Evidence From Modeling Studies For Benefit Of Poc Hiv Viral Load Monitoring
The direct health gains from replacing clinical or laboratory-based CD4 count-based monitoring with laboratory-based viral load monitoring appear to be modest. Randomized trials in Zimbabwe and Uganda , Cameroon , and Thailand found CD4 count-based monitoring to be noninferior to viral load monitoring and not substantially different from clinical monitoring over the first 3 years of ART. In contrast to centralized testing, POC HIV viral load testing provides results more rapidly, allowing for earlier adherence counseling and/or ART regimen switching to reduce the risk of HIV drug resistance, worsening immunosuppression, and onward HIV transmission. In multiple modeling studies, the benefits at the individual level of POC HIV viral load testing were estimated to be small relative to the impact of increasing coverage and retention on first-line ART . However, these studies were based on modeled estimates of the effectiveness of POC viral load testing, which were not informed by clinical trial results.
Why Is Viral Load Important
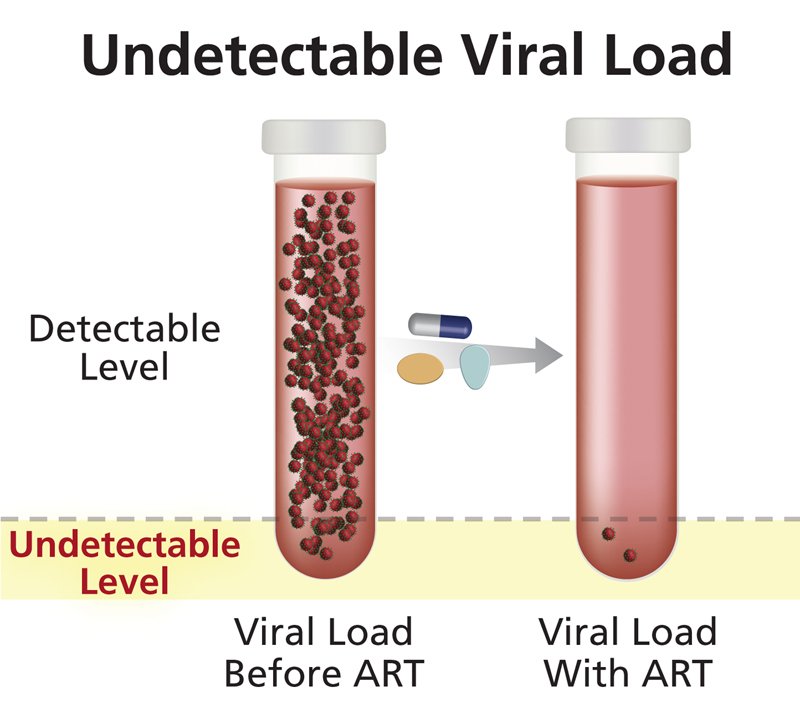
The viral load is a measure of how active HIV is in your blood. The virus kills white blood cells called CD4 cells, which are an important part of your immune system. When the viral load is high then the CD4 count goes down, the immune system weakens and you are more likely to become sick.
When you start anti-HIV treatment , the viral load test is used to measure how well your treatment is working. One of the goals of ART is to have an undetectable viral load, so the immune system can begin to repair itself. You should have a viral load test every three to six months. The test results are used to monitor how well your HIV treatment is working and whether you may need to change the drugs you are taking.
We now know that even low levels of HIV in the body can cause inflammation which can damage your body. It is recommended that people start treatment as early as possible after they have been diagnosed. This helps reduce the damage that can be caused by HIV-related inflammation.
We also know that people who are engaged in care, taking ART and have an ongoing undetectable viral load are substantially less likely to transmit HIV to others. In fact studies show that people with an undetectable viral load do not pass HIV to their sexual partners.
Evidence And Results From Clinical Studies
Several randomized clinical trials in LMICs are investigating the clinical impact of POC HIV viral monitoring for PLHIV receiving ART . Study populations vary but include children, adolescents, adults, and pregnant women, with interventions of POC viral load test alone or combined with new models of HIV care. Most studies include viral suppression as an outcome, alongside various process evaluation measures.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take For Hiv Symptoms To Appear
Study Design And Duration
We conducted a concurrent explanatory mixed methods cross-sectional study using secondary data as a quantitative component and a descriptive qualitative component. The study was conducted as a single snapshot between April and May 2021. However, we abstracted data spanning the period from February 2018 to February 2020 prior to the first COVID-19 lockdown in Uganda which was characterized by significant disruption in patient visit schedules .
Are Test Results Accurate
HIV viral load testing is a vital tool for monitoring the state of a patients HIV infection. To ensure accuracy in monitoring changes in a patients viral load over time, patients may be encouraged to have the same type of test conducted each time and, preferably, at the same laboratory.
There are several methods that may be used by laboratories to measure a patients HIV viral load. To ensure that test results can be compared and interpreted consistently over time, its best for patients to have the same type of viral load test each time. This helps to provide an accurate picture of whether the virus is replicating or stable with the current ART regimen.
A patients doctor can discuss how to ensure that the viral load testing method is consistent across multiple tests.
Don’t Miss: Do I Have Hiv Or Aids
Hiv Transmission In Drug Users
For people who inject drugs, estimates of the risk of transmission from a contaminated needle range from 0.3% to 4.0%, with several of these estimates falling in the range of 0.7% to 0.8%. Sharing ancillary injecting equipment, such as filters or cookers, has been shown to increase the risk of transmission, even in the absence of sharing needles and syringes. Other factors that have been shown to increase the risk of HIV transmission for injection drug users include: unsafe locations, type of drug and frequency of drug injection. Non-injection drug users are also at risk of HIV infection. Drug use often alters sexual behaviours by increasing risk taking. As well, several drugs have been reported to be independent risk factors of HIV transmission.
Viral Load Test Procedure
A doctor can test the viral load using a simple blood test. No preparation is needed.
The doctor or technician will draw a small amount of blood and send the sample to the labs to test the viral load and CD4 count.
It often takes a few days for the results to come back. Once they are back, the doctor will likely call to discuss the results with the individual.
Also Check: Do Babies Get Tested For Hiv
Generating The Evidence For Implementation Of Decentralized Hiv Viral Load Testing
Approaches to improve the delivery of HIV viral load testing that are effective, scalable, and sustainable are urgently needed, but under resource constraints, the allocation of resources for decentralizing HIV viral load testing should be based on evidence . If health facility factors are not properly taken into consideration, then implementation of decentralized HIV viral load testing will be jeopardized . Introducing new diagnostic devices into clinics with heavy workloads may cause disruptions in the clinical workflow , which can result in a loss of efficiency and a decline in service quality . Alternatively, the experience of staff in primary health facilities with routine use of rapid diagnostic tests for HIV diagnosis may facilitate the expansion of POC HIV viral load testing . An assessment of the barriers and facilitators is required to address challenges at both the facility and health system levels . In a systematic review of 132 studies, the most common barriers to POC implementation in HIV programs were related to integration into clinical practice, followed by concerns regarding diagnostic accuracy .
Canadas Progress On Meeting The 90
In Canada at the end of 2020, an estimated 62,790 people were living with HIV . Among those living with HIV, an estimated 90% were diagnosed. Of those diagnosed, 87% were estimated to be on treatment and an estimated 95% of persons on treatment had a suppressed viral load .
Canada achieved both the 1st and 3rd 90-90-90 targets set out for 2020.
Canada’s 90-90-90 estimates for 2020 lie within the range reported by other developed countries such as the United States of AmericaReference 10, FranceReference 11, GermanyReference 11, AustraliaReference 12, the NetherlandsReference 13 and FinlandReference 14.
Figure 7. Estimated number and percentage of persons living with HIV, diagnosed, on treatment, and virally suppressed in Canada at the end of 2020 .
This vertical bar graph shows the estimated number of persons in Canada at the end of 2020 who were living with HIV, diagnosed, on treatment, and virally supressed. The horizontal axis shows the four components that were estimated . The vertical axis shows the estimated number of persons, with the low and high ranges associated with each component.
This graph also shows the point estimate and plausible range associated with each of the three 90-90-90 targets. The first target is the percentage of persons living with HIV who are diagnosed the second target is the percentage of persons diagnosed who are on treatment and the third target is the percentage of persons on treatment who had suppressed viral load.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Common Mode Of Transmission Of Hiv
Use Of Poc Assays By Nurses And Health Care Workers Within Hiv Programs
A key component of decentralized, differentiated care services has been the development of POC technologies that have enabled testing to be conducted by nonlaboratory staff in both clinic and community settings . The use of antibody-based POC HIV tests by trained lay workers has been successful and recommended by the WHO . The ease of use and portability of RDTs has allowed them to be implemented in large community-based HIV testing campaigns to increase overall HIV testing coverage for achieving the first 90-90-90 target . Despite the simplicity of RDTs, quality assurance and supply chain management have remained challenging in programmatic settings .
The WHO recommends CD4 count testing to stage disease at HIV diagnosis, and rapid, portable POC CD4 count assays have been developed to measure CD4 counts using venous or capillary whole blood in under 30 min . The Pima CD4 can be operated by nurses in primary care clinics and had acceptable performance characteristics in two meta-analyses, with sensitivities to detect a CD4 count of < 350cells/mm3 of 93% and 92% and specificities of 86% and 87% . POC CD4 count testing has been accepted by patients and health care workers in many resource-limited settings , although failure rates ranging from 0% to 23.3% have been reported . These may have been due to deficiencies in quality assurance procedures, such as inadequate sample collection or machine calibration .
Where To Access Testing Services
Standard HIV testing can generally be accessed through any health provider across the country. Each province is responsible for licensing the laboratories that provide HIV screening and confirmatory testing in its jurisdiction. In general, all provincial Public Health Laboratories provide both screening and confirmatory testing. Reference and specialized services, when required, are provided by the National HIV Reference Serology Laboratory after consultation with the provincial laboratory. It is advisable to contact your testing laboratory to confirm the specimen collection details.
Anonymous or POC testing locations can be found by calling a local HIV/AIDS hotline .
Don’t Miss: Do You Have To Tell Someone You Have Hiv
What Is It Used For
An HIV viral load test may be used to:
- Check how well your HIV medicines are working
- Monitor any changes in your HIV infection
- Diagnose HIV if you think you’ve been recently infected
An HIV viral load is an expensive test and is mostly used when a quick result is needed. Other less expensive types of tests are used more often for diagnosing HIV.
Terms And Technologies Used In Hiv Testing

This section provides detailed definitions and descriptions of the terms and technologies used in HIV testing.
4.2.1 Algorithms
Algorithms for HIV testing have been developed to ensure optimal sensitivity while preserving specificity by confirming reactive results as antibody-positive. The test sequence starts with the most sensitive screening test to identify all those with antibodies. A confirmatory assay is then performed only on the samples that tested reactive/positive on the initial screening test. This ensures that the screen test reaction is due to detection of HIV antibodies rather than a non-specific reaction. In the case of indeterminate or inconclusive results, additional supplementary testing may be necessary to determine if someone is infected with HIV. Each laboratory develops and validates its own algorithm to ensure that it provides the most accurate results possible. The positive predictive value and negative predictive value of a validated algorithm are close to 100%.
A typical laboratory testing algorithm follows:
Figure 3: Laboratory Testing Algorithm
A typical laboratory testing algorithm starts by screening with an enzyme immune assay test. If the EIA is non-reactive, then no HIV infection is present and no further testing is done.
If the initial EIA is reactive, then the EIA test should be repeated two additional times. If neither of the additional EIA tests is reactive, then the test is considered non-reactive, with no evidence of HIV infection.
Read Also: When Did Hiv Emerge In The Population
Study Population And Eligibility Criteria
For the quantitative component, we focused on medical records of PLHIV on ART during the study period, between February 2018 and February 2020. Eligible individuals needed to have been on follow-up care in the same ART clinic for at least 6 months after initiating the ART. For the qualitative component, we interviewed health facility, laboratory, and ART clinic mangers.
Role Of Modeling In Evaluation Of Poc Hiv Viral Load Testing
Modeling population-level impact and cost-effectiveness plays an important role in translating clinical trial findings into a broader set of population estimates . Through modeling, trial results can be translated into standardized impact metrics such as disability-adjusted life years averted or quality-adjusted life years gained, as well as indirect benefits such as reduced HIV transmission . Models are typically individual based and simulate a cohort of individuals with HIV or a population with births, deaths, and dynamic disease transmission . Modeling can help to define the timing and detection threshold for POC viral load assays, based on cost-effectiveness analyses that account for the higher cost of second-line ART . The impact of POC HIV viral load testing on health outcomes can be estimated at multiple levels, including individual patients, the population, or national health systems.
Read Also: Can You Get Hiv From Someone On Medication
Recommendations For Hiv Testing
The purpose of this chapter is to make recommendations on who should be tested for HIV, and at what interval. The chapter also presents recommendations for increasing opportunities to offer HIV testing by integrating HIV testing with testing services for related infections and explores other possible occasions that evidence suggests may be effective in identifying undiagnosed cases. Additional provider and client resources, other HIV testing guidelines, and guidelines for HIV testing in specific contexts are provided in Chapter Five.
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of HIV viral load testing depends on where a patient has the test conducted and whether they have health insurance. Additionally, laboratory and other charges vary. Patients should discuss the costs of testing with their doctor, the laboratory, and/or their health insurance provider.
If paying for HIV testing and treatment is a concern, resources are available to help people with HIV gain access to medical care through the US Department of Health and Human Services: How to Find HIV Treatment Services.
Read Also: Can You Transmit Hiv Through Oral
Introduction And Guiding Principles
A request was made by the Federal/Provincial/Territorial Committee on AIDS for the Public Health Agency of Canada to develop guidelines on HIV testing that reflect the realities facing care providers and their clients, as well as advances in HIV testing policy and practice. To inform the development of this guide, the Agency commissioned a literature review and consultations with key stakeholders, including people living with HIV/AIDS and other affected populations, academics, nurses, physicians, professional associations, non-governmental organizations, policy-makers, community workers, and legal and ethical experts. As a result, the recommendations outlined in the guide are based on the most up-to-date evidence and expert opinion.
Sample Size And Sampling Procedure
For the quantitative component, a sample size of 420 participants was estimated using the Kish Leslie formula for a single population proportion . We considered a 95% confidence interval, a 5% margin of error, and a conservative 50% proportion given unknown extent of adherence to VL testing in our setting. We factored a 10% non-response rate in the sample size calculation. We analyzed data for 395 participants with complete data on the duration on ART. Systematic random sampling was used to select 105 PLHIVs records per HIV clinic depending on total number of PLHIV active in care returned by the EMR database query. We divided the number of potential participants by 105 to establish the sampling interval per study site. If the number of potential participants was not divisible by 105, we rounded off the quotient to the nearest whole number. Beginning with a randomly assigned starting clinic ID, we generated the nth ID until 105 participant IDs were generated.
For the qualitative component, we purposively sampled 12 providers by selecting the three focal persons per health facility for the four participating sites, i.e. health facility, HIV clinic and laboratory manager.
You May Like: How Do You Know If Your Partner Has Hiv
Appendix C: Hiv Transmission Risk
This appendix is condensed from a more detailed technical report, HIV Transmission Risk: A Summary of the EvidenceFootnote 3 which synthesises the scientific evidence on the risk of HIV transmission through sexual activities, injection and other drug use, and mother-to-child transmission. Over 200 references formed the basis of the review, based on a search of the literature for the period between 2001 and March 2012 Footnote 4. The findings from this large body of evidence demonstrated the difficulties inherent in quantifying the risk of HIV transmission, in part due to the role of behavioural and biological co-factors, including viral load and the presence of co-infections, in increasing or decreasing the risk of transmission.
How It Is Done
The health professional drawing blood will:
- Wrap an elastic band around your upper arm to stop the flow of blood. This makes the veins below the band larger so it is easier to put a needle into the vein.
- Clean the needle site with alcohol.
- Put the needle into the vein. More than one needle stick may be needed.
- Attach a tube to the needle to fill it with blood.
- Remove the band from your arm when enough blood is collected.
- Apply a gauze pad or cotton ball over the needle site as the needle is removed.
- Apply pressure to the site and then a bandage.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hiv From Sticking It In Once
Submission And Collection Notes
Freshly drawn whole blood specimens may be stored and/or transported at 2°C – 25°C for up to 24 hours before centrifugation. Following centrifugation, remove plasma from cells immediately, and transfer plasma into sterile screw-capped cryovials.
Plasma can be stored and/or transported at 2°C – 8°C for up to 6 days after separation or at -18°C for up to 12 weeks. If more extended storage of plasma specimens is required, they must be frozen at -60°C.
Unspun whole blood must be received at Public Health Ontarios Laboratory within 24 hours of collection before 2:00 p.m. Monday Friday.