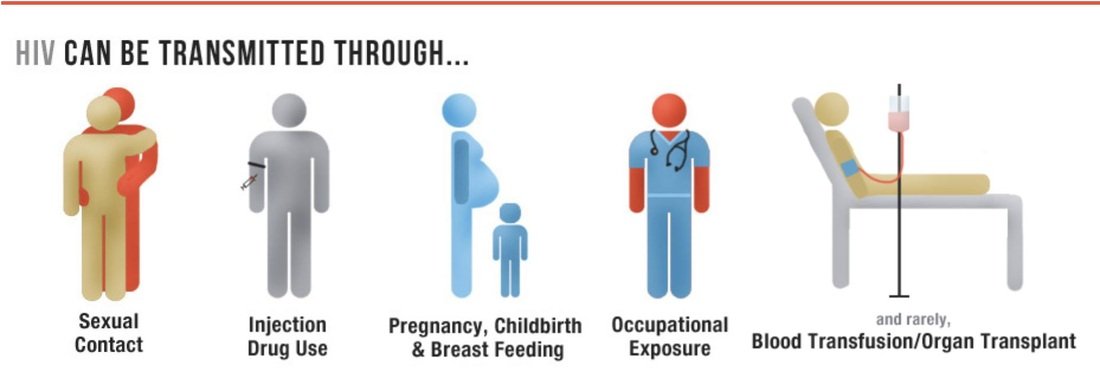
Ways Hiv Can Be Transmitted
How is HIV passed from one person to another?
Most people who get HIV get it through anal or vaginal sex, or sharing needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment . But there are powerful tools that can help prevent HIV transmission.
Can I get HIV from anal sex?
You can get HIV if you have anal sex with someone who has HIV without using protection .
- Anal sex is the riskiest type of sex for getting or transmitting HIV.
- Being the receptive partner is riskier for getting HIV than being the insertive partner .
- The bottoms risk of getting HIV is very high because the rectums lining is thin and may allow HIV to enter the body during anal sex.
- The top is also at risk because HIV can enter the body through the opening at the tip of the penis , the foreskin if the penis isnt circumcised, or small cuts, scratches, or open sores anywhere on the penis.
Can I get HIV from vaginal sex?
You can get HIV if you have vaginal sex with someone who has HIV without using protection .
Can HIV be transmitted from a mother to her baby?
HIV can be transmitted from a mother to her baby during pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding. However, it is less common because of advances in HIV prevention and treatment.
Can I get HIV from sharing needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment?
You are at high risk for getting HIV if you with someone who has HIV. Never share needles or other equipment to inject drugs, hormones, steroids, or silicone.
Do Condoms Stop Hiv Being Passed On
Yes.Using a condom correctly prevents contact with semen or vaginal secretions , stopping HIV from being passed on. The virus cannot pass through the latex of the condom.
Condoms should only be used with a water-based lubricant as oil-based lube weakens them.
People with HIV who are on effective treatment and have an undetectable viral load cannot pass on HIV through any of their body fluids.
Its also important to remember that if you have sex without a condom other sexually transmitted infections can be passed on.
Sex without a condom can also result in pregnancy if other contraception is not being used.
Living With Hiv: What To Expect And Tips For Coping
More than 1.2 million people in the United States are living with HIV. Its different for everybody, but with treatment, many can expect to live a long, productive life.
The most important thing is to start antiretroviral treatment as soon as possible. By taking medications exactly as prescribed, people living with HIV can keep their viral load low and their immune system strong.
Its also important to follow up with a healthcare provider regularly.
Other ways people living with HIV can improve their health include:
- Make their health their top priority. Steps to help people living with HIV feel their best include:
- fueling their body with a well-balanced diet
- exercising regularly
- avoiding tobacco and other drugs
- reporting any new symptoms to their healthcare provider right away
You May Like: Does Nba Youngboy Have Hiv
Whats The Difference Between Hiv And Aids
HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. HIV and AIDS are not the same thing. And people with HIV do not always have AIDS.
HIV is the virus thats passed from person to person. Over time, HIV destroys an important kind of the cell in your immune system that helps protect you from infections. When you dont have enough of these CD4 cells, your body cant fight off infections the way it normally can.
AIDS is the disease caused by the damage that HIV does to your immune system. You have AIDS when you get dangerous infections or have a super low number of CD4 cells. AIDS is the most serious stage of HIV, and it leads to death over time.
Without treatment, it usually takes about 10 years for someone with HIV to develop AIDS. Treatment slows down the damage the virus causes and can help people stay healthy for several decades.
How Is Hiv Spread From Person To Person

HIV can only be spread through specific activities. In the United States, the most common ways are:
- Having vaginal or anal sex with someone who has HIV without using a condom or taking medicines to prevent or treat HIV. Anal sex is riskier than vaginal sex.
- Sharing injection drug equipment , such as needles, with someone who has HIV.
Less common ways are:
- From mother to child during pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding. However, the use of HIV medicines and other strategies have helped lower the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV to 1% or less in the United States.
- Getting stuck with an HIV-contaminated needle or other sharp object. This is a risk mainly for health care workers. The risk is very low.
HIV is spread only in extremely rare cases by:
- Having oral sex. But in general, the chance that an HIV-negative person will get HIV from oral sex with an HIV-positive partner is extremely low.
Don’t Miss: Does Nba Youngboy Have Hiv
Genital Herpes And Pregnancy
If you get pregnant and contract genital herpes, it is important to seek treatment. It is even more essential if you are infected after becoming pregnant, as research suggests that genital herpes may lead to miscarriage or early delivery.
Additionally, it is possible to transmit the virus to your baby during delivery, which can lead to a potentially deadly infection called neonatal herpes.
Neonatal herpes is rare, occurring in an estimated 10 out of every 100,000 births globally. However, it is a serious condition that can lead to lasting disability or death.
The risk for neonatal herpes is highest when a mother contracts a herpes infection for the first time in late pregnancy, in part because the levels of HSV in the genital tract are highest during the early stages of infection.
If you have herpes symptoms at delivery, your doctor may perform a C-section to protect your baby.
Symptoms Of Hiv/aids And Stages
Many people donât have symptoms at first, and sometimes even for years or decades. But there are signs that can happen, such as flu-like symptoms soon after you become infected with HIV. Even if you donât feel sick, HIV damages the immune system. It hijacks infection-fighting white blood cells called CD4 cells and uses them to churn out thousands of copies of itself. Without treatment, HIV destroys so many of these cells that your body canât protect you from life-threatening infections. If your CD4 count drops below 200, you have AIDS.
There are three stages of HIV infection:
Stage 1: This the earliest stage. You may also hear it called the âacuteâ stage. You might have a fever, rash, fatigue, chills, and other flu-like symptoms. But you might not have any symptoms. If you do, they may start 2-4 weeks after youâre infected. During this time, the virus quickly makes many copies of itself.
Stage 2: During this stage, HIV continues to reproduce, and it slowly damages your immune system over time. You might not feel sick or have symptoms. But HIV isnât gone, and you can still spread it to other people. This stage can last for years or even decades.
Stage 3: This is when you have AIDS. Your immune system has been severely damaged, leaving you vulnerable to other illnesses. With AIDS, many people have symptoms such as chills, fever, sweats, swollen lymph glands, weakness, and weight loss.
Also Check: How Long Can Hiv Go Undetected
What Conditions Are Considered To Be Opportunistic
Some of the most common of these OIs/cancers among HIV-positive people include:
Cancer: The types of cancers that are you are more likely to get if you have AIDs include lymphoma, Kaposis sarcoma, invasive cervical cancer, anal cancer, liver cancer, and cancers of the mouth, throat and lungs.
Candidiasis : This condition is caused by Candida fungus. It can happen in the skin, nails and mucous membranes throughout the body, such as the mouth or the vagina. The cases can be troublesome, but thrush is especially dangerous when it affects the esophagus or parts of the respiratory system .
Pneumonia: This respiratory condition is most commonly caused by _Pneumocystis jirovecii and the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae._
Salmonella: This infection is spread through contaminated food and water. It causes diarrhea, vomiting and nausea.
Toxoplasmosis: This disease is caused by a parasites that live in cats and rodents and other warm-blooded animals. The infection is spread through the feces. Toxoplasmosis can cause severe problems in the lungs, heart, brain and other organs. If you have a cat, wear gloves to change the litter and be thorough in washing your hands.
A Sexually Transmitted Infection
Katie Salerno/Flickr Creative Commons
If you have a sexually transmitted infection , there is a chance you may have HIV as well. The odds may be greater than you think.
Some STIs like syphilis and herpes cause open sores that make it easier for HIV to enter the body. Others like gonorrhea and chlamydia cause inflammation in the genitals that attracts the very immune cells that HIV likes to target and infect.
Having syphilis can increase your risk of HIV by as much as 500%. Other STIs can do the same. Because of this, you should be tested for HIV if you test positive for any STI.
Recommended Reading: How Long Before Hiv Turns Into Aids
How Is Hiv Transmitted Through Needles
HIV isnt transmitted only through sexual contact. Sharing needles also puts a person at higher risk of contracting HIV.
When a needle is injected into a persons body, it breaks the skin barrier. If the needle has already been injected into another person, it can carry traces of their blood, along with any infections they have. The contaminated needle can introduce these infections into the second persons body.
Researchers dont know if having an undetectable viral load reduces the risk of HIV transmission through shared needles, but its reasonable to assume it may provide some risk reduction.
HIV can affect anyone. Whatever their age, gender, sexuality, ethnicity, or race, everyone should take steps to protect themselves. But due to socioeconomic factors, some demographic groups have higher HIV transmission rates and generally are more affected by HIV.
According to the CDC , the general demographic traits most affected by HIV are:
Transgender women are also highly impacted by HIV transmissions as a population, reports the CDC .
These groups are disproportionately affected by HIV, but they arent inherently at greater risk of contracting HIV. An individuals personal risk depends on their behaviors, not on their age, gender, sexuality, ethnicity, race, or any other demographic factor.
Are Women More Likely To Get Hiv
Yes. Biologically speaking, a woman is more vulnerable to heterosexual transmission of the disease because the genitalia are easily exposed to seminal fluids.
Gender inequality has great influence on the spread of HIV/AIDS among women. In some cultures, many women and girls are often put in situations where they engage in non-consensual sex or have sex for money.
In the U.S., minority communities have been hit the hardest by HIV. African American and Hispanic women together represent less than 25% of all U.S. women, yet they account for more than 78% of AIDS cases reported among women in the country.
You May Like: Jania Has Herpes
What Behaviors Are The Most Risky For Getting Or Transmitting Hiv
Since there is a fairly high number of people who have HIV and dont know it, you should be tested for HIV so you know your status. Being intoxicated is risky because you are more likely to engage in risky sex if you are drunk or high. In terms of sex acts, anal sex and vaginal intercourse are the most risky behaviors.
Do I Still Need To Worry About Other Sexually Transmitted Infections
Neither HIV treatment nor PrEP prevents other sexually transmitted infections, or STIs.
Ways to reduce the risk of STIs include having both partners tested, limiting the number of sexual partners and using condoms. Vaccines are available to prevent some STIs, including hepatitis B and human papillomavirus .
Recommended Reading: Is Undetectable Hiv Contagious
What Happens If I Stop Taking Antiretroviral Therapy
When therapy is stopped, viral load rebounds, and the risk of transmitting HIV to a sexual partner in the absence of other prevention methods returns. NIAID-supported research has provided clear-cut scientific evidence to support the benefits of staying on continuous antiretroviral treatment. In 2006, NIAIDs large clinical trial called SMART showed that people receiving intermittent antiretroviral treatment had twice the rate of disease progression compared to those receiving continuous treatment.
Taking antiretroviral treatment daily as directed to achieve and maintain durably undetectable status stops HIV infection from progressing, helping people living with HIV stay healthy and live longer, while offering the benefit of preventing sexual transmission. Stopping and re-starting treatment can cause drug resistance to develop, making that treatment regimen ineffective and limiting future treatment options.
How Does Being Durably Undetectable Affect My Risk Of Transmitting Hiv To A Sexual Partner
People living with HIV who take antiretroviral medications daily as prescribed and who achieve and then maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting the virus to an HIV-negative partner.
Three large multinational research studies involving couples in which one partner was living with HIV and the other was notHPTN 052, PARTNER and Opposites Attractobserved no HIV transmission to the HIV-negative partner while the partner with HIV had a durably undetectable viral load. These studies followed approximately 3,000 male-female and male-male couples over many years while they did not use condoms. Over the course of the PARTNER and Opposites Attract studies, couples reported engaging in more than 74,000 condomless episodes of vaginal or anal intercourse.
Learn more about HIV treatment as prevention.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have A Std
Whats The Hiv Window Period
As soon as someone contracts HIV, it starts to reproduce in their body. The persons immune system reacts to the antigens by producing antibodies .
The time between exposure to HIV and when it becomes detectable in the blood is called the HIV window period. Most people develop detectable HIV antibodies within 23 to 90 days after transmission.
If a person takes an HIV test during the window period, its likely theyll receive a negative result. However, they can still transmit the virus to others during this time.
If someone thinks they may have been exposed to HIV but tested negative during this time, they should repeat the test in a few months to confirm . And during that time, they need to use condoms or other barrier methods to prevent possibly spreading HIV.
Someone who tests negative during the window might benefit from post-exposure prophylaxis . This is medication taken after an exposure to prevent getting HIV.
PEP needs to be taken as soon as possible after the exposure it should be taken no later than 72 hours after exposure but ideally before then.
Another way to prevent getting HIV is pre-exposure prophylaxis . A combination of HIV drugs taken before potential exposure to HIV, PrEP can lower the risk of contracting or transmitting HIV when taken consistently.
Timing is important when testing for HIV.
What About Breastfeeding
chance that they will pass on the virus to their infant during labor, delivery, or breastfeeding. This is due to contact with relevant body fluids.
Antiretroviral therapy can reduce the chances of transmission to below 5%. The recommend that people with HIV combine exclusive breastfeeding with the use of antiretroviral therapy.
Also Check: Does Cookie Johnson Have Hiv Aids
Male Vs Female Partners
When having vaginal sex without a condom with a partner who has a penis, the vaginal membranes are more likely to tear than the partners penis.
In condomless anal sex with a partner who has a penis, the rectal membranes are also more likely to tear than the partners penis. Microscopic tears create an easier path for HIV and other STIs to enter the body when exposed.
Its possible for a partner with a penis to contract HIV during vaginal and anal sex. If a female partner is living with HIV with a detectable viral load, it can be carried in her vaginal secretions. If her partner has open sores on their mouth or penis, they can create a gateway for vaginal secretions or other bodily fluids with HIV to enter the body.
Uncircumcised men are at higher risk of contracting HIV from condomless sex than circumcised men. The delicate membranes of foreskin can tear during sex, creating a pathway for HIV to enter the body.
How Hiv Infects The Body
HIV infects the immune system, causing progressive damage and eventually making it unable to fight off infections.
The virus attaches itself to immune system cells called CD4 lymphocyte cells, which protect the body against various bacteria, viruses and other germs.
Once attached, it enters the CD4 cells and uses it to make thousands of copies of itself. These copies then leave the CD4 cells, killing them in the process.
This process continues until eventually the number of CD4 cells, also called your CD4 count, drops so low that your immune system stops working.
This process may take up to 10 years, during which time you’ll feel and appear well.
Page last reviewed: 22 April 2021 Next review due: 22 April 2024
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have Hiv