How Do You Get Or Transmit Hiv
You can only get HIV by coming into direct contact with certain body fluids from a person with HIV who has a detectable viral load. These fluids are:
- Blood
- Semen and pre-seminal fluid
- Rectal fluids
- Vaginal fluids
- Breast milk
For transmission to occur, the HIV in these fluids must get into the bloodstream of an HIV-negative person through a mucous membrane open cuts or sores or by direct injection.
People with HIV who take HIV medicine daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners.
What Is The Most Common Route Of Hiv Transmission
The most common route of infection varies from country to country and even among cities, reflecting the population in which HIV was introduced initially and local practices. Co-infection with other viruses that share similar routes of transmission, such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and human herpes virus 8 , is common.
Does An Undetectable Viral Load Prevent Hiv Transmission While Breastfeeding
People on antiretroviral treatment who maintain an undetectable viral load are not at risk of transmitting HIV to sexual partners. This has led to the question of whether women living with HIV who are undetectable can breastfeed without fear of passing HIV to their infant.
Research on breastfeeding women living with HIV that includes viral load data is limited. What evidence does exist indicates that an undetectable viral load provides significant protection from HIV transmission. However, there have been cases of HIV transmission among breastfeeding women with undetectable viral loads.14
Currently, most high-income countries recommend women living with HIV do not breastfeed whether they are virally suppressed or not. This is because formula feed and clean, boiled water are widely accessible. So any risks around dirty water or malnutrition have been eliminated. In low- and middle-income countries this risk is far greater, leading WHOs advice on infant feeding to differ.
You May Like: Hiv From Semen
How Is Hiv Passed Through Needles And Other Drug Use Or Body Work Equipment
HIV can be passed through blood that remains in used needles or other drug injection equipment, even if the amount of blood is so small it cant be seen. When a used needle containing blood with HIV breaks the skin of another person, HIV can get directly into their bloodstream. Once inside the bloodstream it can then cause a permanent infection. In the same way, HIV can be passed on by reusing unsterilized equipment for tattooing or piercing and through accidental needlestick injuries.
Sharing needles or other equipment used to inject drugs is the most common way that HIV is transmitted through broken skin. When a person injects drugs, blood can get into the needle/syringe or on other equipment they are using to inject or prepare their drugs. When someone uses a needle/syringe that has already been used by another person, there is a possibility that blood containing HIV is present. When a person prepares and injects drugs using shared equipment, blood that may contain HIV can directly enter their bloodstream through the broken skin. This is an efficient mode of transmission because the immune cells are the only natural defence against this type of HIV transmission. A larger amount of residual blood in the needle/syringe or other equipment and a higher amount of HIV in the blood can both increase the risk of injection-related HIV transmission.
Hiv Transmission Risk Factors And Prevention
Joseph Bennington-CastroLaura Martin, MDYaroslav Danylchenko/Stocksy Everyday Health
When the human immunodeficiency virus causes infection, it attacks certain immune system cells called T helper cells, or CD4 cells. The virus replicates itself and, over time, damages its host cells, impairing the body’s ability to fight off infections and making it susceptible to other diseases. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS, is the final stage of an infection with HIV.
Anyone can get HIV, but certain populations are at greater risk. There are, however, a number of ways to reduce your risk, and certain medicines and precautions can prevent the spread of the virus.
Recommended Reading: Jania Has Herpes
Preventing Hiv Transmission From A Woman Living With Hiv To Her Infant
Since 2010, 1.4 million infections among children have been averted33 and there has been a 48% decline in new child infections among the 23 UNAIDS priority countries.34
However, in 2017, 180,000 children became HIV positive, the vast majority through vertical transmission.35
In the same year, 80% of pregnant women living with HIV were receiving ART.36 At least nine of UNAIDS 23 priority countries have reached or nearly reached the target of 95% of pregnant women living with HIV on lifelong ART, and another six countries appear on track to do so.37
Recent gains have been particularly impressive in eastern and southern Africa where in 2017 an estimated 93% of women living with HIV had initiated, or were already on, ART during pregnancy. As a result, the percentage of children in the region who acquired HIV from their mother declined from around 18% in 2010 to 10% in 2017.38
ART coverage for pregnant women living with HIV is considerably lower in western and central Africa at 48%. In 2017, an alarming one in five children born to mothers living with HIV in the region became HIV positive during childbirth or breastfeeding.39
Because Nigeria is a densely populated country with high HIV prevalence, the lack of progress here is of particular concern for western and central Africa. Nigeria is one of four countries in the world where annual infections among children are above 10,000, the others being Mozambique, South Africa and Tanzania.40
Providing Support For Hiv Exposed Infants
There is emerging evidence about the negative impact on the health and development of infants who are exposed to HIV, even if they do not become HIV positive.
Some studies have found higher levels of illness, death and stunted growing among HIV exposed infants compared to those who have been born to HIV negative mothers.52 The reasons behind this are not yet fully understood, and may be attributable to co-existing factors such as malnutrition, however research is growing.
Also Check: Does Nba Youngboy Have Herpies
Interval Of Mild Or No Symptoms
After the first symptoms disappear, most people, even without treatment, have no symptoms or only occasionally have a few mild symptoms. This interval of few or no symptoms may last from 2 to 15 years. The symptoms that most commonly occur during this interval include the following:
-
Swollen lymph nodes, felt as small, painless lumps in the neck, under the arms, or in the groin
-
White patches in the mouth due to candidiasis
-
Anemia
Some people progressively lose weight and have a mild fever or diarrhea.
These symptoms may result from HIV infection or from opportunistic infections that develop because HIV has weakened the immune system.
Myth #: People Living With Hiv Shouldnt Have Babies
Incorrect. When HIV-positive pregnant women adhere to life-saving HIV treatment throughout their pregnancy and during breastfeeding, they can give birth to HIV-free children.
Ending mother-to-child transmission of HIV is a crucial piece to ending AIDS as an epidemic by 2030. Worldwide, 84% of HIV-positive pregnant women are receiving this life-saving treatment for the prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV, a massive scale-up from 45% in 2010. We must continue to scale up prevention services to ensure that every child, everywhere is born HIV-free.
Read Also: Do Youngboy Got Herpes
Through Needles Or Other Instruments
Health care workers who are accidentally pricked with an HIV-contaminated needle have about a 1 in 300 chance of contracting HIV unless they are treated as soon as possible after exposure. Such treatment reduces the chance of infection to less than 1 in 1,500. The risk increases if the needle penetrates deeply or if the needle is hollow and contains HIV-contaminated blood rather than simply being coated with blood .
Infected fluid splashing into the mouth or eyes has less than a 1 in 1,000 chance of causing infection.
Lowering The Risk Of Sexual Transmission
There are several protective measures which dramatically reduce the risk of HIV transmission during sex. You can find out more about these on other pages.
Undetectable viral load: when people with HIV take effective treatment, the amount of HIV in their body fluids falls drastically, to the point where they cannot pass HIV on to their sexual partners. An extremely low level of HIV in body fluids is referred to as an undetectable viral load. The knowledge that this prevents transmission is often referred to ‘Undetectable equals Untransmittable’ .
PrEP: if the HIV-negative person takes antiretroviral medications as pre-exposure prophylaxis , this significantly reduces the risk of acquiring HIV. The most common form of PrEP is in a tablet, but it can also be provided as a vaginal ring or an injection.
Condoms: if male condoms or female condoms are used, this significantly reduces the risk of acquiring HIV.
Male circumcision: if you are circumcised, this partially lowers your risk of acquiring HIV during vaginal sex.
You May Like: How Long Does Aids Take To Show
Myth #: You Can Contract Hiv From Touching Someone Who Is Hiv
False. According to the Center for Disease Control, HIV can NOT be transmitted through air, water, saliva, sweat, tears, or sharing a toiletmeaning you cant catch it from breathing
the same air as an HIV-positive person, or hugging, kissing, or shaking hands.
The virus can only be transmitted through certain body fluids like blood, semen, vaginal fluid, rectal fluid, or breast milk. Therefore, its often transmitted through sex, when protection is not used, or through needle or syringe use. The virus can also be passed from mother to child during pregnancy, if the mother is not accessing antiretroviral medication. This is why it is so critical to ensure pregnant mothers living with HIV not only get tested, but can access and adhere to treatment throughout pregnancy and during breastfeeding.
In instances of sex between an HIV-positive and an HIV-negative partner, condoms are highly effective in preventing the transmission of HIV. When condoms are paired with antiretroviral medication, they provide even more protection. And with the introduction of new medication and treatment like PrEP and long-lasting injectables, the most-at-risk communities are able to further protect themselves from contracting HIV.
How Is Hiv Not Transmitted
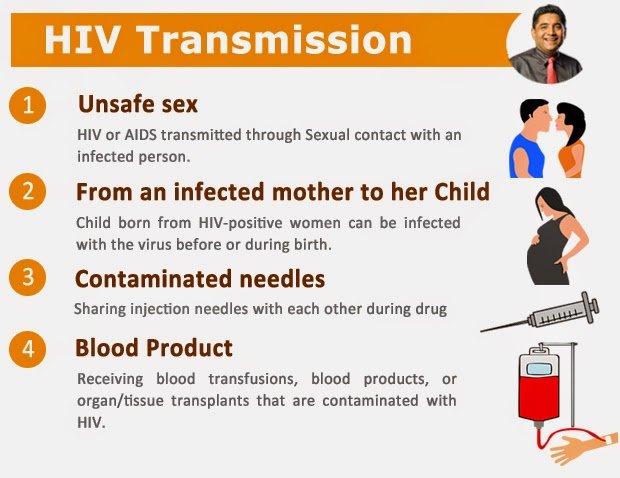
HIV is not transmitted by saliva, tears, sweat, urine or feces. HIV does not survive well outside the human body. It cannot be transmitted through casual contact with a person who has HIV, or through objects such as toilet seats, doorknobs or dishes used by a person who has HIV.
In the past, some people got HIV after receiving a blood transfusion or organ or tissue transplant. However, Canada implemented HIV screening for all blood and tissue donations in 1985.
References
Arkell C.
Read Also: Nba Youngboy Stds
Preventing Transmission From Mother To Newborn
Pregnant women infected with HIV can transmit the virus to the newborn.
The following can help prevent HIV transmission from mother to newborn Prevention of transmission for infected mothers Human immunodeficiency virus infection is a viral infection that progressively destroys certain white blood cells and causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome . Human immunodeficiency… read more :
-
Testing pregnant women to determine whether they are infected with HIV
-
If they are infected, treating them with antiretroviral drugs during pregnancy and labor
-
Delivering the baby by cesarean rather than by vaginal delivery
-
After birth, treating the newborn with zidovudine, given intravenously, for 6 weeks
-
If possible, using formula instead of breastfeeding
Contact With Contaminated Blood
Before, the absence of blood screening and tests was considered as one reason for HIV transmission. Without proper testing, a blood bag possible of HIV contamination can be administered for blood transfusion. Note that the percentage of acquiring the infection is high, making it impossible to avoid health complications. Thankfully, at the present day, a series of blood screening and tests are already available to conduct if a certain blood sample is suitable for transfusion.
One of the prevalent causes of infection aside from blood transfusion is the irresponsible use of shared needles. Individuals who always use shared needles or even syringes without knowing that its contaminated by an HIV blood are at high risk of getting the disease. This explains the glaring number of cases involving drug users. Other than that, using needles for tattoos, ear-piercing, and other punctures to the skin using the same needle also increases someones chance to get the infection. Thats why if you are trying to get a tattoo, ensure that the needle to use is new and is sterilized for better protection.
Don’t Miss: Hiv Screen 4th Generation Wrfx Non Reactive
Through Blood Transfusions Or Organ Transplants
Currently, HIV infection is rarely transmitted through blood transfusions or organ transplants.
Since 1985 in most developed countries, all blood collected for transfusion is tested for HIV, and when possible, some blood products are treated with heat to eliminate the risk of HIV infection. The current risk of HIV infection from a single blood transfusion is estimated to be less than 1 in about 2 million in the United States. However, in many developing countries, blood and blood products are not screened for HIV or are not screened as stringently. There, the risk remains substantial.
HIV has been transmitted when organs from infected donors were unknowingly used as transplants. HIV transmission is unlikely to occur when corneas or certain specially treated tissues are transplanted.
The Most Common Sexually Transmitted Infections
A sexually transmitted infection is any disease that is spread primarily by sexual contact. One person passes the infection to another during oral, vaginal, or anal sex.
STIs are some of the most difficult diseases to catch. You have to be up close and personal to spread them. So why are STIs so common? The answer may be that people don’t know how to recognize, treat, or prevent them. Or when they do, they often don’t do so effectively.
This article explores some of the most common sexually transmitted infections in the United States. It also discusses their causes and symptoms.
Verywell / Brianna Gilmartin
Not all diseases that affect the sex organs are considered STIs. In fact, some are not related to sex at all. Others aren’t transmitted during sex but occur as a result of it.
Here are some common STIs and diseases associated with sex, along with their symptoms.
You May Like: Is Hair Loss A Symptom Of Hiv
Stigma In Healthcare Settings
I know of a woman living with HIV who went to antenatal at the point of delivery, went through the files and when he saw her file he said, This one, am not touching her. She was on the stretcher already and in labour. He said, Its a positive case… I didnt leave my house to come and do a positive case today. I am not prepared. The woman was left on the stretcher.
– A woman living with HIV from Nigeria86
For women living with HIV, experiences of stigma, discrimination and abuse often occur when they seek maternal healthcare. This can take many forms including physical abuse, non-consented clinical care, non-confidential care, non-dignified care, abandonment or denial of care, and detention in facilities.87
The International Community of Women Living With HIV reports how pregnant women living with HIV have experienced service providers using extra gloves or bleach when dealing with them and asking women to not come close to them, touch things, and cover their mouths while talking. This discrimination and fear means that many women avoid going to hospitals and accessing PMTCT services.88
Many healthcare workers dont have the necessary skills or equipment to confidently handle delivery for an HIV-positive woman, and given the risk of accidental exposure, most nurses shy away from dealing with such patients.89
Sabera, a woman living with HIV in Sudan.90
– A woman living with HIV from Mexico, describing another womans experiences.92
Hiv And Maternal Transmission
HIV can be passed from mother to child during pregnancy, delivery, or through breastfeeding. If left untreated throughout these stages, there is a 15-45% chance of an HIV positive mother transmitting the virus to their child . However there are treatment options to prevent this from happening.
If pregnancy occurs and there has been potential HIV exposure, ask a healthcare provider about getting tested for HIV as early as possible. Taking medications called antiretroviral therapy as prescribed can reduce the viral load so that the baby has a very low chance of contracting HIV .
A person with HIV should not breastfeed their child, as breast milk can transmit HIV. Even if a person is taking ART and their viral loads are undetectable, they should still not breastfeed.
Also Check: Hiv Stays Alive In Dried Blood
Screening And Diagnostic Tests
If doctors suspect exposure to HIV infection, they do a screening test for HIV. Doctors also recommend that all adults and adolescents, particularly pregnant women, have a screening test regardless of what their risk appears to be. Anyone who is concerned about being infected with HIV can request to be tested. Such testing is confidential and often free of charge.
The current combination screening test tests for two things that suggest HIV infection:
-
to HIV
-
HIV antigens
Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system to help defend the body against a particular attack, such as that by HIV. Antigens are foreign substances that can trigger an immune response.
The body takes several weeks to produce enough antibodies to be detected by the test, so results of the antibody test are negative during the first few weeks after the virus enters the body . However, results of the p24 antigen test can be positive as early as 2 weeks after the initial infection. The combination tests can be done quickly by a laboratory. Also, a version of these tests can be done in a doctor’s office or clinic . If results are positive, doctors do a test to distinguish HIV-1 from HIV-2 and a test to detect the amount of HIV RNA in the blood .
Other, older rapid bedside tests are also available. These tests can be done using a sample of blood or saliva. If results of these rapid screening tests are positive, they are confirmed by ELISA or by repetition of one or more other rapid tests.