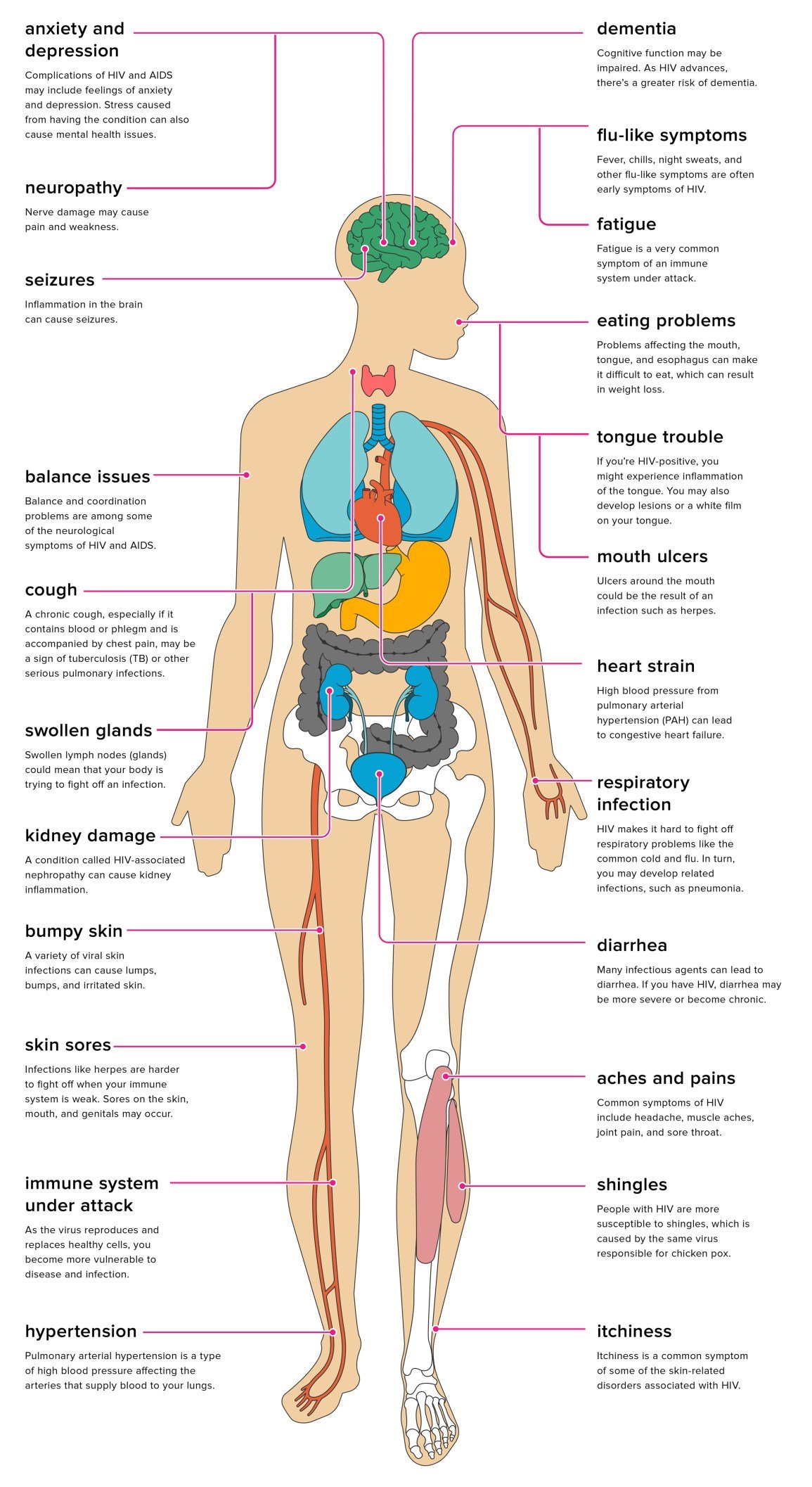
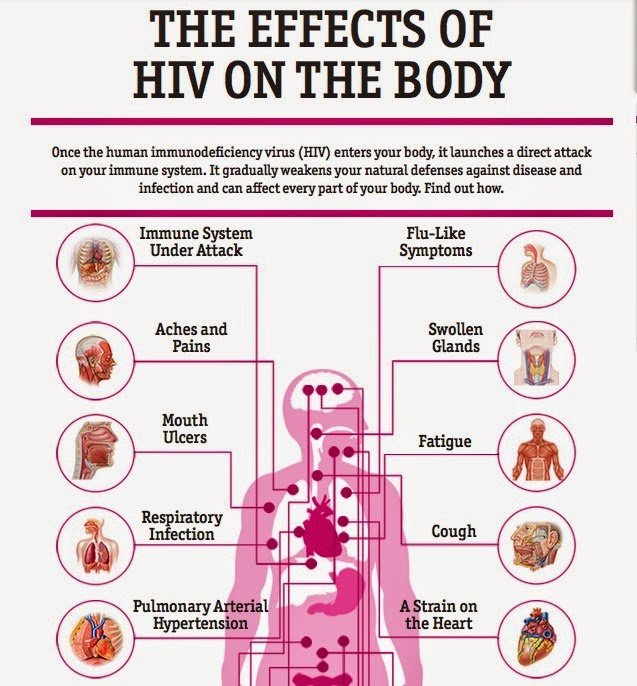
Preventing Transmission By Blood Transfusions And Organ Transplants
In the United States, the following have almost eliminated transmission of HIV infection by organ transplantation or blood transfusion:
-
Screening donors of organs or blood for risk factors for HIV infection
-
Screening donated blood for HIV
Risk is reduced further by asking people with risk factors for HIV infection, regardless of their test results for HIV, not to donate blood or organs for transplantation.
However, developing countries have not consistently used sensitive HIV screening tests and have not restricted donors. Consequently, transmission by these routes is still a problem in these countries.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Is there any sure way to avoid acquiring HIV?
- What is the best treatment for me?
- How can I avoid getting any infections that will make me very sick?
- How can I find support groups in my community?
- What diagnostic tests will you run?
- How often will I need to see my doctor?
- Will there be any side effects to my treatment?
- How does this affect my plans for having a family?
- Is it safe for me to breastfeed my baby?
- Will using a condom keep my sex partners from acquiring HIV?
- Should I follow a special diet?
Can Hiv Be Prevented Or Avoided
The best way to prevent HIV is to not have sex with a person who has HIV, or share a needle with a person who has HIV. However, there is also a medicine called PrEP that people can take before coming into contact with HIV that can prevent them from getting an HIV infection.
PrEP stands for pre-exposure prophylaxis. It is for people who are at long-term risk of getting HIV either through sexual activity or by injecting drugs. If youre taking PrEP and come into contact with HIV, the medicine makes it difficult for HIV to develop inside your body.
Other ways to prevent HIV include:
- When you have sex, practice safer sex by using a condom. The best condom is a male latex condom. A female condom is not as effective but does offer some protection.
- Do not share needles and syringes.
- Never let someone elses blood, semen, urine, vaginal fluid, or feces get into your anus, vagina, or mouth.
Also Check: Is Hiv In Semen
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus Essay
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus affects the human wellbeing by attacking the bodys immune system which is the natural defense system in the human body to resist infections. When the immune system is compromised, the body becomes less capable of fighting diseases, allowing the body to become more susceptible to infections. Different from other viruses that the body can get rid of, HIV will remain in the body for life . HIV works by attacking the CD4 cells, which assist
Cytopathic Effects Produced By In Vitro Infection With Hivs
The molecular mechanism by which HIV induces cytopathology in susceptible cells is not well understood. In vitro HIV infected cells formed multinucleated giant cells that can produce large amounts of virus before they die, within a period of a few days, normally within 48 hours. Syncytia formation in culture results from fusion of infected cells with uninfected CD4+ cells and involves the CD4 molecule and HIV gp120 and gp41 proteins., Although the precise mechanism is still not known, syncytia formation is linked to the V3 loop of gp120 envelope region., Thus, the differences in the amino acids sequences of the V3 loop determine SI versus NSI isolates and whether an HIV isolate will induce syncytia formation or not. T cell tropic viruses generally have a basic amino acid at one or more of the positions 11, 24, 25 and 32 of the V3 loop, whereas macrophage tropic viruses have either an acidic amino acid or alanine at position 25.
Generally syncytia formation is the most common event preceding cell death in vitro. There is some evidence that syncytia can occur in vivo and syncytia have been observed in the lymph nodes of homosexual men with lymphadenopathy, in lymph nodes and lungs of children with AIDS and in brain tissues of some adult patients who died with AIDS and is therefore possibly important in the pathogenesis of AIDS.
You May Like: Nba Youngboy Has Herpes
Is Hiv And Aids An Occupational Concern
Where ever there is the possibility of contact with blood in the workplace, workers should take precautions to prevent contact with the skin, eyes or mucous membranes .
Routine Practices are recommended to prevent the spread of HIV in the workplace. Routine practices are based on the principle that all blood, body fluids, secretions, and excretions except sweat, non-intact skin, and mucous membranes, unless they contain visible blood, may contain transmissible infectious agents. Steps involve using protective clothing such as gloves, gowns or aprons, masks and protective eye wear when dealing with people’s blood and other blood-contaminated body fluids such as semen and vaginal secretions. They also do not apply to saliva except in dentistry where saliva is likely to be contaminated with blood.
Hand washing after contact with blood, blood-contaminated body fluids and soiled items is also recommended to reduce the risk of infection.
The best approach to most diseases is to prevent their occurrence – occupationally-related diseases are no exception. In the case of HIV, prevention is the only cure.
How Is Hiv Diagnosed
A doctor may suspect HIV if symptoms last and no other cause can be found.
If you have been exposed to HIV, your immune system will make antibodies to try to destroy the virus. Doctors use tests to find these HIV antibodies or antigens in urine, saliva, or blood.
If a test on urine or saliva shows that you are infected with HIV, you will probably have a blood test to confirm the results.
Most doctors use a blood test to diagnose HIV infection. If the test is positive , a test to detect HIV DNA or RNA will be done to be sure.
HIV antibodies or antigens usually show up in the blood within 3 months. If you think you have been exposed to HIV but you test negative for it:
- Get tested again. A repeat test may be done after a few weeks to be sure you are not infected.
- Meanwhile, take steps to prevent the spread of the virus, in case you do have it.
You can get HIV testing in most doctors’ offices, public health clinics, hospitals, and Planned Parenthood clinics. You can also buy a home HIV test kit in a drugstore or by mail order. Make sure it’s one that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration . If a home test is positive, see a doctor to have the result confirmed and to find out what to do next.
Don’t Miss: Does Nba Youngboy Have Herpies
Inhibition Of Hivs Entry
The entry of HIVs is currently understood to be essentially a three-step process consisting of attachment, chemokine co-receptor interaction, and fusion. Therefore, specific areas of interest to inhibit HIVs entry include blocking gp120 binding to CD4 cell receptors , blocking the binding sites of co-receptors such as CCR5 and CXCR4 , and disrupting the fusion process .
The fusion inhibitor, enfuvirtide , a 36-amino acid peptide being developed jointly by Trimeris and Roche, is in the most advanced stage of clinical development. HIV fusion with CD4 cells is a complex process, and not very well understood, and involves a conformational change in the HIV envelope gp120/gp41, leading to an interaction between gp41 that lead to intimate proximity between the HIV envelope and the cell membrane, allowing fusion to occur. Enfuvirtide is active against both CCR-5- and CXCR4-using viruses and are synergistic with CCR5 and CXCR4 antagonists.
How Is Hiv Spread From Person To Person
HIV can only be spread through specific activities. In the United States, the most common ways are:
- Having vaginal or anal sex with someone who has HIV without using a condom or taking medicines to prevent or treat HIV. Anal sex is riskier than vaginal sex.
- Sharing injection drug equipment , such as needles, with someone who has HIV.
Less common ways are:
- From mother to child during pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding. However, the use of HIV medicines and other strategies have helped lower the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV to 1% or less in the United States.
- Getting stuck with an HIV-contaminated needle or other sharp object. This is a risk mainly for health care workers. The risk is very low.
HIV is spread only in extremely rare cases by:
- Having oral sex. But in general, the chance that an HIV-negative person will get HIV from oral sex with an HIV-positive partner is extremely low.
Recommended Reading: Hiv From Dried Blood
Who Is At Risk For Hiv Infection
Anyone can get HIV, but certain groups have a higher risk of getting it:
- People who have another sexually transmitted disease . Having an STD can increase your risk of getting or spreading HIV.
- People who inject drugs with shared needles
- Gay and bisexual men, especially those who are Black/African American or Hispanic/Latino American
- People who engage in risky sexual behaviors, such as not using condoms
Transmission Of Hiv Infection
The transmission of HIV requires contact with a body fluid that contains the virus or cells infected with the virus. HIV can appear in nearly any body fluid, but transmission occurs mainly through blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk. Although tears, urine, and saliva may contain low concentrations of HIV, transmission through these fluids is extremely rare, if it occurs at all.
HIV is not transmitted by casual contact or by close, nonsexual contact at work, school, or home. No case of HIV transmission has been traced to the coughing or sneezing of an infected person or to a mosquito bite. Transmission from an infected doctor or dentist to a patient is extremely rare.
HIV is usually transmitted in the following ways:
HIV is more likely to be transmitted if skin or a mucous membrane is torn or damagedeven if minimally.
In the United States, Europe, and Australia, HIV has been transmitted mainly through men who have sex with men and the sharing of needles among people who inject drugs, but transmission through heterosexual contact accounts for about one fourth of cases. HIV transmission in Africa, the Caribbean, and Asia occurs primarily between heterosexuals, and HIV infection occurs equally among men and women. In the United States, fewer than 25% of adults who have HIV infection are women. Before 1992, most American women with HIV were infected by injecting drugs with contaminated needles, but now most are infected through heterosexual contact.
You May Like: How Long Can Hiv Go Undetected
Adaptive Immune Response To Hiv
Cellular immune response to HIV. The cellular immune response is induced upon the entry of HIV into the target cells and synthesis of viral proteins . MHC class I on the cell surface displays the intracellularly degraded HIV peptide fragments for recognition by T-cell receptors on CD8+ T cells . CD8+ T cells lyse HIV infected cells and secrete cytokines, i.e. interferon- , tumor necrosis factor , and chemokines, i.e. MIP-1 , MIP and RANTES, that inhibit virus replication and block viral entry into CD4+ T cells. Development of CD8+ T cells is crucial for control of HIV replication. This results in declining viraemia after primary infection. In the early stages of infection, CD4+ T cells lose their proliferative capacity and therefore their contribution to viral control is minor. However, during chronic infection CD4+T cells are present and secrete interleukin-2 or cytokines, such as IFN-, to control viraemia.
Figure 3.
Preventive Treatment After Exposure
People who have been exposed to HIV from a blood splash, needlestick, or sexual contact may reduce the chance of infection by taking antiretroviral drugs for 4 weeks. These drugs are more effective when they are started as soon as possible after the exposure. Taking two or more drugs is currently recommended.
Doctors and the person who was exposed typically decide together whether to use these preventive drugs. They base the decision on the estimated risk of infection and the possible side effects of the drugs. If they do not know whether the source is infected with HIV, they consider how likely the source is to be infected. However, even when the source of the exposure is known to be infected with HIV, the risk of infection after exposure varies, depending on the type of exposure. For example, risk from a blood splash is less than that from a needlestick.
Immediately after exposure to HIV infection, what is done depends on the type of exposure:
-
If skin is exposed, it is cleaned with soap and water.
-
Puncture wounds are cleaned with antiseptic.
-
If mucous membranes are exposed, they are flushed with large amounts of water.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have Hiv
Treatment Of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Essay
Human immunodeficiency virus is a blood-borne virus typically transmitted via sexual intercourse, shared intravenous drug paraphernalia, and mother-to-child transmission , which can occur during the birth processor during breastfeeding. There is no cure for HIV or AIDS but over time different types of medications have been developed that slows down the advancement of the disease. AIDS is a lethal disease that is caused by HIV. HIV destroys the immune system and causes the body to not
Why Does The Immune System Fail To Fight The Hiv Virus
There are various reasons which can contribute to the failure of the immune system to control HIV infection and prevent AIDS development. By infecting CD4+ T cells, HIV is able to replicate predominantly in activated T cells and paralyse one of the main components of adaptive immune system. HIV can also establish latent infection in CD4+ T cells and remain invisible to CD8+ T cells and therefore replication can occur later in the infection and generate new virions. Antigenic mutation within the T-cell epitopes can affect the binding capacity of MHC molecules to the viral peptides, resulting in the inability of the TCRs to recognise the MHC-peptide complex. Finally, HIV is able to hide from anti-HIV antibodies by expressing non-immunogenic glycans on key antibody epitopes.
Read Also: Hiv To Aids Time
Simplified Life Cycle Of The Human Immunodeficiency Virus
|
Like all viruses, human immunodeficiency virus reproduces using the genetic machinery of the cell it infects, usually a CD4+ lymphocyte.
Drugs used to treat HIV infection were developed based on the life cycle of HIV. These drugs inhibit the three enzymes that the virus uses to replicate or to attach to and enter cells. |
HIV also infects other cells, such as cells in the skin, brain, genital tract, heart, and kidneys, causing disease in those organs.
Hiv Its Origin And Evolutionary Effects Essay
Biology Essay.TITLE: HIV, its origin and evolutionary effects. Name: Alice Herrera / 00053342 ContentsPageAbstract……………………………………………………………………………………………….1Introduction…………………………………………………………………………………………..1-2Origin of HIV………………………………………………………………………………………….3-4How HIV is spread……
Don’t Miss: How Long Can Hiv Be Dormant
Stage : The Asymptomatic Stage
Once a person has been through the acute primary infection stage and seroconversion process, they can often start to feel better. In fact, HIV may not cause any other symptoms for up to 10 or even 15 years .
However, the virus will still be active, infecting new cells and making copies of itself. HIV can still be passed on during this stage. If left untreated, over time, HIV infection will cause severe damage to the immune system.
Resistance To Hiv Infection
The poorly understood phenomenon associated with the HIV-1 epidemic is the existence of individuals who have been repeatedly exposed to the virus but remain uninfected. It has been suggested that HIV-1 resistant individuals may have a non functioning co-receptor preventing the virus from entering cells., The CCR-5 receptor was demonstrated as one of the main co-receptors for NSI strains of HIV-1. Samson et al., reported that a 32 bp deletion within the coding region for the CCR-5 generating a non-functional receptor that did not support infection by NSI strains of HIV-1. Moreover, white blood cells from individuals homozygous for the mutant CCR-5 were found to be highly resistant to infection by NSI viruses., Population studies indicate that the homozygous defect is found in only 1% of Caucasians of western European ancestry whereas the heterozygous defect is present in approximately 20% of this population. These results indicate that variants of the CCR-5 receptor could be responsible for the relative resistance to HIV-1 infection exhibited by some individuals and also for the variability of the course of the disease in infected patients.
Also Check: Can You Get Aids From Dried Blood
Hiv Diagnosis And ‘window Period’
You wonât know if you have HIV right after youâre infected. It takes time for your body to make antibodies and for antigens to show up.
The âwindow periodâ is the time between when you might have been exposed to HIV and a test can tell for sure you have it. This varies from person to person and test to test. Your testing counselor can tell you more about the window period for the test youâre taking. Here are some general guidelines:
An antibody test can detect HIV 23 to 90 days after youâre exposed to the virus. The window for a test that uses blood from a vein is faster than one that uses oral fluid or blood from a finger stick.
An antigen/antibody test done in a lab on blood from a vein can detect HIV infection within 18 to 45 days. It takes longer if the testâs done with blood from a finger stick.
A nucleic acid test usually has the shortest window: 10 to 33 days. This test is not generally used to diagnose HIV infection unless you have symptoms and a history that suggest you were infected only a few days ago.
If you have a negative test and werenât exposed to the virus during the window period for that test, you can be certain you didnât have HIV when you were tested.
The CDC recommends that all adults have an HIV test at least once, even if theyâre not at risk. If your risk is higher — for example, you have multiple sex partners or use needles for drugs — you should be tested every year.