What Type Of Cells Does The Novel Coronavirus Attack
- Date:
- Berliner Institut für Gesundheitsforschung / Berlin Institute of Health
- Summary:
- Scientists have examined samples from non-virus infected patients to determine which cells of the lungs and bronchi are targets for novel coronavirus infection.
Scientists from the Berlin Institute of Health , Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin and the Thorax Clinic at Heidelberg University Hospital, whose collaboration is taking place under the auspices of the German Center for Lung Research , have examined samples from non-virus infected patients to determine which cells of the lungs and bronchi are targets for novel coronavirus infection. They discovered that the receptor for this coronavirus is abundantly expressed in certain progenitor cells. These cells normally develop into respiratory tract cells lined with hair-like projections called cilia that sweep mucus and bacteria out of the lungs. The scientists have now published their findings in The EMBO Journal.
Infection requires receptors and cofactors
60,000 single cells were sequenced
Why does the infection progress so differently?
Tech firms provide expertise
BIH is supporting COVID-19 research
Story Source:
How Is Hiv Treated
Treatments for HIV typically involve antiretroviral therapy. This isnt a specific regimen, but instead a combination of three or four drugs. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has currently approved nearly 50 different medications to treat HIV.
Antiretroviral therapy works to prevent the virus from copying itself. This maintains immunity levels while slowing the progression of HIV.
Before prescribing medication, a healthcare provider will take the following factors into consideration:
- a persons health history
- the levels of the virus in the blood
HIV doesnt cause a lot of outward or noticeable symptoms until the disease has progressed. For this reason, its important to understand how HIV is transmitted and the ways to prevent transmission.
HIV can be transmitted by:
- having sex, including oral, vaginal, and anal sex
- sharing needles, including tattoo needles, needles used for body piercing, and needles used for injecting drugs
- coming into contact with body fluids, such as semen, vaginal fluid, blood, and breast milk
HIV is not transmitted by:
- breathing the same air as a person living with HIV
- getting bitten by a mosquito or other biting insect
- hugging, holding hands with, kissing, or touching a person living with HIV
- touching a door handle or toilet seat thats been used by an HIV-positive person
Keeping this in mind, some of the ways a person can prevent HIV include:
Symptoms can take years to appear, which is why its so important to get tested regularly.
What Type Of A Cell Does Hiv Attack
Who are the experts?Our certified Educators are real professors, teachers, and scholars who use their academic expertise to tackle your toughest questions. Educators go through a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team.
The human body is amazing in its ability to fight off diseases. The body has a collection of cells in the blood steam and tissues that fight off foreign bodies. The most numerous cells in the immune system are called leukocytes, otherwise known as white blood cells. They are created…
Read Also: Does Cookie Johnson Have Hiv
What Else Can Affect Your Cd4 Count
Things other than the HIV virus can influence how high or low your CD4 count is, too.
An infection like the flu, pneumonia, or a herpes simplex virus can make your CD4 count go down for a while.
Your CD4 count will go way down when you’re having chemotherapy for cancer.
To get the most accurate and helpful results for your CD4 count, try to:
- Use the same lab each time.
- Wait for at least a couple of weeks after you’ve been sick or gotten a shot before you get a test.
Mechanism Of Hiv Infection
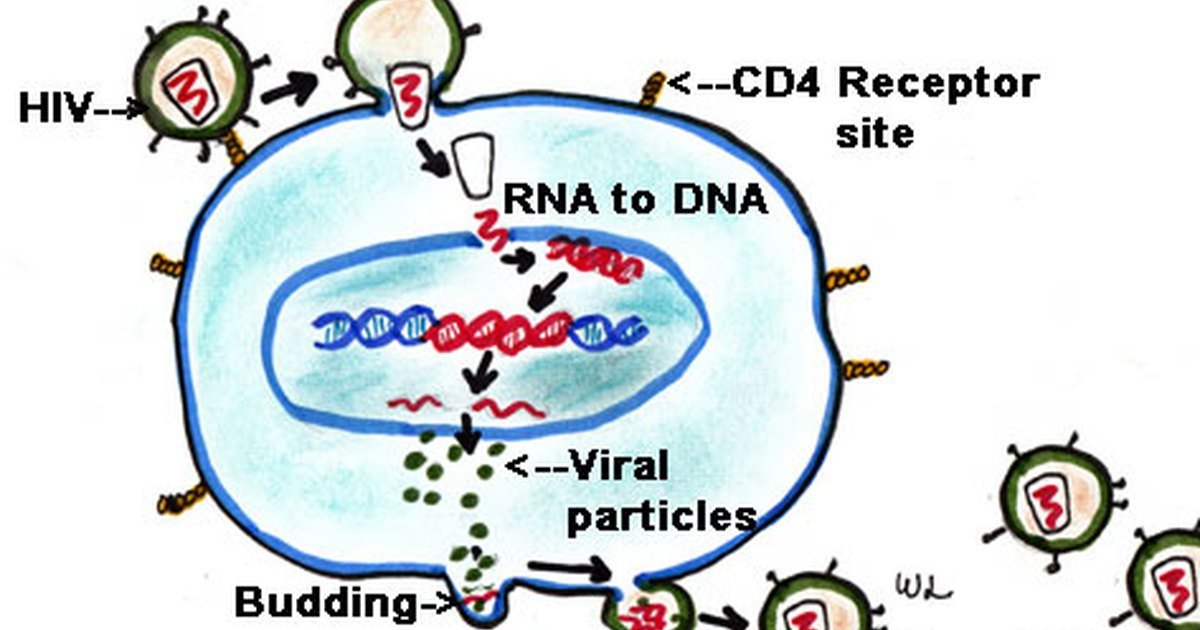
Once in the body, HIV attaches to several types of white blood cells. The most important are certain helper T lymphocytes involves white blood cells that travel through the bloodstream and into tissues, searching for and attacking microorganisms and… read more ). Helper T lymphocytes activate and coordinate other cells of the immune system. On their surface, these lymphocytes have a receptor called CD4, which enables HIV to attach to them. Thus, these helper lymphocytes are designated as CD4+.
). Once inside a CD4+ lymphocyte, the virus uses an enzyme called reverse transcriptase to make a copy of its RNA, but the copy is made as deoxyribonucleic acid that contain the code for a specific protein that functions in one or more types of cells in the body. Chromosomes are structures within cells… read more ). HIV mutates easily at this point because reverse transcriptase is prone to making errors during the conversion of HIV RNA to DNA. These mutations make HIV more difficult to control because the many mutations increase the chance of producing HIV that can resist attacks by the persons immune system and/or antiretroviral drugs.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hiv From Dried Blood
What Are The Seven Stages Of The Hiv Life Cycle
The seven stages of the HIV life cycle are: 1) binding, 2) fusion, 3) reverse transcription, 4) integration, 5) replication, 6) assembly, and 7) budding. To understand each stage in the HIV life cycle, it helps to first imagine what HIV looks like.
Now follow each stage in the HIV life cycle, as HIV attacks a CD4 cell and uses the machinery of the cell to multiply.
Transmission Of Hiv Infection
The transmission of HIV requires contact with a body fluid that contains the virus or cells infected with the virus. HIV can appear in nearly any body fluid, but transmission occurs mainly through blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk. Although tears, urine, and saliva may contain low concentrations of HIV, transmission through these fluids is extremely rare, if it occurs at all.
HIV is not transmitted by casual contact or by close, nonsexual contact at work, school, or home. No case of HIV transmission has been traced to the coughing or sneezing of an infected person or to a mosquito bite. Transmission from an infected doctor or dentist to a patient is extremely rare.
HIV is usually transmitted in the following ways:
HIV is more likely to be transmitted if skin or a mucous membrane is torn or damagedeven if minimally.
In the United States, Europe, and Australia, HIV has been transmitted mainly through men who have sex with men and the sharing of needles among people who inject drugs, but transmission through heterosexual contact accounts for about one fourth of cases. HIV transmission in Africa, the Caribbean, and Asia occurs primarily between heterosexuals, and HIV infection occurs equally among men and women. In the United States, fewer than 25% of adults who have HIV infection are women. Before 1992, most American women with HIV were infected by injecting drugs with contaminated needles, but now most are infected through heterosexual contact.
Read Also: Does Cookie Johnson Have Hiv
How Does Chronic Hiv Affect The Body
The chronic HIV stage is known as the latent or asymptomatic stage. During this stage, a person usually wont have as many symptoms as they did during the acute phase. This is because the virus doesnt multiply as quickly.
However, a person can still transmit HIV if the virus is left untreated and they continue to have a detectable viral load. Without treatment, the chronic HIV stage can last for many years before advancing to AIDS.
Advances in antiretroviral treatments have significantly improved the outlook for people living with HIV. With proper treatment, many people who are HIV-positive are able to achieve viral suppression and live long, healthy lives. Learn more about HIV and life expectancy.
A normal CD4 count ranges from approximately 500 to 1,600 cells per cubic millimeter of blood in healthy adults, according to HIV.gov.
A person receives an AIDS diagnosis when they have a CD4 count of fewer than 200 cells/mm3.
A person may also receive an AIDS diagnosis if theyve had an opportunistic infection or another AIDS-defining condition.
People with AIDS are vulnerable to opportunistic infections and common infections that may include tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, and pneumonia.
People with weakened immune systems are also more susceptible to certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma and cervical cancer.
The survival rate for people with AIDS varies depending on treatment and other factors.
How Are T Cells Linked To Hiv And Aids
HIV enters its genetic information into helper T cells to make copies of itself. When this happens, the helper T cells die. This severely disrupts the immune response. Low levels of helper T cells mean killer T cells and other white blood cells do not receive as much information about pathogens in the body. As a result, disease-causing bacteria and viruses multiply with minimal detection.
When the amount of helper T cells falls below 200 cells/mm3 , a person may receive an AIDS diagnosis. But healthcare professionals will also take into account other variables such as overall white blood cell count and the percentage of lymphocytes.
AIDS is the most severe stage of HIV. When a person receives an AIDS diagnosis, their immune system is severely compromised, and they are at risk for opportunistic illnesses. The survival rate without treatment at this stage is typically
200 cells/mm3 , they will likely receive an AIDS diagnosis.
When a person has HIV, a healthcare professional will collect a blood sample and request a CD4 count. The CD4 count helps determine how many helper T cells a person has.
But when analyzing a CD4 count, healthcare professionals must take into account that:
- CD4 levels could be lower in the morning
- stress and fatigue may affect CD4 levels
- corticosteroid levels could increase or decrease CD4 levels
The CD4 count helps healthcare professionals monitor HIV progression and if the person is at risk for opportunistic illnesses.
100â150cells/mm3 after 1 year.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take For Hiv To Become Aids
How Are Hiv And Aids Treated
Medicines can help people with HIV stay healthy. They can also prevent HIV from progressing to AIDS.
Health care providers prescribe a combination of different medicines for people with HIV and AIDS. They must be taken exactly as prescribed or they won’t work. These medicines:
- help keep the number of CD4 cells high
- reduce the viral load of HIV
Regular blood tests will check the number of CD4 cells in the body and the viral load.
If an HIV-positive person’s CD4 count gets low, doctors prescribe daily antibiotics. This prevents pneumocystis pneumonia, which happens in people with weakened immune systems.
Preventive Treatment Before Exposure
Taking an antiretroviral drug before being exposed to HIV can reduce the risk of HIV infection. Such preventive treatment is called preexposure prophylaxis . However, PrEP is expensive and is effective only if people take the drug every day. Thus, PrEP is recommended only for people who have a very high risk of becoming infected, such as people who have a partner who is infected with HIV.
PrEP may also be recommended for people who engage in high-risk sexual activities, such as the following:
-
Men who have anal sex with men without using a condom
-
Heterosexual men and women who do not regularly use condoms during sex with partners whose HIV status is unknown and who are at increased risk of HIV infection
People who use PrEP still need to use other methods to prevent HIV infection, including consistent use of condoms and not sharing needles to inject drugs.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have Hiv
Distinguishing Features Of Cd4+ T
One of the best ways of elucidating the intriguing nature of immunopathogenesis of HIV infection is studying naturally occurring HIV infection with different clinical outcomes. HIV-2 infection provides an ideal situation for this investigation as it has a lower degree of pathogenicity as compared to HIV-1. Although HIV-2 also eventually causes immunodeficiency syndrome indistinguishable from HIV-1-induced AIDS , many HIV-2-infected individuals do not develop immunodeficiency during their lifetime and retain stable CD4+ T lymphocyte counts and low levels of viremia for many years . This striking difference has prompted the search for the reason for variations in T-cell homeostasis and imbalances in cytokine production and identification of factors that contribute to an effective immune response that delays progression of disease during infection.
How Hiv Attacks The Body And Progresses To Aids

As viruses go, HIV ranks among the most wily. In fact, it is a retrovirus, meaning it is composed not of DNA but of RNA. Like other retroviruses, HIV has the capacity to enter a cell and then use the machinery of its host to replicate itself. It does this by transcribing its RNA into the DNA of the host cell. After this occurs, the cell will translate and transcribe viral genes along with its own. Once a cell is infected, then, it is transformed into the perfect factory for producing copies of the virus.
Another reason HIV is highly dangerous is it attacks the immune system, the bodys defense system that detects and destroys intruding bacteria and viruses. In particular, HIV goes after T cells. A type of white blood cell, T cells always work in teams of two. Scientists divide them into two categories based on their function . CD4 cells, referred to as helper T cells, lead the fight against infections by signaling for help, and CD8 cells swoop in for the kill.
Healthy T CellNIAID
However, HIV penetrates CD4 cells before they can sound the alarm. Carried through the blood stream, the virus injects its own genes into these helper cells which begin to replicate the virus. With the helper cells unable to perform their crucial function, other immune system cells begin to fail in their duties. And so begins the methodical destruction of the immune system.
HIV-infected T cellNIAID
Also Check: Can You Get Hiv From Dried Blood
Resistance To Hiv Infection
The poorly understood phenomenon associated with the HIV-1 epidemic is the existence of individuals who have been repeatedly exposed to the virus but remain uninfected. It has been suggested that HIV-1 resistant individuals may have a non functioning co-receptor preventing the virus from entering cells., The CCR-5 receptor was demonstrated as one of the main co-receptors for NSI strains of HIV-1. Samson et al., reported that a 32 bp deletion within the coding region for the CCR-5 generating a non-functional receptor that did not support infection by NSI strains of HIV-1. Moreover, white blood cells from individuals homozygous for the mutant CCR-5 were found to be highly resistant to infection by NSI viruses., Population studies indicate that the homozygous defect is found in only 1% of Caucasians of western European ancestry whereas the heterozygous defect is present in approximately 20% of this population. These results indicate that variants of the CCR-5 receptor could be responsible for the relative resistance to HIV-1 infection exhibited by some individuals and also for the variability of the course of the disease in infected patients.
How Does Acute Hiv Affect The Body
Once a person contracts HIV, the acute infection takes place immediately.
Symptoms of the acute infection may take place days to weeks after the virus has been contracted. During this time, the virus is multiplying rapidly in the body, unchecked.
This initial HIV stage can result in flu-like symptoms. Examples of these symptoms include:
- myalgias, or muscle pain
However, not all people with HIV experience initial flu-like symptoms.
The flu symptoms are due to the increase of copies of HIV and widespread infection in the body. During this time, the amount of CD4 cells starts to fall very quickly. The immune system then kicks in, causing CD4 levels to rise once again. However, the CD4 levels may not return to their pre-HIV height.
In addition to potentially causing symptoms, the acute stage is when people with HIV have the greatest chance of transmitting the virus to others. This is because HIV levels are very high at this time. The acute stage typically lasts between several weeks and months.
You May Like: Can You Get Aids From Dried Blood
Prevention Of Hiv Infection
At present, there is no effective HIV vaccine to prevent HIV infection or slow the progression of AIDS in people who are already infected. However, treating people who have HIV infection reduces the risk of their transmitting the infection to other people.
Transmission of HIV through its most common routessexual contact or sharing of needlesis almost completely preventable. However, the measures required for preventionsexual abstinence or consistent condom use Prevention Sexually transmitted diseases are infections that are typically, but not exclusively, passed from person to person through sexual contact. Sexually transmitted diseases may be caused… read more and access to clean needlesare sometimes personally or socially unpopular. Many people have difficulty changing their addictive or sexual behaviors, so they continue to put themselves at risk of HIV infection. Also, safe sex practices are not foolproof. For example, condoms can leak or break.
Preventing Transmission From Mother To Newborn
Pregnant women infected with HIV can transmit the virus to the newborn.
The following can help prevent HIV transmission from mother to newborn Prevention of transmission for infected mothers Human immunodeficiency virus infection is a viral infection that progressively destroys certain white blood cells and causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome . Human immunodeficiency… read more :
-
Testing pregnant women to determine whether they are infected with HIV
-
If they are infected, treating them with antiretroviral drugs during pregnancy and labor
-
Delivering the baby by cesarean rather than by vaginal delivery
-
After birth, treating the newborn with zidovudine, given intravenously, for 6 weeks
-
If possible, using formula instead of breastfeeding
Recommended Reading: Does Nba Youngboy Have Hiv