What If There Is An Actual Or Suspected Exposure To Hiv
The decision to begin a post-exposure prophylaxis for HIV infection is based on the judgment of a health care professional and should be a joint decision with the exposed worker. PEP often involves taking a combination of 2 or 3 antiretroviral drugs for about 4 weeks. PEP can help reduce, but not eliminate, a personâs risk of infection. The PEP should begin as soon as possible, as it may be less effective if started more than 72 hours after exposure.
Occupational Groups Risking Exposure to the AIDS Virus
The occupational groups listed below risk exposure to HIV in the workplace. The table that follows suggests preventive measures for these groups. For many situations, using all protective barriers listed in the table is not necessary, but workplaces should always make them available in case of emergency response scenarios.
Surgeons, Nurses and Nurses Aides
Surgeons, nurses and nurses’ aides should take precautions to avoid needlestick injuries, cuts with sharp instruments and exposure through skin lesions to potentially infectious blood and body fluids.
Physicians and Laboratory Workers
These people continuously handle infectious samples. Doctors, in diagnosing HIV patients, carry out physical examinations and collect blood samples. Laboratory technicians analyze potentially infected samples.
Ambulance Workers
Dental Workers
Embalmers
Embalming the bodies of persons with a HIV infection presents a risk because HIV can live for hours in a deceased body.
Cleaners
What Is Acute Hiv Infection
There are three stages of HIV infection:
- Stage 1:Acute HIVinfection
- Stage 2:Chronic HIV infection
- Stage 3:AIDS
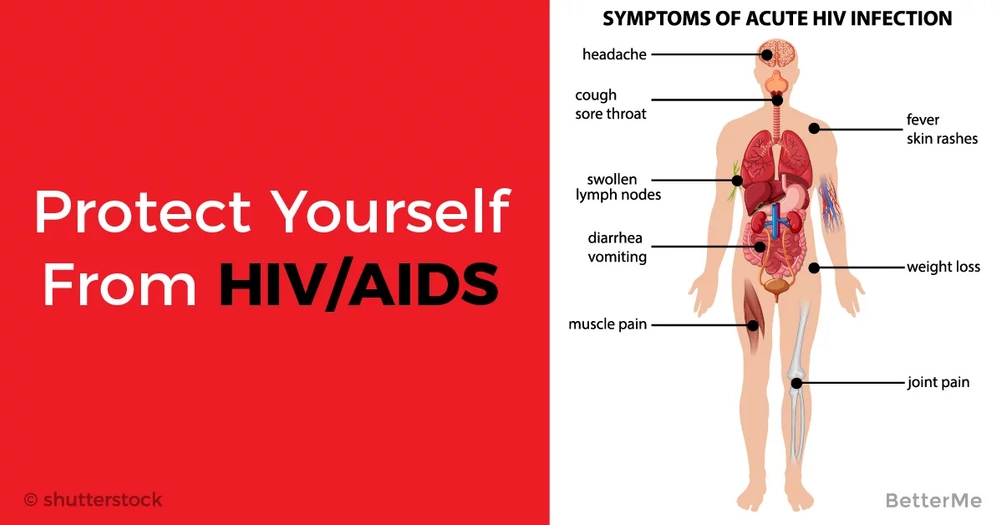
Acute HIV infection is the first stage of the infection. Usually within two to four weeks of infection, two-thirds of those with HIV will experience flu-like symptoms. These symptoms may last for several days or even weeks. However, some people may experience no symptoms at all.
In this stage, there is a large amount of HIV in your blood, which is known as the viral load. Studies have noted incredibly high viral loads during the acute stage, meaning you are more contagious at this time.
All Exposures Are Not Equal
The results of several meta-analyses suggest that some types of sex carry on average a higher risk of HIV transmission than others. Below are estimates from meta-analyses that have combined the results of studies conducted in high-income countries. For types of sex where meta-analysis estimates do not exist, numbers from individual studies are provided.
Anal sex
A meta-analysis exploring the risk of HIV transmission through unprotected anal sex was published in 2010.1 The analysis, based on the results of four studies, estimated the risk through receptive anal sex to be 1.4%. This risk was similar regardless of whether the receptive partner was a man or woman.
No meta-analysis estimates currently exist for insertive anal sex but two individual studies were conducted to calculate this risk. The first, published in 1999, calculated the risk to be 0.06% .2 However, due to the design of the study, this number likely underestimated the risk of HIV transmission. The second study, published in 2010, was better designed and estimated the risk to be 0.11% for circumcised men and 0.62% for uncircumcised men.3
Vaginal sex
A meta-analysis of 10 studies exploring the risk of transmission through vaginal sex was published in 2009.4 It is estimated the risk of HIV transmission through receptive vaginal sex to be 0.08% .
A meta-analysis of three studies exploring the risk from insertive vaginal sex was estimated to be 0.04% .4
Oral sex
Don’t Miss: How Long After Contracting Hiv Do You Get Symptoms
Stage : Acute Primary Infection
The early symptoms of HIV can feel like having the flu. Around one to four weeks after getting HIV, you may start to experience these flu-like symptoms. These normally dont last long . You may only get some of the symptoms and some people dont have any symptoms at all.
Symptoms can include:
- joint aches and pains
- muscle pain.
These symptoms happen because your body is reacting to the HIV virus. Cells that are infected with HIV are circulating throughout your blood system. In response, your immune system tries to attack the virus by producing HIV antibodies this process is called seroconversion. Timing varies but once you have HIV it can take your body up to a few months to go through the seroconversion process.
Having these symptoms alone does not mean you definitely have HIV. The only way to know if you have HIV is by taking a test. You should always visit your healthcare professional if youre worried about or think youve been at risk of getting HIV, even if you feel well and dont have any symptoms. They can then arrange for you to get tested.
HIV will not always show up in a test at this early stage, and you may need to test again later to confirm your result . Your healthcare professional will talk to you about the timing of your test and answer any concerns. Its important not delay speaking to a healthcare worker if you are worried about HIV.
How Well Does Prep Work
PrEP is very effective when you take it every day. It reduces the risk of getting HIV from sex by more than 90%. In people who inject drugs, it reduces the risk of HIV by more than 70%. PrEP is much less effective if you do not take it consistently.
PrEP does not protect against other STDs, so you should still use latex condoms every time you have sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
You must have an HIV test every 3 months while taking PrEP, so you’ll have regular follow-up visits with your health care provider. If you are having trouble taking PrEP every day or if you want to stop taking PrEP, talk to your health care provider.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take To Be Undetectable Hiv
People Unaware Of Having Hiv
Its estimated that about 1 in 7 people living with HIV in the United States dont know they have the virus.
People who are unaware that they have HIV are less likely to take precautions to avoid transmission to other people. They also likely dont take medications to suppress the virus.
If you dont currently have HIV, you can prevent your chances of infection by:
- discussing HIV and STIs with your partner before engaging in sexual activity
- using a barrier method every time you engage in sexual activity
- avoiding sharing needles
- talking with your doctor about postexposure prophylaxis if you may have been exposed to HIV in the past 72 hours
- getting tested for other STIs regularly or before engaging in sexual activity with a new partner
If you do have HIV, you can prevent transmitting it to others by:
- discussing HIV and STIs with your partner before engaging in sexual activity
- using a barrier method every time you engage in sexual activity
- taking your medications as prescribed
- avoiding sharing needles or drug injection equipment
- having your viral load tested regularly as recommended by your doctor
How Long Does It Take To Show Symptoms Of Hiv
The human immunodeficiency virus is a virus that attacks your bodys immune system. Left untreated, it can lead to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome . Early diagnosis is key to slowing down disease progression.
Symptoms may vary from person to person, but knowing the early symptoms that could present can help you get diagnosed and treated as soon as possible.
This article will discuss the various stages of HIV, how symptoms may present, how testing works, and what to expect if you test positive for the virus.
Verywell / Danie Drankwalter
Also Check: How Long Hiv To Aids
Interpreting The Numberswhat Additional Information Needs To Be Provided
Some clients may see these numbers and think their risk of HIV transmission is low. Therefore, caution is needed when interpreting them. If these numbers are provided to clients, they should be accompanied by information that helps shed light on why the risk may be higher than it seems.
Transmission can occur after one exposure.
It is important to emphasize that a person could become infected from having unprotected sex once or a person could have unprotected sex many times and not become infected, regardless of how low or high the risk per exposure is.
A risk of 1% would mean that an average of one infection would occur if 100 HIV-negative people were exposed to HIV through a certain type of sex. It does not mean that a person needs to be exposed 100 times for HIV infection to occur.
These are estimates of average risk in the absence of biological factors that increase risk.
The numbers in the table above are rough estimates. They are averages and do not represent the risk from all exposures to HIV through a certain type of sex.
The risk of HIV transmission may be much higher than these averages if biological risk factors are present. For example, research shows that STIs and some vaginal conditions, such as bacterial vaginosis, can increase the risk of HIV transmission by up to 8 times.6,7,8 As a result, the risk of an HIV-negative woman becoming infected through unprotected receptive vaginal sex could be closer to 1% if she has a vaginal STI.
Symptoms Of Hiv Infection
Most people experience a short flu-like illness 2 to 6 weeks after HIV infection, which lasts for a week or 2.
After these symptoms disappear, HIV may not cause any symptoms for many years, although the virus continues to damage your immune system.
This means many people with HIV do not know they’re infected.
Anyone who thinks they could have HIV should get tested.
Some people are advised to have regular tests as they’re at particularly high risk.
Also Check: Do Nba Youngboy Have Herpes
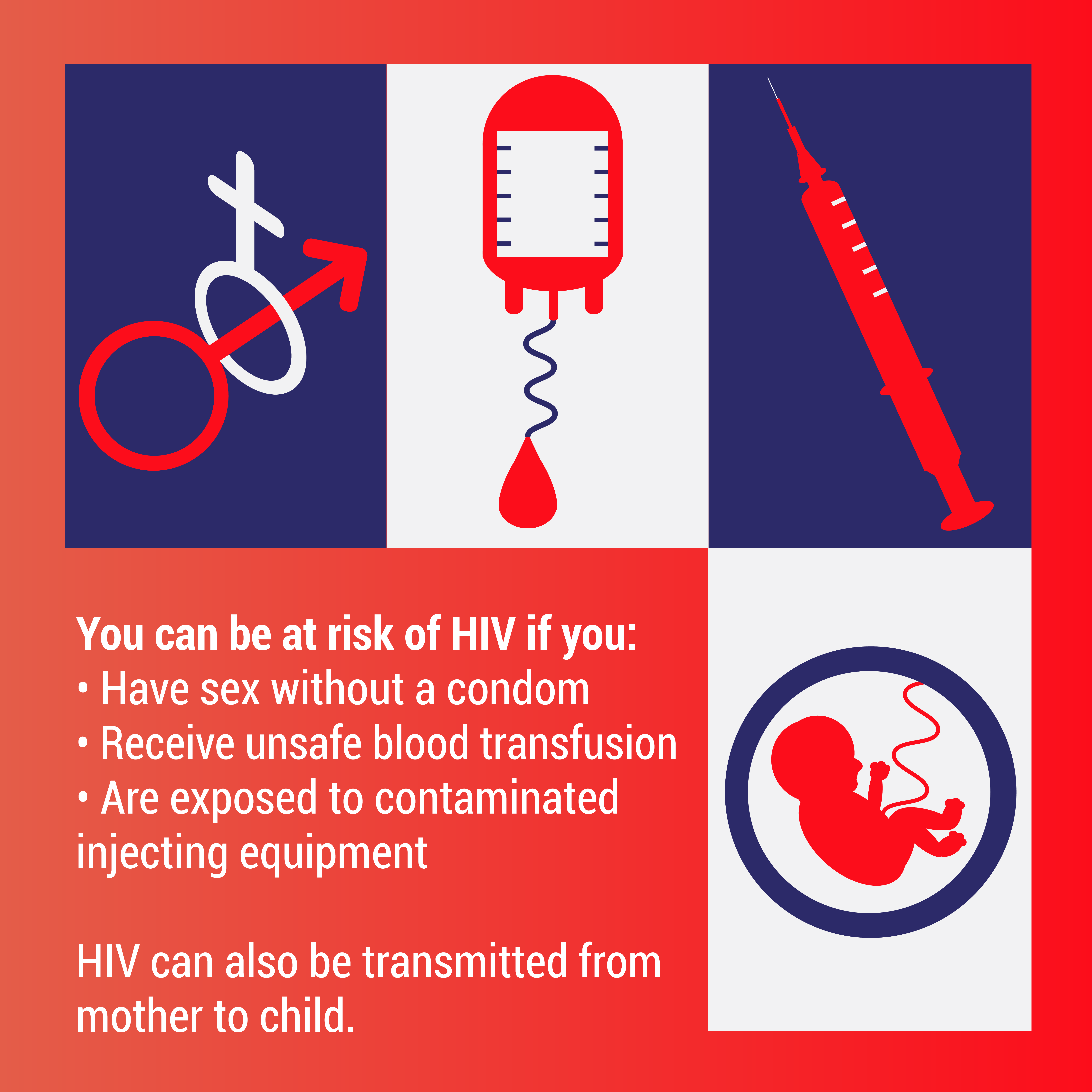
How Is Hiv Transmitted
The person-to-person spread of HIV is called HIV transmission. People can get or transmit HIV only through specific activities, such as sex or injection drug use. HIV can be transmitted only in certain body fluids from a person who has HIV:
- Blood
- Vaginal fluids
- Breast milk
HIV transmission is only possible if these fluids come in contact with a mucous membrane or damaged tissue or are directly injected into the bloodstream . Mucous membranes are found inside the rectum, the vagina, the opening of the penis, and the mouth.
In the United States, HIV is spread mainly by:
- Having anal or vaginal sex with someone who has HIV without using a condom or taking medicines to prevent or treat HIV
- Sharing injection drug equipment , such as needles, with someone who has HIV
HIV can also spread from a woman with HIV to her child during pregnancy, childbirth , or breastfeeding. This is called perinatal transmission of HIV. Perinatal transmission of HIV is also called mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
You cannot get HIV from casual contact with a person who has HIV, such as a handshake, a hug, or a closed-mouth kiss. And you cannot get HIV from contact with objects, such as toilet seats, doorknobs, or dishes used by a person who has HIV.
Use the You Can Safely ShareWith Someone With HIV infographic from HIVinfo to spread this message.
Who Should Consider Taking Prep
PrEP is for people without HIV who are at very high risk for getting it. This includes:
Gay/bisexual men who:
- Have an HIV-positive partner
- Have multiple partners, a partner with multiple partners, or a partner whose HIV status is unknown and
- Have anal sex without a condom OR
- Have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease in the last 6 months
Heterosexual men and women who:
- Have an HIV-positive partner
- Have multiple partners, a partner with multiple partners, or a partner whose HIV status is unknown and
- Don’t always use a condom when having sex with people who inject drugs OR
- Don’t always use a condom when having sex with bisexual men
People who inject drugs and:
- Share needles or other equipment to inject drugs OR
- Are at risk for getting HIV from sex
If you have a partner who is HIV-positive and are considering getting pregnant, talk to your health care provider about PrEP. Taking it may help protect you and your baby from getting HIV infection while you try to get pregnant, during pregnancy, or while breastfeeding.
You May Like: Is Hair Loss A Symptom Of Hiv
Where To Get Pep
PEP is available on the NHS for free, but is only given to people who meet guidelines about its use.
The best place to get PEP is a sexual health or HIV clinic. If you need PEP over the weekend or outside of office hours, when clinics will often be closed, the best place to go is an Accident and Emergency department.
PEP is not normally available from GPs.
As PEP is a powerful course of drugs, and is expensive to prescribe, you might be asked about:
- the person you had sex with
- what sort of sex you had
- if the other person had HIV, what their viral load is.
If the person you had sex with is living with HIV and has an undetectable viral load, you will not need PEP as it wont be possible for the virus to have been transmitted.
Once a doctor decides that its appropriate for you to have PEP, you will be asked to take an HIV test. This is to make sure you dont already have HIV. If HIV is detected by a test, other forms of treatment will be recommended to you.
What Is Hiv And Aids
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus is a virus that infects the immune system. Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome . AIDS is the most advanced stage of the HIV infection and causes the immune system to become vulnerable to other infections. HIV can also be known as “the AIDS virus.”
The full name for AIDS describes several of the characteristics of the disease.
Acquired indicates that it is not an inherited condition.
Immune Deficiency indicates that the body’s immune system breaks down.
Syndrome indicates that the disease results in a variety of health problems.
It takes on average, 5-10 years for the initial HIV infection to progress to AIDS if not treated. While there is presently no cure or vaccine for HIV, with proper medical care, HIV can be managed and a near-normal lifespan can be expected with early treatment.
Recommended Reading: How Long From Hiv To Aids
How Do I Access Pep
If you think you have been exposed to HIV, do not wait for an appointment to see a GP. Call the PEP info line at the Victorian HIV Prevention Service for guidance and information about where to find your closest PEP provider.
Your PEP provider will ask you a series of questions to determine your risk and whether PEP is appropriate.
PEP is available from the emergency department of most public hospitals, sexual health clinics and some other general practice clinics which specialise in sexual health.
If the exposure happens after hours, emergency departments are often the best place to go to make sure you start PEP as soon as possible.
PEP is widely available in Victoria and further information can be found at:
Get yourself tested for STIs, and treated if necessary, by your local GP .
PEP is not a morning-after pill that makes it easy and safe to have sex without a condom. You must take the medication every day for 28 days for PEP to work.
How Can You Get Hiv
HIV is found in the following bodily fluids of someone living with the virus:
- blood
- vaginal fluids
- breastmilk.
For you to get HIV, these bodily fluids need to get into your blood through a mucous membrane , via shared injecting equipment, or through broken skin .
There is not enough HIV virus in other bodily fluids, like saliva, sweat or urine, to transmit it from one person to another.
Someone living with HIV who has an undetectable viral load, meaning effective treatment has lowered the amount of virus in their blood to levels where it cannot be detected by a normal blood test, cannot pass on HIV.
A person living with HIV with a detectable viral load can pass the virus to others whether they have symptoms or not.
HIV is most infectious in the first few weeks after infection. At this time many people are unaware of their status.
The main ways you can get HIV are:
Also Check: Does Nba Youngboy Still Have Herpes
How Do I Get Pep
You can get PEP from emergency rooms. It might also be available at some health clinics or Planned Parenthood health centers, and some doctors offices, but call first to make sure they have PEP in stock.
You can start PEP up to 72 hours after you were exposed to HIV, but dont wait its really important to start PEP as soon as possible. So if you cant get to a doctor or nurse right away, go to the emergency room as soon as you can. Every hour counts.
Before you get PEP, the nurse or doctor will talk with you about what happened, to decide whether PEP is right for you. Theyll give you a blood test for HIV . Youll also be tested for Hepatitis B. And if you were exposed to HIV through sex, youll get tests for other STDs like gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis.
Aids Is The Final Stage
Controlling HIV with medications is crucial to both maintaining quality of life and helping prevent progression of the disease. Stage 3 HIV, also known as AIDS, develops when HIV has significantly weakened the immune system.
According to the CDC National Prevention Information Network, CD4 levels give one indication that HIV has progressed to its final stage. CD4 levels decreasing below 200 cells per cubic millimeter of blood is considered a sign of AIDS. A normal range is considered 500 to 1,600 cells/mm3.
AIDS can be diagnosed with a blood test to measure CD4. Sometimes its also determined simply by a persons overall health. In particular, an infection thats rare in people who dont have HIV may indicate AIDS. Symptoms of AIDS include:
- persistent high fevers of over 100°F
- pneumonia
AIDS is the final stage of HIV. According to AIDSinfo, it takes at least 10 years without treatment for most people with HIV to develop AIDS.
At that point, the body is susceptible to a wide range of infections and cant effectively fight them off. Medical intervention is necessary to treat AIDS-related illnesses or complications that can otherwise be fatal. Without treatments, the CDC estimates the average survival rate to be three years once AIDS is diagnosed. Depending on the severity of their condition, a persons outlook may be significantly shorter.
Recommended Reading: Nba Youngboy Herpes In My Blood