Learning Objective Performance Indicators
- List the major classes of antiretroviral medications and describe the mechanism of action with each class of drugs
- Discuss evidence supporting antiretroviral treatment of all persons with HIV
- List recommended antiretroviral regimens for treatment-naïve individuals and discuss factors to consider when selecting an initial regimen
- Summarize recommended laboratory studies to obtain at baseline and while monitoring response to therapy
Recommended Initial Regimens For Most People With Hiv
The Adult and Adolescent ARV Guidelines regimens listed as Recommended Initial Regimens for Most People with HIV include an INSTI anchor drug in combination with at least one NRTI . The choice of the specific first-line antiretroviral regimen depends on multiple factors, including medical comorbidities, potential drug interactions, and patient preferences the baseline HIV RNA level is greater than 500,000 copies/mL, the persons undergoing treatment has chronic hepatitis B virus or the HBV status is unknown, or results from the HIV genotypic resistance testing are not available at the time antiretroviral therapy is planned to start. Except for the HIV RNA level restriction for dolutegravir-lamivudine, all of these regimens can be used without regard to pretreatment HIV RNA level or CD4 cell count.
Acquired Hiv Drug Resistance
Viral load suppression the goal of HIV treatment is the prevention of HIV drug resistance. When viral load suppression is achieved and maintained, drug-resistant HIV is less likely to emerge. In 14 nationally representative surveys implemented between 2015 and 2020, the level of viral load suppression among adults receiving ART was generally high. The pooled results for viral load suppression in Africa were 94% among adults receiving first-line ART and 84% among adults receiving second-line ART. In the Americas, the pooled results for viral load suppression were 81% among adults receiving first-line ART and 70% among adults receiving second-line ART.
Despite treatment with potent medicines and even when adherence to treatment is supported, some HIV drug resistance is expected to emerge. Surveillance of acquired HIV drug resistance in populations receiving ART provides valuable information for the optimal selection and management of ART regimens. Among populations failing NNRTIs-based ART, the levels of resistance to commonly used NNRTIs ranged from 50% to 97%.
The high levels of HIV drug resistance to NNRTIs among individuals with treatment failure emphasize the need to scale up viral load testing and enhanced adherence counselling, and to promptly switch individuals with treatment failure.
You May Like: How Does Hiv Aids Spread
Tobacco And Smoking Cessation Products
Reviewed and updated: John Faragon, PharmD, BCPS, AAHIVP, with the Medical Care Criteria Committee updated July 2021
| Table 35: Tobacco and Smoking Cessation Products |
| Class or Drug |
|
|
Abbreviations: NNRTI, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors NRTI, nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor P-gP, P-glycoprotein PI, protease inhibitor TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate UGT, uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase. Note: Cyclosporine can cause renal toxicity, which may be increased with coadministration of TDF. Clinicians are advised to monitor for signs of renal dysfunction in patients who are taking these two medications at the same time. |
Art: Monitoring For Tolerability

Antiretroviral drugs have early and late-onset side effects that can affect tolerance. Some side effects, such as headache and nausea, are common at treatment initiation but are usually transient and manageable. Table 27-9 lists some of the most common severe antiretroviral side effects.
Directed assessments for adverse events can help ensure that early side effects are identified when it is possible to change therapy to prevent their progression. As ART continues, the frequency of assessment can be decreased. It is not currently possible to identify which patients will develop side effects however, the risk for ART-related events may be greater in patients with more advanced disease .
If available, routine laboratory monitoring is an important adjunct to care and can be used to monitor for ART-associated toxicities . Laboratory monitoring, however, is not a prerequisite for the initiation of ART . In high-income settings, guidelines typically recommend quarterly or semi-annual testing of complete blood counts, serum chemistries and urinalyses, as well as CD4 cell count and plasma HIV RNA viral load . If resources are limited, laboratory testing should be directed by clinical signs and symptoms . The WHO also recommends testing that is tailored to the ART .
E. De Crignis, T. Mahmoudi, in, 2017
You May Like: How To Protect Yourself From Hiv Infection
Resistance To Fusion Inhibitors
Early in vitro studies showed that enfuvirtide resistance involves the selection of changes in a three amino acid domain within the HR1 region of gp41. Subsequent results obtained in clinical studies have shown that resistance in patients receiving enfuvirtide may also be due to changes expanding from codon 36 to 45 within HR1 . A spectrum of different mutations has been described in this amino acid region , each one reducing significantly, although to a different extent, the susceptibility to the drug., Overall, enfuvirtide should be considered as a drug with a low genetic barrier for resistance.
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the gp41 linear structure. Enfuvirtide and T-1249 sequences mimic HR2. FP, fusion peptide CC, cysteine-cysteine TM, transmembrane domain.
There is controversy regarding the impact of HIV co-receptor use on susceptibility to enfuvirtide. While some in vitro studies have shown that R5 strains could be more resistant to enfuvirtide,,in vivo studies have not found significant differences in the response to enfuvirtide therapy when comparing patients harbouring R5 strains with those harbouring X4 strains.,
Patent Filed And Fda Approval
A rigorous double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial of AZT was subsequently conducted by Burroughs-Wellcome and proved that AZT safely prolongs the lives of people with HIV. Burroughs-Wellcome filed for a patent for AZT in 1985. The Anti-Infective Advisory Committee to United States Food and Drug Administration voted ten to one to recommend the approval of AZT. The FDA approved the drug for use against HIV, AIDS, and AIDS Related Complex on March 20, 1987. The time between the first demonstration that AZT was active against HIV in the laboratory and its approval was 25 months, the shortest period of drug development in recent history.
AZT was subsequently approved unanimously for infants and children in 1990. AZT was initially administered in significantly higher dosages than today, typically 400 mg every four hours, day and night, compared to modern dosage of 300 mg twice daily. The paucity of alternatives for treating HIV/AIDS at that time unambiguously affirmed the health risk/benefit ratio, with inevitable slow, disfiguring, and painful death from HIV outweighing the drug’s side-effect of transient anemia and malaise.
Read Also: Can I Get Hiv If Someone Is Undetectable
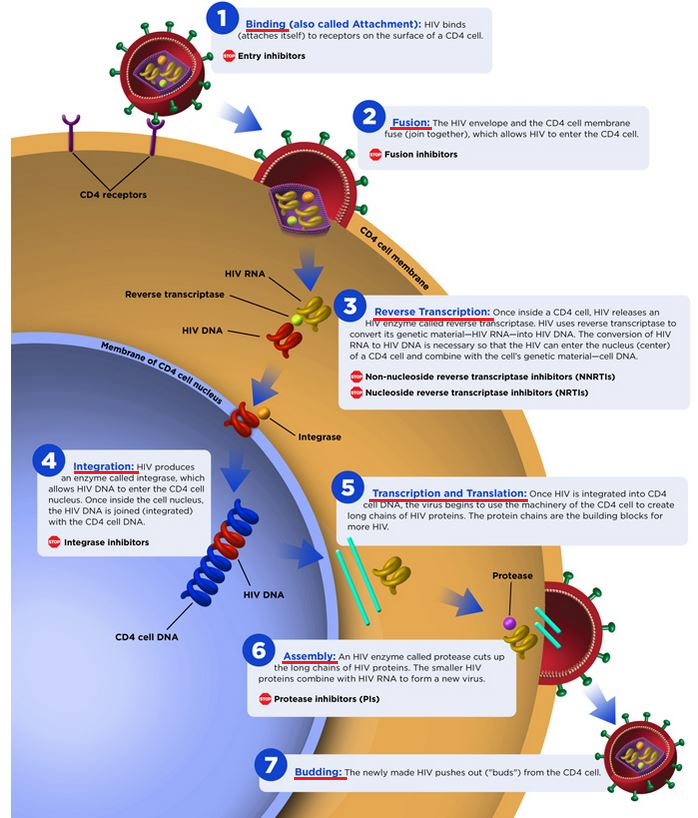
Hiv Life Cycle And Antiretroviral Drug Targets
Understanding the basic HIV life cycle is the foundation for understanding the mechanism of action of the different classes of antiretroviral medications. The following discussion will focus on key HIV enzymes and relevant steps in the HIV life cycle related to HIV antiretroviral therapy. The Howard Hughes Medical Institute has produced an excellent HIV Life Cycle video that summarizes the key steps in the HIV life cycle.
Resistance To Cd4gp120 Inhibitors
Several in vitro models have tried to describe the mechanism of action of all these inhibitors, which still remains unclear. Because all these molecules act in different ways, it is expected that their mechanisms of action will differ as well. As a consequence, resistance may develop in any of the different pathways and no cross-resistance should be expected among these compounds.
In vitro studies conducted with BMS-806 and related compounds have shown that gp120 amino acids involved in resistance are those surrounding the Phe-43 cavity and a water-filled channel that extends from this cavity to the inner domain. Several changes in gp120 residues Trp-112, Thr-257, Ser-375, Phe-382, Met-426, Met-434 and Met-475 result in the escape of HIV strains from BMS-806 and BMS-155 inhibitors.,, It is interesting to note that the degree of sequence conservation in the nearby V1/V2 variable loops indirectly influences the susceptibility to these drugs. Even though V1/V2 regions are not absolutely required for BMS-806 or BMS-155 binding to gp120, its deletion may alter the susceptibility of some HIV strains to these inhibitors. Thus, natural gp120 variability among different HIV-1 subtypes may account for differences in baseline susceptibility to these compounds. Preliminary data suggest that BMS-806 activity might be compromised in some non-B subtypes, particularly in subtypes C and CRF01_AE, which seem to be naturally resistant to BMS-806.
Also Check: Which Country Has The Highest Hiv Rate
Historical Background Of Antiretroviral Therapy
Antiretroviral drugs act by interfering with vital viral replication processes and are classified according to the step they inhibit in the viral life-cycle . A sub-classification may be based on their chemical structure. A milestone in the history of HIV disease has been the availability of new classes of drugs, in 199596, allowing the introduction of combination ARV therapy and the gradual evolution of HIV infection into a chronical, usually nonfatal condition . Currently, there are seven categories of ARV drugs: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors , Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase inhibitors , Protease Inhibitors , drugs that interfere with viral entry , Integrase Inhibitors and Maturation Inhibitors .
Also, Integrase strand transfer inhibitors are the class of ARV drugs most recently approved by the FDA for the treatment of HIV-1 infections. INSTIs block the strand transfer reaction catalyzed by HIV-1 integrase and have been shown to potently inhibit infection by wild-type HIV-1. The new INSTIs, Bictegravir , are currently in late-stage clinical trial .
Because many of antiretroviral drugs belong to the same drug class, if HIV becomes resistant to one drug in a class, it may have varying degrees of resistance to other drugs in the same family. This is called cross-resistance and it can limit future treatment options. Cross-resistance highlights the need for new effective therapies.
Hiv Infection: Entry Into The Cell
The life cycle of HIV can be as short as 1.5 days starting from viral entry into a cell, through the processes of viral replication, to infection of other cells . The HIV virus enters macrophages and other CD4+ cells by adsorption of the gp120 viral glycoprotein to CD4 and either CCR5 or CXCR4 on the surface of the immune host cell . Insertion of viral gp41 into the cell membrane of the host, followed by a series of conformational changes results in fusion of the viral envelop with the host cell membrane, and entry of the viral capsid into the host cell.
Figure 2.The mechanism of HIV entry into a CD4+ cell. 1) Viral gp120 comes into contact with CD4 on the cell surface. 2) A conformational change in gp120 allows for secondary interaction with either the -chemokine CCR5 receptor or CXCR4 . This provide a more stable two-point attachment that allows the gp41 peptide to penetrate the cell membrane. 3) The distal tips of gp41 are inserted in to the cellular membrane. 4) gp41 undergoes a significant conformational change collapsing into a hairpin, which pulls the viral and cellular membranes together, fusing them. This results in subsequent entry of the viral capsid into the host cell..
Figure 3. Replication cycle of HIV in a host cell & Four Classes of Anti-HIV Drug Targets. Modified from a figure by Thomas Splettstoesser posted on Wikimedia Commons.
Read Also: What Disease Is Caused By Hiv
Pharmacologic Enhancers Or Drug Boosters
Ritonavir , taken in a low dose, increases blood levels of lopinavir and the drug LPV/r .
- Zidovudine + Lamivudine or ZDV/3TC
Descovy and Truvada have also been approved as ways to prevent HIV infection for people who are at high risk. But if you take either of them, you have to practice safe sex, too.
Mode Of Action Entry Inhibitors
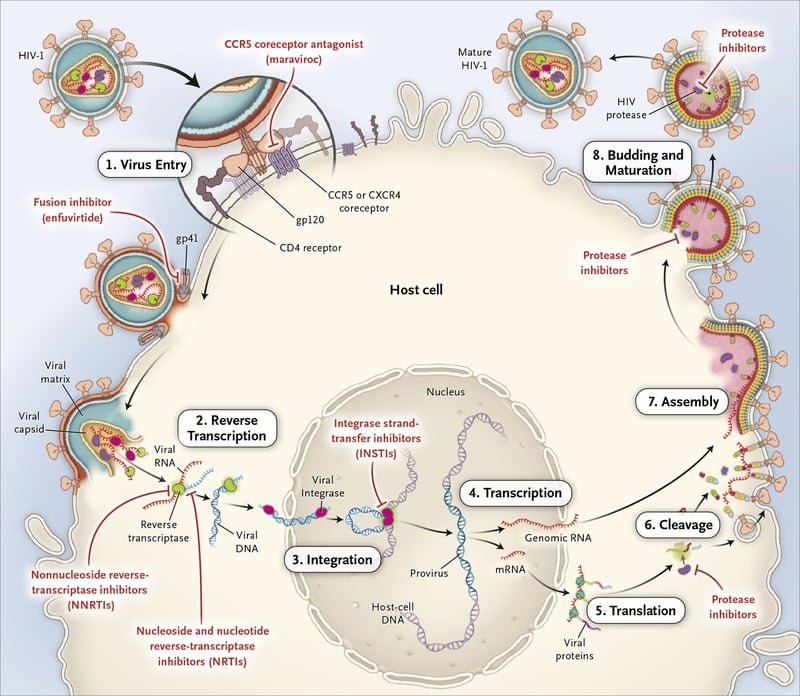
Entry Inhibitors interfere with the receptor-mediated entry of the virus into a cell. Two subclasses known as fusion inhibitors and CCR5 antagonists, are new classes of antiretroviral drugs used in combination therapy for the treatment of HIV infection.
This class of drugs interferes with the binding, fusion and entry process of HIV into a human cell.
Also Check: Can Hiv Be Transmitted Through Genital Rubbing
Choosing Nrti Backbone In Regimen
The Adult and Adolescent ARV Guidelines include four different NRTI backbone combinations: abacavir-lamivudine, tenofovir alafenamide-emtricitabine, tenofovir DF-emtricitabine, and tenofovir DF-lamivudine.Abacavir has been associated with increased cardiovascular risk, and although data is conflicting about this association, many experts would avoid abacavir in the setting of known cardiovascular disease risk factors. Tenofovir DF is linked to increased risk of renal dysfunction and loss of bone mineral density accordingly, tenofovir DF is not recommended for patients with renal disease or osteoporosis. Tenofovir alafenamide has a less favorable lipid profile than tenofovir DF.
Antiretroviral Guidelines For Adults And Adolescents And Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State Are Serious Acute Complications Of Diabetes Mellitus Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State Occurs Due To A Relative Deficiency Of Insulin Or Insulin Resistance Leading To Severe Hyperglycemia And Elevated Serum Osmolality Hyperglycemic Crises 2019
- Antiretroviral therapy recommended to:
- Reduce morbidityMorbidityThe proportion of patients with a particular disease during a given year per given unit of population.Measures of Health Status
Read Also: What Is The Best Way To Prevent Hiv
Why Do We Need New Anti
Almost 50 million people worldwide are infected with HIV, and a significant number of these infections have become resistant to current antiretroviral therapies. The need to constantly develop new antiretroviral drugs to combat HIV resides in the basic fact that the replication of this virus is a very inefficient process. The viral enzymes used during replication make many mistakes while copying the parental viral genome into progeny virus, and these mistakes translate into numerous mutations. Some of these mutations contribute to make the virus resistant to antiretroviral drugs, and this resistance results in treatment failure . Therefore, the need for novel targets for drugs to defeat HIV is paramount.
Resistance To Ccr5 And Cxcr4 Antagonists
Two main resistance pathways are theoretically possible for CCR5 and CXCR4 antagonists. The first is a shift in co-receptor usage and the second results from changes in HIV envelope genomic regions which allow the interaction between gp120 and the co-receptor despite the presence of the inhibitor.
Data available so far suggest that most CCR5 antagonist-resistant strains continue the use of the CCR5 co-receptor rather than shifting to CXCR4. Furthermore, multiple mutations within different regions of HIV gp120 account for the drug-resistant phenotype. Most resistance mutations are specific for each of the different compounds, which may hopefully limit cross-resistance. However, large clinical studies are needed to prove this concept. Preliminary findings with HIV isolates resistant to maraviroc have demonstrated that they remain susceptible to SCH-C, vicriviroc and aplaviroc. In contrast, vicriviroc-resistant strains show cross-resistance to SCH-C, AD101 and RANTES derivates, most probably because they share their interaction site with the CCR5 co-receptor. In any case, CCR5 antagonist-resistant strains do not show cross-resistance with the current approved antiretrovirals, RT and protease inhibitors. Nor are they cross-resistant to other entry blockers, such as CD4gp120 binding inhibitors and enfuvirtide.
You May Like: How Many People Have Hiv
Recommendations For Initiation Of Antiretroviral Therapy
The Adult and Adolescent ARV Guidelines recommend initiation of antiretroviral therapy for all persons with HIV to reduce morbidity and mortality associated with HIV infection and to prevent HIV transmission to others . In addition, antiretroviral therapy should be started immediately, or as soon as possible, after the HIV diagnosis.
Hiv Protein Processing And Hiv Protease Inhibitors
HIV Protease
The HIV protease enzyme is a 99-amino-acid dimer made up of two identical subunits . This enzyme has a key role in post-transcriptional processing of the Gag and Gag-Pol polyproteins. The HIV protease has three major conformational forms: open, semi-open, and closed . The protease enzyme has an active site near the center of the heterodimer and the active site includes two opposed aspartic acid residues. Movement from the open to closed causes the flap ends to overlap and functionally act as a molecular scissor.
Polyprotein Processing and Maturation
Protease Inhibitors
The HIV protease inhibitors are structurally complex molecules that bind to the active site of HIV protease and inhibit the protease enzyme activity . The HIV protease inhibitors disrupt the normal Gag and Gag-Pol polyprotein processing, causing arrest of the normal maturation process, which thereby prevents infection of new cells. The protease inhibitors do not have an impact on cells already infected with HIV .
Also Check: How Long Before Hiv Symptoms
What Not To Use
The Adult and Adolescent ARV Guidelines provides a category for antiretroviral medications which, either alone or in combination, should not be offered for use at any time. Regimens that are considered in the What Not to Use category include:
Antiretroviral Drugs Not Recommended
- Monotherapy with any antiretroviral medication
- Dual therapy with two NRTIs
- Triple therapy with three NRTIs
Antiretroviral Components Not Recommended
- Cobicistat plus ritonavir as pharmacokinetic enhancers
- Didanosine plus stavudine
- Etravirine plus an unboosted protease inhibitor
- Etravirine plus ritonavir-boosted fosamprenavir
- Etravirine plus ritonavir-boosted tipranavir
- Nevirapine in women with CD4 count above 250 cells/mm3 or in men with CD4 count above 400 cells/mm3
- Unboosted darunavir, saquinavir, or tipranavir
- Stavudine plus zidovudine,
A Short History Of Antiretroviral Therapy
Prior to 1996, the average life expectancy of a 20-year-old man newly infected with HIV was a mere 19 years. While the antiretroviral drugs of the time managed to slow the progression of the disease, drug resistance developed quickly, and people would often find themselves with few if any treatment options after a few short years.
At the same time, the daily pill burden could be astonishing. In some cases, a person would be faced with 30 or more pills per day, often taken around the clock at four- to six-hour intervals.
Then, in 1995, a new class of drugs called protease inhibitors was introduced. Barely a year later, three different studies confirmed that the use of a triple-drug therapy could completely control the virus and stop the disease from progressing.
Within two short years, the introduction of combination therapy resulted in a remarkable 60% drop in HIV-related deaths. This revelation ushered in what would come to be known as the age of HAART .
You May Like: When Should I Get Tested For Hiv After Exposure