Conditions Needed To Transmit Hiv
As serious an infection as HIV is, the virus itself is not all that robust. Others, like the flu and cold viruses, are far more sturdy and can be passed from one person to next by sneezing. HIV cannot. Instead, there four conditions that must take place in order for infection to occur:
- There must be body fluids in which HIV can thrive. For HIV, this meanssemen, blood, vaginal fluids, or breast milk. HIV cannot survive for very long in the open air or in parts of the body where is high acid content .
- There must be a way for body fluids to enter the body. This happens primarily through sexual contact but can also be spread through , accidental blood exposure in healthcare settings, or transmission of the virus from mother to child during pregnancy.
- The virus must be able to reach vulnerable cells inside the body. Skin contact with a body fluid is not enough.It needs to enter the bloodstream through a break in the skin or penetrate vulnerable mucosal tissues of the vagina or rectum. The depth and size of the penetration also matter, with a deep cut being riskier than a scrape.
- There must be sufficient amounts of virus in the body fluid. This is why saliva, sweat, and tears are unlikely sources of infection since the enzymes in these fluids actively break down HIV and its genetic structure.
How Hiv Cannot Be Spread
From both a biological and epidemiological evidence, HIV cannot and has never been shown to be passed from one person to the next by the following means:
- Touching, hugging, kissing or shaking hands
- Touching an object an HIV-positive person has touched
- Sharing utensils or cups
- Eating food prepared by an HIV-positive person
- Sharing grooming items, even toothbrushes or razors
- Getting spit on by an HIV-positive person
- Getting bitten by an HIV-positive person
- Touching semen or vaginal fluid
- Getting blood from an HIV-positive person on you
- Using public fountains, toilet seats, or showers
To date, there has not been a single documented case of transmission by any of these means.
Blood Transfusions And Organ Donation
The risk of contracting HIV from a blood transfusion, other blood products, or organ donation is now extremely rare in the United States. All donated blood or blood products in the United States are for several types of bloodborne pathogens, including HIV.
Organ donations are also screened for HIV. Although very rare, its possible for HIV transmission to occur following an organ transplant.
However, testing of organ recipients after surgery can quickly detect transmission so that antiretroviral medications can be started promptly.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have Hiv
Sharing Injection Drug Equipment
most efficiently . This is because used needles and syringes can still contain blood, which can carry the virus.
HIV is not the only virus that can be transmitted by sharing drug injection equipment. The viruses that cause hepatitis B and hepatitis C can be
- having other types of sexually transmitted infections
Bites That Break The Skin
A bite that opens the skin and causes bleeding can lead to the transmission of HIV. However, according to the
goes up with increasing viral load.
Viral load is highest both during the early phase of HIV and without treatment with antiretroviral medications. Taking antiretroviral medications every day can reduce a persons viral load to very low levels that cannot be detected through testing.
In this way, antiretroviral medications are not only a treatment, but an important tool for prevention. When HIV cannot be detected in the blood, a person living with HIV cannot sexually transmit the virus to a partner without HIV.
This principle is called Undetectable = Untransmittable .
It can take up to 6 months of taking antiretroviral medications each day to achieve an undetectable viral load.
A persons viral load is said to be durably undetectable when all test results are undetectable for at least 6 months after the first undetectable result.
There are a couple reasons that STIs can raise HIV risk. First, the symptoms of many STIs include genital inflammation, sores, or ulcers. These can all increase the chance of transmitting the virus from one person to another.
Second, like HIV, transmission of STIs is associated with some of the same types of behaviors, such as engaging in sex without a condom or other barrier method.
Some research has also indicated that certain STIs may be more with HIV transmission than others. These STIs include:
Also Check: Nba Youngboy Herpes Song
How Does Hiv Get Inside The Body In The First Place
It turns out that its relatively difficult for HIV to get inside the body and lock on to those white blood cells. This can only happen during intimate contact between two peopleby which we mean anal sex, vaginal sex, or sharing injection-drug equipment.
HIV cannot pass through a persons skin. This means that you will not become positive by touching bodily fluid that contains HIV, unless you have an open wound where youre touching the fluid. Even if you ingest the viruslets say, by eating food with traces of HIV inside itthe acid inside your stomach will protect you.
HIV almost always enters the body in one of three ways:
- Direct contact with the bloodstream, either through an open wound or with a needle.
- Direct contact with certain mucous membranesspecifically, the soft, permeable tissues inside the rectum, vagina, penis, and mouth.For newborns, exposure is possible during pregnancy, delivery, or shortly after birth by consuming breast milk from an HIV-positive person.
For adults, its important to remember that HIV can only enter the body when its exposed to an open wound, injected directly into the bloodstream, or passed through a mucous membrane, typically through anal or vaginal sex.
In addition, anyone who is pregnant should get an HIV test. If the results come back positive, your doctor can help you stay healthy and prevent your baby from getting HIV.
How Viruses Spread Through Blood
HIV infection can occur when a person is exposed to this virus. Typically, this involves sexual contact or direct blood to blood contact, either via an open wound or penetration of skin by a contaminated needle.
The virus then travels to the lymph nodes, where it enters cells of the immune system called T cells. Here, a cat and mouse battle begins. The virus and immune system use complex tactics to outsmart each other.
Perhaps the greatest of these tricks belong to HIV the virus incorporates itself into the DNA of host T cells, and hides from the immune system in protected sites, such as the central nervous system. This makes it impossible to clear the virus from the body completely, and without treatment HIV remains detectable in blood.
The cells responsible for attacking the virus instead produce new virus particles and attack other, infected, T cells. Without treatment, this leads to destruction of the immune system, unusual infections and a syndrome known as the acquired immune deficiency syndrome , which is almost invariably fatal.
In contrast, influenza is spread by respiratory droplets. Virus particles are transmitted when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Droplets are inhaled by a new host, the virus binds to target receptors on the respiratory tract surface, and replicates in cells of the respiratory tract.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Aids From Dried Blood
Factors That Increase The Risk Of Sexual Transmission
Not every act of unprotected sex with an HIV-positive person results in HIV transmission. But other factors can make HIV transmission more likely.
pre-exposure prophylaxis
Antiretroviral drugs used by a person who does not have HIV to be taken before possible exposure to HIV in order to reduce the risk of acquiring HIV infection. PrEP may either be taken daily or according to an event based or on demand regimen.
If the HIV-negative person has an untreated sexually transmitted infection , the risk is greater.
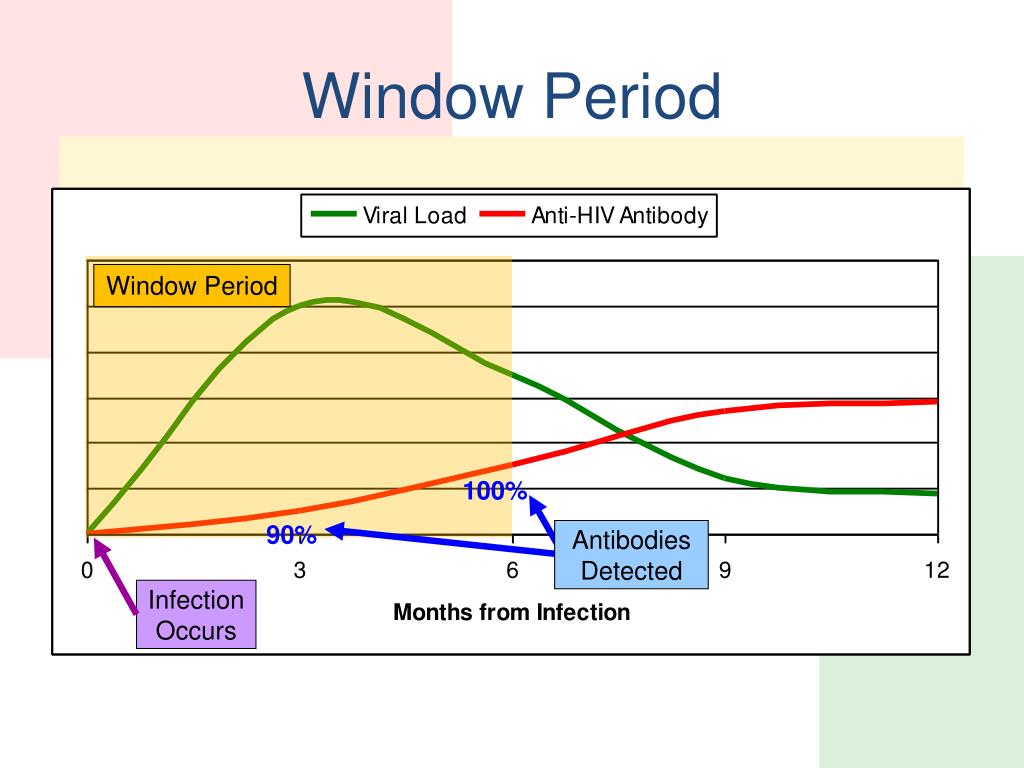
Just as HIV treatment and an undetectable viral load prevents HIV transmission, a high viral load makes it more likely. Viral load refers to the quantity of HIV in a persons body fluids. It is extremely high in the first few weeks after a person is first infected with HIV. It may also be high if a person does not take HIV treatment and has advanced disease. People who have HIV without realising it cannot take HIV treatment, so there is a strong possibility that they have a high viral load.
Can Hiv Be Spread From Females To Males
Yes. HIV can be spread from male to female, female to male, men who have sex with men , and women who have sex with women. Before we knew a lot about HIV/AIDS, people thought that AIDS spread by gays. Today, we know that this and other misconceptions are not true. Globally, HIV/AIDS is most commonly spread between heterosexuals.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Really Have Herpes
How Is Hiv Spread From Person To Person
HIV can only be spread through specific activities. In the United States, the most common ways are:
- Having vaginal or anal sex with someone who has HIV without using a condom or taking medicines to prevent or treat HIV. Anal sex is riskier than vaginal sex.
- Sharing injection drug equipment , such as needles, with someone who has HIV.
Less common ways are:
- From mother to child during pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding. However, the use of HIV medicines and other strategies have helped lower the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV to 1% or less in the United States.
- Getting stuck with an HIV-contaminated needle or other sharp object. This is a risk mainly for health care workers. The risk is very low.
HIV is spread only in extremely rare cases by:
- Having oral sex. But in general, the chance that an HIV-negative person will get HIV from oral sex with an HIV-positive partner is extremely low.
Implementation Of Recommended Precautions
Employers of health-care workers should ensure that policies exist for:
- 1.
-
Initial orientation and continuing education and training of all health-care workersincluding students and traineeson the epidemiology, modes of transmission, and prevention of HIV and other blood-borne infections and the need for routine use of universal blood and body-fluid precautions for all patients.
- 2.
-
Provision of equipment and supplies necessary to minimize the risk of infection with HIV and other blood-borne pathogens.
- 3.
-
Monitoring adherence to recommended protective measures. When monitoring reveals a failure to follow recommended precautions, counseling, education, and/or re-training should be provided, and, if necessary, appropriate disciplinary action should be considered.
Professional associations and labor organizations, through continuing education efforts, should emphasize the need for health-care workers to follow recommended precautions.
Read Also: How Long Does Hiv Last
Doubts Persist Even When Risk Is Statistically Zero
Despite increased public awareness about HIV, there remains a lot of confusion about how you can get infected and how you cannot. For example, even though people understand that you can’t get HIV from utensils, there are many who will experience a twinge of concern if they learned that the chef of their favorite restaurant has HIV.
HIV has a way of spurring anxieties in even the best of us and, with it, our sense of reason. Relieving those anxieties often requires us to do more than just lay out the rules. Instead, we need to understand what conditions are required for an infection to take place and why things like hugging, touching, sneezing, or kissing simply do not satisfy those conditions.
Which Bodily Fluids Can Pass Hiv

Bodily fluid is a blanket term that refers to any of the liquids floating around inside the human body. Were talking blood, sweat, tears, semen, vaginal fluids, urine, and all the rest.
HIV does not spread throughout the body evenly. Some bodily fluids have it, but most dont. In fact, HIV can only be transmitted to another person through these three types of bodily fluids:
- blood
- sexual fluid
- breast milk
Thats it.
HIV cannot be passed from person to person via other fluids like tears, saliva, vomit, or feces. This is an incredibly important point about HIV transmission that is often misunderstood.
For decadesand still todaypeople have worried they might catch HIV from a toilet seat, perhaps by touching the urine or fecal matter of an HIV-positive person. This absolutely does not happen.
People have also worried they might catch the virus from the saliva of an HIV-positive person who kisses them or spits on them. In fact, this fear is so pervasive that some states have made it a felony for people with HIV to spit at or bite someone else. Those laws are based on outdated science.
The only way it would be possible to transmit HIV through saliva is if the HIV-positive person had bleeding gums or sores, and somehow that bloody saliva got into the bloodstream of the HIV-negative person. However, experts agree that the risk of this happening is so statistically tiny that its not worth worrying about.
So, to recap:
Don’t Miss: Does Aids Cause Hair Loss
Tattoos And Body Piercings
- There are no known cases in the United States of anyone getting HIV this way.
- However, it is possible to get HIV from tattooing or body piercing if the equipment used for these procedures has someone elses blood in it or if the ink is shared. This is more likely to happen when the person doing the procedure is unlicensed because of the potential for unsanitary practices such as sharing needles or ink.
- If you get a tattoo or a body piercing, be sure that the person doing the procedure is properly licensed and that they use only new or sterilized needles, ink, and other supplies.
Lowering The Risk Of Sexual Transmission
There are several protective measures which dramatically reduce the risk of HIV transmission during sex. You can find out more about these on other pages.
Undetectable viral load: when people with HIV take effective treatment, the amount of HIV in their body fluids falls drastically, to the point where they cannot pass HIV on to their sexual partners. An extremely low level of HIV in body fluids is referred to as an undetectable viral load. The knowledge that this prevents transmission is often referred to ‘Undetectable equals Untransmittable’ .
PrEP: if the HIV-negative person takes antiretroviral medications as pre-exposure prophylaxis , this significantly reduces the risk of acquiring HIV. The most common form of PrEP is in a tablet, but it can also be provided as a vaginal ring or an injection.
Condoms: if male condoms or female condoms are used, this significantly reduces the risk of acquiring HIV.
Male circumcision: if you are circumcised, this partially lowers your risk of acquiring HIV during vaginal sex.
Recommended Reading: Hiv Dormancy Period
Ok But What About My Specific Hiv Risk Question
Over the years, we’ve receivedand our experts have answeredliterally thousands of questions from people concerned about a potential exposure to HIV. Some of them have been extremely detailedbut those details don’t change any of the basic facts about how HIV is and isn’t transmitted.
You can figure out the answer to just about every question that could possibly exist about HIV transmission by reading the rest of our article above. But let’s dive into a handful of the most common kinds of questions we’ve seen over the years:
Question & Answer: How Is Hiv Transmitted
Most of people misunderstand about AIDS and HIV. Some of them are accustomed to say AIDS infection that is wrong. The correct world is HIV Infection. Lets learn what is the difference between HIV and AIDS?
HIV is a virus that causes AIDS. Many people live for many years with HIV without symptoms.
AIDS is a set of symptoms caused by HIV. It attacks the immune system. A persons immune system will get weaker and weaker until no longer fight off life-threatening infections and diseases.
The complications caused by AIDS may not result to death. People with HIV can enjoy a long life and control its by taking antiretroviral treatment which is effective and helps boost their immune system.
How do you catch HIV?
All bodily fluids contain dissimilar concentration of the virus:
- High concentration of the virus: blood, vaginal fluids, leucorrhea, menstrual blood, breast milk
- Low concentration of the virus: tear, saliva, snot, sputum
- Almost completely virus free: stools, urine, sweat
Why does each bodily fluid contain dissimilar concentration of the virus?
HIV cannot grow or reproduce on its own. Instead, the virus attached itself to white blood cell and fuses with it. Therefore, bodily fluids that contain white blood cell or blood have high concentration of the virus such as blood, vaginal fluids, leucorrhea, menstrual blood, pus. On the other hand, bodily fluids that do not contain blood or white blood cell have low concentration of the virus such as urine, stools and sweat.
Also Check: How Long Does Aids Take To Show
Is There Any Hiv Risk From A Nude Body
If all you had was a massage, with no penetrative intercourse or other high-risk activity, there is absolutely no reason to be concerned about HIV.
Generally, massages involve little or no contact with infectious body fluids. You might come into contact with another person’s semen or vaginal fluids, but you’re unlikely have any contact with blood. It’s worth remembering that saliva, tears, and urine don’t have infectious quantities of HIV.
And it is not enough to simply come into contact with an infected fluid to become infected. Healthy, unbroken skin does not allow HIV to get into the body it is an excellent barrier to HIV infection. HIV can enter only through an open cut or sore, or through contact with the mucous membranes in the anus and rectum, the vagina, the genitals, the mouth, and the eyes.
So if the massage involved penetrative sex without a condom, an infectious body fluid might have contact with mucus membranes in the genital area. But if it was just massage, there’s no way for an infectious body fluid to enter the bloodstream.