Countries With The Highest Rates Of Hiv/aids
Human Immunodeficiency Virus is a virus that weakens the human immune system, sometimes leading to AIDS. If detected early, HIV can be managed to prevent it from progressing to the final stage of AIDS. HIV attacks CD4 cells exposing the infected person to opportunistic infections. Proper diagnosis, treatment, and medical care are essential factors to effective management and control of AIDS which has no permanent cure. While HIV is majorly a sexually transmitted disease, the virus can be transmitted through blood transfusion and during birth or breastfeeding, as well as through a few other means.
Funding For Hiv In South Africa
South Africa largely funds its HIV programmes domestically, only receiving 12% of its HIV funding from external sources in 2018.126
South Africas National Strategic HIV, STI and TB Plan 2017-2022 is predicted to cost 207 billion rand in total. In light of this, in 2017 the South African government increased its budget allocation for HIV and AIDS, despite general budget reductions across the health sector.127
Still the South African National AIDS Council has predicted there will be some funding gaps. However, it is unclear how severe these will be, especially since there is a level of uncertainty around the availability of international funding for HIV and AIDS in the coming years.128
An encouraging sign came with the announcement from the US Presidents Emergency for AIDS Relief that it will be providing 10 billion rand in funding for 2019/2020, an increase from 2018 and 2017 funding levels.129
Treatment and care make up the biggest proportion of the costs, outlined in the NSP. In recent years South Africa has been working hard to negotiate better prices for ARVs, having previously been paying more than most other low- and middle-income countries despite having the worlds largest procurement programme.130 In September 2017 UNAIDS announced a breakthrough pricing agreement, which will allow the single pill regime of Dolutegravir to be sold at around $75 per person per year in south Africa and 90 other low- and middle-income countries.131
Global Hiv & Aids Statistics Fact Sheet
GLOBAL HIV STATISTICS
- 37.7 million people globally were living with HIV in 2020.
- 1.5 million people became newly infected with HIV in 2020.
- 680 000 people died from AIDS-related illnesses in 2020.
- 27.5 million people were accessing antiretroviral therapy in 2020.
- 79.3 million people have become infected with HIV since the start of the epidemic.
- 36.3 million people have died from AIDS-related illnesses since the start of the epidemic.
People living with HIV
- In 2020, there were 37.7 million people living with HIV.
- 36.0 million adults.
- 1.7 million children .
- 53% of all people living with HIV were women and girls.
People living with HIV accessing antiretroviral therapy
- At the end of December 2020, 27.5 million people were accessing antiretroviral therapy, up from 7.8 million in 2010.
- In 2020, 73% of all people living with HIV were accessing treatment.
- 74% of adults aged 15 years and older living with HIV had access to treatment, as did 54% of children aged 014 years.
- 79% of female adults aged 15 years and older had access to treatment however, just 68% of male adults aged 15 years and older had access.
New HIV infections
AIDS-related deaths
COVID-19 and HIV
Key populations
Don’t Miss: Can Breast Milk Transmit Hiv
People With Diagnosed Hiv In The Us And Dependent Areas By Region Of Residence 2019*
*Rates per 100,000 people.
a American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, the Republic of Palau, and the US Virgin Islands.b In the 50 states and the District of Columbia.c The term male-to-male sexual contact is used in CDC surveillance systems. It indicates a behavior that transmits HIV infection, not how individuals self-identify in terms of their sexuality.d Includes infections attributed to male-to-male sexual contact and injection drug use .
Prevalence And New Infections
Read Also: Does Hiv Die When It Hits The Air
Continuum Of Hiv Care By Public Health District
The Finalized 2019 HIV Continuum of Care depicts persons living with HIV in Alabama who are engaged in selected stages of HIV treatment. Successful HIV Prevention and Care programs exhibit high linkage to care among newly diagnosed clients, as well as effective retention in care and adequate viral load suppression among existing HIV-positive clients. As viral load is considered a measure of infectivity, maintaining a suppressed viral load decreases the likelihood of infecting another person and is the focus of Treatment as Prevention strategies. PWH who adhere to antiretroviral treatment and maintain suppressed viral loads can reduce the risk of sexual transmission of HIV by 96 percent. For PWH who reach undetectable levels, there are no documented cases of sexual transmission. This is the premise of the Prevention Access Campaign’s Undetectable Equals Unstransmittable initiative, which the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention supports, agreeing there is “effectively no risk” of sexually transmitting HIV when on treatment and undetectable.
The Preliminary 2020 HIV Continuum of Care is now available. Note that 2020 data should be interpreted with extreme caution as not all reported cases have been investigated and entered into the HIV Surveillance database. 2020 data will be finalized December 31, 2021, allowing a full twelve months for reporting delays.
Efforts Towards Reducing Hiv/aids Prevalence
Countries with the highest rates of HIV infection have taken several measures towards reducing the rate of infection among the population. Awareness programs are conducted to educate the public about HIV/AIDS. Antiretroviral therapies have been provided at low costs to treat HIV positive patients. Pregnant women who test positive for HIV are monitored strictly to prevent mother-to-child transmission of the infection. Other remedial measures have also been implemented to curb HIV/AIDS in these countries.
Also Check: When Did Magic Get Hiv
Appendix 2 Key Populations Used For The National Estimates Of Hiv Incidence And Prevalence
| Key Population | |
|---|---|
| Exposure during heterosexual sex | |
| Other | Persons who were exposed during: receipt of transfusion of blood or clotting factor, perinatal exposure, or occupational exposure |
In previous reports, the heterosexual category was separated into an “endemic” group and a “non-endemic” group . This separation is no longer considered appropriate, for reasons of increasing data incompleteness. The Public Health Agency of Canada is working with communities and with provinces and territories to find ways to better reflect the HIV situation in these communities.
Newer Tools To Target Hiv Prevention
Knowing your epidemic has been the basis and opportunity for countries to critically assess and match the prevention response to meet the priority needs . Whilst these have been useful as a national response and scaled up towards attaining universal access to prevention and treatment including care and support for all, these have failed to address social and economic factors and power in relationships. These relationships, together with physiological differences, determine to a great extent an individuals risk of infection and their ability to protect themselves. However, country level HIV data masks diverse, complex and heterogeneous epidemics at sub-national, regional and district level. Furthermore, as new HIV infections continue one or more sub-populations of virus emerge resulting in the spread of HIV viral variants.
The complexity and heterogeneity of local epidemics evolve with localized differences, highlighting the importance of locations and populations as the overall country level HIV prevalence may mask the true complex mosaic nature of the epidemic in relation to key risk factors and populations. As evidenced by district level prevalence and geospatial mapping of HIV South Africa, Nigeria, Mozambique, Burkina Faso and Malawi experience significant variability with hotspots clustered around truck stops, main transport routes, sex work and further complicated by migration and limited access to health care .
You May Like: Do You Have To Tell Someone You Have Hiv
Effects Of Hiv/aids On Society
HIV/AIDS has far-reaching adverse effects on the economic, cultural, and social spheres of society. The epidemic drains the economy of the country as funds need to be diverted to treat the infected patients. It is also a great economic burden on individual families with HIV/AIDS as a significant portion of the income needs to be spent on treatment procedures. High prevalence of HIV/AIDS cripples the entire society and reduced the nation’s productivity.
The Haitian Connection Controversy
The Haitian connection controversy refers to the debate regarding the origins of the HIV virus in Haiti and the United States and whether or not HIV was spread into the US by Haitians or into Haiti by Americans. The controversy began in the 1982, when the CDC noted that 34 cases of immunodeficient patients were Haitian. This “connection” noted by physicians caused the erroneous labeling of Haitians as a risk factor group for HIV, leading to the rise of the term “the 4-H’s” referring to Homosexuals, Hemophiliacs, Heroin addicts, and Haitians as the major groups prone to HIV infection.
In his 1990 book “AIDS and Accusation,” Paul Farmer refutes the idea that Haiti was an HIV entry point to the USA. Referencing an epidemiological study on the prevalence of sarcomas associated with HIV/AIDS contraction, Farmer suggests that Cambronne’s plasma business occurred before identifiers of HIV infection were recorded in Haiti, indicating that the disease did not arrive in Haiti until at least the late-1970s. Farmer instead argues that HIV/AIDS in Haiti was introduced by visitors from the US.
Regardless of origin, the consequences of HIV/AIDS in Haiti were severe. The disease spread rapidly throughout Haiti, infecting thousands. Haiti’s burgeoning tourist industry suffered greatly from the association with HIV/AIDS, and Haitians living in the USA were placed on the banned list for blood donations, alongside homosexuals and intravenous drug users, until 1990.
Recommended Reading: How Does Hiv Affect The Body Physically
People Who Inject Drugs
It is now widely accepted that the USA is experiencing a nationwide public health emergency in the form of an opioid epidemic.3940
Heroin use is increasing in the USA among men and women in most age groups and across all income levels, rising by 63% between 2002 and 2013 alone. A study published in 2019 estimated that more than 750,000 people in the USA inject drugs and that this number is rising.41
A huge contributing factor to this is misuse of prescription opioids, which has seen an increasing number of people turn to injecting drug use, particularly in non-urban areas where previously, injecting drugs had not been a significant issue. This has created new HIV prevention challenges as it has placed more people at risk of HIV.
Between 2010 and 2016, new infections among people who inject drugs fell by 30% overall.42 However, there are concerns that the level of new infections may have stagnated or reversed in recent years due to increased levels of injecting.4344
Evidence is emerging of increases in hepatitis C infections and new, localised outbreaks of HIV.45 For instance, Scott County in Indiana, with a population of only 23,744, experienced 181 new HIV infections in 2015.46
The impacts of the opioid epidemic are far reaching: the US has experienced the fastest proportional rise of drug-related overdose deaths ever recorded, which rose by 21.4% between 2015-2016 alone.47
Estimated Number Of People Living With Hiv

The Agency estimates that approximately 62,050 people were living with HIV at the end of 2018 . This estimate represents a 3% increase from the estimated 58,291 at the end of 2016 .
The estimated prevalence rate in Canada at the end of 2018 was 167 per 100,000 population .
Figure 10. HIV Prevalence: Estimated number of people living with HIV in Canada
This graph shows estimated number of people living with HIV by year. The vertical axis shows point estimates for number of people living with HIV, along with the associated low estimate and high estimate. The horizontal axis shows the calendar years.
| Year | |
|---|---|
| 62,050 | 70,500 |
Of the estimated 62,050 people living with HIV in Canada at the end of 2018:
- Nearly half were among gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men. .
- 14.0% were people who inject drugs, and 33.4% were heterosexuals.
- About one in four PLHIV was female and this proportion has been consistent over the past 6 years.
- One in ten was Indigenous. This proportion remained stable compared to the 2016 estimates.
Figure 11. Proportion of people living with HIV, by key population, Canada, 2018
This pie chart shows the estimated percentage of people living with HIV by key population in 2018.
| Key population |
|---|
|
|
Read Also: Is Hiv Transmitted Through Feces
New Hiv Diagnoses In The Us And Dependent Areas For The Most
NOTE: Subpopulations representing 2% or less of all people who received an HIV diagnosis in 2019 are not represented in this chart.
*Black refers to people having origins in any of the black racial groups of Africa. African American is a term often used for people of African descent with ancestry in North America.Hispanic/Latino people can be of any race.
Source: CDC. Diagnoses of HIV infection in the United States and dependent areas, 2019. HIV Surveillance Report 2021 32.
There are also variations by age. Young people aged 13 to 24 are especially affected by HIV. In 2019, young people accounted for 21% of all new HIV diagnoses. All young people are not equally at risk, however. Young gay and bisexual men accounted for 83% of all new HIV diagnoses in people aged 13 to 24 in 2019.d Young Black/African American gay and bisexual men are even more severely affected, as they represented 50% of new HIV diagnoses among young gay and bisexual men.
CDCs fact sheets explain the impact of HIV on various populations in the United States.
Civil Societys Role In The Usa
Freedom of expression in the USA has allowed political activism has been a key part of the countrys HIV response since the very beginning.
In the early days of the response, HIV activism was closely associated with gay communities in the USA . To some extent, grassroots activism in many parts of the USA declined as antiretroviral treatment became more available in the late 1980s and the early 1990s. During the early 1990s, activists shifted their focus more into providing HIV prevention and treatment programmes for people most affected by HIV.117 However, concerns over the rollback of sexual and reproductive health rights, and rights for people who are lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex under President Trump has seen a resurgence of activism in recent years.118
There is a systematic and sinister erasing of LGBTQ protections and policies happening at the hands of this Administration. Now more than ever, its vital LGBTQ Americans and marginalised communities raise their voices and tell their stories. The LGBTQ community will not go into hiding, and we will not be silenced.
– Zeke Stokes, Chief Programs Officer at GLAAD.119
Read Also: Does Hiv Attack Red Blood Cells
People Living With Hiv
San Francisco has one of the largest populations of people living with HIV in the United States with an estimated 15,811 people living with HIV .
Of the total number of San Franciscans living with HIV/AIDS at the end of 2020, 8,950 were living with HIV ever classified as AIDS. AIDS is a late-stage HIV disease defined by a low count of CD4 cells or an opportunistic infection .
As of December 2020, 71% of people living with HIV in San Francisco were over age 50 .
New Hiv Diagnoses In The Us And Dependent Areas By Transmission Category 2019
NOTE: Does not include other and perinatal transmission categories.
Source: CDC. Diagnoses of HIV infection in the United States and dependent areas, 2019. HIV Surveillance Report 2021 32.
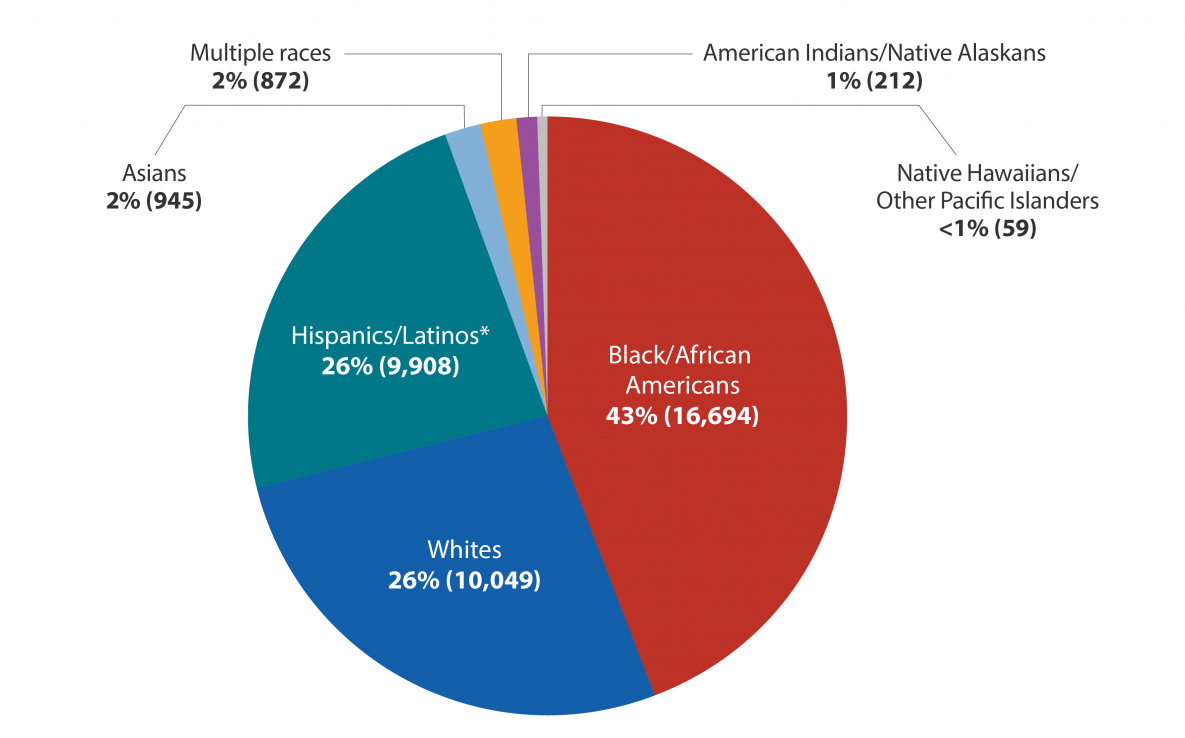
If we look at HIV diagnoses by race and ethnicity, we see that Black/African American people are most affected by HIV. In 2019, Black/African American people accounted for 42% of all new HIV diagnoses. Additionally, Hispanic/Latino people are also strongly affected. They accounted for 29% of all new HIV diagnoses.
Also Check: How Many People Are Living With Hiv
Estimates Number Of New Hiv Infections
The Agency estimates that 2,242 new infections occurred in Canada in 2018. This estimate is a slight increase from the estimate for 2016 .
The resulting estimated incidence rate in Canada for 2018 was 6.0 per 100,000 population which is a slight increase from the estimate for 2016 .
Figure 8. HIV incidence: Estimated annual number of new HIV infections in Canada
This graph shows the point estimates of new HIV infections by year with each associated plausible ranges for point estimates. The vertical axis shows the estimated number of new HIV infections per year, with the low and high ranges. The horizontal axis shows the calendar years.
| Year |
|---|
| gbMSM-PWID | 2.7% |
Among the estimated new infections in 2018, an estimated 1,109 were among gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men , representing just under half of all new HIV infections in 2018, despite representing approximately 3-4% of the Canadian adult male population. Although the gbMSM population continues to be over-represented in new HIV infections in Canada, the proportion of new infections among this population has decreased compared to 2016. .
Three hundred and twelve of the estimated new infections in 2018 were among people who inject drugs , accounting for 13.9% of new infections. The proportion of new infections attributed to heterosexuals increased slightly to 34.0% from 31.7% in 2016.