How Is Hiv Spread
The spread of HIV from person to person is called HIV transmission. HIV is spread only through certain body fluids from a person who has HIV. These body fluids include:
- Blood
- Rectal fluids
- Breast milk
HIV transmission is only possible through contact with HIV-infected body fluids. In the United States, HIV is spread mainly by:
- Having anal or vaginal sex with someone who has HIV without using a condom or taking medicines to prevent or treat HIV
- Sharing injection drug equipment , such as needles or syringes, with someone who has HIV
The spread of HIV from a woman with HIV to her child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding is called perinatal transmission of HIV. For more information, read the HIVinfo fact sheet on Preventing Perinatal Transmission of HIV.
You cannot get HIV by shaking hands or hugging a person who has HIV. You also cannot get HIV from contact with objects, such as dishes, toilet seats, or doorknobs, used by a person with HIV. HIV is not spread through the air or water or by mosquitoes, ticks, or other blood-sucking insects. Use the HIVinfo You Can Safely ShareWith Someone With HIV infographic to spread this message.
When Was The First Human Case Of Aids
A man from Congo in 1959. An HIV-1 infection was first documented in 1959 in a preserved blood sample taken from a Belgian Congo man named Léopoldville. The anonymous person may have never developed AIDS, nor did he or she die from its complications, but it is unknown whether he or she ever developed AIDS.
Where Did Hiv Come From A Look At The Origins Of The Pandemic Of Our Time
A chimpanzees virus has killed 35 million humans.
That virus, commonly known as HIV, is the defining pandemic of our time. More than 35 million people have been killed by the virus to date. But the virus itself didnt get its start in humans.
HIV/AIDS is, like the vast majority of emerging viruses infecting people, zoonotic in nature. The AIDS crisis, as we generally think of it, began in the 1980s. First as a mysterious illness primarily infecting gay men in urban areas in the United States. But thats not really the beginning. Before the diseases first mention in 1982 in the New York Times, people had been dying of AIDS for at least a decade, though probably not much longer. In Africa, HIVthe virus that causes AIDShad jumped from chimpanzees to humans sometime early in the 20th century.
To date, the earliest known case of HIV-1 infection in human blood is from a sample taken in 1959 from a man whod died in Kinshasa in what was then the Belgian Congo.
Its this fact which keeps me awake at night. Imagine, for a moment, that the HIV virus in that 1959 sample had been studied and identified. If, in the 1950s, the scientific community realized the potential harm this new virus could unleash. What could we have done? What therapies could we have developed before it became one of the deadliest pandemics in human history? Would we have a cure by now?
That work takes several forms, including:
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have An Std
When Did Hiv Enter The Population
By looking at the genome sequences of different viruses over time, researchers can calibrate a molecular clock based on the rate of sequence change, or mutations. Scientists can then use this to infer the rate of evolution and thus determine approximately when the most recent common ancestor existed.
Using this technique, researchers estimated that HIV-1 group M originated in 1908 and group O in 1920. HIV-2 groups A and B originated a bit later approximately in 1940 and 1945, respectively.
How Can I Keep From Getting Hiv
The best way to protect yourself is to avoid activities that put you at risk. There’s no way to tell by looking at someone if he or she has HIV. Always protect yourself. Use latex condoms whenever you have any type of sex .
- Don’t use condoms made from animal products.
- Use water-based lubricants .
- Never share needles to take drugs.
- Avoid getting drunk or high. Intoxicated people might be less likely to protect themselves.
- Consider getting testedit is really important to be aware of your HIV status.
If you are a healthcare worker, you are at a slightly higher risk of getting HIV from a needle-stick injury, skin contact with contaminated fluid or from human bites. You should follow universal precautions:
- Always wear protective equipment when dealing with blood and body fluids.
- Follow careful hand-washing guidelines when dealing with such fluids.
- Follow safe handling guidelines for needles and sharp instruments.
- Be aware of post-exposure policies at your workplace.
If you are in a relationship with a partner who has HIV, or you are at high risk for any other reason, consider using pre-exposure prophylaxis, commonly called PrEP. This means taking one of two medicines every day, emtricitabine-tenofovir or emtricitabine-tenofovir alafen .
If you are a person with HIV who is in a relationship with a person who is HIV-negative, you should also be on a medication regimen.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take To Be Undetectable Hiv
How Is Hiv/aids Diagnosed
Early HIV infection often causes no symptoms, and must be detected by testing a person’s blood for the presence of antibodiesdisease-fighting proteinsagainst HIV. These HIV antibodies generally do not reach levels high enough to detect by standard blood tests until 1 to 3 months following infection, and may take as long as 6 months. People exposed to HIV should be tested for HIV infection as soon as they think they may have been exposed to HIV.
When a person is highly likely to be infected with HIV and yet antibody tests are negative, a test for the presence of HIV itself in the blood is used. Repeat antibody testing at a later date, when antibodies to HIV are more likely to have developed, is often recommended.
How Do You Get Or Transmit Hiv
You can only get HIV by coming into direct contact with certain body fluids from a person with HIV who has a detectable viral load. These fluids are:
- Blood
- Semen and pre-seminal fluid
- Rectal fluids
- Vaginal fluids
- Breast milk
For transmission to occur, the HIV in these fluids must get into the bloodstream of an HIV-negative person through a mucous membrane open cuts or sores or by direct injection.
People with HIV who take HIV medicine daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners.
You May Like: How Long Does Aids Take To Show
Spread To The Western Hemisphere
Further isolated occurrences of this infection may have been emerging as early as 1966. The virus eventually entered gay male communities in large United States cities, where a combination of casual, multi-partner sexual activity and relatively high transmission rates associated with anal intercourse allowed it to spread explosively enough to finally be noticed.
Because of the long incubation period of HIV before symptoms of AIDS appear, and because of the initially low incidence, HIV was not noticed at first. By the time the first reported cases of AIDS were found in large United States cities, the prevalence of HIV infection in some communities had passed 5%. Worldwide, HIV infection has spread from urban to rural areas, and has appeared in regions such as China and India.
Epidemiology Of Hiv And Aids
Epidemiology is the study of how disease is distributed in populations and the factors that influence the distribution. Epidemiologists try to discover why a disease develops in some people and not in others. Clinically, AIDS was first recognized in the United States in 1981. In 1983 HIV was discovered to be the cause of AIDS. Since then, the number of AIDS cases has continued to increase both in the United States and in other countries.
HIV and AIDS cases are reportable each state has its own laws and healthcare workers must be familiar with those of the state in which they are licensed.
The discovery of combination antiviral drug therapies in 1996 resulted in a dramatic in the number of deaths due to AIDS among people given the drug therapies. On the down side, many people who have access to the therapies may not benefit from them or may not be able to tolerate the side effects. The medications are expensive and require strict dosing schedules. Furthermore, in developing countries many people with HIV have no access to the newer drug therapies.
CDC estimates that that there are only 4 transmissions per year for every 100 people living with HIV in the United States, which means that at least 95% of people living with HIV do not transmit the virus to anyone else. This represents an 89% decline in the transmission rate since the mid-1980s, reflecting the combined impact of testing, prevention counseling, and treatment efforts targeted to those living with HIV infection .
Read Also: Nba Youngboy Std
Are Women More Likely To Get Hiv
Yes. Biologically speaking, a woman is more vulnerable to heterosexual transmission of the disease because the genitalia are easily exposed to seminal fluids.
Gender inequality has great influence on the spread of HIV/AIDS among women. In some cultures, many women and girls are often put in situations where they engage in non-consensual sex or have sex for money.
In the U.S., minority communities have been hit the hardest by HIV. African American and Hispanic women together represent less than 25% of all U.S. women, yet they account for more than 78% of AIDS cases reported among women in the country.
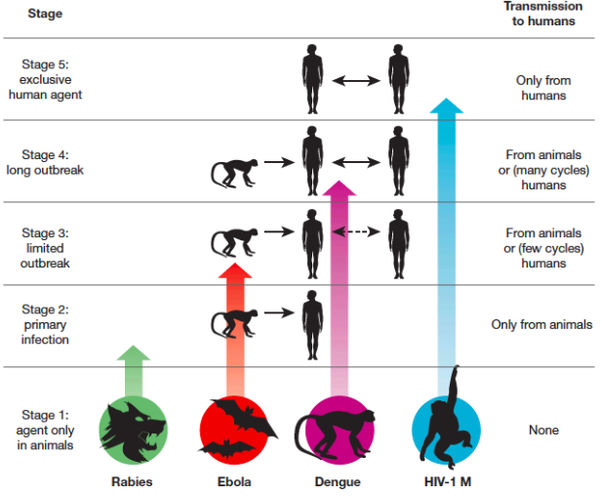
Groups And Subtypes Of Hiv
Genetic studies have led to a general classification system for HIV that is primarily based on the degree of similarity in viral gene sequence. The two major classes of HIV are HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-1 is divided into three groups, known as group M , group O , and group N . Worldwide, HIV-1 group M causes the majority of HIV infections, and it is further subdivided into subtypes A through K, which differ in expression of viral genes, virulence, and mechanisms of transmission. In addition, some subtypes combine with one another to create recombinant subtypes. HIV-1 group M subtype B is the virus that spread from Africa to Haiti and eventually to the United States. Pandemic forms of subtype B are found in North and South America, Europe, Japan, and Australia. Subtypes A, C, and D are found in sub-Saharan Africa, although subtypes A and C are also found in Asia and some other parts of the world. Most other subtypes of group M are generally located in specific regions of Africa, South America, or Central America.
In 2009 a new strain of HIV-1 was discovered in a woman from Cameroon. The virus was closely related to a strain of SIV found in wild gorillas. Researchers placed the new virus into its own group, HIV-1 group P, because it was unique from all other types of HIV-1. It was unclear whether the newly identified virus causes disease in humans.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can Hiv Be Dormant
Should I Get Vaccines If I Have Hiv/aids
Check with your healthcare provider. Certain vaccines are generally recommended, including:
- Influenza vaccine.
- Human papillomavirus vaccine if you are age 26 or younger.
- Meningococcal series of shots.
- Pneumonia vaccine.
- Tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis vaccine, with a repeat every 10 years of the tetanus/diphtheria vaccine.
You should probably avoid live vaccines, such as the ones for chickenpox and measles, mumps and rubella . This is true especially if your CD4 numbers are 200 or lower. Make sure you discuss vaccine questions with your healthcare provider.
HIV can affect how well the vaccine works. It can also make your viral load increase for a time because your immune system is stimulated by the vaccine.
Origin And Epidemic Emergence

Several of the theories of HIV origin accept the established knowledge of the HIV/SIV phylogenetic relationships, and also accept that bushmeat practice was the most likely cause of the initial transfer to humans. All of them propose that the simultaneous epidemic emergences of four HIV groups in the late 19th-early 20th century, and the lack of previous known emergences, are explained by new factor that appeared in the relevant African regions in that timeframe. These new factor would have acted either to increase human exposures to SIV, to help it to adapt to the human organism by mutation , or to cause an initial burst of transmissions crossing an epidemiological threshold, and therefore increasing the probability of continued spread.
Genetic studies of the virus suggested in 2008 that the most recent common ancestor of the HIV-1 M group dates back to the Belgian Congo city of Léopoldville , circa 1910. Proponents of this dating link the HIV epidemic with the emergence of colonialism and growth of large colonial African cities, leading to social changes, including a higher degree of non-monogamous sexual activity, the spread of prostitution, and the concomitant high frequency of genital ulcer diseases in nascent colonial cities.
Social changes and urbanization
Colonialism in Africa
This theory was later dubbed “Heart of Darkness” by Jim Moore, alluding to the book of the same title written by Joseph Conrad, the main focus of which is colonial abuses in equatorial Africa.
Also Check: Youngboy Has Herpes
How Can I Protect Myself
The best way to protect yourself from HIV is to not have sex and not share needles.
If you decide to have sex, reduce your risk of getting HIV by:
- using a condom every time you have sex
- getting tested for HIV and making sure all partners do too
- reducing the number of sexual partners you have
- getting tested and treated for STDs having an STD increases the risk of HIV infection
Understanding how HIV spreads can help you make safer choices about sex. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about HIV and if you want to get tested.
Whats The Difference Between Hiv And Aids
HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. HIV and AIDS are not the same thing. And people with HIV do not always have AIDS.
HIV is the virus thats passed from person to person. Over time, HIV destroys an important kind of the cell in your immune system that helps protect you from infections. When you dont have enough of these CD4 cells, your body cant fight off infections the way it normally can.
AIDS is the disease caused by the damage that HIV does to your immune system. You have AIDS when you get dangerous infections or have a super low number of CD4 cells. AIDS is the most serious stage of HIV, and it leads to death over time.
Without treatment, it usually takes about 10 years for someone with HIV to develop AIDS. Treatment slows down the damage the virus causes and can help people stay healthy for several decades.
Recommended Reading: Hiv From Dried Blood
How Can A Person Reduce The Risk Of Getting Hiv
To reduce your risk of HIV infection, use condoms correctly every time you have sex, limit your number of sexual partners, and never share injection drug equipment.
Also talk to your health care provider about pre-exposure prophylaxis . PrEP is an HIV prevention option for people who do not have HIV but who are at high risk of becoming infected with HIV. PrEP involves taking a specific HIV medicine every day. For more information, read the HIVinfo fact sheet on Pre-exposure Prophylaxis .
HIV medicines, given to women with HIV during pregnancy and childbirth and to their babies after birth, reduce the risk of perinatal transmission of HIV. In addition, because HIV can be transmitted through breast milk, women with HIV who live in the United States should not breastfeed their babies. Baby formula is a safe and healthy alternative to breast milk and is readily available in the United States.
Natural History Of Sivcpz Infection
Initially, SIVcpz was thought to be harmless for its natural host. This was because none of the few captive apes that were naturally SIVcpz infected suffered from overt immunodeficiency, although in retrospect this conclusion was based on the immunological and virological analyses of only a single naturally infected chimpanzee . In addition, SIV-infected sooty mangabeys and African green monkeys showed no sign of disease despite high viral loads in blood and lymphatic tissues , leading to the belief that all naturally occurring SIV infections are nonpathogenic. However, the sporadic prevalence of SIVcpz, along with its more recent monkey origin, suggested that its natural history might differ from that of other primate lentiviruses. To address this, a prospective study was initiated in Gombe National Park, Tanzania, the only field site where SIVcpz infected chimpanzees are habituated and so can be observed in their natural habitat.
Recommended Reading: Hiv Gestation Period
How Could Aids Have Remained Unidentified For 40 Years In Humans
If HIV was introduced to the human population before the Second World War, why didn’t it cause recognisable AIDS cases before the 1970s?
Kevin de Cock pointed out in his Monday presentation that the small number of HIV case reports come predominantly from academic centres, and that unusual diseases were most likely to be noticed in Europeans with access to care at academic medical centres. Unusual cases of cryptococcal meningitis went un-noted until the late 1970s, although polio researcher Stanley Plotkin said that in his experience, “you don’t recognise things unless you are prepared for them, especially if they are low incidence illnesses”.
This pattern prior to the early 1980s suggests that HIV was causing a low incidence of AIDS. If it had been causing a high incidence of illness, argues tropical medicine specialist Alan Fleming, the illness would have been recognised by local people without the aid of epidemiologists. That is what happened in Uganda, where a new disease was named Slim by local people before any epidemiological investigation was conducted.