Antiretroviral Treatment And The Hiv Lifecycle
Antiretroviral treatment for HIV combines several different types of drugs, each of which targets a different stage in the HIV lifecycle. This means that the replication of HIV is stopped on multiple fronts, making it very effective.
If taken correctly, it keeps the immune system healthy, prevents the symptoms and illnesses associated with AIDS from developing, and means that people can enjoy long and healthy lives.
If someone doesnt take their treatment correctly or consistently , the level of HIV in their blood may increase and the drugs may no longer work. This is known as developing drug resistance.
Pick The Document Template You Need In The Collection Of Legal Forms
Biology of osmosis jones worksheet answer key. Tonicity And Osmosis Answer Key Worksheets Learny Kids DOWNLOAD. This worksheet along with the movie Osmosis Jones to reinforce concepts about the human body and immune system with your students. Osmosis jones worksheet answer key osmosis and tonicity worksheet answer key and osmosis jones worksheet answer key are three main things we want to show you based on the gallery title.
HIV graphic students read how HIV infects the cell and color the. Severe weather study guide. Does the size of a frogs lungs affect its ability to take in oxygen.
Some of the worksheets for this concept are Questions over osmosis jones Osmosis jones video work answers Answers to osmosis jones work Osmosis jones video work answers Osmosis jones movie questions and answers Diffusion and osmosis work answer key biology Osmosis jones questions Osmosis jones. This worksheet and answer key will help teach your students the biology behind Osmosis Jones. Displaying top 8 worksheets found for Answer Key For Osmosis.
Besides it can provide the inspiration and spirit to face this life. Era of reform study guide. THE BIOLOGY OF OSMOSIS JONES ANSWER KEY PDF Reading is a hobby to open the knowledge windows.
Fill out Osmosis Jones Video Worksheet Answer Key Pdf within a few moments by using the guidelines below. This worksheet and answer key will help teach your students the biology behind Osmosis Jones. Chapter 2 section 4.
Pin On Clean House
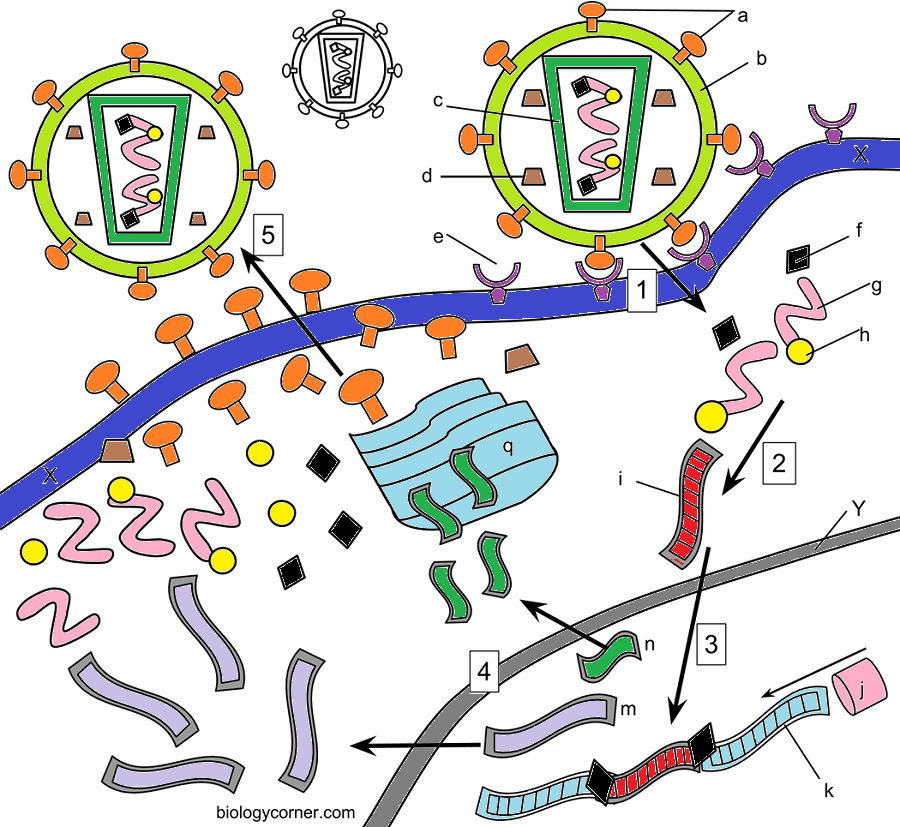
Hiv Enters The Host By Attaching To Specific Host Receptors It Is As If The Virus Has A Specific
key that only works on the host cell with the right lock. In thecase of HIV, the lock is the CD4 cell
surface antigen located on the surface of T Helper cells. Color the CD4 antigens dark purple.CD4 antigens are located on the cell membranes of the cell which should be colored darkblue. At this point, the virus and the cell membrane fuse and the virion core enters the cell. Thecore contains the RNA and several associated proteins that are essential to viral replication. Colorall instances of viral RNA pink.
You May Like: How Long Does Hiv Last
The Evolving Genetics Of Hiv
Can genes stop HIV?
People can be infected with many different bacteria and viruses — but some people get more sick from these bugs than others. Do our genes cause some of that difference?
The answer is yes–different versions of important genes change how easy it is for a person to be infected. The study of these genes might lead to new drugs to block or slow down an infection.
Since the 1980s many people have been afflicted with AIDS, caused by the virus HIV . However, not everyone who is exposed to the virus gets sick. Scientists have carefully studied people who seem resistant to HIV infection. What’s going on?
The answer comes from an understanding of how HIV interacts with our cells. HIV, like all viruses, can’t make new copies of itself without help. It needs to enter cells and use their machinery to reproduce and spread throughout the body.
HIV can only enter certain cells. How does it find the right cells? By special proteins called receptors.
Receptors sit on the outside of cells to receive messages and transmit them into the cell. HIV grabs onto cells that have a receptor called CD4.
Cells with the CD4 receptor are an important part of the body’s system for fighting all diseases . HIV gradually destroys these cells and cripples the immune system.
It turns out that CD4 isn’t enough. Another protein called CCR5 is needed as well. CCR5, called a co-receptor because it works with CD4, is the door that opens to allow HIV to enter the cell.
How Does Hiv Affect The Body
The human immune system involves many types of cells which guard against germs responsible for most diseases. The immune system’s most important guard cells are B-cells and T-cells, which are special white blood cells. B-cells and T-cells cooperate to fight any germ that attacks the human body.
B-cells produce particular proteins, called antibodies, that try to neutralize the invading germ. After a person recovers from an infection, these antibodies continue to circulate in the bloodstream, acting as part of the immune system’s “memory.” Immune system memory explains why a person rarely suffers a second attack from an infectious disease such as measles. If the same germ is encountered again, the antibodies will recognize and neutralize it. T-cells attack the germ directly and try to kill it.
Read Also: How Long Can Hiv Be Dormant In Your System
How Hiv Infects Cells
In general, viruses have very small genomes which means they can encode a very limited number of their own proteins. For this reason, most viruses must use the proteins provided by their host in order to reproduce and make more viruses. In a way, viruses are parasitic, they bring very little with them and steal what they need from the host cell. Because they cannot reproduce on their own, viruses are not considered living organisms, they are simply genetic information, either DNA or RNApackaged within a protein coat. HIV infects a particular type of immune system cell, the T Helper Cell. Once infected, the T-Helper cell turns into an HIV replicating cell. There are typically 1 million T-cells per one milliliter of blood. HIV will slowly reduce the number of these cells until the person develops the disease AIDS.
Hiv Will Slowly Reduce The Number Of These Cells Until The Person Develops The Disease Aids
How hiv infects cells worksheet. In reality we found that how hiv infects cells worksheet answers worksheets weather instruments weather worksheets pdf was being one of the subjects about instances of business archives. This how hiv infects cells worksheet is suitable for 8th 9th grade. Hiv infection hiv infects a particular type of immune system cell the cd4 t helper cell or just plainly the t helper cell.
Some of the worksheets displayed are 1 viruses the ultimate parasites reading viruses bacteria work the infection game the shape of change how hiv infects cells activity 1 emerging diseases causes and effects uf cpet ssi starts lesson plan 1 lesson 2 teach joness class about microbes infectious diseases work. Hiv infects a particular type of immune system cell the t helper cell. Cd4 t helper cell or just plainly the.
Students explain the role of various structures in hiv infection. How hiv infects cells answer key. Hiv infects a particular type of.
Answer keys are no longer provided due to an overwhelming number of requests to. Once infect the t helper cell turns into an hiv replicating cell. Showing top 8 worksheets in the category infect.
Hiv infection hiv infects a particular type of immune system cell the cd4 t helper cell or just plainly the t helper cell. Once infected the t helper cell turns into an hiv replicating cell. Answer key and coloring guide to the hiv worksheet students read about how hiv infects the cell and color a diagram on the life cycle of a virus.
Don’t Miss: Hiv Without Ejaculation
S Of Virus Infections
A virus must use cell processes to replicate. The viral replication cycle can produce dramatic biochemical and structural changes in the host cell, which may cause cell damage. These changes, called cytopathic effects, can change cell functions or even destroy the cell. Some infected cells, such as those infected by the common cold virus known as rhinovirus, die through lysis or apoptosis , releasing all progeny virions at once. The symptoms of viral diseases result from the immune response to the virus, which attempts to control and eliminate the virus from the body and from cell damage caused by the virus. Many animal viruses, such as HIV , leave the infected cells of the immune system by a process known as budding, where virions leave the cell individually. During the budding process, the cell does not undergo lysis and is not immediately killed. However, the damage to the cells that the virus infects may make it impossible for the cells to function normally, even though the cells remain alive for a period of time. Most productive viral infections follow similar steps in the virus replication cycle: attachment, penetration, uncoating, replication, assembly, and release.
Pathway to viral infection: In influenza virus infection, glycoproteins attach to a host epithelial cell. As a result, the virus is engulfed. RNA and proteins are made and assembled into new virions.
The Science Of Hiv And Aids
Key Points
- HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus, a pathogen that works by attacking the human immune system.
- HIV specifically targets CD4 cells, the bodys principal defenders against infection, using them to make copies of themselves.
- Antiretroviral drugs target specific stages of the HIV lifecycle to stop HIV from replicating.
Explore this page to find out more about , , and .
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus, a pathogen that works by attacking the human immune system. It belongs to a class of viruses called retroviruses and more specifically, a subgroup called lentiviruses, or viruses that cause disease slowly. 1
HIV cannot replicate on its own, so in order to make new copies of itself, it must infect cells of the human immune system, called CD4 cells. CD4 cells are white blood cells that play a central role in responding to infections in the body. 2
Over time, CD4 cells are killed by HIV and the bodys ability to recognise and fight some types of infection begins to decline. If HIV is not controlled by treatment, the loss of CD4 cells leads to the development of serious illnesses, or opportunistic infections. In people with normal CD4 cell levels, these infections would be recognised and cleared by the immune system. 3
Don’t Miss: Jania Has Herpes
Chapter 3 Cells Review Key This Is A Review Worksheet Intended To Help You Study The Powerpoint And In Class Notes We Have Discussed
How hiv infects cells worksheet answer key. Once infected the T-Helper cell turns into an HIV replicating cell. Get the Facts. At this point B cells interact with the virus and those B cells because of the ability to recognize HIV will transformed into a cell called the plasma cell.
DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key. Abasophils bred blood cells cCD4 cells dplatelets Which of these things can transmit HIV. How hiv infects cells worksheet.
Quiz Answer Key What kinds of sex can transmit HIV. The cytoskeleton supports and shapes the cell positions and transports organelles provides strength assists in cell division and aids cell. Students will describe the structure and function of cells tissues organs and organ.
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. HIV only infects humans and Ebola infects both humans and bats. Who does not want to obtain a occupation right after graduating from higher education.
This How HIV Infects Cells Worksheet is suitable for 8th 10th Grade. On Chapter 14 Cells of the immune system and watch from time 1913 to 1955. Published by Shannan Muskopf.
Prokaryotic cells answer key 1. In the case of HIV the lock is the CD4 cell-surface antigen located on the surface of T Helper cells. Hiv infection hiv infects a particular type of immune system cell the cd4 t helper cell or just plainly the t helper cell.
HIV will slowly reduce the number of these cells. How hiv infects cells answer key. HIV infects the immune system.
Hiv Coloring Key
Hiv Infects A Type Of White Blood Cell In The Bodys Immune System Called A T
How hiv infects cells worksheet. So we endeavor to discover a few references that may likewise be utilized as your reference in making a business archive. HIV human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus and a member of the retrovirus family. How hiv infects cells worksheet answer key.
HIV cannot reproduce on its own. These vital cells keep us healthy by fighting off infections and diseases. There are typically 1 million T-cells per one milliliter of blood.
HIV will slowly reduce the number of. HIV human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus and a member of the retrovirus family. This How HIV Infects Cells Worksheet is suitable for 8th 10th Grade.
In the case of HIV the lock is the CD4 cell-surface antigen located on the surface of T. HIV infects and damages. How HIV Infects Cells AP Download Lesson Plan High School Worksheet.
These vital cells keep us healthy by fighting off infections and diseases. A person is diagnosed with AIDS when the person has a very. Loss of CD4 cells leads to generalized failure of the immune system and susceptibility to life threatening opportunistic infections.
HIV will slowly reduce the. Once infected the T-Helper cell turns into an HIV replicating cell. Prokaryotic cells answer key 1.
Hiv infection hiv infects a particular type of immune system cell the cd4 t helper cell or just plainly the t helper cell. On Chapter 14 Cells of the immune system and watch from time 1913 to 1955. HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus.
You May Like: Does Nba Youngboy Have An Std
How Long Does It Take To Develop The Disease
There is no fixed period between the first contact with HIV and the development of the disease. Signs and symptoms resulting from infection with HIV develop in stages. Many infected individuals may have no symptoms for several years. But others may develop symptoms within three years from the time of infection.
Symptoms of HIV infection are fever, swollen lymph glands in the neck and armpits, sweating, aches, fatigue, unexplained weight loss and diarrhea.
Within eight years, about 50 percent of all infected people develop specific conditions categorized as AIDS. These conditions include a lung disease called “pneumocystis carinii pneumonia,” skin tumours called “Kaposi’s sarcoma,” fungal and viral infections such as candidiasis and herpes zoster, and severe diarrhea.
Some AIDS patients also suffer from dementia resulting in problems with memory and thinking. AIDS patients are prone to various infections of the brain, just as they suffer from an unusually high number of cancers, bacterial and viral infections of other parts of the body.
Different Hosts And Their Viruses
Viruses are often very specific as to which hosts and which cells within the host they will infect. This feature of a virus makes it specific to one or a few species of life on earth. So many different types of viruses exist that nearly every living organism has its own set of viruses that try to infect its cells. Even the smallest and simplest of cells, prokaryotic bacteria, may be attacked by specific types of viruses.
Bacteriophage: This transmission electron micrograph shows bacteriophages attached to a bacterial cell.
Don’t Miss: What Does Antiretroviral Therapy Do Brainly
Stages Of The Hiv Lifecycle
Binding and fusion
HIV attaches to a T-helper cell. It then fuses to it and releases its genetic information into the cell.
The types of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called fusion or entry inhibitor drugs because they stop HIV from entering the cell.
Reverse transcription and integration
Once inside the T-helper cell, HIV converts its genetic material into HIV DNA, a process called reverse transcription. The new HIV DNA then enters the nucleus of the host cell and takes control of it.
The types of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called NRTIs , NNRTIs and integrase inhibitor drugs.
Transcription and translation
The infected T-helper cell then produces HIV proteins that are used to produce more HIV particles inside the cell.
Assembly, budding and maturation
The new HIV is put together and then released from the T-helper cell into the bloodstream to infect other cells and so the process begins again.
The type of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called protease inhibitor drugs.
What Is Hiv And Aids
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus is a virus that infects the immune system. Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome . AIDS is the most advanced stage of the HIV infection and causes the immune system to become vulnerable to other infections. HIV can also be known as “the AIDS virus.”
The full name for AIDS describes several of the characteristics of the disease.
Acquired indicates that it is not an inherited condition.
Immune Deficiency indicates that the body’s immune system breaks down.
Syndrome indicates that the disease results in a variety of health problems.
It takes on average, 5-10 years for the initial HIV infection to progress to AIDS if not treated. While there is presently no cure or vaccine for HIV, with proper medical care, HIV can be managed and a near-normal lifespan can be expected with early treatment.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take For Hiv To Show
Using The Proteins Assembled From The Golgi Apparatus And The Completed Viral Rna From The
long strands, the mature virus buds off from its host cell.
The process of budding often destroys the host cell. Once virus infection can create millions of
new viruses by hijacking the cell’s DNA and cellular machinery. With most viral infections, the
immune system will learn to identify infected cells and destroy them before they can make new
copies of the virus.