Results Reporting Critical Findings
The CD4 count normal range is 500 to 1500 cell/mm^3. If a patient is left untreated, levels can drop below 200 cells/mm^3, which is one indication for the diagnosis of AIDS. The broad range in the normal value is the product of three variables: the white blood cell count, the percentage of lymphocytes, and the percentage of lymphocytes that bears the CD4 receptor.
How Is Hiv Infection Diagnosed
HIV infection is usually screened for with a test for HIV antibody and antigen . If the screening test is positive, it must be followed with another test, such as a second antibody test that can differentiate HIV-1 and HIV-2. If results of the first and second test do not agree, then an HIV-1 RNA test is performed. If either the second antibody test or the HIV-1 RNA is positive, then you are diagnosed with HIV infection.
What Does Hiv Do To Cd4 Cells
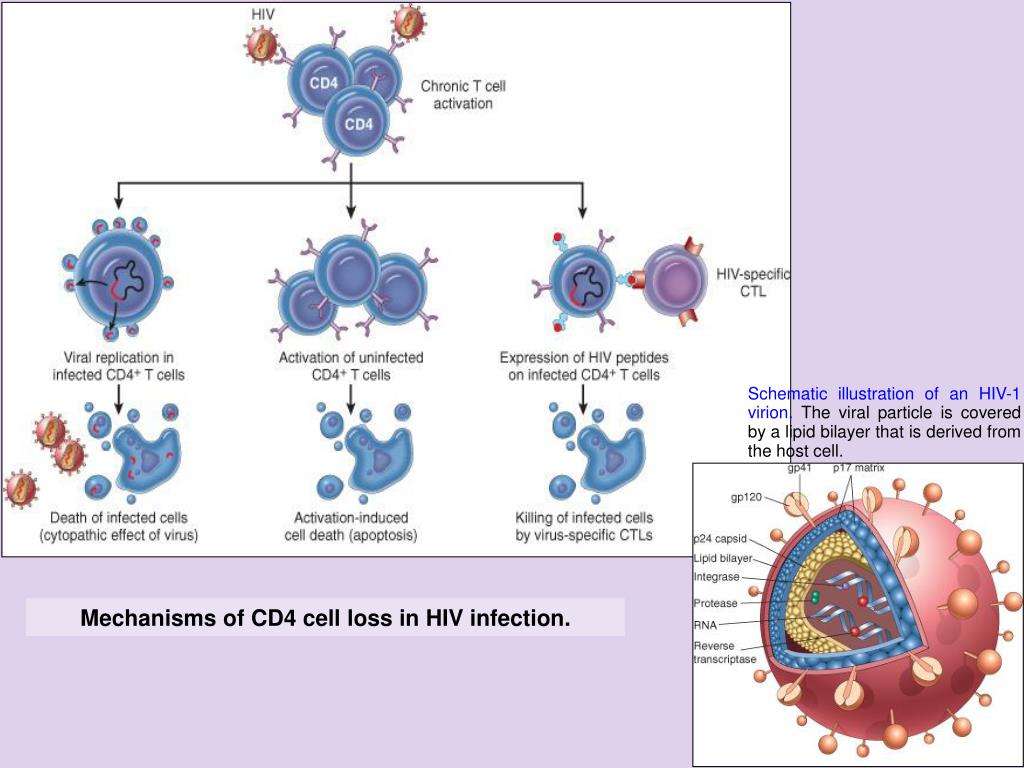
HIV damages your immune system by targeting CD4 cells. The virus grabs on to the surface of a cell, gets inside, and becomes a part of it. When the infected CD4 cell dies, it releases more copies of HIV into your bloodstream.
Those new viruses find and take over more CD4 cells, and the cycle continues. This leads to fewer and fewer HIV-free, working CD4 cells.
HIV can destroy entire “families” of CD4 cells, and then the germs these cells fight have easy access to your body. The resulting illnesses are called opportunistic infections because they take advantage of your body’s lack of defense.
If you have very low CD4 counts, you may need to take drugs to prevent opportunistic infections in addition to taking ART. Once your CD4 count goes up in response to ART, you may be able to stop taking these OI medications.
Recommended Reading: How Do They Do Hiv Test
Immunologic Assessment Of Hiv
The CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is the most widely used measure of HIV-induced damage to the immune system. In the United States, absolute counts of less than 200 cells/mL or a CD4+ percentage of less than 14% is strongly associated with an increased risk of opportunistic infections and is now accepted as definitional for AIDS.222,223
The CD4+ count can be performed manually and read visually, but usually it is done with an automated fluorescence-activated flow cytometer. CD4+ cell counts are vulnerable to biologic and technical errors. The main biologic error in CD4+ cell counts is attributable to a pronounced diurnal variation that can be up to 150 cells/mL in healthy adults but is usually less in patients with lower T-cell counts. This effect can be minimized by performing counts at a fixed time of day. Another common contributor to inaccurate CD4+ cell counts is simple errors in measuring the percentage of lymphocytes on a standard differential white blood cell count. Normal values for total CD4 cell counts, the percentage of lymphocytes that are CD4+ cells, and CD4+/CD8+ count ratios may differ among adults in different countries. Ideally, every clinician managing HIV-infected patients should know the local laboratory CD4+ count standard values and variability.
Mark W. Hull, … Julio S.G. Montaner, in, 2017
Your Cd4 Cell Count When Youre Taking Treatment
Once you start taking HIV treatment, and your viral load starts to fall, your CD4 cell count should gradually increase, over several years.
The rate at which this happens can vary a lot between individuals. It depends in particular on your CD4 count before starting treatment. The higher it was to begin with, the higher it is likely to end up. If you are able to start treatment within a few months of infection, your CD4 count is more likely to recover quickly and completely.
If you are starting treatment with a low CD4 count, you may gain a large number of CD4 cells, without necessarily reaching the same level as a person who doesnt have HIV. This doesnt mean that you will have health problems, as long as you maintain an undetectable viral load.
CD4 cells
The primary white blood cells of the immune system, which signal to other immune system cells how and when to fight infections. HIV preferentially infects and destroys CD4 cells, which are also known as CD4+ T cells or T helper cells.
Falls in CD4 counts have more serious implications in people who have started treatment at low counts. This means it is especially important to keep taking treatment that suppresses your viral load to an undetectable level. That way, whether or not your CD4 count continues to rise, viral load should stay at a satisfactory level.
However, if your viral load increased, or you had HIV-related symptoms, then your CD4 cell count would be monitored again.
You May Like: Can You Get Hiv Without Being Sexually Active
What Does The Cd4 Count Test Result Mean
A CD4 count is typically reported as an absolute level or count of cells . A normal CD4 count ranges from 5001,200 cells/mm³ in adults and teens. Sometimes results are expressed as a percent of total lymphocytes .
In general, a normal CD4 count means that the persons immune system is not yet affected by HIV infection. A low CD4 count indicates that the persons immune system has been affected by HIV and/or the disease is progressing. However, any single CD4 test result may differ from the last one even though the persons health status has not changed. Usually, a health practitioner will take several CD4 test results into account rather than a single value and will evaluate the pattern of CD4 counts over time.
CD4 counts that rise and/or stabilize over time may indicate that the person is responding to treatment. If someones CD4 count declines over several months, a health practitioner may recommend starting prophylactic treatment for opportunistic infections such as Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia or candidiasis .
Why Do I Need A Cd4 Count
Your health care provider may order a CD4 count when you are first diagnosed with HIV. You will probably be tested again every few months to see if your counts have changed since your first test. If you are being treated for HIV, your health care provider may order regular CD4 counts to see how well your medicines are working.
Your provider may include other tests with your CD4 count, including:
- A CD4-CD8 ratio. CD8 cells are another type of white blood cell in the immune system. CD8 cells kill cancer cells and other invaders. This test compares the numbers of the two cells to get a better idea of immune system function.
- HIV viral load, a test that measures the amount of HIV in your blood.
You May Like: Do I Have Hiv Or Aids
In The Long Term You May Only Need The Viral Load Test
As long as your viral load stays undetectable, frequent CD4 counts arent useful.
- If your CD4 level stays at 300 to 500 cells per microliter , you should get the CD4 test only once a year.
- If your CD4 level is over 500 cells/L, you shouldnt need more CD4 tests, unless your condition changes.
- You usually get a viral load test 2 to 8 weeks after you start or change treatment. Usually you get tested every three to four months after that. If your viral load stays very low for more than two years, you may only have a viral load test every six months.
Unneeded Cd4 Tests Can Cause Problems
Your CD4 count can vary a lotdepending on the time of day, the lab, and whether you have an infection, such as the flu. The count can vary due to exercise, lack of sleep, or smoking. This is not important if your viral load stays undetectable. But it can still cause worry. It can lead to more unneeded tests. It can even lead to inappropriate changes in treatment.
Also Check: How Do You Get Rid Of Hiv
Is A Cd4 Cell Count Used In Conditions Other Than Hiv Infection
Yes. It may be ordered when a person has had an organ transplant to help evaluate the effect of immunosuppressive medications. In transplantation, the immune system must be suppressed so that it does not attack the transplanted organ and cause rejection. In this case, it is desirable to have low levels of CD4 cells, and a decreased count shows that the drug is working. A CD4 count may be repeated periodically to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
CD4 counts are sometimes done in conjunction with CD8 counts. CD8 cells are another type of lymphocyte called T-suppressor cell or cytotoxic T cell. CD8 cells identify and kill cells that have been infected with viruses or that have been affected by cancer.
Evaluation of CD4 and CD8 cells may be used to help classify lymphomas. Typically, several markers on the surface of lymphocytes in addition to CD4 and CD8 are evaluated. The tests help determine whether the lymphoma is due to the proliferation of B lymphocytes or T lymphocytes and which specific type. This information is useful in determining appropriate therapy.
These tests may also help diagnose DiGeorge syndrome, a rare congenital disorder characterized by, among other things, low levels of T cells in the blood. For more information on DiGeorge syndrome, visit the Mayo Clinic web site.
What Else Can Affect Your Cd4 Count
Things other than the HIV virus can influence how high or low your CD4 count is.
An infection like the flu, pneumonia, or a herpes simplex virus can make your CD4 count go down for a while.
Your CD4 count will go way down when you’re having chemotherapy for cancer.
Even things as simple as smoking or changes in sleep or exercise habits can make a difference in the count. Regular alcohol use can also lower CD4 counts.
To get the most accurate and helpful results for your CD4 count, try to:
- Get tested on a normal day after typical sleep and exercise.
- Use the same lab each time.
- Wait for at least a couple of weeks after you’ve been sick or gotten a shot before you get a test.
Recommended Reading: How Many Stages Does Hiv Have
How To Increase Cd4 Count
Theres no cure for HIV/AIDS, but many different drugs are available to control the virus. Such treatment is called antiretroviral therapy, or ART. Each class of drug blocks the virus in different ways. ART is now recommended for everyone, regardless of CD4 T cell counts. Its recommended to combine three drugs from two classes to avoid creating drug-resistant strains of HIV.
The classes of anti-HIV drugs include:
- Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors turn off a protein needed by HIV to make copies of itself. Examples include efavirenz , etravirine and nevirapine .
- Nucleoside or nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors are faulty versions of the building blocks that HIV needs to make copies of itself. Examples include Abacavir , and the combination drugs emtricitabine/tenofovir , Descovy , and lamivudine-zidovudine .
- Protease inhibitors inactivate HIV protease, another protein that HIV needs to make copies of itself. Examples include atazanavir , darunavir , fosamprenavir and indinavir .
- Entry or fusion inhibitors block HIVs entry into CD4 T cells. Examples include enfuvirtide and maraviroc .
- Integrase inhibitors work by disabling a protein called integrase, which HIV uses to insert its genetic material into CD4 T cells. Examples include raltegravir and dolutegravir .
What Are My Treatment Options

In general, treatment is recommended regardless of whether the CD4 count is low or within the normal range. You and your health care provider should discuss your treatment options to determine what will work best for you. The Mayo Clinic web page HIV/AIDS: Treatments and drugs has detailed information on various therapies.
You May Like: What Does Hiv Feel Like
What The Cd4 Percentage Tells Us
The CD4 percentage represents the percentage of total lymphocytes that are CD4 cells and is measured using the same blood test as that for the absolute CD4 count.
Typically, HIV-negative people will have a CD4 percentage of about 40%, while HIV-infected people’s CD4 percentage can be as low as 25% or less. Clearly, the higher the percentage, the more robust the immune response.
If your CD4 count is lower than you expect, the CD4 percentage can put it into better perspective by telling this whether this is an actual change or just a fluctuation.
How Do Cd4 Levels Affect Viral Load
The goal of ART is to lower the level of HIV in your blood â your âviral loadâ â to an undetectable level. This means the level of HIV in your blood is so low that it doesnât show up in tests.
You still have the virus. And your HIV levels will grow again if you stop treatment. But properly followed, ART can control HIV levels so well that doctors canât find HIV with typical lab tests.
The results are twofold.
First, as ART lowers your viral load, it gives your immune system a chance to make more CD4 cells. These help you fight infections and HIV-related cancers. Your doctor can tell because your CD4 levels start to go up.
Second, you become far less likely to pass HIV on to sexual partners. Thatâs because people who maintain an undetectable viral load with ART have almost no chance of passing HIV on to others through sex.
With careful ART treatment, many people can go on for decades or more without progressing to the third and most serious stage of HIV infection. Thatâs the stage known as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS.
ART is so effective that most people in the U.S. with HIV who get ART will never develop AIDS.
Thatâs why ART is so important. Without it, your HIV levels will grow and your CD4 levels will fall. Eventually, typically in about 10 years without treatment, you will develop AIDS.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hiv From Topping
Frequency And Timing Of Testing
After you start HIV treatment, not all lab tests will be conducted at every medical visit. Some will occur every few visits. Others will depend on whether you are stable on HIV treatment and doing well. View this chart about the timing of various tests and talk to your provider about what is recommended for you.
Topics
What Can You Do To Look After Yourself
The most important thing is to start HIV treatment, and to take it exactly the way you are advised to .
Attend your HIV clinic for regular check-ups. These monitor how your treatment is working, with regular screening for other health problems. Having a good relationship with your healthcare team is important, so that you feel able to be honest about your health, lifestyle, adherence and any other issues, to help you receive the best possible care and support.
“Once your CD4 count improves, with continued treatment and care, your life expectancy is very good.”
Register with a GP for non-HIV-related health problems. GPs can give you an annual flu vaccination , and provide advice on lifestyle factors that help keep you well, including healthy eating, exercise and giving up smoking.
While your CD4 count is low , ensure your drinking water is free from infection and take extra care in preparing and storing food to avoid food poisoning. Be careful to avoid infections if you are handling animals or gardening. Your healthcare team can talk to you about any risks and give you advice.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Cure Hiv
How Do I Know If I Have Hiv
The only way to know for sure if you have HIV is to get tested. Testing is relatively simple. You can ask your health care provider for an HIV test. Many medical clinics, substance abuse programs, community health centers, and hospitals offer them too.
To find an HIV testing location near you, use the HIV Services Locator.
HIV self-testing is also an option. Self-testing allows people to take an HIV test and find out their result in their own home or other private location. You can buy a self-test kit at a pharmacy or online. Some health departments or community-based organizations also provide self-test kits for a reduced cost or for free.
What Is Being Tested
CD4 cells are white blood cells called T lymphocytes or T cells that fight infection and play an important role in immune system function. CD4 tests measure the number of these cells in the blood and, in conjunction with an HIV viral load test, help assess disease status in a person who has been diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus infection.
CD4 cells are made in the thymus gland and they circulate throughout the body in the blood and lymphatic system. They are so called because they have markers on their surfaces called clusters of differentiation . The CD number identifies the specific type of cell.
CD4 cells are sometimes called T-helper cells. They help to identify, attack, and destroy specific bacteria, fungi, and viruses that cause infections. CD4 cells are also a major target for HIV, which binds to the surface of CD4 cells, enters them, and either replicates immediately, killing the cells in the process, or remains in a resting state, replicating later.
If HIV goes untreated, the virus gets into the cells and replicates, the viral load increases, and the number of CD4 cells in the blood gradually declines. The CD4 count decreases as the disease progresses. If left untreated, this process may continue for several years until the number of CD4 cells drops to a low enough level that symptoms associated with AIDS begin to appear.
CD4 tests may be used occasionally in other conditions, such as lymphomas and organ transplantation .
Don’t Miss: How Does Hiv Affect The Immune System
How Are T Cells Linked To Hiv And Aids
HIV enters its genetic information into helper T cells to make copies of itself. When this happens, the helper T cells die. This severely disrupts the immune response. Low levels of helper T cells mean killer T cells and other white blood cells do not receive as much information about pathogens in the body. As a result, disease-causing bacteria and viruses multiply with minimal detection.
When the amount of helper T cells falls below 200 cells/mm3 , a person may receive an AIDS diagnosis. But healthcare professionals will also take into account other variables such as overall white blood cell count and the percentage of lymphocytes.
AIDS is the most severe stage of HIV. When a person receives an AIDS diagnosis, their immune system is severely compromised, and they are at risk for opportunistic illnesses. The survival rate without treatment at this stage is typically
200 cells/mm3 , they will likely receive an AIDS diagnosis.
When a person has HIV, a healthcare professional will collect a blood sample and request a CD4 count. The CD4 count helps determine how many helper T cells a person has.
But when analyzing a CD4 count, healthcare professionals must take into account that:
- CD4 levels could be lower in the morning
- stress and fatigue may affect CD4 levels
- corticosteroid levels could increase or decrease CD4 levels
The CD4 count helps healthcare professionals monitor HIV progression and if the person is at risk for opportunistic illnesses.
100â150cells/mm3 after 1 year.