Timing Of Viral Entry Into The Brain
In the absence of technology for imaging the HIV reservoirs, extrapolations of viral entry into the central nervous system have been made by viral detection in the CSF. A recent study shows that HIV RNA could be detected in the CSF in 15 of 18 patients as early as 8 days after estimated HIV transmission. On average, the CSF HIV RNA level was 2.42 log copies/ml lower than that in plasma. There were no cases in which the CSF HIV RNA level exceeded that in plasma . However, the presence of virus in the CSF does not necessarily mean that it has established reservoir in the brain. In fact in some patients even at autopsy no evidence of any productive viral infection of other neuropathological changes could be found even in the preantiretroviral era. This situation suggests that timing of viral invasion into the brain may be variable and there might be a window of opportunity to clear the virus from the periphery before it enters the brain at least in some individuals.
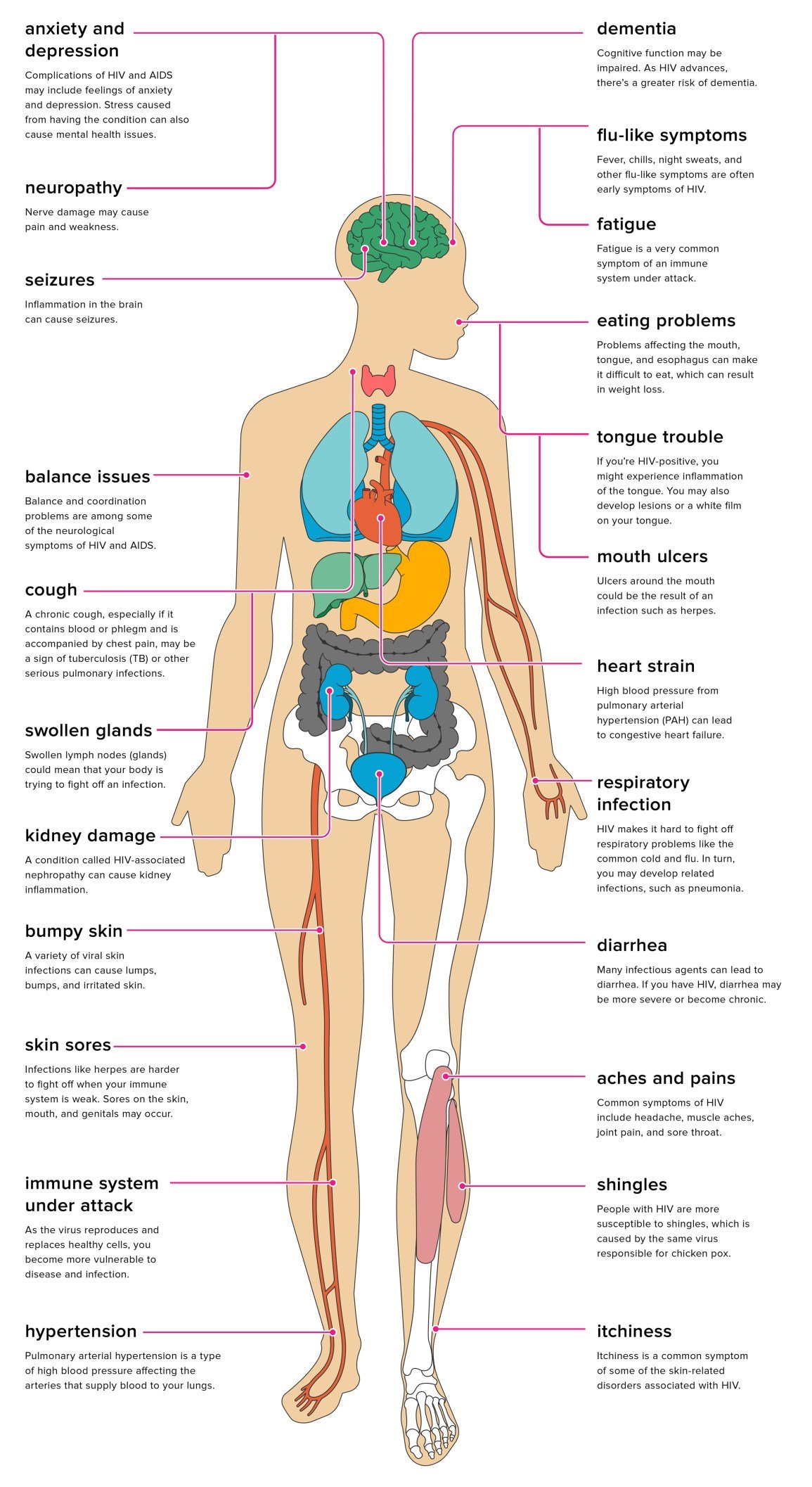
Neurological Complications Associated With Hiv And Aids
HIV doesnt appear to attack nerve cells. But as virus-related inflammation damages the CNS, people with advanced HIV or AIDS may experience various symptoms, such as confusion, forgetfulness, behavioral issues, headaches, weakness, and numbness in the extremities.
Complications from the virus or drugs to treat it may include the following :
- Pain
- Coordination issues and gait disorders
- Problems with swallowing
- Vision loss
- Coma
In addition to the opportunistic infections listed above, people with HIV or AIDS are vulnerable to other viruses and microbes that affect the CNS, including Cryptococcus neoformans, which causes Cryptococcal meningitis, and Treponema pallidum, which causes neurosyphilis, according to the National Institutes of Health.
Other neurological complications unrelated to infections are also possible, such as AIDS dementia complex or HIV-associated dementia, CNS lymphomas, neuropathies , vacuolar myelopathy , and various psychological and neuropsychiatric disorders.
Clinical Features Of Hiv Infection
In primary infection of HIV-1, patients may be asymptomatic though sometimes the disease is self-limiting. Within the incubation period of about 6 weeks, patients can present with a mononucleosis-like syndrome, which is characterized by fever, cough, painful swallowing, myalgias, arthralgias, diarrhea as well as maculopapular rash and lymphadenopathy . In most circumstances, the symptoms are usually mild as contrasted to severe cases, where pneumonitis, oropharyngeal and esophageal ulcers may occur. Encephalitis, meningitis, neuropathy, radiculopathy and myelopathy are not common sickneses in HIV infection. Although the true incidence of this syndrome is not precisely known, it may also depend on the degree of exposure to the virus, it may be as high as over 50% in persons who acquire HIV-1 infection .
World Health Organization categorized an adult or adolescent as having AIDS in presence of at least two of the major signs in combination with one of the minor signs .
| Major signs |
3.3.3.2. Coagulopathy in HIV patients
Don’t Miss: How Hiv Affects The Immune System
Effects Of Antiretroviral Drugs On The Body
Antiretroviral therapy helps people who have HIV live longer, healthier lives and lowers their risk of spreading the virus. The drugs can have side effects, many of which go away with time. Overall, the benefits outweigh the risks.
There are several kinds of antiretroviral drugs, and your doctor might combine them in different ways. Side effects can vary from drug to drug or from person to person.
Common side effects of these drugs include:
- Upset stomach and vomiting
Kaminski, D. The Body: The Complete HIV/AIDS Resource: “HIV and Inflammation: A New Threat.”
Summit Medical Group: “HIV and the Eyes.”
American Academy of Ophthalmology: “How Does HIV/AIDS Affect the Eye?”
American Heart Association: “HIV and Cardiovascular Disease,” “Wellness Checklist: Know Where You Stand.”
American Family Physician: “Common Side Effects of HIV Medicines.”
AIDS.gov: “Staying Healthy with HIV/AIDS: Potential Related Health Problems: Kidney Disease.”
New York State Department of Health: âHIV: The Basics.â
Merck Manual Consumer Version: âHuman Immunodeficiency Virus Infection.â
Mayo Clinic: âHIV/AIDS.â
Nemours/TeensHealth: âHIV and AIDS.â
AIDSinfo: âAIDS-Defining Condition,â âOpportunistic Infection ,â âSide Effects of HIV Medicines.â
CDC: âAIDS and Opportunistic Infections.â
Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice: âHIV and the Gastrointestinal Tract.â
American Dental Association: âHIV/AIDS and Dental Health.â
HIV.gov: âHIV Treatment.â
Frequency Of Administration Type And Amount Of Blood Products
Blood components: Since 2004 only 2 HIV transmissions through blood components have been reported in Germany . HIV is transmitted if 1 HID is present in the administered blood component . There is evidence that immediate initiation of HIV post exposure prophylaxis can prevent an infection after needle stick injury in individual cases .
Plasma derivatives: Transmission of HIV by plasma derivatives occurred between 1979 and 1989 primarily via factor VIII, factor IX and prothrombin complex concentrates . HIV has never been transmitted via albumin, antithrombin III and i.m. or i.v. immunoglobulin preparations, not even before the introduction of specific process steps for the depletion and inactivation of viruses. The implementation of donor selection, antibody screening and inactivation procedures has made a transmission of enveloped viruses no longer possible.
Recommended Reading: Does Walmart Sell Hiv Tests
What’s The Difference Between Hiv And Aids
HIV/AIDS is often written as one word with one meaning. However, HIV and AIDS are different things.
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. A person becomes infected with HIV when the virus enters their blood stream.
HIV attacks the immune system, which is the bodys defence against disease. If a persons immune system is severely damaged by the virus, they will develop AIDS . This means they are likely to get infections and illnesses that their body would normally fight off.
Being diagnosed with HIV does not mean a person has AIDS or that they are going to die. Treatments slow down damage to the immune system so that people with HIV can remain well, and live healthy and fulfilling lives.
How Is An Hiv Test Performed
Before taking an HIV test:
- Ask the clinic what privacy rules it follows.
- Ask your healthcare provider any questions you have about HIV, AIDS, or the HIV test.
To do the HIV test, a small sample of blood is taken from your arm. The blood is sent to a lab and tested for HIV.
Home testing is available. The sample can be obtained via oral secretions , or a blood sample from a finger-stick test strip that is then mailed to a laboratory for screening. Positive results must be confirmed by your doctor before a diagnosis of HIV infection can be established.
Some clinics perform HIV tests without ever taking your name . You must go back to the clinic to get your results. A positive test means you have HIV. A negative test means no signs of HIV were found in your blood.
If your test comes back positive, your healthcare provider is likely to recommend other tests to assess your health. These may include a complete blood count , along with:
- Viral hepatitis screening.
You May Like: Can You Get Hiv Without Having Sex
Cancers Common In People With Hiv Infection
Kaposi sarcoma Kaposi Sarcoma Kaposi sarcoma is a skin cancer that causes multiple flat pink, red, or purple patches or bumps on the skin. It is caused by human herpesvirus type 8 infection. One or a few spots may appear… read more , a cancer caused by a sexually transmitted herpesvirus, appears as painless, red to purple, raised patches on the skin. It occurs mainly in men who have sex with men.
Cancers of the immune system . Often, lymph nodes in the neck, under the arms, or in the groin enlarge rapidly and painlessly… read more ) may develop, sometimes first appearing in the brain. When the brain is affected, these cancers can cause weakness of an arm or a leg, headache, confusion, or personality changes.
Having AIDS increases the risk of other cancers. They include cancer of the cervix, anus, testes, and lungs as well as melanoma and other skin cancers. Men who have sex with men are prone to developing cancer of the rectum due to the same human papillomaviruses Human Papillomavirus Infection Human papillomavirus causes warts. Some types of HPV cause skin warts, and other types cause genital warts . Infection with some HPV… read more that cause cancer of the cervix in women.
Effects On The Immune System
HIV primarily affects the body by targeting and damaging cells in the immune system. The immune system protects the body against viruses, bacteria, and fungi.
After attaching itself to a type of white blood cell called a CD4 T cell, the virus merges with it. These T cells are an important part of the immune system.
Once inside the CD4 T cell, the virus multiplies. It damages or destroys the cell, then moves on and targets other cells.
A persons CD4 T-cell count is an indication of the health of their immune system.
A healthy CD4 T-cell count is 5001,600 cells/mm3 of blood. If a person does not receive treatment for HIV, their CD4 T-cell count drops over time.
When it drops below 200 cells/mm3, the persons immune system is significantly impaired, making them more susceptible to opportunistic infections.
Read Also: How Does The Immune System Fight Hiv
What Is The Outlook For Someone With Hiv/aids
If you are diagnosed with HIV and you start ART soon after, your immune system will not be as compromised. If you continue to take your medicines every day, your outlook is very good.
ART can keep blood levels undetectable but cannot entirely rid the body of the virus . If you do not keep up on your medication, the virus goes back into the blood.
If you have HIV and dont treat it, it can take about 10 years to lead to AIDS. If you have AIDS and dont treat it, the survival rate is about three years.
It is so important to know that people who have HIV and who follow treatment guidelines are able to live full lives for nearly as long as HIV-negative people.
What Are The Symptoms Of Kidney Disease
Kidney disease can advance very slowly. Slowly worsening kidney disease is called chronic kidney disease.
As kidney disease gets worse, a person may have swelling of the legs, feet, or ankles . Symptoms of advanced chronic kidney disease can include:
- Increased or decreased urination
- Feeling tired or having trouble sleeping
- Nausea and vomiting
- Itching or numbness
Blood and urine tests are used to detect kidney disease. Care for people with HIV includes testing for kidney disease.
Don’t Miss: Can You Gain Weight With Hiv
How A Weak Immune System Affects Your Skin
For some people with HIV, skin conditions are one of the most obvious signs of infection. Skin conditions can appear in the earliest stage of HIV, but may increase in frequency as the disease progresses.
HIV weakens your immune system, so your body is more likely to develop infection since it cant fight disease effectively. Common skin conditions that people with HIV experience include:
- Bacterial infections
- Inflammatory dermatitis
- Skin cancer
Inflammatory dermatitis can take many forms, and its common for people with HIV. Dermatitis can appear like areas of dry skin or red and itchy patches. Some examples of skin infections that people with HIV may contract include syphilis, oral thrush, and shingles.
Another condition that can develop if you have HIV is lipodystrophy. HIV can cause fat distribution in the body to change, resulting in fat loss around the face or fat buildup between the shoulder blades or elsewhere.
Taking antiretroviral medications for HIV generally helps reduce the number of skin conditions that people with HIV develop. Along with taking medication, getting regular skin exams and seeking treatment for specific skin conditions can help them from getting worse. For patients bothered by fat loss from HIV lipodystrophy, Sculptra® Aesthetic at Z-Roc Dermatology is an injectable filler to fill contours and improve your appearance.
Trust our team for all your skin care needs. Make an appointment at Z-Roc Dermatology online or call our office today.
Effects Of Hiv/aids On The Body

The human immunodeficiency virus seeks and destroys CD4+ cells, a type of T lymphocyte . T cells are critical to the immune system. Theyre responsible for warding off diseases and most infections, including viral infections.
HIV targets the type of cells that would normally fight off an invader like HIV. As the virus replicates, it damages or destroys the infected CD4+ cell and produces more virus to infect more CD4+ cells. Without treatment, this cycle continues in most infected people until the immune system is badly compromised, leaving them open to many serious infections and illnesses. Many of the illnesses that people compromised immune systems get are rare in people with functioning immune systems.
How quickly the virus progresses varies from person to person. Factors like your age, overall health, and how quickly youre diagnosed and treated can make a difference.Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is the final stage of HIV. At this stage, the immune system is severely weakened, and the risk of contracting opportunistic infections is much greater. Not everyone with HIV will go on to develop AIDS.
Importantly, many of the effects described here are related to the failure of the immune system in progressing HIV and AIDS. Many of these effects are preventable with early antiretroviral treatment, which can preserve the immune system. However, for anyone without access to effective antiretroviral treatment, these effects remain possible.
You May Like: Can You Get Hiv From Hand To Genital Contact
The Science Of Hiv And Aids
Key Points
- HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus, a pathogen that works by attacking the human immune system.
- HIV specifically targets CD4 cells, the bodys principal defenders against infection, using them to make copies of themselves.
- Antiretroviral drugs target specific stages of the HIV lifecycle to stop HIV from replicating.
Explore this page to find out more about , , and .
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus, a pathogen that works by attacking the human immune system. It belongs to a class of viruses called retroviruses and more specifically, a subgroup called lentiviruses, or viruses that cause disease slowly. 1
HIV cannot replicate on its own, so in order to make new copies of itself, it must infect cells of the human immune system, called CD4 cells. CD4 cells are white blood cells that play a central role in responding to infections in the body. 2
Over time, CD4 cells are killed by HIV and the bodys ability to recognise and fight some types of infection begins to decline. If HIV is not controlled by treatment, the loss of CD4 cells leads to the development of serious illnesses, or opportunistic infections. In people with normal CD4 cell levels, these infections would be recognised and cleared by the immune system. 3
Can Neurological Complcations Develop In Individuals Treated With Antiretroviral Therapy
Even when HIV is well controlled with ART, many infected individuals still develop HIV-associated neurological and cognitive difficulties. This is because many drugs used to combat HIV cannot cross the protective layer called the blood-brain barrier and enter the brain, and even those that can may not completely control the virus in the brain. Antiretroviral drugs can also become toxic after long-term use and cause neurological side effects.
You May Like: How Do You Get Hiv
Hiv Effects On The Nervous System
About half of people with AIDS have nerve problems related to the virus. Infection or inflammation can damage your spinal cord or brain and keep your nerve cells from working the way they should. Some medications can also affect your nervous system.
Brain
Inflammation in your brain and spinal cord can lead to confusion and other thinking problems as well as weakness, headaches, seizures, and balance problems.
When AIDS is far along, you might get dementia and have problems remembering things.
Having HIV can also affect your mental health. Many people living with it have depression or anxiety. Mental health professionals and support groups can help you work through your concerns and manage your life with HIV.
Nerves
The opportunistic infection cytomegalovirus can attack your nerves, making it hard for you to control your arms and legs or your bladder.
Itâs common for tiny holes to form in spinal fibers when people with AIDS donât get treatment. This is called vacuolar myelopathy and causes trouble walking.
HIV or the drugs that treat it can also damage nerves all over your body, causing neuropathy. You might have pain, numbness, weakness, burning, stiffness, or tingling.
Antiretroviral therapy to treat HIV can lower your risk of getting these conditions or complications. If a medication is causing the problems, your doctor might switch you to a different one.
Budding Off The Host Cell
Now that the proteins are assembled from the apparatus and the long strands have completed the viral RNA, the virus buds off the living host cell. In the majority of cases, the budding process completely destroys the host cell, which means that more and more cells are destroyed as the virus multiplies.
Once the infection creates millions of new virus cells by hijacking the healthy DNA in the hosts body, it comes closer to the person developing AIDS. With most viruses, the immune system fails to identify the virus inside the cells, which is why it starts destroying the infected cells before the virus manages to make new copies.
Drugs that can stop and slow down this process are called protease inhibitors. Nowadays, the most popular treatment is the antiretroviral treatment, where people infected with HIV use medicines to treat this infection. By combining several medicines that target the life cycle of HIV, such medicines prevent the reproduction of HIV. This helps people live longer and healthier lives.
Unfortunately, a cure for HIV is yet to be discovered.
Also Check: Can Breast Milk Transmit Hiv
Strategies For Preventing The Transmission Of Hiv
|
Condoms made of latex provide good protection against HIV , but they are not foolproof. Oil-based lubricants should not be used because they may dissolve latex, reducing the condom’s effectiveness.
Other measures can help. For men, circumcision, an inexpensive, safe procedure, reduces the risk of becoming infected during vaginal intercourse with an infected woman by about half. Whether circumcision reduces the risk of HIV infection in other circumstances is unclear. Because circumcision provides only partial protection against HIV infection, people should also use other measures to prevent HIV infection. For example, if either partner has a sexually transmitted disease or HIV infection, it should be treated, and condoms should be used correctly and consistently.