Interval Of Mild Or No Symptoms
After the first symptoms disappear, most people, even without treatment, have no symptoms or only occasionally have a few mild symptoms. This interval of few or no symptoms may last from 2 to 15 years. The symptoms that most commonly occur during this interval include the following:
-
Swollen lymph nodes, felt as small, painless lumps in the neck, under the arms, or in the groin
-
White patches in the mouth due to candidiasis
-
Anemia
Some people progressively lose weight and have a mild fever or diarrhea.
These symptoms may result from HIV infection or from opportunistic infections that develop because HIV has weakened the immune system.
Preventive Treatment Before Exposure
Taking an antiretroviral drug before being exposed to HIV can reduce the risk of HIV infection. Such preventive treatment is called preexposure prophylaxis . However, PrEP is expensive and is effective only if people take the drug every day. Thus, PrEP is recommended only for people who have a very high risk of becoming infected, such as people who have a partner who is infected with HIV.
PrEP may also be recommended for people who engage in high-risk sexual activities, such as the following:
-
Men who have anal sex with men without using a condom
-
Heterosexual men and women who do not regularly use condoms during sex with partners whose HIV status is unknown and who are at increased risk of HIV infection
People who use PrEP still need to use other methods to prevent HIV infection, including consistent use of condoms and not sharing needles to inject drugs.
Other Prevention Benefits Of Hiv Treatment
In addition to preventing sexual transmission of HIV there are other benefits of taking HIV medication to achieve and maintain an undetectable viral load:
- It reduces the risk of mother-to-child transmission from pregnancy, labor, and delivery. If a woman living with HIV can take HIV medication as prescribed throughout pregnancy, labor, and delivery and if HIV medication is given to her baby for 4-6 weeks after delivery, the risk of transmission from pregnancy, labor, and delivery can be reduced to 1% or less. Scientists dont know if a woman living with HIV who has her HIV under control can transmit HIV to her baby through breastfeeding. While it isnt known if or how much being undetectable or virally suppressed prevents some ways that HIV is transmitted, it is reasonable to assume that it provides some risk reduction.
- It may reduce HIV transmission risk for people who inject drugs. Scientists do not yet know whether having a suppressed or undetectable viral load prevents HIV transmission through sharing needles or other injection drug equipment, but it is reasonable to assume that it provides some risk reduction. Even if you are taking HIV medication and are undetectable, use new equipment each time you inject and do not share needles and syringes with other people.
Topics
Read Also: How Long Does It Take To Show Hiv Symptoms
Hiv Symptoms In Men: Is There A Difference
Symptoms of HIV vary from person to person, but theyre similar in men and women. These symptoms can come and go or get progressively worse.
If a person has been exposed to HIV, they may also have been exposed to other sexually transmitted infections . These include:
- human papillomavirus , which can cause genital warts and lead to cervical cancer
While not related to HIV symptoms, another risk for women with HIV is that the virus can be transmitted to a baby during pregnancy. However, antiretroviral therapy is considered safe during pregnancy.
Women who are treated with antiretroviral therapy are at very low risk for transmitting HIV to their baby during pregnancy and delivery. Breastfeeding is also affected in women with HIV. The virus can be transferred to a baby through breast milk.
In the United States and other settings where formula is accessible and safe, its recommended that women with HIV not breastfeed their babies. For these women, use of formula is encouraged.
Options besides formula include pasteurized banked human milk.
For women who may have been exposed to HIV, its important to know what symptoms to look for.
AIDS refers to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. With this condition, the immune system is weakened due to HIV thats typically gone untreated for many years.
If HIV is found and treated early with antiretroviral therapy, a person will usually not develop AIDS.
Symptoms of AIDS can include:
- recurrent fever
HIV does NOT transfer through:
Can Hiv Be Prevented
To reduce the risk of getting HIV, people who are sexually active should:
- use a condom every time they have sex
- get tested for HIV and make sure all partners do too
- reduce their number of sexual partners
- get tested and treated for STDs having an STD increases the risk of HIV infection
- consider taking a medicine every day if they are at very high risk of getting infected
For everyone:
- Do not inject drugs or share any kind of needle.
- Do not share razors or other personal objects that may touch blood.
- Do not touch anyone else’s blood from a cut or sore.
Recommended Reading: How Fast Does Hiv Spread
Hiv Testing After A Recent Infection
If you are concerned about a possible recent HIV infection, you should take an HIV test. If this test result is non-reactive or negative, it can be repeated in a few weeks to be sure. Not everyone has symptoms after a recent infection and thus testing is the only reliable way to know whether you have HIV.
If you might have been exposed to HIV within the last 72 hours, you and your doctor should also discuss whether post-exposure prophylaxis is appropriate in your case. PEP is taken in order to prevent HIV from taking hold and to remain HIV negative.
The most accurate tests for HIV diagnosis after recent infection are antigen/antibody laboratory tests . An HIV antigen is part of the virus itself and is present in high levels in the blood between HIV infection and seroconversion. During seroconversion, HIV antibodies are produced by the body in response to infection and they persist for life.
Symptomatic seroconversion illness occurs in at least 50%, and possibly as many as 80 or 90%, of infected individuals.
HIV antigen/antibody tests will detect the majority of those infected with HIV within four weeks of infection but can sometimes detect infections as early as ten days afterward. While they are extremely accurate, they require blood to be drawn with a needle and results are not available immediately. These tests tend to be offered in hospital settings or for confirmatory purposes.
How Can You Tell If You Have Hiv
The only way to know for sure if you have HIV is to get tested. You cant rely on symptoms to tell whether you have HIV.
Knowing your HIV status gives you powerful information so you can take steps to keep yourself and your partner healthy:
- If you test positive, you can take medicine to treat HIV. By taking HIV medicine daily as prescribed, you can make the amount of HIV in your blood very lowso low that a test cant detect it . Getting and keeping an undetectable viral load is the best thing you can do to stay healthy. If your viral load stays undetectable, you have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex.
- If you test negative, there are more HIV prevention tools available today than ever before.
- If you are pregnant, you should be tested for HIV so that you can begin treatment if you’re HIV-positive. If an HIV-positive woman is treated for HIV early in her pregnancy, the risk of transmitting HIV to her baby can be very low.
Use the HIV Services Locator to find an HIV testing site near you.
HIV self-testing is also an option. Self-testing allows people to take an HIV test and find out their result in their own home or other private location. You can buy a self-test kit at a pharmacy or online, or your health care provider may be able to order one for you. Some health departments or community-based organizations also provide self-test kits for free.
You May Like: Do Youngboy Have Herpes
Stage : Acute Hiv Infection
Within 2 to 4 weeks after infection with HIV, about two-thirds of people will have a flu-like illness. This is the bodys natural response to HIV infection.
Flu-like symptoms can include:
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Mouth ulcers
These symptoms can last anywhere from a few days to several weeks. But some people do not have any symptoms at all during this early stage of HIV.
Dont assume you have HIV just because you have any of these symptomsthey can be similar to those caused by other illnesses. But if you think you may have been exposed to HIV, get an HIV test.
Heres what to do:
Research Reveals Why Vaccines Fail To Prevent Infection
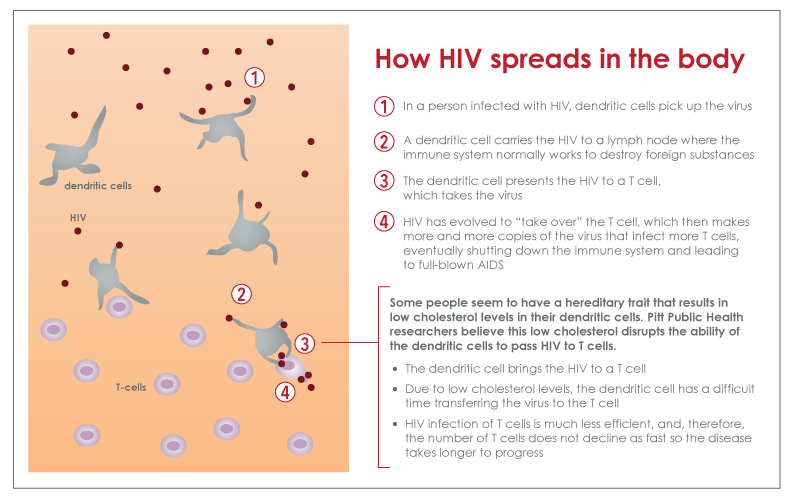
For decades, it was believed that HIV progressed to AIDS in a pretty straightforward manner: spreading through the body as a free-circulating virus, attaching itself to immune cells and hijacking their genetic machinery in order to create multiple copies of itself. By doing so, HIV is able to disseminate throughout the entire system, expanding in numbers until enough T-cells are killed to fully compromise a person’s immune defenses .
Emerging research suggests that this is probably not the case, or at least not the disease pathway we had long presumed. In fact, since as far back as the late-1990s, scientists had begun to observe that HIV can also spread directly from cell to cell without creating any free-circulating virus.
This secondary mode of transmission, according to research from the San Francisco-based Gladstone Institute of Virology and Immunology, is between 100 and 1,000 times more efficient in depleting CD4 cells than a free-circulating virus and may help explain, in part, why current vaccine models are unable to adequately prevent or neutralize HIV.
Don’t Miss: Does Cookie Johnson Have Hiv Aids
Stages Of The Hiv Lifecycle
Binding and fusion
HIV attaches to a T-helper cell. It then fuses to it and releases its genetic information into the cell.
The types of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called fusion or entry inhibitor drugs because they stop HIV from entering the cell.
Reverse transcription and integration
Once inside the T-helper cell, HIV converts its genetic material into HIV DNA, a process called reverse transcription. The new HIV DNA then enters the nucleus of the host cell and takes control of it.
The types of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called NRTIs , NNRTIs and integrase inhibitor drugs.
Transcription and translation
The infected T-helper cell then produces HIV proteins that are used to produce more HIV particles inside the cell.
Assembly, budding and maturation
The new HIV is put together and then released from the T-helper cell into the bloodstream to infect other cells and so the process begins again.
The type of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called protease inhibitor drugs.
Who Is At Risk For Hiv Infection
Anyone can get HIV, but certain groups have a higher risk of getting it:
- People who have another sexually transmitted disease . Having an STD can increase your risk of getting or spreading HIV.
- People who inject drugs with shared needles
- Gay and bisexual men, especially those who are Black/African American or Hispanic/Latino American
- People who engage in risky sexual behaviors, such as not using condoms
Read Also: Does Hiv Make Your Hair Fall Out
Aids Diagnosis Is More Complicated
AIDS is late stage HIV infection. Healthcare providers look for a few factors to determine if HIV latency has progressed to stage 3 HIV.
Because HIV destroys immune cells called CD4 cells, one way healthcare providers diagnose AIDS is to do a count of those cells. A person without HIV can have anywhere from 500 to 1,200 CD4 cells. When the cells have dropped to 200, a person with HIV is considered to have stage 3 HIV.
Another factor signaling that stage 3 HIV has developed is the presence of opportunistic infections. Opportunistic infections are diseases caused by viruses, fungi, or bacteria that would not make a person with an undamaged immune system sick.
You May Like: What Are The Chances Of Getting Hiv
Through Blood Transfusions Or Organ Transplants

Currently, HIV infection is rarely transmitted through blood transfusions or organ transplants.
Since 1985 in most developed countries, all blood collected for transfusion is tested for HIV, and when possible, some blood products are treated with heat to eliminate the risk of HIV infection. The current risk of HIV infection from a single blood transfusion is estimated to be less than 1 in about 2 million in the United States. However, in many developing countries, blood and blood products are not screened for HIV or are not screened as stringently. There, the risk remains substantial.
HIV has been transmitted when organs from infected donors were unknowingly used as transplants. HIV transmission is unlikely to occur when corneas or certain specially treated tissues are transplanted.
You May Like: Nba Youngboy Stds
If You Already Have Hiv
If you are infected with HIV, you can greatly lower the risk of spreading the infection to your sex partner by starting treatment when your immune system is still healthy.
Experts recommend starting treatment as soon as you know you are infected.footnote 21
Studies have shown that early treatment greatly lowers the risk of spreading HIV to an uninfected partner.footnote 22, footnote 23
Your partner may also be able to take medicine to prevent getting infected.footnote 17 This is called pre-exposure prophylaxis .
Steps to avoid spreading HIV
If you are infected with HIV, you can greatly lower the risk of spreading the infection to your sex partner by starting treatment when your immune system is still healthy.
- Take antiretroviral medicines. Getting treated for HIV can help prevent the spread of HIV to people who are not infected.
- Tell your sex partner or partners about your behaviour and whether you are HIV-positive.
- Follow safer sex practices, such as using condoms.
- Do not donate blood, plasma, semen, body organs, or body tissues.
- Do not share personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or sex toys, that may be contaminated with blood, semen, or vaginal fluids.
Phases Of Hiv Infection
Clinical HIV infection undergoes 3 distinct phases: acute seroconversion, asymptomatic infection, and AIDS. Each is discussed below.
Acute seroconversion
Animal models show that Langerhans cells are the first cellular targets of HIV, which fuse with CD4+ lymphocytes and spread into deeper tissues. In humans, rapid occurrence of plasma viremia with widespread dissemination of the virus is observed 4 days to 11 days after mucosal entrance of the virus.
There is no fixed site of integration, but the virus tends to integrate in areas of active transcription, probably because these areas have more open chromatin and more easily accessible DNA. This greatly complicates eradication of the virus by the host, as latent proviral genomes can persist without being detected by the immune system and cannot be targeted by antivirals.
During this phase, the infection is established and a proviral reservoir is created. This reservoir consists of persistently infected cells, typically macrophages, and appears to steadily release virus. Some of the viral release replenishes the reservoir, and some goes on to produce more active infection.
The proviral reservoir, as measured by DNA polymerase chain reaction , seems to be incredibly stable. Although it does decline with aggressive antiviral therapy, the half-life is such that eradication is not a viable expectation.
Asymptomatic HIV infection
AIDS
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take To Be Hiv Positive
Side Effects And Costs
Side effects of antiretroviral therapy vary and may include nausea, headache, and dizziness. These symptoms are often temporary and disappear with time.
Serious side effects can include swelling of the mouth and tongue and liver or kidney damage. If side effects are severe, the medications can be adjusted.
Costs for antiretroviral therapy vary according to geographic location and type of insurance coverage. Some pharmaceutical companies have assistance programs to help lower the cost.
To develop AIDS, a person has to have contracted HIV. But having HIV doesnt necessarily mean that someone will develop AIDS.
Cases of HIV progress through three stages:
- stage 1:acute stage, the first few weeks after transmission
- stage 2: clinical latency, or chronic stage
- stage 3: AIDS
As HIV lowers the CD4 cell count, the immune system weakens. A typical adults CD4 count is 500 to 1,500 per cubic millimeter. A person with a count below 200 is considered to have AIDS.
How quickly a case of HIV progresses through the chronic stage varies significantly from person to person. Without treatment, it can last up to a decade before advancing to AIDS. With treatment, it can last indefinitely.
Theres currently no cure for HIV, but it can be managed. People with HIV often have a near-normal lifespan with early treatment with antiretroviral therapy.
Also, treatment can typically help manage opportunistic infections.
HIV and AIDS are related, but theyre not the same thing.
Should I Get Vaccines If I Have Hiv/aids
Check with your healthcare provider. Certain vaccines are generally recommended, including:
- Influenza vaccine.
- Human papillomavirus vaccine if you are age 26 or younger.
- Meningococcal series of shots.
- Pneumonia vaccine.
- Tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis vaccine, with a repeat every 10 years of the tetanus/diphtheria vaccine.
You should probably avoid live vaccines, such as the ones for chickenpox and measles, mumps and rubella . This is true especially if your CD4 numbers are 200 or lower. Make sure you discuss vaccine questions with your healthcare provider.
HIV can affect how well the vaccine works. It can also make your viral load increase for a time because your immune system is stimulated by the vaccine.
Recommended Reading: How Long From Hiv To Aids