What Are The Risk Factors For Hiv
- Engaging in unprotected anal, vaginal, or oral sex, especially with multiple partners or anonymous partners
- Having sex in exchange for drugs or money
- Sharing needles and other equipment for injecting drugs
Of risks associated with different sex practices, receptive anal intercourse rates the highest because the lining of the anus is thin, allowing HIV to enter the body followed by insertive anal intercourse and receptive penile-vaginal intercourse, according to the CDC.
Young People Most At Risk Of Hiv
Resource date: 2010
Interagency Youth Working Group, USAID, IATT on HIV and Young People, and FHI
Publisher: FHI
This paper is designed to call more attention to young people within the groups considered most at risk for HIVthose who sell sex, those who inject drugs, and young men who have sex with men. Despite the growing attention that has been given to programming for these groups, little explicit focus has emerged onthe particular needs of young people in these populations. Efforts to prevent HIV among young people have tended to focus on the general population of young people, for whom more is known about effective programming, instead of focusing on young people in most-at-risk groups. Research has begun to show the importance of focusing on young people within most-at-risk populations, and there are increasing examples of programmatic approaches for meeting their needs. But many challenges remain, including the fact that there are significant differences among young people between the ages of 10 and 24.
Interpreting The Numberswhat Additional Information Needs To Be Provided
Some clients may see these numbers and think their risk of HIV transmission is low. Therefore, caution is needed when interpreting them. If these numbers are provided to clients, they should be accompanied by information that helps shed light on why the risk may be higher than it seems.
Transmission can occur after one exposure.
It is important to emphasize that a person could become infected from having unprotected sex once or a person could have unprotected sex many times and not become infected, regardless of how low or high the risk per exposure is.
A risk of 1% would mean that an average of one infection would occur if 100 HIV-negative people were exposed to HIV through a certain type of sex. It does not mean that a person needs to be exposed 100 times for HIV infection to occur.
These are estimates of average risk in the absence of biological factors that increase risk.
The numbers in the table above are rough estimates. They are averages and do not represent the risk from all exposures to HIV through a certain type of sex.
The risk of HIV transmission may be much higher than these averages if biological risk factors are present. For example, research shows that STIs and some vaginal conditions, such as bacterial vaginosis, can increase the risk of HIV transmission by up to 8 times.6,7,8 As a result, the risk of an HIV-negative woman becoming infected through unprotected receptive vaginal sex could be closer to 1% if she has a vaginal STI.
Read Also: How Long Can Hiv Go Undetected
The Biologic Basis For Aids
The specific details of the disease process that leads to AIDS are not fully understood despite considerable progress in the virology of HIV and the immunology of the human host, much of which has been driven by the urge to better understand AIDS.
There is a specific decline in the CD4+ helper T cells, resulting in inversion of the normal CD4/CD8 T-cell ratio and dysregulation of B-cell antibody production. Immune responses to certain antigens begin to decline, and the host fails to adequately respond to opportunistic infections and normally harmless commensal organisms. Because the defect preferentially affects cellular immunity, the infections tend to be nonbacterial .
The pattern of opportunistic infections in a geographic region reflects the pathogens that are common in that area. For example, persons with AIDS in the United States tend to present with commensal organisms such as Pneumocystis and Candida species, homosexual men are more likely to develop Kaposi sarcoma because of co-infection with HHV8, and tuberculosis is common in developing countries.
Gut-associated lymphoid tissue plays a role in HIV replication. Although the portal of entry for HIV infection is typically through direct blood inoculation or exposure of the virus to genital mucosal surfaces, the GI tract contains a large amount of lymphoid tissue, making this an ideal site for HIV replication.
Can You Get Hiv From A Tattoo Or Body Piercing
More in HIV/AIDS. Body art, which includes tattooing and body piercing, has become of increasingly popular among older teens and young adults. As the art form continues to move from the fringes into the mainstream, many have begun to wonder whether it poses any risk of infection from bloodborne diseases such as HIV or hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Hiv Take
Reducing Your Personal Hiv Risk
The purpose of understanding relative risk is to establish the means by which to reduce your personal risk of infection or the risk of transmitting HIV to others. Oftentimes, it takes little to mitigate risk. For example, the consistent use of condoms correlates to a 20-fold decrease in HIV risk, while choosing insertive fellatio over insertive anal sex results in a 13-fold decrease. Conversely, the presence of an STI or genital ulcer increases the risk of HIV by anywhere from 200% to 400%.
Arguably the most important factor in assessing the likelihood of HIV transmission is the infected person’s viral load. Data suggests that the risk of an HIV-infected person with an undetectable viral load transmitting the virus is essentially zero.
The strategy called treatment as prevention strongly supports the use of antiretroviral therapy to reduce the infectivity of a person with HIV. It also reinforces the need for early testing to mitigate risk in mixed-status couples.
Knowing your serostatus and that of your partner allows you to make an informed choice on how to better protect yourselveswhether it be to abstain from high-risk activities, use condoms, or explore pre-exposure prophylaxis as a means to reduce the HIV-negative partner’s susceptibility to infection.
Routes Of Hiv Transmission
In Scotland, HIV is most commonly transmitted by having sex with someone who has HIV without using any form of protection, such as HIV PrEP or condoms.
A person with HIV can only pass the virus to others if they have a detectable level of virus. People living with HIV who are taking treatment and have undetectable levels of virus in their bodies can’t transmit HIV to others.
Over 90% of people living with HIV in Scotland have undetectable levels of virus.
The main routes of transmission are unprotected receptive or insertive vaginal and anal sex. The risk of transmitting HIV through oral sex is extremely low.
Other ways of getting HIV include:
- sharing needles, syringes and other injecting equipment
- from mother to baby before or during birth when the mother isn’t taking HIV medication
- from mother to baby by breastfeeding when the mother isn’t taking HIV medication
- sharing sex toys with someone infected with HIV and who isn’t taking HIV medication
- blood transfusion
You May Like: How Long Does Hiv Last
Hiv Testing And Counselling For Women And Adolescent Girls
A major gap in HIV service provision for women can be found in HIV testing and counselling , which is a vital gateway to treatment services.
A study conducted in Tanzania between 2003 and 2012 found that young women who were married were more likely to get tested than young women who were not. It also found antenatal care to be an important determinant for HIV testing. Women who had received antenatal care were more likely to get tested as compared with young women who had not given birth. Young women with primary and/or secondary education were also more likely than those without any formal education to test for HIV.70
Lack Of Access To Healthcare Services
In some countries, women face significant barriers to accessing healthcare services. These barriers occur at the individual, interpersonal, community and societal levels.14 Barriers take many forms including denial of access to services that only women require, discrimination from service providers that stems from views around female sexuality and poor quality services.
Procedures relating to a womens sexual and reproductive health , performed without consent, including forced sterilisation, forced virginity examinations and forced abortion also deter women from accessing services.1516 In some cases, healthcare providers do not fully understand laws around childbirth and HIV. This can lead to HIV-positive women choosing to have an abortion because they are misinformed about their options and how to protect their health, as well as their child’s.17
Additionally, in 29 countries women require the consent of a spouse or partner to access SRH services.18
A lack of access to comprehensive HIV and SRH services means that women are less able to look after their sexual and reproductive health and rights and reduce their risk of HIV infection.
Also Check: How Long Can Aids Be Dormant
Hiv Post Exposure Prophylaxis
If you think you may have been exposed to HIV and you haven’t taken PrEP medication or used a condom, you should take PEP medication.
Post exposure prophylaxis is a form of emergency HIV medication taken by someone who does not have HIV but who has or may have been very recently exposed to HIV.
PEP should be taken as soon as possible, but it can be taken up to 72 hours after exposure. The earlier it is taken the more effective it is.
PEP is available from sexual health services or out of hours from A& E.
Should You Get Tested For Hiv If You Dont Think Youre At High Risk
Some people who test positive for HIV were not aware of their risk. That’s why CDC recommends that everyone between the ages of 13 and 64 get tested for HIV at least once as part of routine health care and that people with certain risk factors should get tested more often .
Even if you are in a monogamous relationship , you should find out for sure whether you or your partner has HIV.
You May Like: Does Nba Youngboy Really Have Herpes
Key Affected Populations Hiv And Aids
People who belong to key affected populations are people who, for one reason or another, are more vulnerable to HIV infection.
This could be because they engage in high-risk behaviours such as injecting drugs, or because they are marginalised by society and fearful of accessing HIV services.
An effective response to the HIV epidemic requires that these groups are targeted by HIV prevention programmes with information and services that are specific to them.
The Differential Hiv Experience Of African

While African-Americans make up 12 percent of the U.S. population, they accounted for 46 percent of new HIV infections in 2010, substantially higher than the rate for Whites or Hispanics. The majority of these were men however, African-American women also have a high rate of HIV diagnosis nearly 20 times that of White women . More disheartening is that 1 in 16 African-American men and 1 in 32 African-American women will eventually be diagnosed with HIV.
The causes of this HIV health disparity are complex. HIV infection prevalence is higher and more broadly represented in the African- American community compared to the White population thus African-Americans are at increased risk of infection simply by choosing intimate partners within their own ethnic communities.24 Additionally, African-American communities experience high rates of other sexually transmitted infections, and some of these infections can significantly increase the risk of contracting HIV. African-Americans also tend to be diagnosed at later stages in the disease and therefore begin therapy later, increasing the length of time of their infectivity. Once engaged in HAART, African-Americans are more likely to discontinue therapy prematurely,25 risking resurgence of HIV infectivity and further health complications.
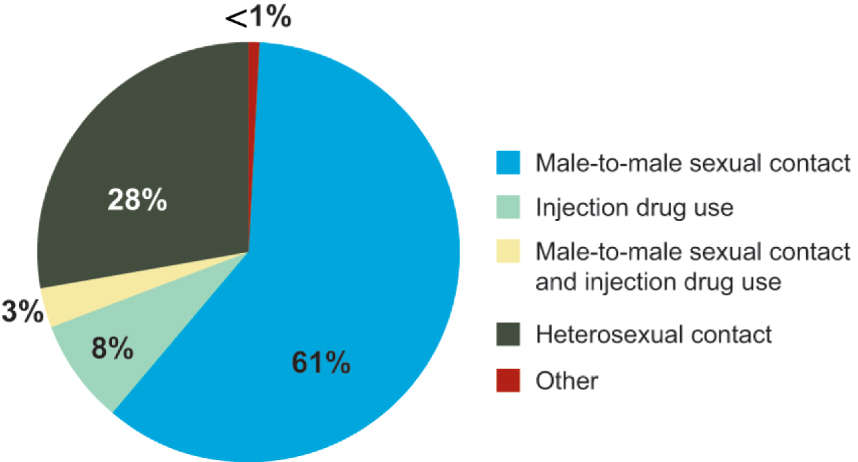
- Text Description: Diagnosis of HIV Infection Among Adults and Adolescents, by Transmission Category Graph
-
Male-to-male sexual contact: 61%
You May Like: How Long After Contracting Hiv Do You Get Symptoms
Who Should Get Tested
The only way to know for sure whether you have HIV is to get tested. CDC recommends that everyone between the ages of 13 and 64 get tested for HIV at least once as part of routine health care. Knowing your HIV status gives you powerful information to help you take steps to keep you and your partner healthy. About 1 in 8 people in the United States who have HIV do not know they have it.
Challenges In Calculating A Number
It isn’t easy for researchers to calculate the risk of transmission from an exposure to HIV through sex. To do this effectively, a group of HIV-negative individuals need to be followed over time and their exposures to HIVboth the number of times they are exposed and the types of exposureneed to be tracked.
As you can imagine, accurately tracking the number of times a person is exposed to HIV is very difficult. Researchers ask HIV-negative individuals enrolled in these studies to report how many times they have had sex in a given period of time, what type of sex they had, how often they used condoms and the HIV status of their partner. Because a person may have trouble remembering their sexual behaviour or may not want to tell the whole truth, this reporting is often inaccurate.
Furthermore, a person does not always know the HIV status of their partner. For this reason, researchers usually enroll HIV-negative individuals who are in stable relationships with an HIV-positive partner . Researchers can then conclude that any unprotected sex reported by a study participant counts as an exposure to HIV.
Don’t Miss: Hiv Hair Loss Symptom
Why Are Some People At Higher Risk Of Contracting Hiv
If a person engages in sexual activity, then they are at some risk of contracting HIV. But, there are certain structural inequalities that exacerbate particular groups’ risk of contracting HIV.
According to the Center for American Progress, several studies show that black Americans â who make up 14% of the U.S. population but 44% of those who contract HIV â actually engage in about the same amount of high-risk behaviors than their white counterparts.
Immunologic Control Of Hiv
The primary mechanism for immunologic control of HIV appears to be CD8+ cytotoxic T-cells. T-cell responses are correlated with the steady-state viral load and hence, the rate of progression. Cellular immunity is apparently responsible for some multiply-exposed, but uninfected individuals.
Although antibodies against HIV can be detected, it is clear that they are not sufficiently neutralizing to assist with immunologic control of the infection.
The role of NK cells may be important in the initial control of HIV. Escape mutations have been detected, implying that immunologic pressure on HIV exists from NK cells.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Has Herpes
How Is Hiv Transmitted Through Sex
HIV can be transmitted through semen, vaginal secretions, blood, and anal secretions. When a person doesnt use a condom during sex, its easier for semen, vaginal fluids, blood, and anal secretions to enter their body either being absorbed across the mucous membrane of the vagina or anus or entering the bloodstream directly.
Anal sex is a known risk factor for contracting HIV if other prevention methods are absent, especially for the receptive partner whose anus is being penetrated by the penis.
Vaginal sex can also lead to HIV transmission if other prevention methods are absent, especially for the receptive partner whose vagina is being penetrated by the penis.
Both anal and vaginal sex can also carry a risk of HIV transmission for the insertive partner .
Oral sex is thought to be very low risk. Rimming is also thought to very low risk.
How Common Is Hiv
At the end of 2017, there were an estimated 5099 people in Scotland living with HIV. The majority got the virus through sex.
Around 1 in every 1087 people in the Scotland has HIV, but the three groups with highest rates of HIV are:
- gay and bisexual men or other men who have sex with men
- people from countries with high HIV prevalence, especially sub Saharan African countries
- people who share injecting equipment or who have sex with people who inject drugs
The World Health Organisation estimates that around 36.9 million people in the world are living with HIV.
You May Like: Can You Get Aids Before Hiv
Vulnerable Groups And Key Populations At Increased Risk Of Hiv
Definitions
Key populations at increased risk of HIV: People are said to be at increased risk of acquiring the HIV infection if what they are doing, or what they might do if placed in a facilitating situation, is associated with a high risk of HIV transmission. Examples of those population groups are injecting drug users , male and female sex workers and men who have sex with men.
Vulnerable groups: People are said to be in a state of vulnerability if their living conditions are prone to shifting factors which would place them at risk of contracting HIV. Examples of those groups are young people, women, migrants, long-distance drivers, displaced populations, men in uniform and others.
Importance of working with vulnerable groups and key populations at increased risk of HIV
The HIV epidemic is usually heightened by the transmission of the virus among populations with high-risk behavior, and then propagating to the general populations via so-called bridging groups, depending on the extent and nature of social linkages and networks between these populations. Evidence has shown that expanding awareness, prevention and behavior change interventions among key populations at increased risk of HIV can slow or even curb the epidemic.
Approaches to working with vulnerable groups and key populations at increased risk of HIV
Services provided to vulnerable groups key populations at increased risk of HIV
Awareness raising and behavior change communication
Counseling and Testing