Take Time To Process The News
- Receiving an HIV diagnosis can be life changing. You may feel many emotionssadness, hopelessness, or anger.
- Allied health care providers and social service providers can help you work through the early stages of your diagnosis. They are often available at your health care providers office.
- Learn more about what a positive test result means.
What Does The Test Measure
HIV tests detect the presence of the HIV virus, HIV antigens, and/or HIV antibodies. If these substances are detected, the test returns a positive result for HIV.
There are three types of HIV tests available:
- Antibody test: Antibodies are produced by the body after an HIV infection. It can take weeks for the body to produce antibodies, so HIV antibody tests can only detect HIV from 3 to 12 weeks after infection.
- Antigen/antibody test: Antigens are foreign substances that activate an immune response. Antigens appear before the body produces antibodies, so HIV antigen/antibody tests can detect an HIV infection earlier than antibody tests, within 2 to 4 weeks of becoming infected.
- HIV viral load test: An HIV viral load test looks for the quantity of HIV virus in the blood. In addition to detecting an HIV infection, viral load testing can also detect how much of the virus is in the blood. Although this type of testing can detect an HIV infection earlier than other HIV tests, its very expensive and is typically only used when someone has symptoms or a possible exposure to HIV.
Distinguishing Between New Hiv Infections And Old Ones
Guidelines for universal HIV testing have existed for a long time now. However, many people do not get tested for HIV on a regular basis. That means that at the time someone is diagnosed with a new HIV infection, they may wonder if there is any way of knowing when they were infected or who infected them.
Recommended Reading: Is Hiv Transmitted From Dental Unit Water
Can Hiv Be Prevented Or Avoided
The best way to prevent HIV is to not have sex with a person who has HIV, or share a needle with a person who has HIV. However, there is also a medicine called PrEP that people can take before coming into contact with HIV that can prevent them from getting an HIV infection.
PrEP stands for pre-exposure prophylaxis. It is for people who are at long-term risk of getting HIV either through sexual activity or by injecting drugs. If youre taking PrEP and come into contact with HIV, the medicine makes it difficult for HIV to develop inside your body.
Other ways to prevent HIV include:
- When you have sex, practice safer sex by using a condom. The best condom is a male latex condom. A female condom is not as effective but does offer some protection.
- Do not share needles and syringes.
- Never let someone elses blood, semen, urine, vaginal fluid, or feces get into your anus, vagina, or mouth.
Hiv Is Detected With A Blood Test
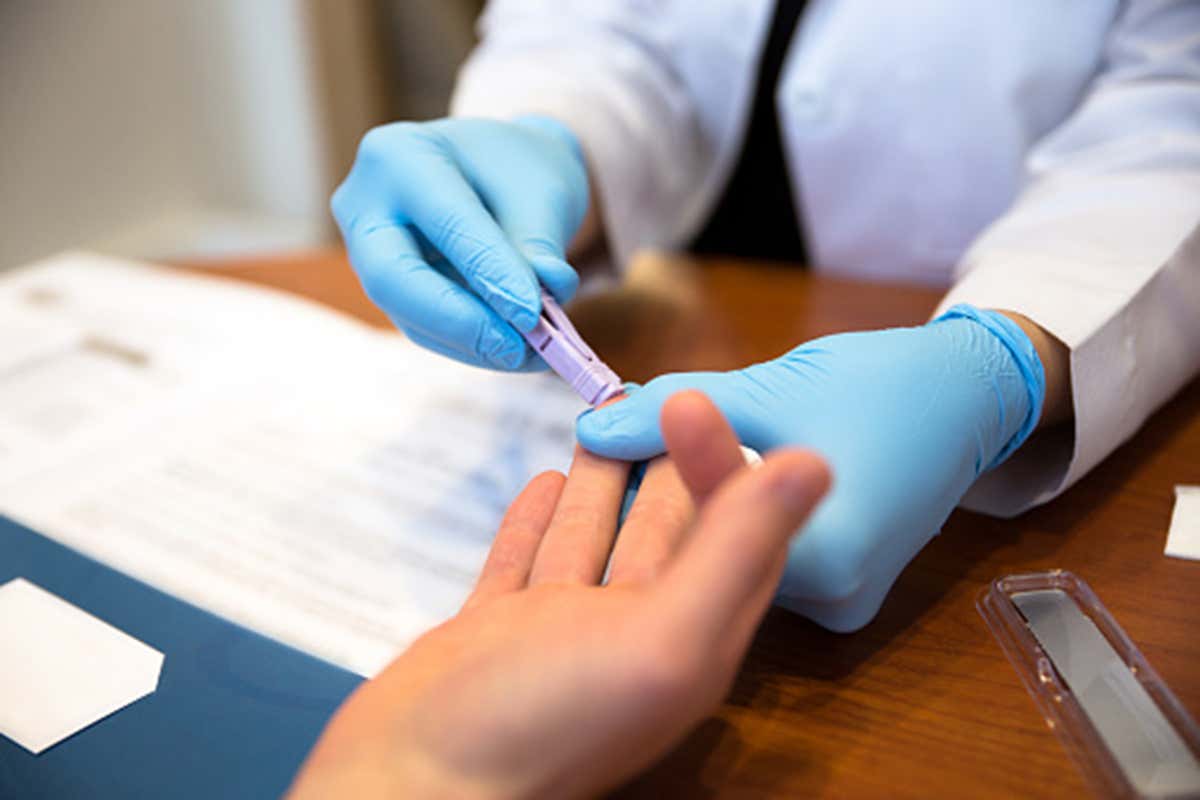
Blood tests are the most common and reliable tests for HIV. The virus is detected by taking a sample of your blood either with a conventional blood test or a rapid test .There is a short period of time between exposure to HIV and the ability for tests to detect HIV or its antibodies. This is often referred to as the ‘window period’ between 2 and 12 weeks.
Most tests used in Australia can detect HIV as early as 2 to 4 weeks after infection.
If your blood test shows that HIV or its antibodies are present, you are HIV-positive.
If you have no antibodies in your blood you are HIV-negative. Sometimes negative results might also mean you are in the window period, so you might need a follow-up blood test to make sure.
Don’t Miss: Is Hiv Curable Or Treatable
A Sexually Transmitted Infection
Katie Salerno/Flickr Creative Commons
Contracting other sexually transmitted diseases can significantly increase the risk of getting HIV. For instance, some STDs like syphilis and herpes cause skin lesions that make it easier for HIV to enter the body.
STDs may also cause inflammation, which is something that is triggered by the body’s immune system. HIV preferentially infects defensive white blood cells, so when there are more of them around, it’s easier to contract HIV.
Having an STD like gonorrhea or syphilis means that you’ve engaged in unprotected sex, a key risk factor for HIV. So if you have been diagnosed with an STD, talk to your healthcare provider about how you can reduce your HIV risk.
Ask A Laboratory Scientist
This form enables patients to ask specific questions about lab tests. Your questions will be answered by a laboratory scientist as part of a voluntary service provided by one of our partners, American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science. Please allow 2-3 business days for an email response from one of the volunteers on the Consumer Information Response Team.
Read Also: What Is Hiv 1 And 2 Antibody Test
I Am An Hiv Positive Doctor
In 2002, when I was in my mid-20s, I went down with a severe cold and was in bed for a couple of days. I was feeling lousy, with a headache and stiff neck, so a GP friend looked in on me to check that I was OK. Neither of us recognised my symptoms as anything more than a bad bout of flu.
Eight weeks later, at a routine check-up, I was diagnosed as HIV positive. I felt shocked, although the result wasn’t a complete surprise. As a gay man there was a chance that I’d be exposed to the virus, and might acquire it.
My first thought was how the diagnosis would affect my job. I’d been a doctor for only four years. This was something for which I had worked very hard, something I desperately wanted to do. I was terrified I would be told I could not practise any more.
The next day, I arranged to meet an occupational health consultant. It was my responsibility to inform my employers, but I was fearful of their reaction. I hadn’t sustained a needle-stick injury while working in the developing world or been given an infected blood product, but had contracted the disease through the potentially more blameworthy unsafe, random sexual encounter.
Six months after telling my superiors I felt overwhelmed by my workload, I eventually took myself out of work. Even then, I was given no advice other than that maybe medicine wasn’t for me after all.
· Do you have an experience to share? Email:
Polymerase Chain Reaction Test
If a person had a recent exposure to HIV, or is experiencing symptoms of acute HIV infection such as fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes, a doctor may order a polymerase chain reaction test. Unlike antibody and antigen tests that look for the bodys response to HIV, the PCR test detects HIV itself. This test is typically used three days to one month after an exposure. An early diagnosis allows people to begin treatment immediately and helps them take extra precautions to prevent spreading HIV to others.
If a person receives a positive HIV test result, a doctor schedules a follow-up appointment to discuss the results and the next steps for treatment. The doctor may order several additional blood tests to estimate how long the person has been infected and how far the condition has progressed.
A doctor may also use blood tests to screen for complications or other infections, such as other sexually transmitted infections, as well as toxoplasmosis, which is a parasitic infection, or hepatitis, a liver infection.
Read Also: Is Hiv Transmitted Through Sperm
When Do Symptoms Occur
Some people have flu-like symptoms within two to four weeks after infection, but others may not feel sick or not develop symptoms at all until later.
See a healthcare provider if you have symptoms of HIV and think you may have been exposed to HIV. Getting tested for HIV is the only way to know for sure.
In the United States, HIV is spread mainly through having anal or vaginal sex or sharing needles or syringes with an HIV-positive partner. Anal sex is the highest-risk behavior.
You can prevent HIV by using condoms correctly every time you have sex pre-exposure prophylaxis, a prevention method in which the HIV-negative partner takes daily HIV medicine to prevent HIV and treatment as prevention, a method in which the HIV-positive partner takes daily HIV medicine to achieve and maintain an undetectable viral load.
Only antigen/antibody tests or nucleic acid tests can diagnose acute HIV infection. NATs look for actual virus in the blood, and antigen/antibody tests look for HIV antibodies and antigens. Antibodies are produced by your immune system when youre exposed to viruses like HIV, and antigens are foreign substances that cause your immune system to activate.
However, no test can detect HIV immediately after infection. NATs can usually tell if you have an HIV infection 10 to 33 days after exposure, while antigen/antibody tests can tell 18 to 45 days after exposure.
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Mouth ulcers or sores
What Tests Can Help Monitor Your Hiv Infection
Your health care provider will use blood tests to monitor your HIV infection. The results of these blood tests, which measure the amount of HIV virus and the number of CD4 cells in your blood, will help you and your health care provider understand how well your HIV treatment is working to control your HIV infection. These test results will also help your health care provider decide whether he or she should make changes to your treatment.
These blood tests include regular CD4 counts and viral load tests. Read about these tests below.
Read Also: How Would You Know If You Had Hiv
How Do The Symptoms Of Hiv Progress A Complete Timeline
HIV is a virus that compromises the bodys immune system. There is no cure for HIV. However, there are many treatment options available to considerably reduce the effect of this virus on the patients life. In most cases, once the patient has been infected with HIV, it stays in their body for their entire lifetime.
However, unlike many other types of viruses, HIV symptoms dont happen overnight they take several months to progress. The outcome of the HIV treatments mainly depends on how early the HIV infection has been detected.
ELISA Kits are used to diagnose HIV. Its advised by doctors to take the test frequently to determine the positive effects of treatment. This test is continuously done for several months after the successful treatment to ensure that HIV has not retracted.
If untreated, the HIV infection grows with time through stages to become life-threatening, with each phase having its own set of symptoms and compilations.
Letting Partners Know You Have Hiv

If you have just been diagnosed with HIV, it will likely be a difficult time. You might still be struggling to come to terms with diagnosis.
During this time, it is important to let any sexual or injecting partners know they may have been exposed to HIV as soon as you can, so they can be tested and offered PEP if appropriate.
You do not have to do this alone. Your doctor or the Department of Health and Human Services Partner Notification Officers can help you through this process and ensure your identity is not revealed.. Both groups can provide information, support, and guidance for people living with HIV.
Don’t Miss: How Can Hiv Be Controlled
How Soon After Exposure To Hiv Can Tests Detect I Have The Virus
The window of time between exposure to HIV and when a test will show you have the virus varies from person to person and by the type of test:
- Nucleic acid test : The NAT test can detect HIV infection the earliest. It can tell if you have HIV infection 10 to 33 days after exposure.
- Antigen/antibody test: The antigen/antibody test can detect infection 18 to 45 days after exposure when performed by a lab using blood from a vein. If the sample is from a finger prick, the window is 18 to 90 days after exposure.
- Antibody test: Antibody tests can detect infection 23 to 90 days after exposure.
If your initial test is negative, get a second test after the window of time has passed. The second test can confirm your negative result in case you got tested before the infection was active in your body.
Remember, post-exposure prophylaxis can help prevent infection, but you must start it within 72 hours of possible infection. Talk to your healthcare provider about how to start PEP.
Be Aware Of Possible Complications
HIV also is an inflammatory disease that affects many parts of the body, not just the immune system. That means that HIV can affect organs like the brain, kidneys, liver, and heart and may increase the risk of some cancers.
HIV medicines can sometimes have side effects. Sometimes these can raise the risk of heart disease or kidney disease. It is important that you let your providers know if you notice any concerning symptoms. For more information on opportunistic infections and other complications of HIV, see HIV-related conditions.
Know when to call your provider
You don’t need to panic every time you have a headache or get a runny nose. But if a symptom is concerning you or is not going away, it is always best to have a provider check it out.
The following symptoms may or may not be serious, but don’t wait until your next appointment before calling your provider if you are experiencing them. Breathing problems:
- Appearance of brownish, purple or pink blotches on the skin
- New or worsening rash–especially important if you are taking medication
Eye or vision problems:
- blurring, wavy lines, sudden blind spots
- eye pain
- numbness, tingling, or pain in hands and feet
- headache, especially when accompanied by a fever
- stiffness in neck
- pain in lower abdomen, often during sex
Other symptoms:
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Hiv Test Take
Hiv Testing And Your Rights
Testing for HIV is voluntary and can only be done with your informed consent, except in exceptional circumstances.
Before you are tested, you will be provided with information about what is involved. what the results might mean for you, and how to prevent HIV transmission in the future. All people who request an HIV test must receive this information from the test provider.
Under Australian and Victorian law, it is unlawful to discriminate against anyone who has HIV. Test results, and details on whether someone has been tested are strictly confidential. It is illegal for any information about a person being tested or a person with HIV to be disclosed without their permission.
When Is It Ordered
An HIV viral load test is typically ordered with a CD4 count when you are first diagnosed with HIV infection as part of a baseline measurement. After the baseline, a viral load test will usually be ordered at intervals over time, depending on a few different factors.
The following table summarizes recommendations* for the timing of viral load testing and CD4 counts:
| Your Clinical Status | ||
| With new HIV symptoms or start of new treatment with interferon, corticosteroids or cancer drugs | Every 3 months | Perform test and monitor according to health status |
*Adapted from Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in HIV-1Infected Adults and Adolescents, Table 4. Recommendations on the Indications and Frequency of Viral Load and CD4 Count Monitoring.
Read Also: Can You Get Hiv Without Ejaculation
How Are Hiv And Aids Diagnosed
A doctor may suspect HIV if symptoms last and no other cause can be found.
If you have been exposed to HIV, your immune system will make antibodies to try to destroy the virus. Doctors use tests to find these HIV antibodies or antigens in urine, saliva, or blood.
A diagnosis of HIV infection is not made until a positive ELISA test is confirmed by a positive test to detect HIV DNA or RNA. A PCR test can do this.
HIV antibodies or antigens usually show up in the blood within 3 months. If you think you have been exposed to HIV but you test negative for it:
- Get tested again. A repeat test may be done after a few weeks to be sure you are not infected.
- Meanwhile, take steps to prevent the spread of the virus, in case you do have it.
- Avoid sexual contact with others. If you do have sex, practice safer sex.
- Do not share needles, syringes, cookers, cotton, cocaine spoons, or eyedroppers.
Getting tested and home test kits
You can get HIV testing in most doctors’ offices, public health clinics, hospitals, and Planned Parenthood clinics.
A home test kit for HIV has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration . For the test, you rub your gums with a swab supplied by the kit. Then you place the swab into a vial of liquid. The test strip on the swab indicates if you have HIV or not.
If the results from a home test kit show that you have an HIV infection, talk with a doctor.
Tests after a positive result
- Syphilis.
- Hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
- Tuberculosis .
What Is Acute Hiv Infection
There are three stages of HIV infection:
- Stage 1:Acute HIVinfection
- Stage 2:Chronic HIV infection
- Stage 3:AIDS
Acute HIV infection is the first stage of the infection. Usually within two to four weeks of infection, two-thirds of those with HIV will experience flu-like symptoms. These symptoms may last for several days or even weeks. However, some people may experience no symptoms at all.
In this stage, there is a large amount of HIV in your blood, which is known as the viral load. Studies have noted incredibly high viral loads during the acute stage, meaning you are more contagious at this time.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hiv From Just Sticking It In