How To Prevent Hiv From Progressing
The most effective way is to take antiretroviral medication as soon as possible and to do so consistently as prescribed.
Antiretroviral therapy keeps the immune system healthy and reduces the risk of transmitting the virus to virtually zero.
The sooner a person receives a diagnosis, the sooner they can begin treatment. Early treatment can improve the persons outlook and lower the risk of the virus passing on to others.
Stages Of Hiv Infection
The stages of infection from person to person vary slightly, both in severity and the speed of progression. These stages map the depletion of immune cells as the body’s defenses further and further degrade.
With each progression, the risk of opportunistic infections increases until the immune system is said to be fully compromised. It is at this stage that the risk of illness and death is particularly high.
The stages of infection can be roughly classified as follows:
You Can Test Yourself For Hiv In The Privacy Of Your Own Home
Several at-home HIV tests have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration and can be bought online or at a drugstore. Many of these tests ask consumers to prick their finger with a needle, place a few drops of blood on a blotter pad, and then mail the sample to a lab. Of course, you can also see your doctor for a conventional blood test or visit almost any public health center for a blood or saliva test . These centers also offer confidential on-site counseling. The CDC notes that if you get a positive result from any at-home test, youll have to get other testing to confirm the results.
Read Also: Hiv Gestation Period
How Do People Get Hiv
HIV spreads when infected blood or body fluids enter the body. This can happen:
HIV also can pass from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
HIV is NOT spread through:
- pee, poop, spit, throw-up, or sweat
- coughing or sneezing
- sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses
In The Weeds: Gaps Between Hiv+ And Hiv

While the overall gap in comorbidity-free years between people living with HIV and HIV-negative people was wide, that width varied between comorbiditiesas did the extent to which the gap size changed over time, and the effect of starting HIV treatment with a high CD4 count.
Specifically, three of the six complications exhibited a gap that closed only slightly from the 2000-2003 period to the 2014-2016 period:
- chronic liver disease: 24-year gap in 2014-2016
- chronic kidney disease: 17-year gap
- chronic lung disease: 14-year gap
The other three complications exhibited a gap that had narrowed over time, but was still substantial:
- cancer: 9-year gap in 2014-2016, improving from a 20-year gap in 2000-2003
- average age at onset in 2014-2016 was 80 among HIV-negative people vs. 71 among people living with HIV
- cardiovascular disease: 8-year gap in 2014-2016, improving from an 18-year gap in 2000-2003
- average age at onset in 2014-2016 was 82 among HIV-negative people vs. 74 among people living with HIV
- diabetes: 8-year gap in 2014-2016, improving from a 15-year gap in 2000-2003
- average age at onset in 2014-2016 was 73 among HIV-negative people vs. 65 among people living with HIV
Marcus noted that for just two of the comorbiditiescancer and cardiovascular diseasetreatment initiation at a CD4 count of 500 or higher delayed the average age of incidence and further closed the gap with HIV-negative people.
Don’t Miss: Does Youngboy Really Have Herpes
How Long Does Hiv Live Outside The Body
Overview
There are many myths and misconceptions about how long HIV lives and is infectious in the air or on a surface outside the body.
Unless the virus is kept under specific conditions, the true answer is not very long.
Although it causes a serious disease that cant be cleared by the body, HIV is very fragile in the outside environment. It quickly gets damaged and becomes inactive, or dies. Once inactive, HIV cant become active again, so its the same as if its dead.
Stage : Chronic Hiv Infection
After the acute stage has ended and if the person has not received treatment the virus remains active, reproducing at very low levels but continuing to damage immune cells.
At this stage, there are usually no symptoms or very mild ones. This is why doctors sometimes call stage 2 asymptomatic HIV infection or clinical latency. The virus can still pass to others during this stage, even if it causes no symptoms.
Without treatment, this stage can last for 10 years or more before the person develops stage 3 HIV.
However, modern antiretroviral medications can stop the infection from progressing. These drugs greatly reduce the amount of HIV in the body, the viral load, to very low levels.
When the viral load is so low that tests cannot detect it, HIV can no longer damage the immune system or transmit to other people. Some people refer to this as undetectable equals untransmittable or U=U.
A person with stage 2 HIV who takes effective antiretroviral therapy may never develop stage 3 HIV.
Also Check: Youngboy Has Herpes
How Long Does Hiv Live Outside The Body In Blood
HIV in blood from something like a cut or nosebleed can be active for several days, even in dried blood. The amount of virus is small, though, and unable to easily transmit infection.
HIV survival time in fluid outside of the body can increase when a small amount is left in a syringe. After an injection in someone with high levels of HIV, enough blood stays in the syringe to transmit the virus. Since its inside a syringe, the blood isnt as exposed to air as it is on other surfaces.
According to the , when the temperature and other conditions are just right, HIV can live as long as 42 days in a syringe, but this typically involves refrigeration.
HIV lives the longest in a syringe at room temperature, but can still live up to
Is There Any Treatment Of A Cure For Hiv/aids
Currently, there is no cure for HIV/AIDS. People living with HIV will need lifelong treatment. The best treatments right now are combinations of prescription drugs. These medications include antiviral treatment, protease inhibitors and other drugs that help people who are living with HIV stay healthy. People living with HIV also can stay healthy by doing things like eating properly, exercising and getting enough sleep.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take For Hiv
How Does Hiv Affect A Person In The Long Term
Though the outlook has gotten much better for those with HIV, there are still some long-term effects that they might experience.
As time passes, people living with HIV may begin to develop certain side effects of treatment or HIV itself.
These may include:
The body may also undergo a shift in how it processes sugars and fats. This can lead to having more fat in certain areas of the body, which can change the bodys shape. However, these physical symptoms are more common with older HIV medications. Newer treatments have far fewer, if any, of these symptoms affecting physical appearance.
If treated poorly or left untreated, HIV infection can develop into stage 3 HIV, or AIDS.
A person develops stage 3 HIV when their immune system is too weak to defend their body against infections. A healthcare provider will likely diagnose stage 3 HIV if the number of certain white blood cells in an HIV-positive persons immune system drops below 200 cells per mL of blood.
Life expectancy is different for every person living with stage 3 HIV. Some people may die within months of this diagnosis, but the majority can live fairly healthy lives with regular antiretroviral therapy.
How Long Does Hiv Survive Outside The Body
In general, the virus doesnât live long once itâs outside of a human body. Studies show that HIV grown in the lab, when placed on a surface, loses most of its ability to infect — 90% to 99% — within several hours. And the level of virus tested was much higher than whatâs found in bodily fluids. So contact with dried blood, semen, or other fluids poses little risk.
Tiny amounts of HIV have been found in saliva, poop, sweat, and tears. But research shows it poses little risk.
The virus canât survive in water, so you donât have to worry about swimming pools or hot tubs.
One study found HIV can live in used needles for over a month if the temperature and conditions are just right. That means sharing needles or syringes, like during drug use, raises your risk of infection.
Recommended Reading: How Fast Does Hiv Spread
Avoid Excessive Alcohol Or Drug Use
If you are living with HIV, there are specific risks associated with alcohol and recreational drug use that you should be aware of. Alcohol can damage the liver which the body uses to process anti-HIV drugs, so it is good to keep your alcohol consumption within the recommended limits. Heavy drinking and taking recreational drugs can also weaken your immune system, making it harder for your body to recover from infections.
Certain anti-HIV drugs can interact with recreational drugs and alcohol to cause unwanted side effects, some of which can be severe. For example, you could feel dizzy or pass out, making you potentially vulnerable. If you are worried about drug interactions, have an honest conversation with a healthcare professional and they will be able to advise you. You should also be aware that being under the influence of alcohol or other drugs may stop you taking your HIV medication properly, for example, you may forget to take a dose or too much alcohol may make you vomit. If you are sick within one hour of taking your HIV medication you should retake the dose.
If youre concerned about your alcohol or drug use, talk to a healthcare professional for advice and support.
How It Feels To Be Diagnosed With Hiv

“I always describe that moment like being hit by a truck,” says 35-year-old Nathaniel Hall.
“I was diagnosed in 2003 and, although effective HIV medication was around, it was still considered a chronic illness, so the diagnosis came with the heaviness of a life-limiting disease. I think I may actually have blacked out momentarily when I heard. I was only 16.”
Nathaniel had only recently come out, and was still working through his internalised homophobia.
“I felt like my sexuality had to be inherently wrong because it was being punished with this disease. There was a lot of shame that controlled my life for a long time afterwards,” he says.
Likewise, Bisi Alimi, 46, had his world changed forever when he was diagnosed with HIV in 2004.
“It was 17 years ago, but it feels like yesterday I went into that booth to take the test. At the time of my diagnosis, I was still dealing with losing my best friend, who died due to complications of AIDS. So, when I was told I was positive, I broke down. I looked at the future I had dreamed of all my life and felt I would never be able to achieve my dreams,” he shares.
Don’t Miss: Do Nba Youngboy Have Herpes
What Else Can I Do To Take Care Of Myself
Many of the things we do to take care of ourselves are common sense, such as eating well, exercising and getting plenty of rest and sleep.
However, if youre living with HIV, checking in with your healthcare professional regularly is also important. They should monitor you for other health conditions, which you may experience more as you age, and adjust your treatment as needed.
Teeth and mouth complaints are more common among people living with HIV. Regular brushing, flossing and seeing your dentist can lower the risk of cavities and mouth infections.
We Know That Men Who Have Sex With Men In Illinois Are At Higher Risk For Hiv What About Women Who Have Sex With Women
It is not a personâs gender, sexual orientation, race or class that puts them at risk for HIV. People are at risk for HIV when they practice risky behaviors. Women who identify as lesbian or gay can be at risk for HIV by practicing any of the behaviors that place women at risk. Lesbian women have become infected with HIV by using injection drugs or having unprotected sex with male or female partners who are already infected with HIV. Women who have sex with other women should follow guidelines in this fact sheet to protect themselves, and can call the Illinois AIDS/HIV/STD Hotline at 800-243-AIDS for specific information.
You May Like: How Long Does Hiv Stay Dormant
How Long Can You Live With Hiv Very
Roz Woodward for Photodisc via Thinkstock
Just this past week, I met John , a 50-year-old long-term survivor with HIV, in our clinic in Denver, Colorado. He was on a well-tolerated treatment regimen, had an undetectable viral load and normal CD4 count. He asked me about new studies on HIV treatments, and about both his projected quality and quantity of life.
I told him that, on average, life expectancy for people living with HIV — provided they get tested, find their way into a care center, initiate antiretroviral treatment and continue taking that treatment regularly — is similar to people who don’t have HIV infection.
He gave me a suspicious look. “Are you sure?” he asked.
Symptoms Of Hiv Infection
Most people experience a short flu-like illness 2 to 6 weeks after HIV infection, which lasts for a week or 2.
After these symptoms disappear, HIV may not cause any symptoms for many years, although the virus continues to damage your immune system.
This means many people with HIV do not know they’re infected.
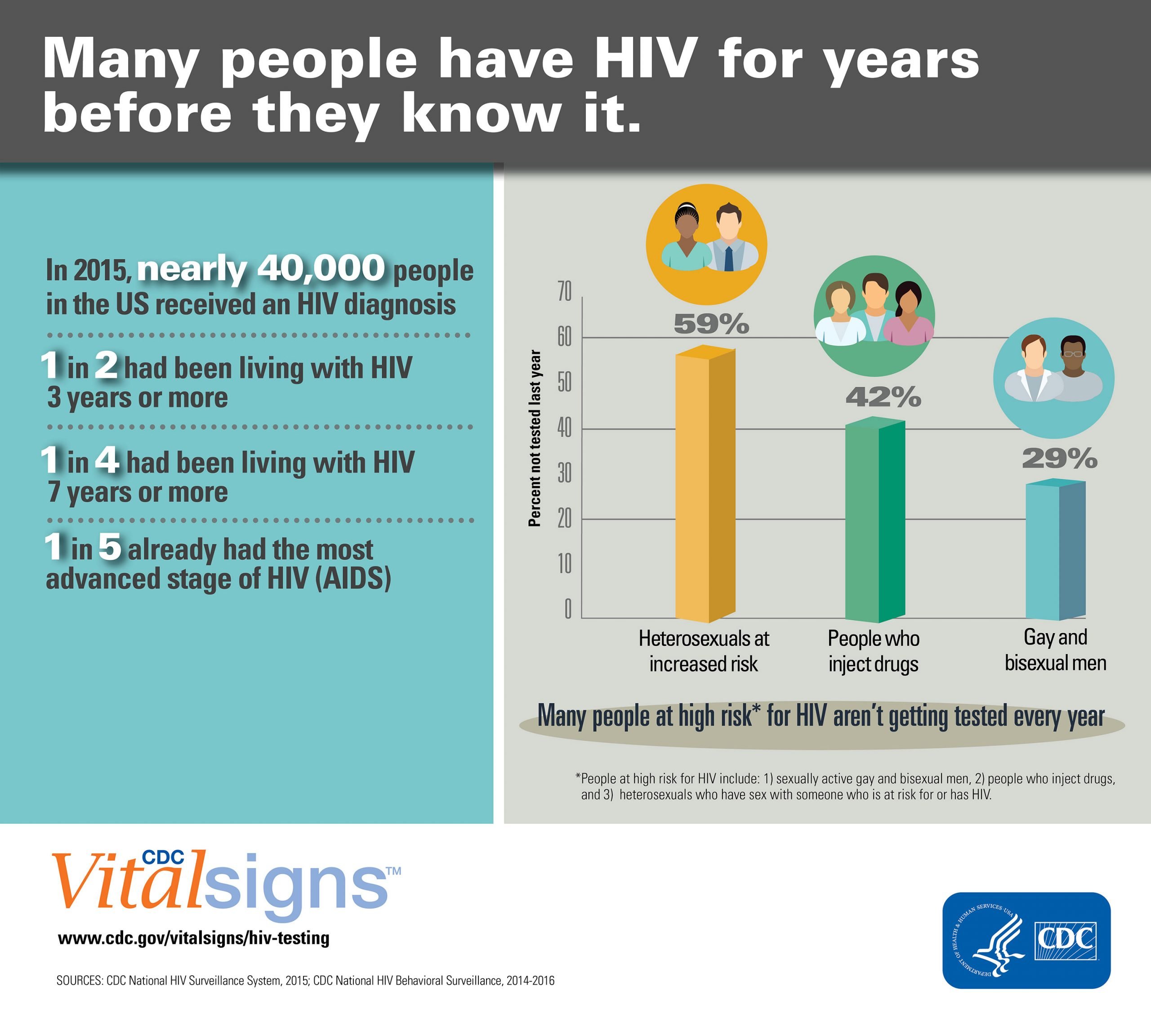
Anyone who thinks they could have HIV should get tested.
Some people are advised to have regular tests as they’re at particularly high risk.
Also Check: How Long Hiv To Aids
How Is Hiv Transmitted Or Spread
The following are the means by which the HIV virus is spread:
-
Vertical transmission. HIV can be spread to babies born to, or breastfed by, mothers infected with the virus.
-
Sexual contact. In adults and adolescents, HIV is spread most commonly by sexual contact with an infected partner. The virus enters the body through the lining of the vagina, vulva, penis, rectum, or abraded or irritated tissues in the lining of the mouth through sexual activity.
-
Blood contamination. HIV may also be spread through contact with infected blood. However, due to the screening of donated blood for evidence of HIV infection, the risk of acquiring HIV from blood transfusions is extremely low.
-
Needles. HIV is frequently spread by sharing needles, syringes, or drug use equipment with someone who is infected with the virus. Transmission from patient to health care worker, or vice-versa, through accidental sticks with contaminated needles or other medical instruments, is rare.
No known cases of HIV/AIDS have been spread by the following:
-
Saliva
-
Malaise
-
Enlarged lymph nodes
An HIV-infected child is usually diagnosed with AIDS when the immune system becomes severely damaged or other types of infections occur. As the immune system deteriorates, complications begin to develop. The following are some common complications, or symptoms, of the onset of AIDS. However, each child may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
Facts About Hiv/aids Everyone Should Know
Learning the truth about HIV and AIDS can help prevent transmission and save lives beginning with your own.
Shutterstock
Contracting the human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, is no longer seen as a death sentence in developed countries, which have the resources to treat it. Still, millions of people around the world contract HIV and die of the last stage of the viruss infection: acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , an estimated 1.1 million Americans over the age of 13 were living with HIV at the end of 2014.
There are a lot of reasons why people need to know about HIV/AIDS, from determining whether they are at risk themselves to even how to speak sensitively to someone who has the disease, says Steven Santiago, MD, the chief medical officer of Care Resource, a nonprofit HIV/AIDS organization in South Florida. Here are 10 facts that you should know.
Read Also: Hiv From Dried Blood
What The Study Shows
It included two adults with HIV who began antiretroviral therapy soon after being infected with the virus. They continued treatment for more than six years and successfully suppressed the virus.
They then joined a clinical trial and stopped taking ART under medical supervision. One patient was followed for four years and the other for more than five, with assessments every two to three weeks.
You May Also Like
Researchers were looking for the timing and size of viral rebounds in each that is, times when levels of HIV in their blood became detectable.
Can You Live A Long Healthy Life With Hiv
An HIV diagnosis was once renowned as a death sentence. However, advances in scientific research and medicine mean it is now possible to manage HIV on a daily basis without passing it on to others. In fact, it was only in 2019 when the oldest known person with HIV died. Miguel – known as The Lisbon Patient – was a Portuguese man who was diagnosed with HIV at the age of 84. He lived to the age of 100.
Reviewed byDr Sarah Jarvis MBE
18-Nov-21·8 mins read
So, how common is it to live a normal, healthy life after testing positive for HIV? How do people with HIV manage their condition? And can an HIV diagnosis shift someone’s perspective on life?
You May Like: Nba Youngboy Has Herpes