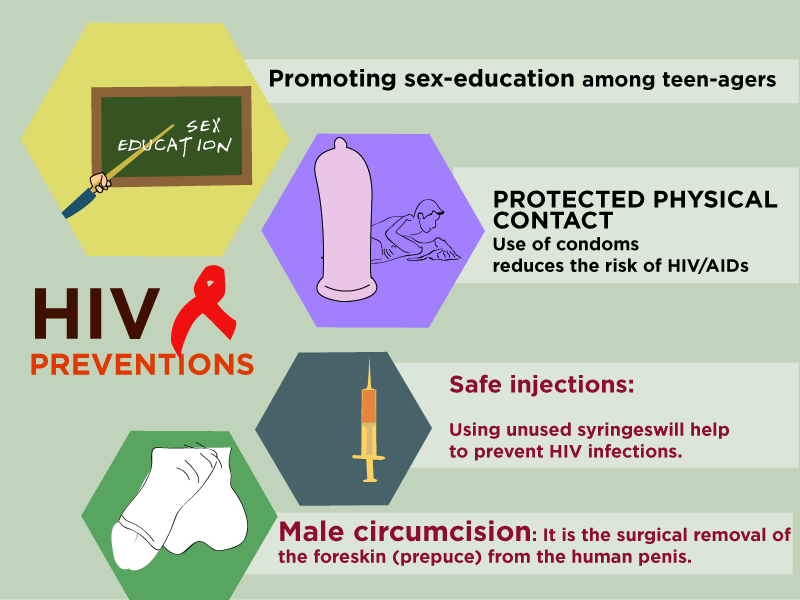
How Can Hiv/aids Be Prevented
If you are sexually active, there are many things you can do to lower your risk of HIV infection, including:
- Know your partners HIV status and avoid multiple sexual partners.
- Use condoms correctly and each time you have vaginal, oral, or anal sex.
- Do not have sex with people whose HIV status you do not know.
- Do not have sex with people who use intravenous drugs.
- Do not engage in unprotected sex unless you know your partner is not infected with HIV.
Not having sex is the only 100% effective way to prevent HIV and other sexually transmitted diseases . There is not a vaccine yet to prevent human immunodeficiency virus and there is no cure however, HIV/AIDS can be prevented in most cases with action on your part. You can remain HIV negative by educating yourself and using safe sex practices, learning how the virus is transmitted, and understanding ways to lower your risk using preventive measures.
Prevent Hiv After An Exposure
If you believe you have been exposed to HIV, either through condomless sex or other high-risk activities, you can take a 28-day course of HIV drugs to potentially avert the infection.
Called post-exposure prophylaxis , the strategy works best if started soon after exposure to the virus. Research has shown that PEP can reduce the risk of HIV by up to 81% if started within 72 hours. The earlier you start treatment, the better.
What Are The Next Steps If You Think Prep Is Right For You
Make an appointment with your doctor and talk about why you think you would like to take this medication. Your doctor will run tests to check for HIV and other sexually transmitted infections as well as hepatitis A, B, and C, and check your kidney function before starting PrEP. Usually your provider will need to get prior authorization for the medication. Most insurances cover the cost. If your provider is uncomfortable prescribing this medication, ask to be referred to an HIV specialist in your area.
You will need to see your doctor initially after one month and then every three months, when HIV and sexually transmitted infection testing will be repeated. Your kidney health will be monitored via a blood test once within six months, and PrEP must be stopped if the kidneys are adversely affected.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Window Period For Hiv Testing
Ongoing Research And Potential Hiv Cures
There is still no universal or permanent cure for HIV. But techniques like gene editing, immune cell modulation, and stem cell transplants are currently being studied to cure HIV. These methods focus on changing and boosting immune cells to fight the virus. Many researchers have also conducted HIV vaccine trials. But more research is required before it can be used to cure HIV.
In the meantime, doctors recommend patients test regularly for HIV to ensure that they dont have the virus. If youre HIV-positive, your doctor will ask you to start antiretroviral treatment immediately. For now, it is the best way to control HIV, prevent AIDS, and live a long and healthy life.
Is The Prep Medication Effective For Treating Hiv Infection
PrEP medications are not effective alone for treating HIV infection. If you acquire HIV infection while taking PrEP, the provider who conducted the HIV test should either provide HIV medical care or refer you to a healthcare provider who can provide HIV care. The HIV care provider will conduct lab tests and determine the most effective regimen to treat your HIV infection. There is no evidence that having taken PrEP will impact the effectiveness of your HIV treatment. People who acquire HIV while on PrEP can be successfully treated with HIV medications.
Also Check: How Hiv Infects Cells Worksheet Answer Key
Treatment For People Living With Hiv
HIV treatment helps people with HIV to stay healthy, and it also helps prevent passing HIV to others. If a person takes HIV treatment as prescribed, the amount of HIV in their blood can become so low that tests cant detect it. This is called having an undetectable viral load. When someone is on treatment and maintaining an undetectable viral load, they will not pass HIV to you through sex. Successful HIV treatment also lowers the chance of passing HIV from sharing equipment for using drugs, but we dont know exactly how much it reduces the risk.
do not
Is There A Permanent Aids
As yet, there is no permanent HIV cure. Antiretroviral treatment can effectively control HIV, prevent AIDS, and help people live a healthy life despite the infection. It can make the viral load undetectable but cant completely cure HIV.
Research is being conducted to find a definitive AIDS-HIV cure. There are two types of HIV cures being researched. One is a functional cure, which reduces the levels of HIV in the body. Antiretroviral therapy is a functional cure, but it needs to be taken throughout life.
Another cure is called a sterilizing cure, which can completely remove HIV from the body. A stem cell transplant is one such treatment. To date, only three patients are known to have been completely cured of HIV through a stem cell transplant. They are as follows:
Stem cell therapy showed promising results in these cases. However, transplants require surgery and can be risky for patients living with HIV.
Also Check: Can You Develop Hiv On Your Own
How Much Risk Are You Comfortable With
Different people are comfortable with different levels of risk for HIV, STIs and other infections. You have the right to set your own boundaries for what you are comfortable with and decide what prevention method you use based on your boundaries. The people you have sex or use drugs with also have this right.
Think about your chance of getting HIV and other infections and how much risk you are comfortable with. If you are currently using a prevention strategy, think about how much it protects you against HIV and other infections. Consider whether you are comfortable with this level of protection. If you would like more protection, you might decide to make a change.
How Would I Know If Prep Is Right For Me
PrEP is one of many options for preventing HIV. HIV is passed from one person to another through sharing injection drug equipment or through anal or vaginal sexual intercourse. People can avoid getting HIV by: 1) not sharing drug injection equipment , 2) avoiding anal or vaginal intercourse 3) having only one monogamous sex partner whose HIV status is known to be negative: 4) having only one partner who is living with HIV and has an undetectable viral load. It is important to be aware that a person living with HIV who is on HIV treatment and is virally suppressed for six months or longer cannot pass HIV to a partner through sex. If you have sex with more than one partner, taking PrEP or consistent and correct use of condoms each time you have sex, can prevent you from getting HIV.
New York HIV State Clinical Guidelines indicate that healthcare providers should discuss PrEP as an HIV/STD prevention option for adults or adolescents who:
It is important to weigh the pros and cons and have an open and honest conversation about PrEP with your healthcare provider before beginning PrEP. PrEP is always voluntary and only you can determine if PrEP is right for you.
Read Also: How Long After Sex Hiv Test
How Can I Prevent Hiv
The best way to prevent HIV is to not have vaginal, oral, or anal sex or share needles at any time. Sharing needles for any reason is very risky.
If you do have sex, lower your risk of getting an STI with the following steps:
The steps work best when used together. No single step can protect you from every single type of STI.
Learn more about your risk for HIV with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s HIV Risk Reduction Tool.
Male latex condoms are a highly effective way to prevent HIV and other STIs, but almost one in every five women who uses only condoms for birth control gets pregnant.3 The best way to prevent both STIs and pregnancy is to use a latex condom along with another highly effective method of birth control such as an intrauterine device , an implant, or the shot.
What Can Women Do
- Talk about it. Learn the facts about HIV, and share this lifesaving information with your family, friends, and community. Let’s Stop HIV Together, part of Act Against AIDS, has many resources for raising awareness about HIV and includes many video testimonials from people living with HIV.
- Start Doing It – getting tested for HIV . Knowing your HIV status gives you powerful information to help keep you and your partner healthy. If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, get an HIV test as soon as possible.
The most effective way to prevent HIV is to abstain from sexual activity and injection drug use. However, if you are sexually active or use injection drugs, today there are more tools available to prevent HIV. You can:
- Use condoms the right way every time you have sex. Learn the right way to use a male condom or a female condom.
- Limit your number of sexual partners.
- Never share needles.
- Talk to your doctor about pre-exposure prophylaxis , taking medicine daily to prevent HIV infection, if you are at very high risk for HIV.
- Talk to your doctor about post-exposure prophylaxis if you think you may have been exposed to HIV within the last 3 days through sex, sharing needles and works, or a sexual assault.
Read Also: Can You Get Hiv Without Having Sex
Can Medications Prevent Hiv
There are medications that can help prevent HIV in people who have been exposed or are at high risk for exposure. These include pre-exposure prophylaxis and post-exposure prophylaxis .
Pre-exposure prophylaxis
PrEP is a pill you take every day if you dont have HIV but are at high risk of getting infected.
Specifically, its recommended that you take PrEP if you dont have HIV, if you have had anal or vaginal sex in the past six months and at least one of the following is true:
- You have a sexual partner with HIV.
- You havent consistently used a condom.
- In the past six months, youve been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease .
PrEP is also recommended if you dont have HIV, you inject drugs and at least one of the following is true:
- You inject drugs with a partner who has HIV.
- You share needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
PrEP is not a replacement for other preventative measures. You should still use condoms and avoid sharing needles to inject drugs while taking PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis
PEP uses HIV medicines to try to prevent an HIV infection soon after you are exposed. PEP is for those who dont have HIV or dont know if they have HIV and think theyve been exposed through consensual sex, sexual assault, shared needles , or work.
You must start PEP within 72 hours of exposure and take it every day for 28 days. PEP is only for emergency use and does not replace other precautions, like condom use.
Men Who Have Sex With Men
A 2018 paper analyzed the findings of four studies that looked at self-reported condom use in men who have sex with men . Researchers reported the effectiveness of condoms per number of HIV-positive sexual partners.
It was found that people who reported that they always used condoms with each sexual partner reduced their odds of contracting HIV by 91 percent.
Meanwhile, people who reported never or only sometimes using condoms with each sexual partner increased their odds of contracting HIV by 83 percent.
Recommended Reading: Where Did Hiv Originate First
Get A Prescription For Prep
Short for pre-exposure prophylaxis, PrEP is a daily pill that can reduce a persons risk of contracting HIV by about 99 percent when taken daily, according to theCenters for Disease Control and Prevention . If you regularly have sex with someone who is HIV positive, have sex without using condoms, or share needles with others, PrEP can be a powerful tool for preventing the spread of HIV.
If you believe you were exposed to HIV during sex for example, if a sexual partner was recently diagnosed with HIV you can take emergency pills called PEP, or postexposure prophylaxis. A 28-day course of medication, PEP needs to be taken within three days after a potential infection to help block the virus from taking root in your body.
Protecting Yourself Against Hiv
Enter a zip code into the search box and the locator will show a listing of nearby PrEP providers.
The most effective methods of protecting yourself against exposure to HIV include sexual abstinence, consistent and correct condom use, abstinence from injection drug use, and use of sterile equipment if using injection drugs.
Also Check: What Is Hiv 4th Generation
What Drugs Are Approved For Prep
There are two oral medications approved for daily use as PrEP. They are combinations of two anti-HIV drugs in a single pill:
- Truvada® is for all people at risk for HIV through sex or injection drug use. Generic products are also available.
- Descovy®) is for sexually active men and transgender women at risk of getting HIV. Descovy® has not yet been studied for HIV prevention for receptive vaginal sex.
A long-acting injectable form of PrEP, , has also been approved by the FDA. It is administered by a health care provider every two months instead of daily oral pills.
Get Tested For Hiv Regularly
If youre currently HIV negative, its important to be tested for any change in your status. If a test shows youve contracted the virus, your risk of spreading it to someone else is greatest in the acute phase, or the first two to four weeks after being infected. During that period, the viral load spikes, increasing the likelihood youll transmit the virus. Although some people experience flu-like symptoms in the acute phase, many are not aware that they are infected because they dont feel sick at all or might not feel sick until later, according to the CDC.
Also Check: Is Hiv Lytic Or Lysogenic
How Often Are Medical Appointments For Prep
People who want to take PrEP to prevent HIV can work with their healthcare provider to determine the schedule of medical appointments that best meets their needs. Here is a general description of the schedule of medical appointments for PrEP.
- Initial Medical Appointment: This first appointment includes education about PrEP, a discussion about readiness to take PrEP, a review of PrEP options, HIV testing, and other lab work. If the person is ready to start PrEP, the medication can be started right after the initial medical appointment.
- First Follow-Up Contact: The healthcare provider and person should make a plan for a follow-up appointment or call at a convenient time, usually within 2-4 weeks, to:
- Check in on how things are going, including side effects
- Troubleshoot any problems with payment or access to support services.
Protect Yourself With Prep
You may be in a situation that makes you more likely to get HIV. You may share needles, or youâre in a relationship with someone whoâs HIV-positive. If your partner takes HIV medication and has undetectable virus, they are unlikely to give it to you. But you may be at risk if they donât take their medication consistently or donât know what their viral load is.
You can protect yourself by taking a daily pill to help avoid infection. Itâs called pre-exposure prophylaxis, or PrEP. There are a few options. The pill, Truvada contains two drugs, emtricitabine and tenofovir. These are antiretrovirals, which means they donât allow the virus to take hold and spread through your body.
If you have unprotected sex with someone whoâs HIV positive, your chance of getting HIV drops by about 99% if you take PrEP daily. It doesnât work as well if you inject drugs, but it still lowers your chances by at least 74%. For it to work this well, you need to take it every day.
A similar drug, Descovy, is approved for PrEP, but itâs not recommended for women having receptive vaginal sex.
The medication cabotegravir are more recent approvals. Vocabria is also taken in pill form. Apretude is is given first as two initiation injections administered one month apart, and then every two months thereafter. It has proven to be 90% effective.
Show Sources
Kaiser Family Foundation: “National Survey of Young Adults on HIV/AIDS.”
HIV.gov: âPre-Exposure Prophylaxis.â
Read Also: What Sleep Aids Are Safe