A Timeline Of Hiv Symptoms
What is HIV?
HIV is a virus that compromises the immune system. Theres currently no cure for it, but there are treatments available to reduce its effects on peoples lives.
In the majority of cases, once HIV infection takes hold, the virus stays in the body for life. However, unlike what may occur with infections by other types of viruses, HIV symptoms dont suddenly appear and peak overnight.
If left untreated, the disease progresses over time through three stages, each with its own set of possible symptoms and complications some severe.
Regular antiretroviral treatment can reduce HIV to undetectable levels in the blood. At undetectable levels, the virus wont progress to the later stages of HIV infection. In addition, the virus cant be transmitted to a partner during sex.
Early Symptoms Of Hiv
When HIV first infects the body, you likely wont notice any changes. Thats why, in the earliest stage of the virus, many people dont realize theyve become infected.
Doctors measure HIV and its signs and symptoms in stages. The first stage, which is called acute HIV infection, is very subtle. After infection, your bodys immune system starts working to fight the virus. This stage typically occurs within two to six weeks after infection.
When the virus is in its first stage, youll start noticing the earliest symptoms of HIV. Unfortunately, these symptoms are similar to the symptoms of other common viruses, such as the flu.
So, if youre experiencing flu-like symptoms, its important to see a doctor. When HIV first begins, youll experience what feels like a typical bout of the flu for about two weeks. Symptoms may include:
- Headache
- Fever, and/or
- Swelling in the lymph nodes.
You may also get a red rash on your torso. This rash doesnt itch, but it does appear while youre experiencing other symptoms.
Typically, these symptoms occur for just a week or two and then they disappear completely. This can make it seem like everything is back to normal in your immune system. However, its important to see a doctor and get tested for HIV.
The Most Common Symptoms Of Seroconversion Are:
- sore throat
- fever
- rash over the body.
Seroconversion is a sign that the immune system is reacting to the presence of the virus in the body. Its also the point at which the body produces antibodies to HIV. Once seroconversion has happened, an HIV test will detect antibodies and give a positive result.
Seroconversion illness happens to most people shortly after infection. It can be severe enough to put someone in hospital or so mild that its mistaken for something like flu although a blocked or runny nose is not usually a symptom.
If you do have HIV, your body fluids are highly infectious during the early weeks and months after transmission. However, once youre on effective treatment and your viral load becomes undetectable you cannot pass on HIV.
It can take up to six months from starting treatment to become undetectable.
Recommended Reading: How Does Hiv Make You Feel
Fever And Night Sweats
People with HIV may experience long periods of low-grade fever. A temperature between 99.8°F and 100.8°F is considered a low-grade fever.
The body develops a fever when something is wrong, but the cause isnt always obvious. Because its a low-grade fever, those who are unaware of their HIV-positive status may ignore the symptom.
Sometimes, night sweats that can interfere with sleep may accompany fever.
Women with HIV can experience changes to their menstrual cycle. Their periods may be lighter or heavier than normal, or they may not have a period at all.
HIV-positive women may also have more severe premenstrual symptoms.
What To Look For
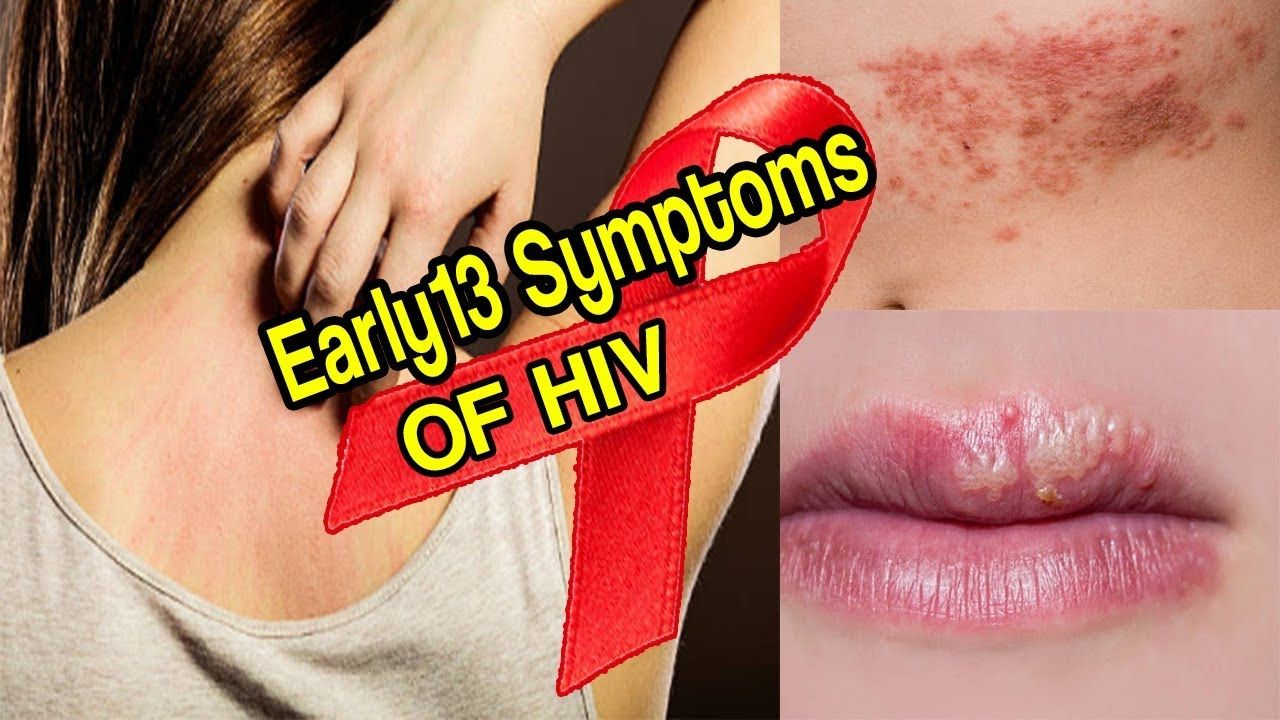
Whether caused by an HIV medication or by HIV itself, the rash typically appears as a red, flattened area on the skin thats usually covered with small red bumps.
A main symptom of the rash is itchiness. It can show up on any part of the body, but it most often occurs on the face and chest, and sometimes on the feet and hands. It can also cause mouth ulcers.
Also Check: How Is Hiv Transmitted Through Blood
Stage : Acute Hiv Infection
Within 2 to 4 weeks after infection with HIV, about two-thirds of people will have a flu-like illness. This is the bodys natural response to HIV infection.
Flu-like symptoms can include:
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Mouth ulcers
These symptoms can last anywhere from a few days to several weeks. But some people do not have any symptoms at all during this early stage of HIV.
Dont assume you have HIV just because you have any of these symptomsthey can be similar to those caused by other illnesses. But if you think you may have been exposed to HIV, get an HIV test.
Heres what to do:
Signs And Symptoms Of Hiv/aids
The stages of HIV infection are acute infection , latency and AIDS. Acute infection lasts for several weeks and may include symptoms such as fever, swollen lymph nodes, inflammation of the throat, rash, muscle pain, malaise, and mouth and esophageal sores. The latency stage involves few or no symptoms and can last anywhere from two weeks to twenty years or more, depending on the individual. AIDS, the final stage of HIV infection, is defined by low CD4+ T cell counts , various opportunistic infections, cancers and other conditions.
You May Like: Which Infection Is Most Often Seen In Hiv Patients
Five Books On Hiv In The Black Community Everyone Should Have
michaeljung via
You, then, are charged by the possibility of your good health, by the broadness of your vision, to remember us.
Black gay writer Melvin Dixon made this call in 1992, in a speech entitled, Ill Be Somewhere Listening for My Name, during an OutWrite conference in Boston. These are among the last words he would deliver during a public speech before his death from AIDS. Darius Bost, Ph.D., professor of Ethnic Studies at the University of Utah, has noted that the title of the speech is drawn from the sorrow songs of slaves, who used them as an expression of collective trauma and as a catalyst for fugitivity in their attempts to escape slavery. The message in Dixons speech, to remember us, resonates loudly today, and especially so during #BlackHistoryMonth, in a moment that is marked by both dramatic medical advancements and lingering inequities surrounding HIV within the Black community. In 2018, African Americans accounted for 42% of new HIV diagnoses in the United States, despite comprising 13% of the population.
To read these books is also to gain insight into the sustained resilience of the Black community despite HIV/AIDS. In the face of stigma and death, the people who emerge in these pages created community and art. These selections illuminate a remarkable but unsung tradition, including figures like Essex Hemphill, Joseph Beam, Assotto Saint, Marlon Riggs, and other individuals who should be more often commemorated during #BlackHistoryMonth.
Lack Of Symptoms In Early Stages
ARS is common once a person has HIV. Still, this isnt the case for everyone. Some people have HIV for years before they know they have it. According to HIV.gov, symptoms of HIV may not appear for a decade or longer. This doesnt mean that cases of HIV without symptoms are less serious. Also, a person who doesnt experience symptoms could still transmit HIV to others.
Symptoms in early HIV tend to appear if the rate of cell destruction is high. Not having symptoms can mean that not as many CD4 cells, a type of white blood cell, are killed early on in the disease. Even though a person has no symptoms, they still have the virus. Thats why regular HIV testing is critical to prevent transmission. Its also important to understand the difference between a CD4 count and a viral load.
Don’t Miss: Can Hiv Be Cured Early
Who Is At Risk For Hiv Infection
Anyone can get HIV, but certain groups have a higher risk of getting it:
- People who have another sexually transmitted disease . Having an STD can increase your risk of getting or spreading HIV.
- People who inject drugs with shared needles
- Gay and bisexual men, especially those who are Black/African American or Hispanic/Latino American
- People who engage in risky sexual behaviors, such as not using condoms
Clinical Latency Stage Of Hiv Infection
The symptoms during ARS may last for a few weeks, according to the National Institutes of Health.
After this point, the infection progresses to the clinical latency stage, a period during which the virus reproduces at very low levels, but it is still active.
Also known as asymptomatic HIV infection or chronic HIV infection, the clinical latency stage typically causes no HIV-related symptoms.
For people who are not taking any anti-retroviral medication for their infection, the clinical latency stage lasts for 10 years, on average, but it may progress quicker.
ART, though, can keep the virus from growing and multiplying, prolonging the clinical latency state for several decades.
It’s important to note that people living with HIV in the clinical latency stage are contagious and can still transmit the virus to other people. But, as the CDC notes, people who take ART exactly as prescribed and maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their HIV negative-partner through sex.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Contracted Hiv
How To Identify An Hiv Rash
This article was co-authored by Dale Prokupek, MD. Dale Prokupek, MD is a board certified Internist and Gastroenterologist who runs a private practice based in Los Angeles, California. Dr. Prokupek is also a staff physician at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and an associate clinical professor of medicine at the Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles . Dr. Prokupek has over 25 years of medical experience and specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the liver, stomach, and colon, including chronic hepatitis C, colon cancer, hemorrhoids, anal condyloma, and digestive diseases related to chronic immune deficiency. He holds a BS in Zoology from the University of Wisconsin Madison and an MD from the Medical College of Wisconsin. He completed an internal medicine residency at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and a gastroenterology fellowship at the UCLA Geffen School of Medicine.There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 87% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 1,852,350 times.
What Is The Difference Between Hiv And Aids
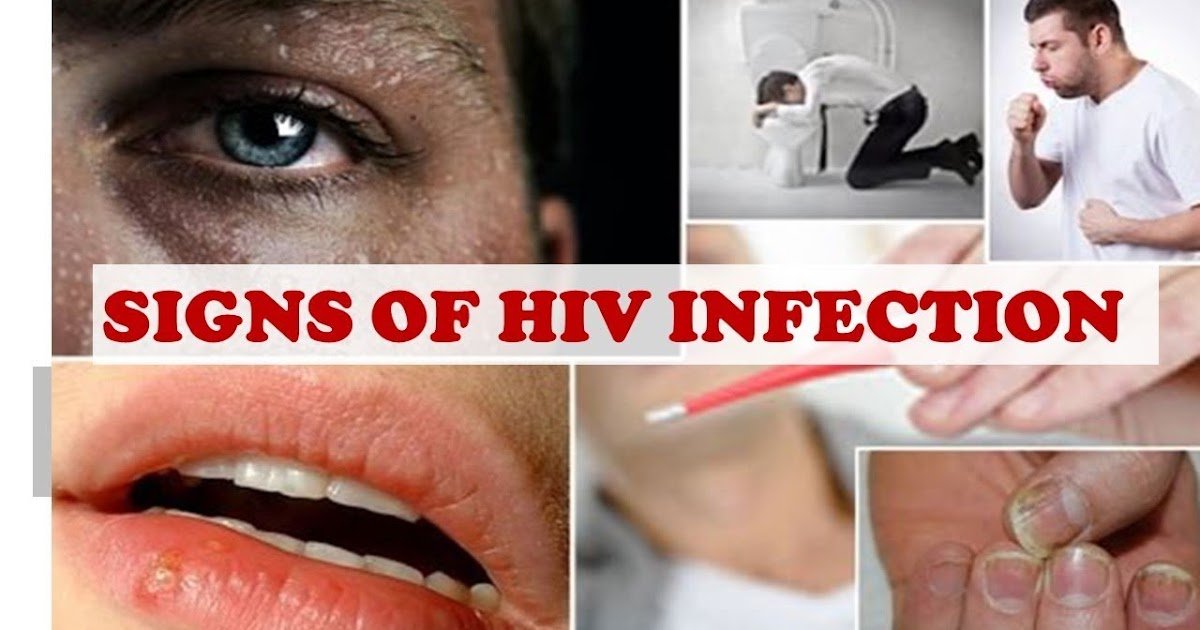
The term AIDS refers to the most advanced stages of HIV infection. Most of the conditions affecting people with AIDS are opportunistic infections that generally do not affect healthy people. In people with AIDS, these infections are often severe and sometimes fatal because the immune system is so ravaged by HIV that the body cannot fight off the infection. Symptoms of opportunistic infections common in people with AIDS include:
- coughing and shortness of breath
- seizures and lack of coordination
- difficult or painful swallowing
- severe headaches
- coma
People with AIDS also are particularly prone to developing various cancers. These cancers are usually more aggressive and difficult to treat in people with AIDS.
Don’t Miss: Can Hiv Be Transmitted Through Eyes
If You Already Have Hiv
If you are infected with HIV, you can greatly lower the risk of spreading the infection to your sex partner by starting treatment when your immune system is still healthy.
Experts recommend starting treatment as soon as you know you are infected.footnote 21
Studies have shown that early treatment greatly lowers the risk of spreading HIV to an uninfected partner.footnote 22, footnote 23
Your partner may also be able to take medicine to prevent getting infected.footnote 17 This is called pre-exposure prophylaxis .
Steps to avoid spreading HIV
If you are infected with HIV, you can greatly lower the risk of spreading the infection to your sex partner by starting treatment when your immune system is still healthy.
- Take antiretroviral medicines. Getting treated for HIV can help prevent the spread of HIV to people who are not infected.
- Tell your sex partner or partners about your behaviour and whether you are HIV-positive.
- Follow safer sex practices, such as using condoms.
- Do not donate blood, plasma, semen, body organs, or body tissues.
- Do not share personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or sex toys, that may be contaminated with blood, semen, or vaginal fluids.
The First Signs Of Hiv
The initial stage of HIV is called an acute HIV infection. Within the first month of being infected with HIV, you may experience flu-like symptoms such as:
- Fever
- Headaches
- Rash and mouth sores
It may be hard to differentiate the initial symptoms of HIV from the flu or mono. If symptoms are accompanied by rashes and mouth sores, that’s usually an indication that the cause is more likely an early stage of HIV than the common flu.
Important: You can only contract HIV by coming in contact with the bodily fluids such as blood, vaginal fluids, semen and pre-seminal fluid, rectal fluids, and breast milk of an HIV-positive person. The transmission happens via contact through open wounds, direct injection, or a mucous membrane .
It’s important to note that HIV symptoms aren’t consistent and vary from one person to another, both in type and severity.
“Some people may have varying degrees of symptoms but no significant differences based on gender or race,” says Aadia I. Rana, MD, associate professor of medicine under the Division of Infectious Diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
It’s also possible to have HIV and be asymptomatic. In fact, approximately 15% of people living with HIV aren’t aware of their status and can unknowingly transmit the virus to others. Some people don’t get tested at all due to the misinformation and stigma surrounding HIV.
You May Like: What Percentage Of The Population Has Hiv
What Are The Symptoms Of Hiv/aids
The first signs of HIV infection may be flu-like symptoms:
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Mouth ulcers
These symptoms may come and go within two to four weeks. This stage is called acute HIV infection.
If the infection is not treated, it becomes chronic HIV infection. Often, there are no symptoms during this stage. If it is not treated, eventually the virus will weaken your body’s immune system. Then the infection will progress to AIDS. This is the late stage of HIV infection. With AIDS, your immune system is badly damaged. You can get more and more severe infections. These are known as opportunistic infections .
Some people may not feel sick during the earlier stages of HIV infection. So the only way to know for sure whether you have HIV is to get tested.
How Do I Avoid Passing Hiv On To Someone Else
If you are infected with HIV, the best way to prevent spreading HIV infection to others is to:
- take your medication as prescribed there is a very low risk of passing on HIV if your own infection is under control
- use condoms and a water-based lubricant for anal and vaginal sex
- never share needles, syringes and other injecting equipment
If you have HIV infection, you are expected to notify anyone who is at risk of exposure from you:
- Tell people you have had sex or taken drugs with. Your doctor can help you decide who may be at risk and help you to contact them either personally or anonymously.
- Tell anyone you intend to have sex with about your HIV status . This is required by law in some states.
If you are pregnant, talk to your doctor about starting antiretroviral treatment to prevent the infection passing to the baby during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding. Read more about HIV and pregnancy.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hiv Non Reactive Mean
You May Like: Can You Test For Hiv
How Often Should A Man Get Tested
Sexually active men should get routine tests for HIV.
Men who are sexually active should get tested for HIV at least once in their lifetime as part of their routine health care.
The CDC recommend that everyone between the ages of should take an HIV test.
The CDC also recommend that people with specific risk factors should take a test at least once a year . This recommendation applies to gay and bisexual men, and men who have sex with men, and users of injectable drugs.
Besides these formal recommendations, everyone who may have been exposed to HIV or had sex without a condom should also take a test.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Is there any sure way to avoid acquiring HIV?
- What is the best treatment for me?
- How can I avoid getting any infections that will make me very sick?
- How can I find support groups in my community?
- What diagnostic tests will you run?
- How often will I need to see my doctor?
- Will there be any side effects to my treatment?
- How does this affect my plans for having a family?
- Is it safe for me to breastfeed my baby?
- Will using a condom keep my sex partners from acquiring HIV?
- Should I follow a special diet?
Read Also: How Long Does Hiv Test Take
Getting Tested And Treated For Hiv
“All adolescents and adults who are sexually active should get screened for HIV as part of their routine primary care,” says Akselrod. “Blood tests for HIV are now extremely accurate both sensitive and specific and can detect HIV, even within the first two to four weeks after becoming infected.”
Here are some tools to help you find HIV testing sites and care services near you:
You can also get tested at sexual health or family planning clinics, your health care provider’s office, or other local health centers.
If you test positive for HIV, you’ll need to take antiretroviral therapy to manage your condition. This medicine can lower the amount of HIV in your blood to the point that a test can no longer detect it, which is known as being “undetectable” or having an “undetectable viral load.”
Important: Pre-exposure prophylaxis and post-exposure prophylaxis both help you avoid contracting HIV, but PrEP is taken by people who may be exposed to HIV in the future whereas PEP is taken by those who were already exposed to HIV within the past 72 hours.
“As long as they take it regularly, the virus is completely controlled and the person can have a normally functioning immune system,” says Rana. Being undetectable also means that there is no risk of transmitting HIV to other people.