Days To 20 Years After Exposure
The chronic stage of infection occurs once the immune system brings the virus under control. During this phase, HIV will go into hiding, where it resides in various cells and tissues throughout the body in a dormant state known as latency. HIV latency can persist without symptoms for 10 years or more, although some people may experience signs within a year or two.
During the early chronic phase, lymphadenopathy may be the only notable sign of an HIV infection. In some cases, the glands may be visibly enlarged and reach up to an inch or more in size. If the condition persists for more than three months, its referred to as persistent generalized lymphadenopathy .
Even during latency, the virus will multiple imperceptibly and gradually deplete immune cells known as CD4 T-cells. As immune deficiency develops, a number of nonspecific symptoms are likely to appear, including:
- Oral candidiasis , a fungal infection that causes the formation of creamy, white lesions on the sides of the tongue and lining of the mouth
- Unexplained fevers and drenching night sweats that soak through bedsheets and nightclothes
- Severe, uncontrolled diarrhea that lasts for more than three days
Each of these symptoms is commonly seen in persons with immune deficiency. They may, in some cases, be caused by HIV itself or by an infection that has yet to be diagnosed.
If Youre Infected Your Current Partner May Not Be To Blame
If you learn you have HPV , dont jump to conclusions about where you contracted the virus.
Some patients assume that their current sexual partner gave it to them, says Robinson. But thats probably not the case. The women who develop cervical cancer at age 40 probably got infected shortly after with their first sexual partner.
Thats because HPV can stay dormant for years before it starts causing the cell damage that can lead to cancer. HPV-triggered cancers can take years, or even decades, to develop.
Hiv Proteins Dysregulate Dopamine Signaling
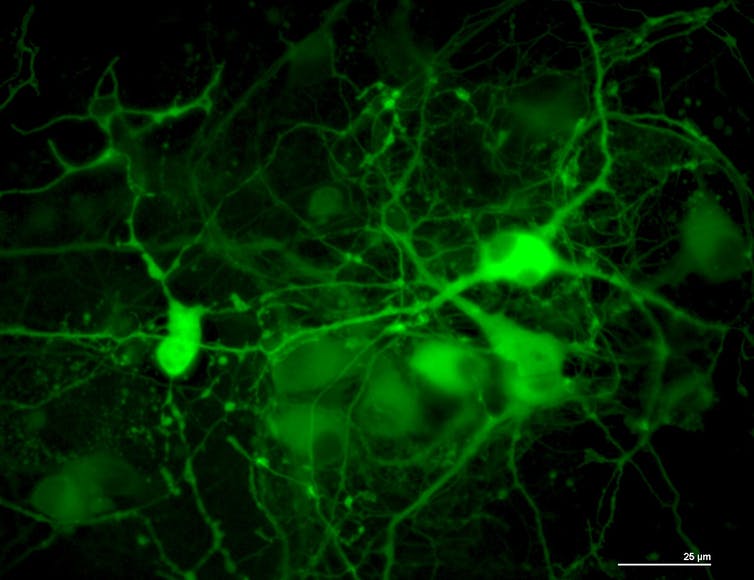
To answer this, we used a mouse in which we can control the levels of HIV viral protein in order to probe the link between HIV infection and neurological disease.
Our lab discovered that an HIV protein, called HIV-1 Tat, reduces the level of an important protein required for the production of a dopamine, a neurotransmitter, in the brain.
Dopamine is produced by neurons in the central nervous system and by immune cells in the blood. Using a confocal microscope to see fine details, my colleagues and I carefully examined the dopamine producing areas in the brains of mice containing HIV-1 Tat protein and were surprised to discover that the neurons were alive. But, many that normally produced dopamine were unable to produce as much. We also found that an enzyme necessary to make dopamine, called tyrosine hydroxylase, was no longer detectable in some neurons. This suggests that the mice can’t make as much dopamine.
When microglial cells secrete the HIV-1 Tat protein, it is able to enter dopamine neurons and lower their activity so that they produce less dopamine. That reduces their ability to communicate with other cells in the brain, which can disrupt the ability to move and reward related behaviors. Also, low levels of dopamine in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra is a hallmark of Parkinson’s and predisposes patients to depression and addiction to drugs like methamphetamine and cocaine.
You May Like: How I Found Out I Had Hiv
Some Hiv Facts You Must Know
How long can HIV go undetected? It is a common question, but people have other concern and questions regarding HIV and AIDs. For instance:
1. Is it possible for tops to get HIV?
The term ‘tops’ refers to the insertive partner in anal sex. Some people believe that male tops are at a lowered risk of getting HIV. A study has confirmed it,;stating that tops have 86% reduction in their risk of contracting the infection.
2. Do you have AIDS when you are tested HIV positive?
No, you do not. Millions of people infected with HIV never develop AIDS, which is the last stage of HIV disease. You can avoid having AIDS through regular medical care and proper treatment to strengthen your immune system.
3. Will you die because of HIV?
No, you will not at least not anytime soon. Yes, there will be complications, but that is true for any chronic condition. With modern-day medications and resources, people with HIV can hope to live a near-normal lifespan. You may be at an increased risk of developing osteoporosis and other age-related conditions early, but you can certainly improve the quality of your life through proper medical care.
4. How you can and cannot get HIV?
Odds Are Youve Probably Had Hpv

HPV is the most common;sexually transmitted infection;in the United States: According to the CDC, 79 million Americans are currently infected with some form of HPV, and 14 million become newly infected each year.
If youve been sexually active, youve got at least a 50 percent chance of having had the virus, says Dr. Robinson. Some data suggests that more than 80 percent of sexually active;women will get HPV;at some point.
HPV is actually an umbrella term for more than 150 strains of related viruses, most of which are relatively harmless. About 40 of them can infect the genital areas in both men and women, and a smaller number can cause;genital warts;or cancer.
Most of the time, youll never even know youve had HPV, because most strains are symptomless. And in 90 percent of cases, the immune system clears the virus naturally within two years, according to the CDC. But when HPV does not go away on its own, some HPV strains can cause a variety of types of cancer.
People living with HIV are more likely to have HPV infections that persist, raising their chances of developing an HPV-related cancer.
Don’t Miss: How Does Hiv Affect The Immune System
How Is Tb Spread
TB germs are spread from person to person through the air. TB germs are put into the air when a person with TB disease of the lungs or throat coughs, sneezes, laughs, or sings. People nearby may breathe in the germs and become infected. TB is NOT spread by sharing silverware or cups, or sharing saliva when kissing someone.
Here Is My Problem After Removal Of My Uterus Could I Still Have It And It Lay Dormant For All Of These Years
How long can HIV go undetected. A persons viral load is considered durably undetectable when all viral load test results are undetectable for at least six months after their first undetectable test result. Some HIV Facts You Must Know. These tests look for HIV infection in the blood and are capable of detecting the infection about 7-28 days after becoming infected. Is it possible for hiv to lie dormant for 4 years before showing symptoms. In rest it may remain for 10 years or longer.
Recommended Reading: How Does Hiv Affect People
Stage : The Asymptomatic Stage
Once a person has been through the acute primary infection stage and seroconversion process, they can often start to feel better. In fact, HIV may not cause any other symptoms for up to 10 or even 15 years .
However, the virus will still be active, infecting new cells and making copies of itself. HIV can still be passed on during this stage. If left untreated, over time, HIV infection will cause severe damage to the immune system.
I Could Do That In My Sleep
A diagram of a virus, showing genetic material in strands in side, and a membrane and envelope protecting this material on the outside. Image by Nossedotti;.
When a tiny virus puts itself to sleep, most researchers stop paying attention. They dont see any proteins being produced, so they assume that the virus is somewhere off in dreamland. However, it turns out that HSV may produce some proteins while latent. They are proteins that are usually made during a lytic infection. If the virus is supposed to be asleep, how are these proteins being made?
To figure this out, the scientists made mutant HSV viruses. These mutant viruses made CRE recombinase, a special protein that activates a silenced gene in the infected cells. This gene allowed the neurons to glow blue if the protein was being made. This would allow the scientists to see when the proteins were made. The proteins they were tracking were proteins usually produced during lytic infection.
This image shows cells with viruses that are making proteins even when they are supposed to be sleeping. Click for more detail.
Scientists infected mice with these mutant viruses and tracked when lytic proteins were made in the mices neurons. They saw the mice neurons glowing blue, during both lytic and latent infection. This meant that lytic proteins were being produced even while the virus was asleep.;
You May Like: How Do You Know If You Got Hiv
Where Else Could The New Coronavirus Persist After Recovery From Covid
Other sites where coronavirus has been detected include the placenta, intestines, blood and of course the respiratory tract. In women who catch COVID-19 while pregnant, the placenta develops defects in the mothers blood vessels supplying the placenta. However, the significance of this on fetal health is yet to be determined.
The new coronavirus can also infect the fetus via the placenta. Finally, the new coronavirus is also present in the blood and the nasal cavity and palate for up to a month or more after infection.
The mounting evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-2 can infect immune privileged sites and, from there, result in chronic persistent but not latent infections. It is too early to know the extent to which these persistent infections affect the health of an individual like the pregnant mother, for example, nor the extent to which they contribute to the spread of COVID-19.
Like many things in the pandemic, what is unknown today is known tomorrow, so stay tuned and be cautious so as not to catch the infection or, worse yet, spread it to someone else.
Hiding Is Better Than Fighting
Creating a vaccine for HSV is difficult because it hides within the nervous system. HSV travels to the nervous system so quickly that it is challenging to have an effective immune response that will prevent it from entering our nerves. One solution to this problem may be to keep HSV latent so that it never wakes up from its deep slumber. This could prevent the virus from causing disease. For this solution to work, we must understand why HSV goes into latency in the first place. Studies like this one are just a start, we still have a lot to learn about what viruses do while they are sleeping.;
Additional images via Wikimedia Commons. Chickenpox image by Jonnymccullagh. 3D herpes virus by Thomas Splettstoesser.
Also Check: Are Hiv Drugs Covered By Insurance
What Are The Different Stages Of An Hiv Infection
Untreated infection with HIV progresses over time and gradually impairs specific parts of the immune system, especially by destroying the white blood cells known as CD4 lymphocyte cells. This progression is described as occurring in stages. All stages require laboratory confirmation of HIV infection.
There are multiple different staging systems. For example, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention case definition uses a staging system based on how much damage has been done to the immune system:
- Stage 1 disease is the earliest phase. Stage 1 has no unusual infections or cancers or other conditions that would be associated with AIDS. In other words, stage 1 disease has no “AIDS-defining conditions” . Although blood tests are positive for HIV, the CD4 cell count is at least 500 cells per microliter of blood .
- Stage 2 disease occurs when the CD4 count is between 200-499 cells per microliter , but again there are no AIDS-defining conditions present.
- Stage 3 disease is synonymous with AIDS and is the most severe stage. There are two ways of diagnosing stage 3 disease: either by CD4 counts below 200 cells per microliter or through documentation of an AIDS-defining condition.
Another way to conceptualize HIV is according to the characteristics or clinical manifestations: acute infection, clinical latency, or AIDS.
How Long Can Chlamydia Lay Dormant
22 February 2021
Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases in the UK. In 2018 alone, 49% of all new diagnoses of STDs were Chlamydia. A possible reason for this is that the Chlamydia can lay dormant for many years without the carrier knowing. In this blog, we will look at how Chlamydia is transmitted, and how to prevent and treat it.;
Read Also: Can I Get Hiv From Spit
When And Who Should Get Tested
The CDC recommends that anyone between ages 13 and 64 should have them tested for the infection. It is important to undergo a repeat test if you have changed your sexual partner. In most cases, you should have your HIV test after 3 months of engaging in sexual activity with a new partner. Some people are at high risk for contracting the virus this is true for IV drug users, homosexual males, and those who change sex partners often. For them, it is important to go for HIV testing every 6-12 months.
Your body may have enough antibodies after 3 months of becoming infected some people may have those antibodies within;20 days of becoming infected. Therefore, it is a good idea to go for testing every six months, especially if you have had unprotected oral, anal, or vaginal sex with a different partner during this time. To get tested, you can go to your local health department, doctor’s office, or hospital. Nowadays, special sites are set up to help you with HIV testing these testing sites keep your data private and share it only with medical experts authorized to see your record.
Risk of HIV
It is worth mentioning that certain factors put you at an increased risk of becoming infected. For instance, you are likely to contract the HIV virus if:
You should talk to your healthcare provider to get more information regarding how long can HIV go undetected and how often you should go for HIV testing.
Show/hide Words To Know
CRE Recombinase: a special protein that can delete a gene or flip it in a specific way.
Gene silencing: switching off the function of a gene.
Herpes Simplex Virus: a virus that affects humans and causes blistering of the skin. Oral herpes and chickenpox are herpes viruses. Herpes simplex virus comes in two varieties: Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 causes cold sores. Herpes Simplex Virus 2 causes sores on the genitals….more
Latent: hidden, concealed, or lying in wait until conditions are better. A latent infection is one where a virus is not actively replicating but is instead sleeping until a better time to replicate.
Lytic: causing lysis, or rupturing of the cell wall, which leads to cell death.
Lytic Infection: a specific type of replication where a virus actively replicates and then leaves the infected cell through the cell membrane.
Replicate: to make a copy or to reproduce.
Vaccine: a substance that provides immune memory using antigens, or dead or weak viruses or bacteria, instead of from an infection.
Read Also: How Long Do Hiv Results Take
Can You Catch Syphilis Twice
A: No. The infection is sequential, so everyone with secondary syphilis has had primary syphilis, although it may have been asymptomatic. However, if you seek treatment for secondary syphilis and the treatment is successful, you will not develop latent or tertiary syphilis unless you contract syphilis again.
Understanding Hiv And Aids
Generally speaking, the time it takes to go from HIV infection to AIDS is around five to 10 years if no medical intervention is made. Differences in time can be due to any number of factors, including:
- The genetic strain of HIV a person has been infected with
- The general health of the individual
- The place where the person lives
- A person’s genetics or family history
- Smoking and other personal lifestyle choices
This is, of course, if the person receives no treatment. The picture changes entirely if he or she does.
Since 1996, the introduction of antiretroviral drugs has dramatically altered the natural progression of HIV infection. While HIV still cannot be cured, people newly diagnosed with HIV who get treated and stay in care can be expected to have near-normal to normal life expectancies. As with other chronic diseases, early detection is key to identifying and treating the infection as soon as possible.
You May Like: How Does Hiv Aids Spread
What Is The Treatment For Syphilis
For detailed treatment recommendations, please refer to the 2021 CDC STI Treatment Guidelines. The recommended treatment for adults and adolescents with primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis is Benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units administered intramuscularly in a single dose. The recommended treatment for adults and adolescents with late latent syphilis or latent syphilis of unknown duration is;Benzathine penicillin G;7.2 million units total, administered as 3 doses of 2.4 million units administered intramuscularly each at weekly intervals. The recommended treatment for neurosyphilis, ocular syphilis, or otosyphilis is Aqueous crystalline penicillin G 18-24 million units per day, administered as 3-4 million units intravenously every 4 hours or continuous infusion, for 10-14 days. Treatment will prevent disease progression, but it might not repair damage already done.
Selection of the appropriate penicillin preparation is important to properly treat and cure syphilis. ;Combinations of some penicillin preparations are not appropriate replacements for benzathine penicillin, as these combinations provide inadequate doses of penicillin. 8
Persons who receive syphilis treatment must abstain from sexual contact with new partners until the syphilis sores are completely healed. Persons with syphilis must notify their sex partners so that they also can be tested and receive treatment if necessary.