What Is The Impact Of Treatment For Hepatitis C Virus Infection On Anemia In Hiv
HCV coinfection is estimated to occur in 30% of HIV-infected individuals in the United States . Ribavirin in combination with IFN or pegylated interferon IFN is the standard of care for treatment of HCV infection, but it has been shown to cause anemia, frequently leading to dosage reduction and potentially suboptimal outcomes .
When treating patients with ribavirin-related anemia, hemoglobin levels should be monitored, and epoetin alfa should be added to the treatment regimen in the presence of anemia. In patients with HCV infection alone, epoetin alfa has been shown to effectively treat anemia associated with ribavirin therapy, to allow maintenance of ribavirin dose, and to reduce discontinuation rates, and it may also improve quality of life . The relative percentage of patients who are able to tolerate optimal doses of ribavirin can be expected to increase by 40%50% with receipt of epoetin alfa therapy . Studies of the utility of epoetin alfa therapy for patients infected with both HIV and HCV are currently in progress.
What Is The Effect Of Haart On The Prevalence Of Anemia In Hiv
Although the prevalence of severe anemia has decreased since the introduction of HAART, mild-to-moderate anemia continues to be common . A subset of 1624 patients was evaluated as part of the EuroSIDA study . Before HAART was initiated, mild anemia was present in 64% of subjects, and severe anemia was present in 1.5% of subjects . After 6 months of HAART therapy, mild anemia was present in 52% of subjects, and severe anemia was present in 1.2%. After 12 months, further improvements were recorded, with 45.6% of patients demonstrating mild anemia and 0.6% demonstrating severe anemia .
Prevalence of anemia during HAART in a cohort of 1624 patients in the EuroSIDA study . No anemia was defined as a hemoglobin level of > 14 g/dL for men and > 12 g/dL for women mild anemia was defined as a hemoglobin level of 814 g/dL for men and 812 g/dL for women and severe anemia was defined as a hemoglobin level of < 8 g/dL for both men and women.
Who Orders My Blood Tests
Your doctor typically orders blood tests for you during a physical, checkup, or an appointment intended to screen for a specific condition.
Its possible to order your own blood tests without a doctor through laboratories like LabCorp and Quest Diagnostics, but health insurance may not cover these tests.
While such blood tests may more accessible and convenient, it may be harder to interpret the results without a medical professional.
Some blood testing facilities may also not give you accurate results.
One infamous case of this is Theranos. The California biotechnology firm shut down in 2018 when an investigation uncovered lies and fraud around the accuracy of its private blood-testing technology.
Currently, litigation is underway against the founder and chief executive of the company, Elizabeth Holmes.
You May Like: Hiv Hair Loss Symptom
What Do The Results Mean
CD4 results are given as a number of cells per cubic millimeter of blood. Below is a list of typical results. Your results may vary depending on your health and even the lab used for testing. If you have questions about your results, talk to your health care provider.
- Normal: 500â1,200 cells per cubic millimeter
- Abnormal: 250â500 cells per cubic millimeter. It means you have a weakened immune system and may be infected with HIV.
- Abnormal: 200 or fewer cells per cubic millimeter. It indicates AIDS and a high risk of life-threatening opportunistic infections.
While there is no cure for HIV, there are different medicines you can take to protect your immune system and can prevent you from getting AIDS. Today, people with HIV are living longer, with a better quality of life than ever before. If you are living with HIV, it’s important to see your health care provider regularly.
What Causes Anemia In Hiv
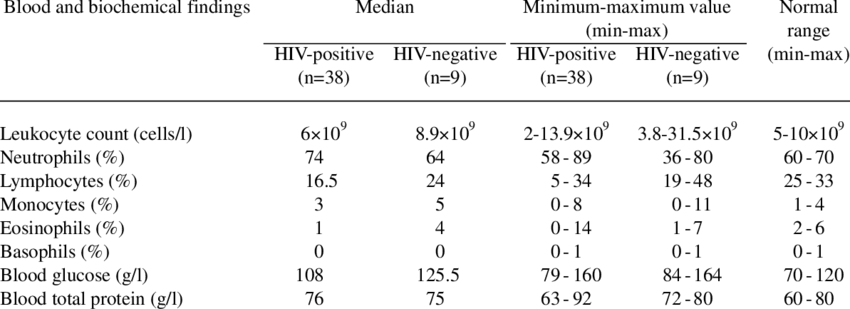
An obvious cause of anemia in patients with HIV infection is blood loss. Blood loss may be associated with such conditions as neoplastic disease or gastrointestinal lesions that accompany opportunistic cytomegalovirus infection. Other than blood loss, the pathophysiology of HIV-associated anemia may involve 3 basic mechanisms: decreased RBC production, increased RBC destruction, and ineffective RBC production.
. Decreased RBC production may be a consequence of infiltration of the bone marrow by neoplasm or infection , use of myelosuppressive medications , HIV infection itself , a decreased production of endogenous erythropoietin, a blunted response to erythropoietin , or hypogonadism.
Drugs that commonly cause myelosuppression in HIV-infected patients.
Increased RBC destruction . Increased or premature RBC destruction in the spleen or the circulator system may occur in patients with HIV infection. Hemolytic anemia may result from RBC autoantibodies, hemophagocytic syndrome, disseminated intravascular coagulation, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, or glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency . Hemolysis may also develop as a consequence of the use of various medications .
Also Check: How Did Nba Youngboy Get Herpes
Why Is It Important To Get Tested Regularly
A single CD4 or viral load test result only represents a snapshot in time. Its important to track both of these and consider trends in test results rather than only looking at individual test results.
Keep in mind that these values may vary for many reasons. The time of day, any illnesses, and recent vaccinations can all affect CD4 count and viral load. Unless the CD4 count is very low, this fluctuation isnt usually worrisome.
Regular viral load tests, not CD4 counts, are used to determine the effectiveness of HIV therapy. The goal of HIV therapy is to reduce or suppress the viral load to an undetectable level.
According to HIV.gov, HIV viral load is typically undetectable below levels of 40 to 75 copies/mL. The exact number depends on the lab that analyzes the tests.
What Is It Used For
A CD4 count may be used to:
- See how HIV is affecting your immune system. This can help your health care provider find out if you are at higher risk for complications from the disease.
- Diagnose AIDS
- The names HIV and AIDS are both used to describe the same disease. But most people with HIV don’t have AIDS. AIDS is diagnosed when your CD4 count is extremely low.
- AIDS is the most severe form of HIV infection. It badly damages the immune system and can lead to opportunistic infections. These are serious, often life-threatening, conditions that take advantage of very weak immune systems.
You may also need a CD4 count if you’ve had an organ transplant. Organ transplant patients take special medicines to make sure the immune system won’t attack the new organ. For these patients, a low CD4 count is good, and means the medicine is working.
Recommended Reading: Does Hiv Cause Hair Loss
What Is The Impact Of Anemia In Hiv
Impact of fatigue. Fatigue is a common symptom of HIV infection and is associated with impaired physical functioning, psychological distress, and decrements in quality of life . Although the etiology of HIV-related fatigue may be multifactorial , anemia is considered an important contributing factor or underlying cause .
In a pre-HAART study of 112 patients by Darko et al. , 50% of HIV-positive subjects reported that fatigue interfered with their daily activities, whereas none of the comparison subjects reported problems with fatigue. Employment problems and sleep disturbances were shown to contribute to morbidity and disability in the HIV-infected group. In a later study of 427 patients by Breitbart et al. , 52.7% of subjects responded positively to both the lack of energy item on the Memorial Symptom Assessment Scale and the persistent or frequent fatigue item on the AIDS-specific Physical Symptom Checklist and were subsequently classified as having fatigue. Serum hemoglobin levels were significantly lower than in nonfatigued patients . A substudy of 148 patients from the ongoing multinational INITIO trial of 913 antiretroviral therapynaive patients revealed an independent relationship between low baseline levels of hemoglobin and overall quality of life .
The Complete Blood Count
The most common laboratory test is the complete blood count . It examines the components of blood, including red and white blood cells and platelets. Most test results are reported as amounts in a sample of blood or as a percentage. Other laboratory tests are discussed in Fact Sheet 122 and Fact Sheet 123.
All blood cells are made in the bone marrow, the center of large bones. Some medications or diseases can damage the bone marrow. This can reduce the numbers of different types of red or white blood cells.
Every laboratory has its own “reference range” or normal values for the results of each test. Most lab reports show the normal range and highlight any test results outside the normal range.
For more information on laboratory test results, see Fact Sheet 120 or Lab Tests online at
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have A Std
Can Wbc Count Detect Hiv
A WBC that is elevated in HIV patients is typically indicative of an infection in their body. In order to determine the cause, 3 other tests will be performed. A low WBC, on the other hand, indicates that some condition, either HIV-related or non-HIV-related, is affecting the bone marrows ability to produce white blood cells from its own cells.
Your Cd4 Cell Count When Youre Taking Treatment
Once you start taking HIV treatment, and your viral load starts to fall, your CD4 cell count should gradually increase, over several years.
The rate at which this happens can vary a lot between individuals. It depends in particular on your CD4 count before starting treatment. The higher it was to begin with, the higher it is likely to end up. If you are able to start treatment within a few months of infection, your CD4 count is more likely to recover quickly and completely.
If you are starting treatment with a low CD4 count, you may gain a large number of CD4 cells, without necessarily reaching the same level as a person who doesnt have HIV. This doesnt mean that you will have health problems, as long as you maintain an undetectable viral load.
Falls in CD4 counts have more serious implications in people who have started treatment at low counts. This means it is especially important to keep taking treatment that suppresses your viral load to an undetectable level. That way, whether or not your CD4 count continues to rise, viral load should stay at a satisfactory level.
CD4 cells
The primary white blood cells of the immune system, which signal to other immune system cells how and when to fight infections. HIV preferentially infects and destroys CD4 cells, which are also known as CD4+ T cells or T helper cells.
However, if your viral load increased, or you had HIV-related symptoms, then your CD4 cell count would be monitored again.
Read Also: Youngboy Has Herpes
What Are The Different Types Of Hiv Testing
There are three main types of HIV tests: antibody tests, RNA tests, and a combination test that detects both antibodies and viral protein called p24 . All tests are designed to detect HIV-1, which is the type of HIV in the United States. Some antibody tests and the combination test can also detect HIV-2 infections, which are usually limited to West Africa. No test is perfect tests may be falsely positive or falsely negative or impossible to interpret .
Positive test results are reportable to the health department in all 50 states and include the patients name. This information is then reported to the CDC so that the epidemiology and infection spread rates can be monitored. The names sent to the state remain confidential and will not be reported to employers, family members, or other such people. Some states allow anonymous testing in which the patients name is not recorded.
HIV antibody tests: HIV possesses many unique proteins on its surface and inside the virus itself. When someone is infected with HIV, their body produces proteins designed to tag the virus for elimination by the immune system. These proteins are called antibodies, and they are directed against the unique proteins of HIV. Unfortunately, these HIV antibodies do not eliminate the virus, but their presence serves as a marker to show that someone is infected with HIV. HIV antibody tests are the most commonly used tests to determine if someone has HIV.
Screening For Hiv In Pregnancy
If you’re pregnant, you’ll be offered a blood test to check if you have HIV as part of routine antenatal screening.
If untreated, HIV can be passed to your baby during pregnancy, birth or breastfeeding. Treatment in pregnancy greatly reduces the risk of passing HIV on to the baby.
Page last reviewed: 22 April 2021 Next review due: 22 April 2024
Also Check: Does Nba Youngboy Have Herpes
Lab Tests And Why They Are Important
Before you start treatment with HIV medicine , your health care provider will order several baseline lab tests. You may start treatment or be referred for treatment before the test results are in.
Your lab test results, along with your physical exam and other information you provide, will help you and your provider work together to manage your HIV care.
Your health care provider will repeat some of these lab tests as part of your ongoing HIV care to see how well your HIV medicine is working so that you can get the virus under control, protect your health, and prevent transmitting the virus to others.
Hiv And Your Complete Blood Count
If you are living with HIV, your doctor will order regular blood tests to check the status of your immune system .
In addition to these tests, others will be performed to ensure that your body is functioning normally and there are no signs of illness or drug toxicity. Central to this is a panel of tests called the complete blood count .
The CBC measures the composition of cells in a sample of blood to flag for changes that fall outside of the “normal” range of values. This can help alert doctors if a drug like Retrovir is causing anemia or there are early signs of an opportunistic infection. The CBC is often the first clue that something is not right.
This article looks at the three major blood cell types in a CBC and what high or low counts of each can mean if you are living with HIV.
You May Like: How Long Can Hiv Be Dormant In Your System
Variations In Cd4 Cell Counts
CD4 cell counts can vary a lot between people. Your own CD4 cell count may go up and down in response to different factors such as exercise, lack of sleep or smoking. But these factors dont seem to make any difference to how well your immune system can fight infections.
“When you are taking HIV treatment, your viral load is a more important indicator of your health and of the effectiveness of your treatment than your CD4 cell count.”
Rather than attach too much significance to an individual test result, it makes good sense to monitor any trends in changes to your CD4 cell count over time. Its best to have your CD4 count measured at the same clinic and at roughly the same time of day wherever possible. If you have another infection, such as the flu or an outbreak of herpes, talk to your clinic about whether it is best to delay your CD4 count until you are feeling better. If you get a result that is very different to that expected, your doctor may want to repeat the test to check whether the first result was a laboratory error.
What Is The 4th Generation Hiv Test
The fourth generation HIV test, also called an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay test, is a more complete screening that can identify acute HIV. This is the time when the virus is multiplying rapidly and youre more likely to pass the infection.
In the first few weeks after exposure to HIV, your body produces an antigen known as p24. This protein is only present in people who have acute HIV infection. It triggers your immune system to respond.
The fourth generation tests can identify both HIV-specific antigen p24 and HIV antibodies with a blood sample.
The fourth generation tests require a blood sample thats sent to a lab for testing. Blood testing done by a lab is the most accurate type of test.
There are many products approved for fourth generation testing, including:
- ADVIA Centaur HIV Ag/Ab Combo Assay
- Elecsys HIV Combi PT
- Genscreen ULTRA HIV Ag-Ab
- VITROS HIV Combo Test
The healthcare clinic or doctors office you visit for an HIV test can tell you more about the exact test they use.
tests that can test for the presence of HIV. HIV testing can be done by drawing blood from a vein, a finger stick, or taking an oral swab of fluid.
Tests can measure antibodies, antigen/antibody , and theres also a nucleic acid test . The NAT test can identify HIV and viral load . It can tell if you have HIV within around 10 to 33 days of exposure.
Older tests like the third generation tests arent reliable until about 3 months after exposure to the virus.
Also Check: How Long Does Hiv Stay Dormant
White Blood Cell Infusions To Treat Hiv Infection
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : November 4, 1999Last Update Posted : March 4, 2008 |
- Study Details
This study will evaluate the safety and immune system effects of infusing HIV-infected patients with multiple doses of lymphocytes from their non-infected identical twin. It will determine whether the donated lymphocytes can improve immune function and reduce viral load in the infected twin.
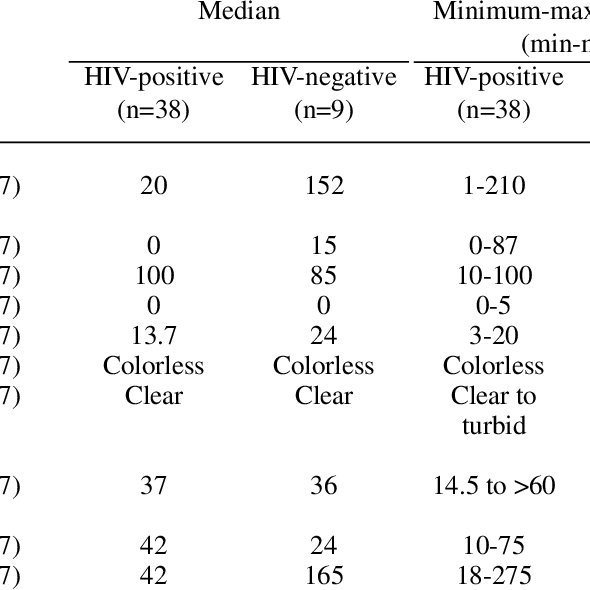
Identical twin pairs-one who is infected with HIV-1 and one who is negative for the virus-may be eligible for this study. Candidates will be screened with blood tests, a medical history and physical examination.
Both twin participants will receive a tetanus booster shot, if needed. The non-infected twin will undergo apheresis to collect white blood cells. For this procedure, whole blood is collected, similar to the procedure for donating a unit of blood from a needle in the arm. The blood flows through a cell separator machine where the white cells are removed, and the rest of the blood is returned to the donor through a catheter in the opposite arm.
DONOR: