Herpes Simplex Or Cold Sores
Fighting off infections and viruses is more difficult for a person with HIV. One of the most common viruses that people have is herpes simplex, or oral herpes. Oral herpes usually appears as red sores in the mouth.
When they appear outside the lips, they may look like blisters. Nicknamed fever blisters, these red, raised bumps can be painful. Theyre also known as cold sores.
Anyone can get oral herpes, but in someone with HIV or a weakened immune system, oral herpes may be more severe and last longer.
Treatment: Oral herpes is treatable with medication. A healthcare provider will likely prescribe acyclovir, an antiviral treatment. This medication helps reduce new outbreaks.
Continue to take any prescription medications until a healthcare provider indicates otherwise.
Contagious? Yes. People with herpes may want to avoid sharing foods.
What To Look For
Whether caused by an HIV medication or by HIV itself, the rash typically appears as a red, flattened area on the skin thats usually covered with small red bumps.
A main symptom of the rash is itchiness. It can show up on any part of the body, but it most often occurs on the face and chest, and sometimes on the feet and hands. It can also cause mouth ulcers.
What If Your Treatment Isn’t Working
Sometimes the HIV medications don’t work. This may occur because the drugs don’t completely stop the virus from reproducing. As the virus makes copies of itself, changes sometimes occur. These changes may result in a new strain of the virus that is resistant to the action of the drugs. If your providers think this has happened, they will do a blood test that can help show which drugs the virus has become resistant to. This can help identify other drugs that might still work against your virus.
If a person has a strain of HIV that is resistant to most or all available drugs, that person may want to consider joining a clinical trial that is testing new drugs that have not yet been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration . See Clinical Trials.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Hiv Early Detection Test
Taking Antiretroviral Treatment With Other Medicines
If you are taking other medications or drugs including: treatments for other health conditions contraception hormonal therapies or use psychoactive drugs, its important that your doctor knows about this. Different drugs can interact, changing the way that they work. This may mean that a drug becomes too strong or that a drug becomes too weak, so that it can no longer control your HIV, prevent pregnancy or treat another health condition. Discuss the medication you take with your healthcare workers so they make sure that the combination is safe and will work well for you.
How Is Hiv Spread From Person To Person

HIV can only be spread through specific activities. In the United States, the most common ways are:
- Having vaginal or anal sex with someone who has HIV without using a condom or taking medicines to prevent or treat HIV. Anal sex is riskier than vaginal sex.
- Sharing injection drug equipment , such as needles, with someone who has HIV.
Less common ways are:
- From mother to child during pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding. However, the use of HIV medicines and other strategies have helped lower the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV to 1% or less in the United States.
- Getting stuck with an HIV-contaminated needle or other sharp object. This is a risk mainly for health care workers. The risk is very low.
HIV is spread only in extremely rare cases by:
- Having oral sex. But in general, the chance that an HIV-negative person will get HIV from oral sex with an HIV-positive partner is extremely low.
Also Check: How Many People Are Living With Hiv
Gum Disease And Dry Mouth
Although these arent sores, gum disease and dry mouth are common problems.
Gum disease causes the gums to swell, and can be painful. In severe cases, it can lead to gum or teeth loss in as quick as 18 months. Gum disease may also be an indication of inflammation, which increases the risk for heart disease and stroke.
Dry mouth occurs when a person doesnt produce enough saliva. Saliva can help protect the teeth as well as prevent infections. Without saliva, the teeth and gums are vulnerable to plaque development. This can also make gum disease worse.
Treatment: Drink water, floss, and brush consistently to keep the mouth clean and hydrated. For gum disease, a dentist will remove the plaque with a deep cleaning method.
If dry mouth persists, ask a healthcare provider about saliva substitutes.
Recognizing The Symptoms Of An Hiv Rash
You May Like: Who Is Most Likely To Contract Hiv
Sticking To Your Medicines
“Adherence” refers to how well you stay on your treatment plan–whether you take your medications exactly as your provider tells you.
If you follow your provider’s instructions, the HIV drugs will work well to lower the amount of virus in your blood. Taking your drugs correctly increases your likelihood of success.
But, if you miss doses, or don’t follow a regular schedule, your treatment may not work, and the HIV virus may become resistant to the medicines.
Before you start a treatment plan, you should:
- Get your provider to write everything down for you: names of the drugs, what they look like, how to take them , and how often to take them. This way, you’ll have something to look at in case you forget what you’re supposed to do.
- With your provider’s help, develop a plan that works for you.
Pop question: True or false. Missing doses and not following a regular schedule can lessen the effect of your HIV medication.
TrueFalse
Pop question: True or false. Missing doses and not following a regular schedule can lessen the effect of your HIV medication.
Answer: TRUE. Missing doses and not following a regular schedule can lessen the effect of your HIV medication. It is very important that you stay on your treatment plan and follow your provider’s instructions for taking your medicine.
Truvada Is Not A Condom Replacement
This pill does not spell the end of condoms. Public-health officials are being very careful to avoid suggesting Truvada is an alternative to other forms of protection especially because it doesn’t protect against the full range of sexually transmitted infections people are exposed to during intercourse. “We are suggesting that for people who are already not using condoms, we have another option to help protect them from HIV infection,” says the CDC’s Dawn Smith, biomedical interventions implementation officer. “It’s part of being practical and realistic.” The hope is that those who get prescriptions are folks who just aren’t using anything to protect themselves at the moment. “We know from our surveillance systems that condom use is not as high as is necessary to control the epidemic,” Smith added.
Read Also: Can You Get Hiv Without Having Sex
How Should I Take My Antiretroviral Treatment
When and how you take your ART will vary depending on the specific antiretroviral drugs you take. Most antiretroviral drugs are taken once a day, with or without food. However, some drugs are taken twice a day. If this might be something you find difficult, talk to your doctor about your options.
Once you start ART its very important that you take it properly and dont miss or skip doses, as this can lead to something called HIV drug resistance, and may mean that your drugs dont work as well for you in the future. If youre finding it hard to take your treatment at the right times and in the right way, speak to your healthcare worker. They can offer you support and give you advice on how to make taking your treatment easier.
Human Papilloma Virus Warts
HPV can cause warts anywhere around the mouth or lips. Warts can look like small cauliflowerlike bumps or masses with folds or projections. They can sprout inside and around the mouth.
Most of the time warts are white, but they can also be pink or gray. Theyre generally not painful, but they can be bothersome. Depending on their location, HPV mouth warts can be picked at and bleed.
HPV is also strongly associated with oropharyngeal cancer, or throat cancer.
Treatment: A healthcare provider will need to perform surgery to remove warts. A prescription cream may be used for warts on the lips, but theres no oral medication to treat warts.
Contagious? Possibly, if broken and theres fluid.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Signs That You Are Hiv Positive
Stages Of The Hiv Lifecycle
Binding and fusion
HIV attaches to a T-helper cell. It then fuses to it and releases its genetic information into the cell.
The types of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called fusion or entry inhibitor drugs because they stop HIV from entering the cell.
Reverse transcription and integration
Once inside the T-helper cell, HIV converts its genetic material into HIV DNA, a process called reverse transcription. The new HIV DNA then enters the nucleus of the host cell and takes control of it.
The types of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called NRTIs , NNRTIs and integrase inhibitor drugs.
Transcription and translation
The infected T-helper cell then produces HIV proteins that are used to produce more HIV particles inside the cell.
Assembly, budding and maturation
The new HIV is put together and then released from the T-helper cell into the bloodstream to infect other cells and so the process begins again.
The type of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called protease inhibitor drugs.
What Is Hiv Treatment
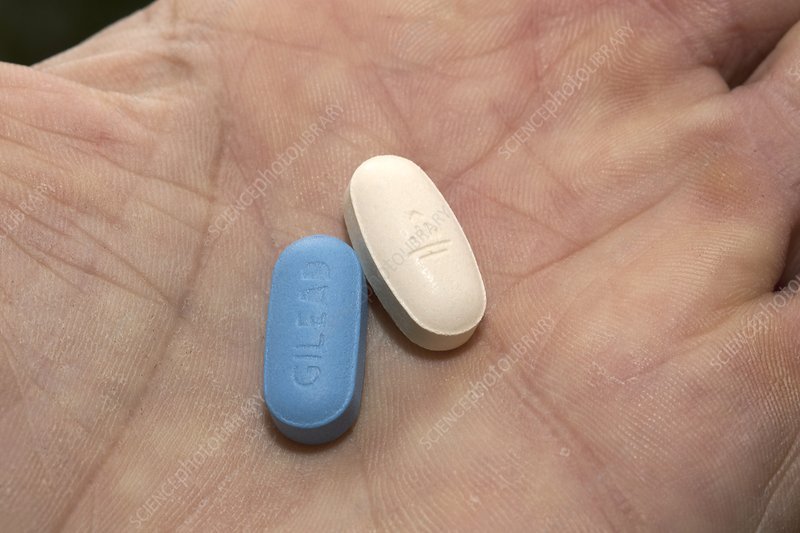
HIV treatment involves taking medicines that slow the progression of the virus in your body. HIV is a type of virus called a retrovirus, and the combination of drugs used to treat it is called antiretroviral therapy . ART is recommended for all people living with HIV, regardless of how long theyve had the virus or how healthy they are. ART must be taken every day, exactly as your health care provider prescribes.
Also Check: What Does Hiv Stand For
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
| Brand Name |
|---|
| abacavir sulfate |
* Cimduo, Combivir, Descovy, Epzicom, Temixys, Trizivir, and Truvada are combination medicines.
For more information about the risks and side effects for each medicine, check
This information does not give the specific side effects or warnings for each medicine. Check the medicine label and talk to your healthcare provider about the side effects and warnings for the combination HIV medicines you are taking.
IMPORTANT TIPS
- Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for HLA-B*5701 prior to taking abacavir or medicines containing abacavir.
- These medicines may cause lactic acidosis .
- These medicines may cause serious liver, pancreas, or kidney problems.
- If you have kidney problems or liver problems, such as hepatitis, talk to your healthcare provider before taking these medicines.
- These medications are taken by mouth. Retrovir can also be given as an intravenous infusion.
WARNING SIGNS
- Stomach pain with nausea and vomiting
- Feeling very weak or tired
- Problems breathing
| nevirapine |
For more information about the risks and side effects for each medicine, check
This information does not give the specific side effects or warnings for each medicine. Check the medicine label and talk to your healthcare provider about the side effects and warnings for the combination HIV medicines you are taking.
IMPORTANT TIPS
WARNING SIGNS
- Flu-like symptoms
| nelfinavir mesylate |
* Evotaz, Kaletra, and Prezcobix are combination medicines.
IMPORTANT TIPS
Different Types Of Arvs
Three established classes of antiretroviral drugs and three newer less established antiretroviral drug classes are currently approved for use. Nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors , non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors and the protease inhibitors are the well established classes of antiretroviral drugs, while the newer classes include fusion inhibitors, CCR5 antagonists, and HIV integrase inhibitors. Almost all the available antiretroviral drugs can only prevent infection of susceptible cells of the patient while these drugs have no impact on cells that are already infected by HIV. Emergence of drug resistance is common with treatment using single drug and hence multidrug therapy is the standard treatment approach.
Recommended Reading: How Is Hiv Not Transmitted
What Should I Tell My Healthcare Provider Before Taking Truvada For Prep
- All your health problems. Be sure to tell your healthcare provider if you have or have had any kidney, bone, or liver problems, including hepatitis.
- If you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if TRUVADA can harm your unborn baby. If you become pregnant while taking TRUVADA for PrEP, tell your healthcare provider.
- If you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Do not breastfeed if you think you may have recently become infected with HIV. HIV can be passed to the baby in breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the risks and benefits of breastfeeding while taking TRUVADA for PrEP.
- All the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. TRUVADA may interact with other medicines. Keep a list of all your medicines and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
- If you take certain other medicines with TRUVADA, your healthcare provider may need to check you more often or change your dose. These medicines include certain medicines to treat hepatitis B or C infection.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.FDA.gov/medwatch, or call .1-800-FDA-1088.
Treating The Rash At Home
Read Also: How Can You Catch Hiv
How To Identify An Hiv Rash
This article was co-authored by Dale Prokupek, MD. Dale Prokupek, MD is a board certified Internist and Gastroenterologist who runs a private practice based in Los Angeles, California. Dr. Prokupek is also a staff physician at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and an associate clinical professor of medicine at the Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles . Dr. Prokupek has over 25 years of medical experience and specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the liver, stomach, and colon, including chronic hepatitis C, colon cancer, hemorrhoids, anal condyloma, and digestive diseases related to chronic immune deficiency. He holds a BS in Zoology from the University of Wisconsin Madison and an MD from the Medical College of Wisconsin. He completed an internal medicine residency at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and a gastroenterology fellowship at the UCLA Geffen School of Medicine.There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 87% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 1,852,350 times.
Questions To Ask About Each Drug
One of the most important things you can do to make sure you take your medicine correctly is to talk with your medical provider about your lifestyle, such as your sleeping and eating schedule. If your provider prescribes a drug, be sure and ask the following questions :
- What dose of the drug should be taken? How many pills does this mean?
- How often should the drug be taken?
- Does it matter if it is taken with food, or on an empty stomach?
- Does the drug have to be kept in a refrigerator?
- What are the possible side effects of the drug?
- What should be done to deal with the side effects?
- How severe do side effects have to be before a provider is called?
During every medical visit you should talk about whether you are having trouble staying on your treatment plan. Studies show that people who take their medicine in the right way get the best results: their viral loads stay down, their CD4 counts stay up, and they feel healthier.
You May Like: Can You Have Sex With Someone Who Has Hiv