Reducing The Risk Of Hiv Transmission
The most effective way to prevent HIV transmission during sex is to use a condom. Get a condom ready before any sexual contact occurs, since HIV can be transmitted through pre-ejaculate, vaginal fluid, and from the anus.
Lubricants can also help reduce the risk of HIV transmission by helping to prevent anal or vaginal tears. The right lubricants also help prevent condoms from breaking. Only water-based lubricants should be used with condoms, because oil-based lube can weaken latex and sometimes cause condoms to break.
The use of a dental dam, a small plastic or latex sheet that prevents direct contact between the mouth and the vagina or anus during oral sex, is also effective at reducing the risk of HIV transmission.
For people who may have a higher risk for contracting HIV, preventive medication is an option. Pre-exposure prophylaxis medication is a daily antiretroviral treatment.
Everyone at increased risk of HIV should begin a PrEP regimen, according to a recent recommendation from the US Preventive Services Task Force. This includes anyone who is sexually active with more than one partner, or is in an ongoing relationship with someone whose HIV status is either positive or unknown.
Although PrEP does provide a high level of protection against HIV, its still best to use condoms as well. PrEP provides no protection against STIs other than HIV.
How Long Does It Take For Hiv To Progress To Aids
How long does it take for HIV to progress to AIDS? In all but a few rare cases, if left untreated, HIV will progress to a stage of infection called AIDS. This is when the immune defenses have been compromised, and the body is less able to defend itself against potentially life-threatening infections.
How Do You Get Hiv
HIV infection can occur in the following ways:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse, especially receptive anal intercourse
- Multiple sexual partners
- Sexually transmitted diseases: Chlamydia and gonorrhea infections increase the HIV transmission risk by three times syphilis raises the transmission risk by seven times and genital herpes raises the infection risk by 25 times during an outbreak
- Sharing IV needles or injections
- Receiving HIV infected blood products
- Needle-stick injuries
- Maternal HIV infection : The risk of transmission can be reduced at birth by practices like cesarean delivery and prenatal antiretroviral therapy in the mother, and antiretroviral therapy in the newborn immediately after birth
Recommended Reading: Does Nba Youngboy Have An Std
Types Of Condomless Sex And Risk Of Hiv
During condomless sex, HIV in the bodily fluids of one person may be transmitted to the body of another person through the mucous membranes of the penis, vagina, and anus. In very rare cases, HIV could potentially be transmitted through a cut or sore in the mouth during oral sex.
Out of any type of condomless sex, HIV can most easily be transmitted during anal sex. This is because the lining of the anus is delicate and prone to damage, which may provide entry points for HIV. Receptive anal sex, often called bottoming, poses more risk for contracting HIV than insertive anal sex, or topping.
HIV can also be transmitted during vaginal sex without a condom, although the vaginal lining is not as susceptible to rips and tears as the anus.
The risk of getting HIV from oral sex without using a condom or dental dam is very low. It would be possible for HIV to be transmitted if the person giving oral sex has mouth sores or bleeding gums, or if the person receiving oral sex has recently contracted HIV.
In addition to HIV, anal, vaginal, or oral sex without a condom or dental dam can also lead to transmission of other STIs.
What Are The Signs Of An Hiv Infection
Fever is usually the first sign of an HIV infection. Many people also experience other flu-like symptoms as the disease manifests itself two to four weeks after exposure. This early, acute phase of HIV can last up to several weeks. Some of the other possible signs of the infection include:
- Chills
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Weight loss
Knowing you have HIV is almost impossible without a test. Thats because the disease can masquerade as other illnesses and sometimes may not have symptoms at all at first. At least 13% of people with HIV dont even know they have the virus. This makes it much more likely that they will spread the disease to others. If youve had unprotected sex recently, the only way to know if you have HIV is to get tested.
You May Like: How Long Can Hiv Lay Dormant
Making Hiv Testing Routine
Its recommended that you test for HIV and other sexually transmitted infections at least once a year if youre having sex, even if you always use protection.
You might want to test more regularly than this, for example, if you are having sex with a new partner or feel you are more at risk. Groups who are more at risk are recommended to test more regularly. Testing every 3-6 months is often advised for men who have sex with men.
Testing regularly helps keep your mind at rest, and if you test positive, it means you can start treatment quickly, protecting your health.
Stage : Acute Hiv Infection
Within 2 to 4 weeks after infection with HIV, about two-thirds of people will have a flu-like illness. This is the bodys natural response to HIV infection.
Flu-like symptoms can include:
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Mouth ulcers
These symptoms can last anywhere from a few days to several weeks. But some people do not have any symptoms at all during this early stage of HIV.
Dont assume you have HIV just because you have any of these symptomsthey can be similar to those caused by other illnesses. But if you think you may have been exposed to HIV, get an HIV test.
Heres what to do:
Also Check: Does Cookie Johnson Have Hiv
Am I Going To Die Of Aids
While complications from HIV infection remain a possibility, current treatments and medications are giving people with HIV a positive prognosis and near-normal life-span. This makes patients living with HIV vulnerable to the same health conditions that affect all people as they age. This is why it is important to maintain good health throughout your life.
What Are The Tests For Detecting Hiv
Various tests may be used for HIV detection:
- HIV antibody test: This test detects the antibodies produced in the body in response to HIV.
- Antigen test: This test can be done at an earlier stage than an HIV antibody test. It measures a protein called p24 antigen, present in the virus and produced in high amounts after the infection.
- Nucleic acid test : It is also called an RNA test. It is a very specific test that looks for the virus itself and can detect HIV as early as about 10 days of infections.
- In-home test kits: Although less accurate than the laboratory-based tests, home-based kits have the advantage of testing in the privacy and comfort of the home. Only FDA approved home-based kits should be used.
- Viral culture: This involves using the patients sample and growing the virus in the lab. It takes longer to get the results and is not the most preferred test for HIV.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Aids From Dried Blood
When To Get Tested For Hiv After Intercourse
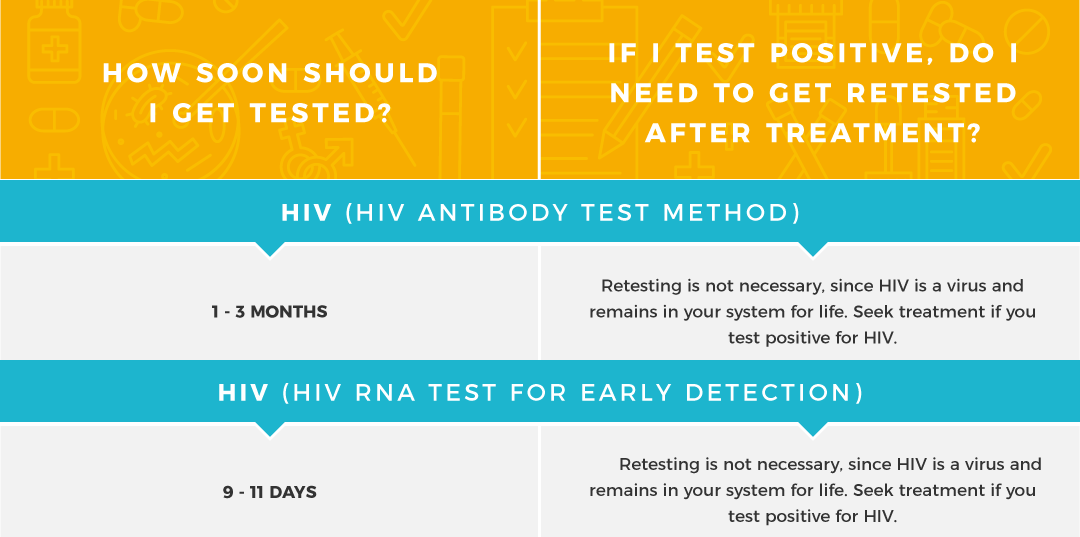
One recommended strategy is to get tested 2-4 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months after a risky exposure. Using a sensitive antigen/antibody HIV test, of those who are infected, most will test positive at 1 month almost all will test positive at 3 months and the rest will test positive at 6 months.13-Jun-2019
Who Should Get Tested For Hiv
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that everyone 13 to 64 years old get tested for HIV at least once as part of routine health care. As a general rule, people at higher risk for HIV should get tested each year. Sexually active gay and bisexual men may benefit from getting tested more often, such as every 3 to 6 months.
Factors that increase the risk of HIV include:
- Having vaginal or anal sex with someone who is HIV positive or whose HIV status you dont know
- Injecting drugs and sharing needles, syringes, or other drug equipment with others
- Exchanging sex for money or drugs
- Having hepatitis or tuberculosis
- Having sex with anyone who has any of the HIV risk factors listed above
Talk to your health care provider about your risk for HIV and how often you should get tested for HIV.
You May Like: What Is Hiv 1 And 2 Antibody Test
How The Oraquick In
What is the OraQuick In-Home HIV Test and how does it work?
The OraQuick In-Home HIV Test is a rapid self-administered over-the-counter test. The OraQuick In-Home HIV Test kit consists of a test stick to collect the specimen, a test tube to insert the test stick and complete the test, testing directions, two information booklets , a disposal bag and phone numbers for consumer support.
This approved test uses oral fluid to check for antibodies to HIV Type 1 and HIV Type 2, the viruses that cause AIDS. The kit is designed to allow you to take the HIV test anonymously and in private with the collection of an oral fluid sample by swabbing your upper and lower gums with the test device. After collecting the sample you insert the device into the kits vial which contains a developer solution, wait 20-40 minutes, and read the test result. A positive result with this test does not mean that an individual is definitely infected with HIV but rather that additional testing should be done in a medical setting to confirm the test result. Additionally, a negative test result does not mean that an individual is definitely not infected with HIV, particularly when exposure may have been within the previous three months. Again an individual should obtain a confirmatory test in a medical setting.
When should I take a test for HIV?
How reliable is the OraQuick In-Home HIV Test?
OraQuick In-Home HIV Test Fact Sheet
Recommended Reading: How Many People Are Living With Hiv
Safer Sex Still Carries Std Risk

It’s also worth noting that concerns about STD incubation periods aren’t restricted to individuals who practice unprotected sex. Although practicing safer sex and other measures that reduce your risk, like using mouthwash, can drastically reduce your stress levels and your level of risk, it isn’t foolproof protection.
Condoms and other barriers can only reduce the risk of diseases that spread skin-to-skin instead of by bodily fluidsthey can’t entirely prevent them. That’s why it’s a good idea to talk about testing and sources of risk before you have sex.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have A Std
Latency Causes A Break In Symptoms
After initial exposure and possible primary infection, HIV may transition into a stage called clinically latent infection. Its also referred to as asymptomatic HIV infection due to a noticeable lack of symptoms. This lack of symptoms includes possible chronic symptoms.
According to HIV.gov, latency in HIV infection can last for 10 or 15 years. This doesnt mean that HIV is gone, nor does it mean that the virus cant be transmitted to others. Clinically latent infection may progress to the third and final stage of HIV, also referred to as AIDS.
The risk for progression is higher if a person with HIV isnt receiving treatment, such as antiretroviral therapy. Its important to take prescribed medications during all stages of HIV even if there arent any noticeable symptoms. There are several medications used for HIV treatment.
A Word About Window Periods
The window period refers to the time it takes for HIV to show up in an HIV test. The length of the window period will depend on the type of test you take.
If you feel like you may be at risk of HIV, do not wait, speak to a healthcare professional as soon as possible. The most important thing is to test.
If you test negative but think you may have been exposed to HIV more recently, you can take another test once the window period has passed.
The picture below shows the window periods for different HIV tests. Some tests can give you an accurate result within four weeks, while others can take three months to be accurate .
A healthcare worker will be able to explain how long the window period is for the test you are taking, and will tell you if they think youll need to test for HIV again.
Recommended Reading: Walgreens At Home Hiv Test
Lack Of Symptoms In Early Stages
ARS is common once a person has HIV. Still, this isnt the case for everyone. Some people have HIV for years before they know they have it. According to HIV.gov, symptoms of HIV may not appear for a decade or longer. This doesnt mean that cases of HIV without symptoms are less serious. Also, a person who doesnt experience symptoms could still transmit HIV to others.
Symptoms in early HIV tend to appear if the rate of cell destruction is high. Not having symptoms can mean that not as many CD4 cells, a type of white blood cell, are killed early on in the disease. Even though a person has no symptoms, they still have the virus. Thats why regular HIV testing is critical to prevent transmission. Its also important to understand the difference between a CD4 count and a viral load.
What Is It Used For
An HIV test is used to find out if you have been infected with HIV. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS . Most people with HIV don’t have AIDS. People with AIDS have an extremely low number of immune cells and are at risk for life-threatening illnesses, including dangerous infections, a severe type of pneumonia, and certain cancers, including Kaposi sarcoma.
If HIV is found early, you can get medicines to protect your immune system. HIV medicines may prevent you from getting AIDS.
You May Like: Does Hiv Cause Hair Loss
Hiv Testing For Detection
Below are the HIV testing options that medical professionals do to determine if an individual is HIV positive.
Early signs recognition is a vital aspect so that patients can seek medical help immediately. In effect, HIV carriers can get more excellent results.
How Does Hiv Spread
HIV spreads when blood or certain bodily fluids that have high amounts of active virus are exposed to ones bloodstream.
For a person to contract HIV, there must be enough active virus in the fluid that encounters the bloodstream. This can occur through:
- a mucous membrane, or moist skin, such as in the mouth, rectum, penis, or vagina
- a significant opening in the skin
- injection
Transmission of the virus most often happens during anal or vaginal sex, but it can also occur by sharing needles.
Factors that affect the survival of HIV outside the body include:
- Temperature. HIV stays alive and active when kept in the cold but is killed by heat.
- Sunlight. Ultraviolet light in sunshine damages the virus, so its no longer able to reproduce.
- Amount of virus in the fluid. Generally, the higher the level of HIV virus in the fluid, the longer it will take for all of it to become inactive.
- Level of acidity. HIV survives best at a pH around 7 and becomes inactive when the environment is even just a little more or less acidic.
- Environmental humidity. Drying will lower the viral concentration of active virus as well.
When any of these factors arent perfect for HIV in its environment, survival time of the virus goes down.
Don’t Miss: Hiv Causes Hair Loss
Why Does Hiv Evolve Rapidly
HIV evolves extremely rapidly, exhibiting the highest recorded biological mutation rate currently known to science. The interpatient genome-wide nucleotide substitution rate of intracellular viral DNA may be as high as 4.1 × 10-3 substitutions per site per year and, in the hypervariable regions of the envelope gene, could reach 5.2 × 10-3 s/s/y.
The rapid rate of HIV evolution is largely attributable to the error-prone nature of reverse transcriptase, which plays an important role in viral replication yet lacks proofreading activity. This, in combination with short generation times, allows mutations to accumulate quickly within the virus at rates that differ across the genome. As the duration of infection is prolongedwith clinical latency lasting around a decade in untreated individualsand the replicating population is large, the degree of viral diversity within a patient can be extensive.
Mutations may accumulate either because of genetic drift or because they confer a relative fitness advantage to the virus, allowing it to persist and replicate more successfully than in its previous state. Escape mutations often confer a degree of resistance against selection pressure exerted by drugs or the host immune response, and evidence of viral evolution driven by cytotoxic lymphocytes and antibodies can even be detected in infants. HIV-1 is known to adapt to host HLA class I,, and up to 56% of polymorphic sites in viral genes may be subject to HLA-associated selection pressure.