What To Do If You Think You Had Sexual Contact With A Possibly Hiv Positive Person
If you think you have shared needles or had oral, vaginal or anal sex with a possibly HIV infected person, rush to your sexologist or a sex specialist near you. He/she may perform some tests and if it has been less than 72 hours after your contact, you may be put on PEP Post Exposure Prophylaxis. These medicines prevent the virus from infecting your body. It is very common to get scared and anxious. Talk to your doctor openly and put forth all your questions and get detailed answers.
As many of you may already be aware, HIV is a life threatening infection that can devastate you mentally, physically , ruin your social life and family life. Always abstain from having sex with an unknown person. Use condoms, dental dams etc to protect yourself from such life threatening diseases.
References:
Can Infected Individuals Have Multiple Strains Of Hiv Virus
Yes. Virus multiplies itself after entering human cells and once they explode out of the human cells, the human cell dies. During multiplication/copying, the resulting virus may have genetically mutated into a different strain. This results in a person having multiple strains of the virus. It is also possible that an infected person acquires infection from another infected person a different strain of HIV may enter his/her body resulting in multiple strains. This is called Superinfection, though rare, people with this condition do exist.
When different strains are acquired by the body or developed in it, there may not be different symptoms experienced by the person. In such case, even though he/she may be using the anti-retroviral drugs, the other strain develops faster and can worsen the health condition of the person.
Before commencing the treatment or writing the prescription, it is important for the sexologist to know what type of strain the patient is carrying. It is also important for the patient and as well as the sexologist to keep checking regularly the type of strains in the body. In some cases, the virus may have developed into multiple strains.
Interval Of Mild Or No Symptoms
After the first symptoms disappear, most people, even without treatment, have no symptoms or only occasionally have a few mild symptoms. This interval of few or no symptoms may last from 2 to 15 years. The symptoms that most commonly occur during this interval include the following:
-
Swollen lymph nodes, felt as small, painless lumps in the neck, under the arms, or in the groin
-
White patches in the mouth due to candidiasis
-
Anemia
Some people progressively lose weight and have a mild fever or diarrhea.
These symptoms may result from HIV infection or from opportunistic infections that develop because HIV has weakened the immune system.
Read Also: What Treatment Is Used For Hiv
Emerging Recombinant Strains Continue To Challenge Researchers
One of the primary barriers to treating or developing effective vaccine for HIV is the high genetic diversity of the virus itself. While viruses that use double-strand DNA to replicate are relatively stable, retroviruses like HIV go backward in their replication cycle and are far less stable. As a result, HIV is highly prone to mutationmutating, in fact, about a million times more frequently than cells using DNA.
As the virus’ genetic diversity widens and different viral subtypes are passed from person to person, the mixed genetic material can create new HIV hybrids. While most of these hybrids die, the few surviving ones often exhibit greater resistance to HIV therapy and, in some cases, faster disease progression.
The variability of HIV, therefore, creates something of a “moving target” for researchers, with new recombinant strains able to resist or altogether evade neutralizing agents. Some, like the A3/02 strain identified by Swedish researchers in 2013, are able to deplete a person’s immune defenses far more aggressively than previously known strains.
What Are Vaccines And What Do They Do
Vaccines are products made from very small amounts of weak or dead germs that can cause diseases. They help your immune system fight infections faster and more effectively.
When you get a vaccine, it sparks your immune response, helping your body fight off and remember the germ so it can attack it if the germ ever invades again. And since vaccines are made of very small amounts of weak or dead germs, they wont make you sick.
Vaccines are usually administered by a shot, but sometimes can be administered by mouth or nasal spray. They are widely used to prevent diseases like polio, chicken pox, measles, mumps, rubella, influenza , hepatitis A and B, and human papillomavirus .
Read Also: Can Hiv Be Transferred By Saliva
Responses To Std Testing How To Where Privacy And Cost
Thank you so much for your help!Can I just go to the test location and pay for the test there?
It was simply excellent, Three day turnaround, electronic convenience for getting results and ordering tests, and no wait time at the lab either. I was in and out within 10 minutes.
Thanks for posting this!
Cancers Common In People With Hiv Infection
Kaposi sarcoma Kaposi Sarcoma Kaposi sarcoma is a skin cancer that causes multiple flat pink, red, or purple patches or bumps on the skin. It is caused by human herpesvirus type 8 infection. One or a few spots may appear… read more , a cancer caused by a sexually transmitted herpesvirus, appears as painless, red to purple, raised patches on the skin. It occurs mainly in men who have sex with men.
Cancers of the immune system . Often, lymph nodes in the neck, under the arms, or in the groin enlarge rapidly and painlessly… read more ) may develop, sometimes first appearing in the brain. When the brain is affected, these cancers can cause weakness of an arm or a leg, headache, confusion, or personality changes.
Having AIDS increases the risk of other cancers. They include cancer of the cervix, anus, testes, and lungs as well as melanoma and other skin cancers. Men who have sex with men are prone to developing cancer of the rectum due to the same human papillomaviruses Human Papillomavirus Infection Human papillomavirus causes warts. Some types of HPV cause skin warts, and other types cause genital warts . Infection with some HPV… read more that cause cancer of the cervix in women.
Also Check: How Did I Get Hiv
What Is The Difference Between Hiv
There are two main types of the human immunodeficiency virus , HIV-1 and HIV-2. The difference between HIV-1 and HIV-2 are as follows
- HIV-1 is the most common type of HIV and accounts for 95% of all infections, whereas HIV-2 is relatively uncommon and less infectious.
- HIV-2 is mainly concentrated in West Africa and the surrounding countries.
- HIV-2 is less fatal and progresses more slowly than HIV-1.
Currently, only one antibody test can distinguish between antibodies to HIV-1 or HIV-2.
The Meaning Of Genetic Diversity Within Hiv
Given the attention paid to them, it is of clear medical importance to understand the nature of the HIV-1 group M subtypes. Recognizing certain lineages as subtypes has certainly aided the tracking of epidemiologically important lineages across the globe.14 But parsing the huge amount of genetic diversity within the main group of HIV-1 into subtypes has also imbued them with an undeserved status. Are they well-defined biological entities with intrinsic, medically meaningful properties? Is it a sound idea, for example, to pursue subtype-specific vaccines against different portions of global HIV-1 M variation ? Answering such fundamental questions requires careful differentiation between pattern and process.
Preston A. Marx, in, 2014
Don’t Miss: How Long For Hiv Test Results To Come Back
Can An Hiv Rna Test Be Used To Screen For Hiv
The recommended test for HIV screening is a combination test that detects HIV antibody and HIV antigen. By detecting both antibody and antigen, the combination test increases the likelihood that an infection is detected soon after exposure. Most HIV screening tests detect only HIV antibody but are good options for screening because they may be available as rapid tests and at the point of care. If any of these screening tests are positive, they must be followed by another different antibody test. If the second test is positive, then HIV diagnosis is confirmed. If, however, the first and second result do not match, then an HIV RNA test may be done to help establish a diagnosis.
The recommended screening test for newborns, however, is an HIV RNA test .
What Does The Test Result Mean
HIV viral load tests are reported as the number of HIV copies in a milliliter of blood.
If your viral load measurement is high, it generally indicates that HIV is present and replicating. Initial, untreated, and uncontrolled HIV viral loads can range as high as one million or more copies/mL.
If you are receiving antiretroviral treatment , a high viral load means that the treatment is not effective. If you are not responding to treatment, then it will likely be changed. You should undergo HIV drug resistance testing to help in the selection of an alternative therapy.
Viral loads that are consistently less than 200 copies/mL indicate that your virus is adequately suppressed and that the risk of disease progression is low. Nevertheless, an undetectable viral load in someone who has a diagnosed HIV infection does not mean that your HIV infection is cured. It means only that the level of your HIV RNA is currently below the threshold needed for detection by the test.
Changes in your viral load can often be more important during HIV monitoring than a single test result. An increasing viral load indicates either that your infection is getting worse or that your virus has developed resistance to the drugs that are being used for therapy and are no longer effective. A decreasing viral load indicates improvement, treatment effectiveness, and suppression of your HIV infection.
You May Like: How Does Hiv Affect People
Do Differences In Subtypes Matter
Some studies suggest that certain subtypes have a greater risk of transmission or faster disease progression than others but more recent research suggests that this may not be the case.9 On the other hand, antiretroviral drugs , although largely tested in people with subtype B, have generally proven to be effective against a wide range of subtypes (although there is conflicting evidence about the effectiveness of protease inhibitors against subtype C virus.10111213
A more practical concern are the tests used to diagnose HIV and monitor the level of virus in the body . Tests that are sensitive to the full range of subtypes do exist but may not be readily available in all settings. This is a concern in places where diverse subtypes are prevalent.
Preventive Treatment After Exposure

People who have been exposed to HIV from a blood splash, needlestick, or sexual contact may reduce the chance of infection by taking antiretroviral drugs for 4 weeks. These drugs are more effective when they are started as soon as possible after the exposure. Taking two or more drugs is currently recommended.
Doctors and the person who was exposed typically decide together whether to use these preventive drugs. They base the decision on the estimated risk of infection and the possible side effects of the drugs. If they do not know whether the source is infected with HIV, they consider how likely the source is to be infected. However, even when the source of the exposure is known to be infected with HIV, the risk of infection after exposure varies, depending on the type of exposure. For example, risk from a blood splash is less than that from a needlestick.
Immediately after exposure to HIV infection, what is done depends on the type of exposure:
-
If skin is exposed, it is cleaned with soap and water.
-
Puncture wounds are cleaned with antiseptic.
-
If mucous membranes are exposed, they are flushed with large amounts of water.
Don’t Miss: How Does The Immune System Fight Hiv
Diagnosis Of Hiv Infection
-
Tests to detect antibodies to the HIV virus in a sample of blood or saliva
-
Tests to detect HIV RNA in a sample of blood
Early diagnosis of HIV infection is important because it makes early treatment possible. Early treatment enables infected people to live longer, be healthier, and be less likely to transmit HIV to other people.
Doctors usually ask about risk factors for HIV infection Transmission of HIV Infection Human immunodeficiency virus infection is a viral infection that progressively destroys certain white blood cells and can cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome . HIV is transmitted… read more and about symptoms .
Doctors also do a complete physical examination to check for signs of opportunistic infections, such as swollen lymph nodes and white patches inside the mouth , and for signs of Kaposi sarcoma of the skin or mouth.
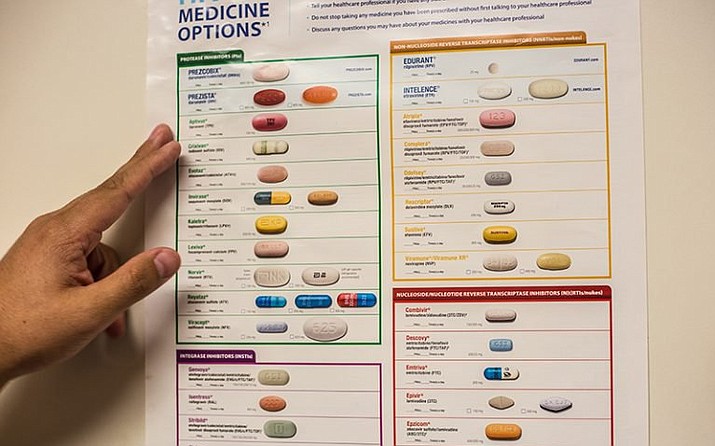
What Are The Types Of Hiv/aids Medicines
There are several different types of HIV/AIDS medicines. Some work by blocking or changing enzymes that HIV needs to make copies of itself. This prevents HIV from copying itself, which reduces the amount of HIV in the body. Several medicines do this:
- Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors block an enzyme called reverse transcriptase
- Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors bind to and later change reverse transcriptase
- Integrase inhibitors block an enzyme called integrase
- Protease inhibitors block an enzyme called protease
Some HIV/AIDS medicines interfere with HIV’s ability to infect CD4 immune system cells:
- Fusion inhibitors block HIV from entering the cells
- CCR5 antagonists and post-attachment inhibitors block different molecules on the CD4 cells. To infect a cell, HIV has to bind to two types of molecules on the cell’s surface. Blocking either of these molecules prevents HIV from entering the cells.
- Attachment inhibitors bind to a specific protein on the outer surface of HIV. This prevents HIV from entering the cell.
In some cases, people take more than one medicine:
- Pharmacokinetic enhancers boost the effectiveness of certain HIV/AIDS medicines. A pharmacokinetic enhancer slows the breakdown of the other medicine. This allows that medicine to stay in the body longer at a higher concentration.
- Multidrug combinations include a combination of two or more different HIV/AIDS medicines
Don’t Miss: How Can Hiv Be Cured
Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis
- HIV medicine is recommended for all people with HIV, regardless of how long theyve had the virus or how healthy they are.
- Talk to your health care provider about any medical conditions you may have or any other medicines you are taking.
- Let your health care provider know if you or your partner is pregnant or thinking about getting pregnant. They will determine the right type of HIV medicine that can help prevent transmitting HIV to your baby.
What if I delay treatment?
- HIV will continue to harm your immune system.
- This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infections.
- This will put you at higher risk for transmitting HIV to your sexual and injection partners.
What are the benefits of taking my HIV medicine every day as prescribed?
Genetic Diversity And Classification
High genetic diversity has been demonstrated in group M HIV-1 viruses, in the DRC, Republic of Congo, Cameroon, and Gabon . The high replication rate , the low integrity of the reverse transcriptase , the viral replication rate at the origin of the quasispecies emergence, as well as the genetic recombination between HIV-1 and HIV-2, give to these viruses an extreme genetic diversity. HIV-1 viruses are classified into four groups: M , O , N , and P . HIV-2 viruses are classified in groups AH. Their origin is simian . Phylogenetic studies showed the existence of 10 subtypes within the M group , sub-subtypes, and several circulating recombinant forms and complex recombinant forms. Group M is the most common with 90% of infections worldwide . Subtype C is also major in the world, the subtype B predomine in Europe, North America, Latin America, and Australia, and the majority of types and subtypes are represented in sub-Saharan Africa. This genetic variability has consequences in the disease progression, the development of antiretroviral resistance mutations, the development of diagnostic tests and viral load quantification, and the development of a vaccine against HIV .
Michael Worobey, Guan-Zhu Han, in, 2012
Recommended Reading: How Can Hiv Be Transmitted From Mother To Child
When To Start Hiv Treatment
Its now recommended that everyone diagnosed with HIV starts treatment straight away after being diagnosed.
In the UK, national guidelines set out standards for HIV treatment. They currently recommend that anyone with HIV who is ready to commit to treatment should start it regardless of their CD4 count .
Genetic Repertoire Influencing The Replication Of Hiv
Viral Factors
Several accessory proteins support and accelerate HIV replication which is usually called viral fitness . The most effective of these proteins is Tat, which acts as viral transcriptional transactivator, Rev, which regulates the RNA transport and Vif, which promotes viral maturation and release from the cell. None of these 3 proteins is involved in the formation of drug resistance.
Human Factors
Both viral and human genetic factors contribute to HIV pathogenesis and some of the viral factors are routinely identified by nucleic acid sequencing as targets to estimate and improve the outcome of the HIV-infected patient. To analyze human genetic factors besides CCR5, APOBEC and HLA might be a future challenge for those involved in the determination of HIV drug resistance.
You May Like: How Can Hiv Be Controlled
What Is An Undetectable Viral Load
The aim of HIV treatment is to make you undetectable. This means that your viral load is so low that it cant be detected by the tests used to measure it.
Different laboratories may have different cut off points when classifying an undetectable viral load. However, most clinics in the UK classify undetectable as being below 20 copies/ml.
When you’re on effective treatment and have an undetectable viral load, you cannot pass on the virus and HIV is not able to damage your immune system.
A large study called PARTNER looked at 888 gay and straight couples where one partner was HIV positive and one was HIV negative. Results found that where the HIV positive partner was on treatment and had an undetectable viral load, there were no cases of HIV transmission whether they had anal or vaginal sex without a condom.
A follow-up study PARTNER 2 also reported zero transmissions after almost 800 gay couples had sex more than 77,000 without condoms.