: Is Hiv In Semen