How Does Antiviral Ribozymes Work In Treating Viral Infections
The recent research studies suggest some of the antiviral ribozymes are capable of breaking the virus RNA and DNA chains. The breaking of viral RNA and DNA sequence leads to dysfunctional virus particle. Ribozymes are enzymes capable of breaking RNA and DNA amino acid sequence. The mechanism of action of antiviral preparation of ribozymes has been found effective against hepatitis C and HIV infection.
What Else Do I Need To Know About Taking Hiv/aids Medicines
It’s important to take your medicines every day, according to the instructions from your health care provider. If you miss doses or don’t follow a regular schedule, your treatment may not work, and the HIV virus may become resistant to the medicines.
HIV medicines can cause side effects. Most of these side effects are manageable, but a few can be serious. Tell your health care provider about any side effects that you are having. Don’t stop taking your medicine without first talking to your provider. He or she may give you tips on how to deal with the side effects. In some cases, your provider may decide to change your medicines.
How Do Cytoplasmic Inhibitors Work In Treating Viral Infection
The viruses rapidly multiply within cells by breaking the amino acids within chromosomes and sequencing to form the new viruses. Viruses alter the physiological sequence of intracellular amino acid and use the chain of amino acids to form new viruses. The mechanism of action of this anti-viral medication or the way cytoplasmic inhibitor works is blocking the multiplication of virus within target cell at various stages.
There are several cytoplasmic inhibiting antiviral medications acting at various stages of viral multiplication.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take To Be Undetectable Hiv
What If I Have Another Illness Or A Co
You may have a co-infection or another illness such as cardiovascular disease, HIV-related cancer, chronic kidney disease or HIV-associated neurocognitive impairment.
In these situations your doctor may need to tailor your antiretroviral treatment or treat your other condition before starting your HIV treatment. This will be explained to you by the clinicians looking after you.
Creating New Antiviral Drugs

“Most antiviral drugs act on specific viruses, which means each time we have a new type of infection, we may need a new type of drug,” says Khubchandani. That makes it tough to have a common set of ingredients, he says.
Moreover, viruses are constantly mutating and adapting to threats. That’s why we have to have a newflu shotmade each year.
Creating a new antiviral is not an easy or quick process, either. And there are a variety of reasons why, including the years of research it takes, the clinical trials and approvals needed, and even the time to market the new medication, says Khubchandani.
For example, the antiviral acyclovir, which treats herpes and chickenpox, was patented in 1974. Clinical trials took place from 1977-78. And clinical use was finally approved in 1981.
Don’t Miss: Hiv Causes Hair Loss
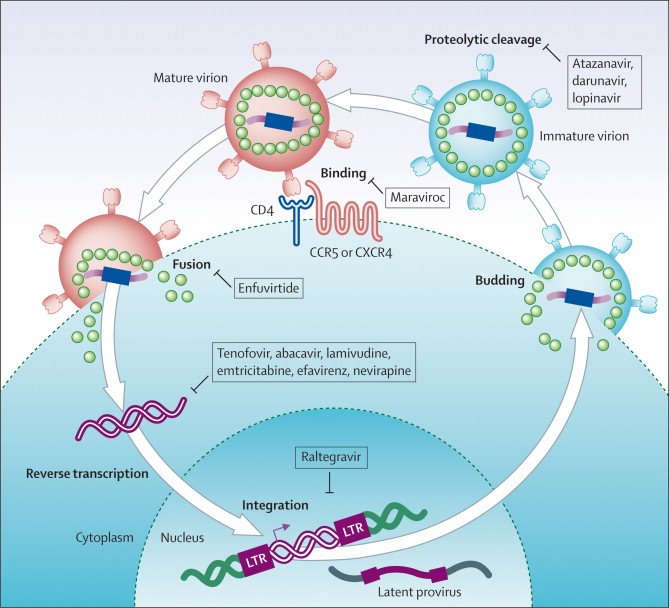
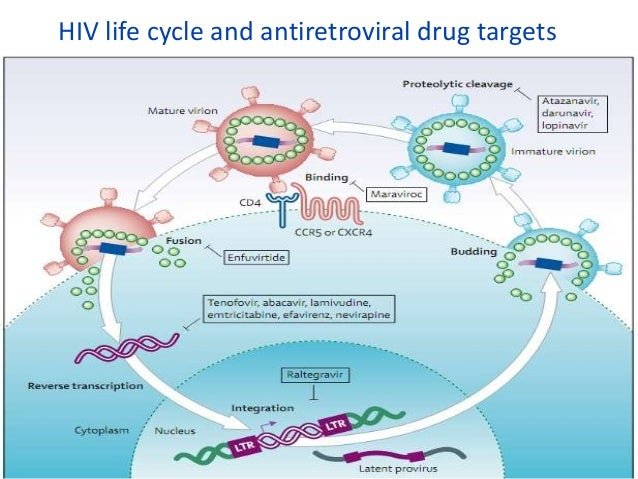
Hiv Life Cycle And Antiretroviral Drug Targets
Understanding the basic HIV life cycle is the foundation for understanding the mechanism of action of the different classes of antiretroviral medications. The following discussion will focus on key HIV enzymes and relevant steps in the HIV life cycle related to HIV antiretroviral therapy. The Howard Hughes Medical Institute has produced an excellent HIV Life Cycle video that summarizes the key steps in the HIV life cycle.
Choosing Nrti Backbone In Regimen
The Adult and Adolescent ARV Guidelines include four different NRTI backbone combinations: abacavir-lamivudine, tenofovir alafenamide-emtricitabine, tenofovir DF-emtricitabine, and tenofovir DF-lamivudine.Abacavir has been associated with increased cardiovascular risk, and although data is conflicting about this association, many experts would avoid abacavir in the setting of known cardiovascular disease risk factors. Tenofovir DF is linked to increased risk of renal dysfunction and loss of bone mineral density accordingly, tenofovir DF is not recommended for patients with renal disease or osteoporosis. Tenofovir alafenamide has a less favorable lipid profile than tenofovir DF.
You May Like: Hiv Screen 4th Generation Wrfx Non Reactive
Which Drugs Should You Take
Now that you have learned a little about the types of drugs that are available and how they work, you may be wondering how your provider will know which treatment you should take.
HIV drugs are used in combination with one another in order to get the best results. The goal is to get the viral load as low as possible for as long as possible.
HIV drugs do different things to the virus–they attack it in different ways–so using combinations works better than using just one by itself. Combinations usually include three antiretroviral drugs. Except in very special circumstances, anti-HIV drugs should never be used one or two at a time. Using only one or two drugs at a time can fail to control the viral load and let the virus adapt to the drug. Once the virus adapts to a drug, the drug won’t work as well against the virus, and maybe it won’t work at all.
There is no one combination of HIV drugs that works best for everyone. Each combination has its pluses and minuses.
So, how will your provider know which combination to choose? You and your provider can consider the options, keeping certain things in mind, such as possible side effects, the number of pills you’ll need to take, and how the drugs interact with each other and with other medications you may take.
Print out these questions to ask your health care provider so that you will be ready to discuss combination therapy.
Types Of Antiretroviral Medications
- There are more than 30 antiretroviral medications in six drug classes these are listed below.
- Each class of drug attacks HIV in a different way.
There are six main types of antiretroviral drugs.
Each class of drug attacks HIV in a different way. Generally, drugs from two classes are combined to ensure a powerful attack on HIV.
Most people start HIV treatment on two drugs from the nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors class combined with either one integrase inhibitor, one non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, or one protease inhibitor hence, triple therapy.
Read Also: Jania Has Herpes
Treatment Options For Antiviral Resistant Pathogens
If a virus is not fully wiped out during a regimen of antivirals, treatment creates a bottleneck in the viral population that selects for resistance, and there is a chance that a resistant strain may repopulate the host. Viral treatment mechanisms must therefore account for the selection of resistant viruses.
The most commonly used method for treating resistant viruses is combination therapy, which uses multiple antivirals in one treatment regimen. This is thought to decrease the likelihood that one mutation could cause antiviral resistance, as the antivirals in the cocktail target different stages of the viral life cycle. This is frequently used in retroviruses like HIV, but a number of studies have demonstrated its effectiveness against influenza A, as well. Viruses can also be screened for resistance to drugs before treatment is started. This minimizes exposure to unnecessary antivirals and ensures that an effective medication is being used. This may improve patient outcomes and could help detect new resistance mutations during routine scanning for known mutants. However, this has not been consistently implemented in treatment facilities at this time.
How Hiv Drugs Work 101
_Adapted from the 1998 edition of _ HIV 101 Positively Aware
There are three categories of HIV antiviral drugs that have FDA approval. Nucleosides and non-nucleosides work to stop HIV from infecting cells and protease inhibitors stop infected cells, from reproducing the virus. In addition, new classes of drugs to treat HIV/AIDS are on the horizon. Fusion inhibitors, nucleotide inhibitors and immune modulators may be available in the near future.
Also Check: How Long Can Aids Go Undetected
What Hiv Medicines Are Included In An Hiv Treatment Regimen
There are many HIV medicines available for HIV treatment regimens. The HIV medicines are grouped into seven drug classes according to how they fight HIV.
The choice of an HIV treatment regimen depends on a person’s individual needs. When choosing an HIV treatment regimen, people with HIV and their health care providers consider many factors, including possible side effects of HIV medicines and potential drug interactions.
How Should I Take My Antiretroviral Treatment
When and how you take your ART will vary depending on the specific antiretroviral drugs you take. Most antiretroviral drugs are taken once a day, with or without food. However, some drugs are taken twice a day. If this might be something you find difficult, talk to your doctor about your options.
Once you start ART its very important that you take it properly and dont miss or skip doses, as this can lead to something called HIV drug resistance, and may mean that your drugs dont work as well for you in the future. If youre finding it hard to take your treatment at the right times and in the right way, speak to your healthcare worker. They can offer you support and give you advice on how to make taking your treatment easier.
Read Also: How Long Does Hiv Last
Adherence To Hiv Medications
What exactly is adherence when talking about HIV medications? Simply put, adherence is sticking to your program — taking the medications you’re supposed to take, on time, every time! Whether you’ve been on HIV medications for 10 years or are just starting out, it takes a strong personal commitment to take your medications on time, every time. Non-adherence is the number one reason why HIV treatments fail. These medications work — but they can’t work if you’re not taking them! So, here are some tips and suggestions to help you achieve adherence with your HIV medications.
Make sure you’re mentally ready to start taking HIV medications.Not sticking to your regimen makes it very easy for the virus to mutate and develop resistance to the medications, and then you may have wasted the regimen. Don’t start taking the medications until you are totally committed to taking them right on time, every time!
Get help from family and friends.Family and friends can help you stick to your regimen, so don’t be afraid to rely on them. Let them know exactly what you’re supposed to take and when. You can also ask them to help you remember to take your drugs, which can be easily done with just a simple phone call!
S Of Viral Infections
Viral infection involves the entry of viral DNA into a host cell, replication ofthat DNA and releasing the new viruses. The six steps of viral replicationinclude viral attachment, invasion, uncoating, replication, assembly andrelease. The steps of virus life cycle highlighting the entry and exit of thevirus are described below .
Common inhibitory actions of antiviral drugs.
Don’t Miss: Hiv Screen 4th Generation Wrfx Reactive
Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy
In 1996, highly active antiretroviral therapy was introduced for people with HIV and AIDS. HAART â often referred to as the anti-HIV “cocktail” â is a combination of three or more drugs, such as protease inhibitors and other anti-retroviral medications. The treatment is highly effective in slowing the rate at which the HIV virus replicates itself, which may slow the spread of HIV in the body. The goal of HAART is to reduce the amount of virus in your body, or the viral load, to a level that can no longer be detected with blood tests.
Learning Objective Performance Indicators
- List the major classes of antiretroviral medications and describe the mechanism of action with each class of drugs
- Discuss evidence supporting antiretroviral treatment of all persons with HIV
- List recommended antiretroviral regimens for treatment-naïve individuals and discuss factors to consider when selecting an initial regimen
- Summarize recommended laboratory studies to obtain at baseline and while monitoring response to therapy
Recommended Reading: Hiv From Dried Blood
What Are The Side Effects Of Antiretrovirals
People who use antiretrovirals can have side effects such as high cholesterol, high blood sugar, liver or kidney damage, bleeding, anaemia, sleep problems, nausea, loss of appetite and rash.
Not everyone has side effects from their drugs and not everyone will have the same side effects.
Another possible side effect is resistance to medication, which means the medication isnt working as well as it should.
You can lower the chance of resistance to medication by choosing effective medication, by not missing doses and by using a combination of medications instead of just one.
Please tell your doctor if you have any symptoms you are concerned about rather than stopping your medication on your own.
You May Like: Does Hiv Attack Red Blood Cells
Protein Processing And Targeting
The mechanism of action of antiviral drugs or medications may also target the protein in the virus, thus controlling its multiplication. Some antiviral drugs are targeted to change the sequence of amino acids once the virus particles are formed within the cell cytoplasm. The change of viral DNA and RNA amino acid sequence causes inactive virus or protein particles.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Aids From Dried Blood
Sticking To Your Medicines
“Adherence” refers to how well you stay on your treatment plan–whether you take your medications exactly as your provider tells you.
If you follow your provider’s instructions, the HIV drugs will work well to lower the amount of virus in your blood. Taking your drugs correctly increases your likelihood of success.
But, if you miss doses, or don’t follow a regular schedule, your treatment may not work, and the HIV virus may become resistant to the medicines.
Before you start a treatment plan, you should:
- Get your provider to write everything down for you: names of the drugs, what they look like, how to take them , and how often to take them. This way, you’ll have something to look at in case you forget what you’re supposed to do.
- With your provider’s help, develop a plan that works for you.
Pop question: True or false. Missing doses and not following a regular schedule can lessen the effect of your HIV medication.
TrueFalse
Pop question: True or false. Missing doses and not following a regular schedule can lessen the effect of your HIV medication.
Answer: TRUE. Missing doses and not following a regular schedule can lessen the effect of your HIV medication. It is very important that you stay on your treatment plan and follow your provider’s instructions for taking your medicine.
When Is It Time To Start Taking Hiv Medicines
People with HIV should start taking HIV medicines as soon as possible after an HIV diagnosis. It is especially important for people with AIDS-defining conditions or early HIV infection to start HIV medicines right away.
Women with HIV who become pregnant and are not already taking HIV medicines should also start taking HIV medicines as soon as possible.
You May Like: How Long Can Hiv Be Dormant In Your System
What If Your Treatment Isn’t Working
Sometimes the HIV medications don’t work. This may occur because the drugs don’t completely stop the virus from reproducing. As the virus makes copies of itself, changes sometimes occur. These changes may result in a new strain of the virus that is resistant to the action of the drugs. If your providers think this has happened, they will do a blood test that can help show which drugs the virus has become resistant to. This can help identify other drugs that might still work against your virus.
If a person has a strain of HIV that is resistant to most or all available drugs, that person may want to consider joining a clinical trial that is testing new drugs that have not yet been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration . See Clinical Trials.
How Are Hiv And Aids Treated
The most effective treatment for HIV is antiretroviral therapy . This is a combination of several medicines that aims to control the amount of virus in your body. Antiretroviral medicines slow the rate at which the virus grows. Taking these medicines can reduce the amount of virus in your body and help you stay healthy.
After you start treatment, it’s important to take your medicines exactly as your doctor tells you. When treatment doesn’t work, it is often because HIV has become resistant to the medicine. This can happen if you don’t take your medicines correctly.
Other steps you can take include the following:
- Keep your immune system strong by eating right, quitting smoking, and learning how to avoid infection.
- Monitor your CD4+ counts to check the effect of the virus on your immune system.
- See a counselor to help you handle the strong emotions and stress that can follow an HIV diagnosis.
- Reduce stress so that you can better manage the HIV illness.
Starting treatment
Medical experts recommend that people begin treatment for HIV as soon as they know that they are infected. Treatment is especially important for pregnant women, people who have other infections , and people who have symptoms of AIDS.
Research suggests that treatment of early HIV with antiretroviral medicines has long-term benefits, such as a stronger immune system.
Treatment to prevent HIV infection
Other treatments for HIV
Treatment for AIDS
Living with HIV
If your partner has HIV:
Recommended Reading: Does Nba Youngboy Still Have Herpes