Screening For Hiv In Pregnancy
If you’re pregnant, you’ll be offered a blood test to check if you have HIV as part of routine antenatal screening.
If untreated, HIV can be passed to your baby during pregnancy, birth or breastfeeding. Treatment in pregnancy greatly reduces the risk of passing HIV on to the baby.
Page last reviewed: 22 April 2021 Next review due: 22 April 2024
Do I Need To Get Tested For Hiv
You should get tested if you:
- have recently been diagnosed with another STI
- have or other injecting equipment
- are worried about HIV and want to put your mind at ease.
For more information on how HIV is passed on, read this page.
Even if you think its unlikely that you will have HIV, the quickest way to stop worrying is by taking a test.
If youre sexually active, its good to get into the habit of testing regularly for HIV, even if you regularly use condoms and dont think you have been at risk.
If I Test Negative Does That Mean My Partner Is Too
No. The test for HIV can only tell you if you have been infected or not. Transmission of the virus does not necessarily occur every time exposure occurs. The only way for an individual to tell if they have been infected with HIV is to be tested. If you are unsure of your partners status, you may want to consider talking to them about it and using protection to reduce your risk.
Don’t Miss: Does Hiv Cause Hair Loss
For Rna Or 4th Generation Antigen Test
These tests can usually detect HIV within 2 weeks after the infection. RNA/4th generation test are not available for in home use. It is important to see your doctor or health care provider as quickly as you can if you think you have been exposed to HIV. Starting treatment very soon after infection can help one’s health. If you think you may have been infected, get tested right away. This is particularly important if you think you have symptoms that might come from acute HIV .
Other Factors Influencing Hiv Transmission Risk
Within each route of transmission, estimates of the risk of transmission vary widely, likely due to the role of behavioural and biological co-factors. Viral load appears to be an important predictor of transmission, regardless of route of transmission. However, the evidence indicates that viral load is not the only determinant, and other co-factors, such as the presence of co-infections, play a role in increasing or decreasing the risk of transmission.
Viral Load
The strongest predictor of sexual transmission of HIV is plasma viral load . A dose-response relationship has been observed, where each ten-fold increase in plasma VL resulted in an increased relative risk of transmission of 2.5 to 2.9 per sexual contact. The concentration of HIV in genital secretions also plays a major role in sexual transmission. While there is a strong correlation between HIV concentrations in plasma and in genital secretions, some studies have found genital tract HIV shedding in 20% to 30% of men and women without detectable plasma viral load. Much of what is known about the impact of viral load on the sexual transmission of HIV is derived from studies of heterosexual populations. Very little is known about the relationship between HIV viral load and rate of transmission through anal intercourse.
Co-infections
Circumcision
Also Check: How Does Cookie Johnson Not Have Hiv
Why Should I Have An Hiv Test During Pregnancy
If you have HIV and are not treated, there is a 1 in 4 risk that your baby will have HIV. If you are treated, the risk drops to about 1 in 100. Most babies born to HIV-positive mothers will NOT get HIV if mothers are treated during pregnancy and delivery, and if babies are treated in the first few weeks after birth. Treatment will also improve your health.
Other Information To Note
When contacting an embassy or consulate to ask about travel restrictions, an individualâs name and HIV status can be kept anonymous.
For British Overseas Territories, The Foreign & Commonwealth Office website is a good place to start at www.fco.gov.uk. It may also be beneficial to contact an HIV organisation in the destination country to ask for information.
If a country does have entry restrictions, people with HIV who still decide to travel risk being refused entry or deported. It is worth noting that some countries will offer waivers under certain circumstances, particularly if the trip is to visit family members, but they may be difficult to obtain.
Travel restrictions for people with HIV can change quickly and so need to be checked before any trip. China and America are two examples of countries that recently lifted their restrictions on HIV-positive visitors.
In countries where restrictions have been recently changed, extra caution should be taken if discussing HIV status. If someone with HIV flouted the regulation and travelled into a country when the ban was in place, they could still be open to deportation following a travel ban being lifted. This could happen if there was proof that the individual knew of their HIV-positive status when the ban was in place and still entered the country. In this circumstance, the individual would have broken the law in the past and could be deported for that reason.
Read Also: Does Cookie Johnson Have Hiv
How Can Testing Help You
The only way to know for sure whether you have HIV is to get tested.
Knowing your HIV status gives you powerful information to help you take steps to keep you and your partner healthy.
- If you test positive, you can take medicine to treat HIV . People with HIV who take HIV medicine as prescribed can live long and healthy lives. Theres also an important prevention benefit. If you take HIV medicine daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex.
- If you test negative, you have more prevention tools available today to prevent HIV than ever before.
- If you are pregnant, you should be tested for HIV so that you can begin treatment if you’re HIV-positive. If an HIV-positive woman is treated for HIV early in her pregnancy, the risk of transmitting HIV to her baby can be very low.
Reducing The Risk Of Hiv Transmission
The most effective way to prevent HIV transmission during sex is to use a condom. Get a condom ready before any sexual contact occurs, since HIV can be transmitted through pre-ejaculate, vaginal fluid, and from the anus.
Lubricants can also help reduce the risk of HIV transmission by helping to prevent anal or vaginal tears. The right lubricants also help prevent condoms from breaking. Only water-based lubricants should be used with condoms, because oil-based lube can weaken latex and sometimes cause condoms to break.
The use of a dental dam, a small plastic or latex sheet that prevents direct contact between the mouth and the vagina or anus during oral sex, is also effective at reducing the risk of HIV transmission.
For people who may have a higher risk for contracting HIV, preventive medication is an option. Pre-exposure prophylaxis medication is a daily antiretroviral treatment.
Everyone at increased risk of HIV should begin a PrEP regimen, according to a recent recommendation from the US Preventive Services Task Force. This includes anyone who is sexually active with more than one partner, or is in an ongoing relationship with someone whose HIV status is either positive or unknown.
Although PrEP does provide a high level of protection against HIV, its still best to use condoms as well. PrEP provides no protection against STIs other than HIV.
Read Also: How Long Does Hiv Live On Surfaces
How Can I Get Tested
To get tested, you can:
- Ask your doctor to test you.
- Go to a local clinic or community health center.
- Go to National HIV and STD Testing Resources to find a testing center near you.
- Buy a test at a pharmacy and do the test at home.
Many testing centers will do an HIV test for free. Ask if there is a fee before you go for testing. In most states you do not need a parent’s permission to get tested for HIV. And you can buy the test at the pharmacy without a parent.
You May Be At Risk Without Realizing It
The CDC estimates that about 1.1 million people live with HIV in the U.S. But about 1 in every 7 of them doesn’t know he or she is infected.
Philip Chan, M.D., an assistant professor of medicine at Brown University and director of the Rhode Island STD Clinic, gives the example of a married couple in which one partner has been unfaithful. That would mean the other could have been exposed unknowingly.
Its uncomfortable talking to patients about these things, Chan says. That may be one reason the rate of screening is so low, he says, and why he and others would like to see it become a more routine part of care.
You May Like: What Do Hiv Bumps Look Like
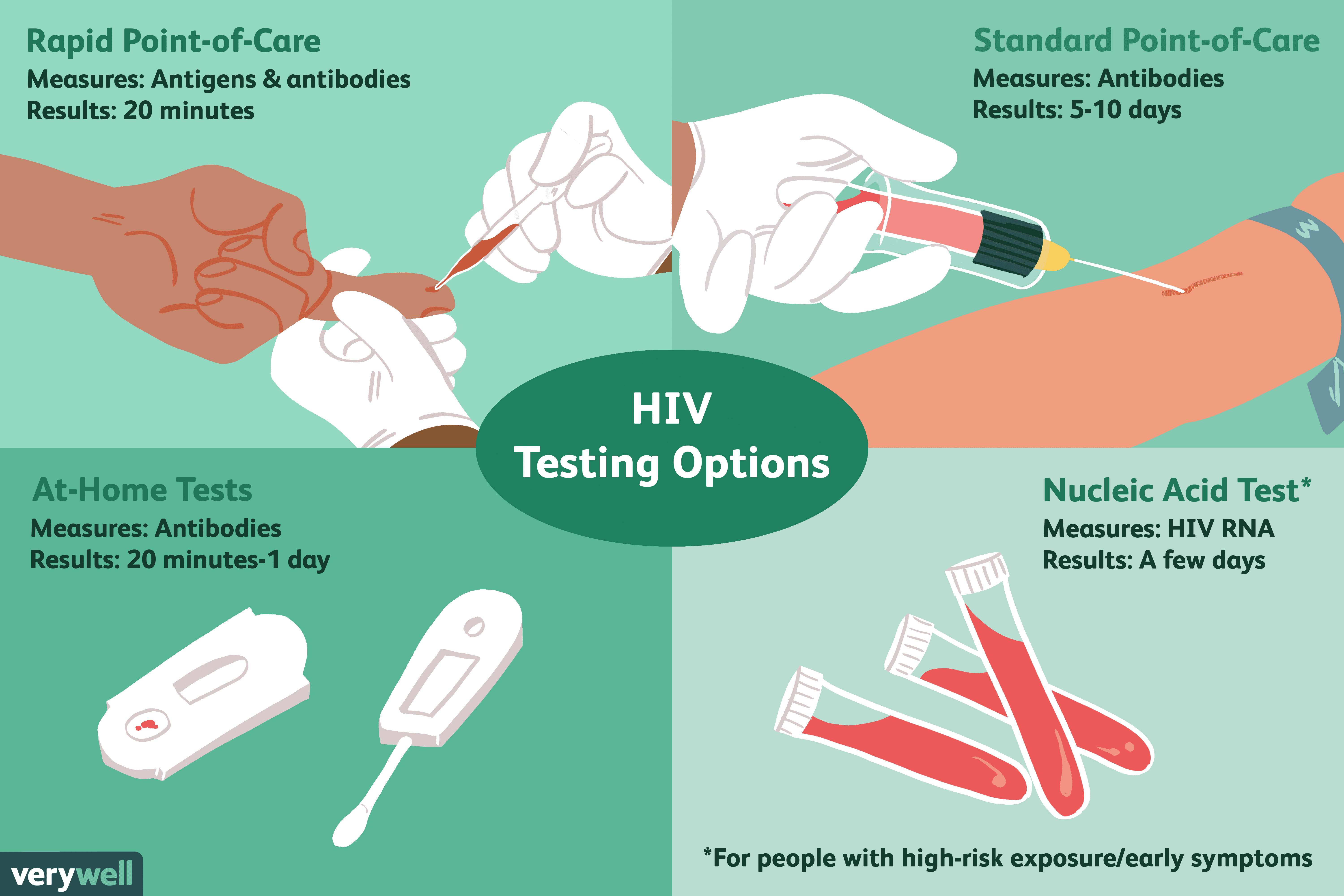
What Types Of Tests Diagnose Hiv
To diagnose HIV, healthcare providers can order any of three tests:
- Nucleic acid test: The NAT test looks for the virus in your blood. It is a thorough laboratory test but can be costly. The results can take several days to receive.
- Antigen/antibody test: This test looks for antibodies and antigens to HIV in your blood. Your immune system forms antibodies when it comes in contact with viruses, such as HIV. Antigens, however, are foreign substances that activate your immune system. HIV has a particular antigen that this test can find. This rapid test uses a drop of blood from a finger prick and can give you results in roughly 30 minutes.
- HIV antibody test: This test is similar to the antigen/antibody test, but it only looks for the antibody. Just like the antigen/antibody test, this test produces results in around 30 minutes. It uses either a drop of blood from a finger prick or a swab of saliva.
Some states allow for home testing. There are two types of home tests:
- Rapid self-test: The only rapid self-test available in the United States uses a saliva sample to check for infection. After you receive your kit, you swab your gums and use the test kit to get results.
- Mail-in self-test: This test uses a blood sample from a simple finger prick. All of the supplies are in the kit to help you take the sample, package it and send it to the lab. A healthcare provider will tell you the results.
Importance Of Hiv Testing

If you have the virus, finding out quickly means you can start treatment right away so you can feel better and live a long, full life. You can also take steps so you don’t pass HIV to other people.
Pregnant women should get tested because early treatment means you probably wonât pass it to your baby.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have Herpies
Should You Get Tested For Hiv
Everyone between the ages of 13 and 64 should get tested for HIV at least once. If your behavior puts you at risk after you are tested, you should think about being tested again. Some people at higher risk should get tested more often.
If your last HIV test result was negative, you should get an HIV test if you answer “yes” to any of the questions below about your risk since that test:
- Are you a man who has had sex with another man?
- Have you had sexanal or vaginalwith an HIV-positive partner?
- Have you had more than one sex partner?
- Have you injected drugs and shared needles or works with others?
- Have you exchanged sex for drugs or money?
- Have you been diagnosed with, or sought treatment for, another sexually transmitted disease?
- Have you been diagnosed with or treated for hepatitis or tuberculosis ?
- Have you had sex with someone who could answer “yes” to any of the above questions or someone whose sexual history you don’t know?
Sexually active gay and bisexual men may benefit from more frequent testing .
If you’re pregnant, talk to your health care provider about getting tested for HIV and other ways to protect you and your child from getting HIV.
Protect Yourself From Hiv
The best way to protect yourself from HIV is to not have sex unless you’re in a relationship with only one person and you have both tested negative.
Here are other steps you can take to help prevent HIV:
- Use a latex condom with water-based lubricant every time you have vaginal or anal sex.
- If you share sex toys with your partner, use a condom and clean them between each use.
- Dont inject drugs or share needles.
Check out these condom do’s and don’ts.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have Herpes
National Hiv Testing Day Is A Good Time To Understand Why It’s So Important
Everyone between the ages of 13 and 64 should be tested for HIV at least once in their lifetime, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
Despite the CDCs sweeping recommendation, fewer than 40 percent of adults in the U.S. have ever gotten an HIV test, according to a study published last year. And even though HIV testing is becoming more common in emergency rooms and community health centers, there has been no increase in testing at doctors’ offices, the CDC reported in a .
In the midst of the COVID-19 crisis, HIV may not be top of mind. But HIV and sexual health services are always needed, says Omi Singh, M.P.H., the director of testing at GMHC, an HIV care and advocacy nonprofit. The current pandemic has not stopped that.
HIV, the virus that leads to the immune-system disease AIDS, is most common among intravenous drug users and men who have sex with men, and the CDC recommends that people in these groups get tested at least once a year. Yet its not just these groups who are at risk.
For example, in 2018, a quarter of new HIV infections were found in heterosexual people. And Black Americanswho make up 13 percent of the populationaccounted for 42 percent of all new HIV diagnoses.
And though infection rates are higher in certain groups, no one is exempt from being at risk, says Singh.
Regardless of your background, here are five reasons to consider getting screened.
How Often Do I Need To Get Tested For Hiv
Everyone ages 15 to 65 needs to get tested for HIV at least once. All pregnant women also need to get tested. People at higher risk for HIV infection may need to get tested more often. Talk to your doctor or nurse about how often you need to get tested.
Get tested for HIV at least once a year if you’re at higher risk.
For example, you may be at higher risk for HIV if you:
- Are a man who has sex with men
- Have sex with someone who has HIV
- Use drugs with needles
- Have sex in exchange for drugs or money
- Have had 1 or more new sex partners who could have HIV since your last test
If you’re a man who has sex with men, you may need to get tested even more often like every 3 to 6 months. Talk to your doctor or nurse about what’s best for you.
Don’t Miss: Can Hiv Lay Dormant
Where Can I Get An Hiv Test
Depending on where you are in the world, there are a number of places that you can get tested for HIV. The best first step is to search online for “HIV testing, plus your location. This will generally give you a good idea of where to go, or at least give you a starting point.
If you have limited internet access, its always worth asking local sexual health charities or health professionals what is available in your area. They should be able to direct you to somewhere where you can test for free. The image below has some examples of the types of places that might offer HIV testing.
Who Should Be Tested For Hiv And How Frequently
It is recommended that the consideration of HIV testing be made a component of routine care. In general, care providers should take an active approach to HIV testing, offering HIV testing to clients whether or not clients have asked for a test. In the provision of routine medical care, and in discussion with the client, care providers should consider whether there is a benefit to an HIV test.
HIV testing is associated with several advantages:
- a negative test result is an opportunity for clients to take an active role in remaining HIV negative
- the early detection of HIV, especially at the acute stage, can improve outcomes for individuals and prevent further transmission of HIV
- detection at any stage of the disease, prior to wasting and dementia, is an opportunity to initiate lifesaving treatment and other related healthcare services
- opportunities arise for conversations with clients about risk-reduction strategies
2.1.1 Testing recommendations
An in-depth comprehensive HIV behavioural risk assessment is not a requirement for offering an HIV test. An assessment that the client understands how HIV is transmitted, the implications of testing , and how to interpret the test results is sufficient.
For occasions when clients may not be able to accurately estimate their risk, the guide includes more detailed guidance in Appendix B for conducting rapid risk assessments and a more detailed technical review of HIV transmission risks can be found in Appendix C.
2.1.2 Couples testing
Also Check: Hiv Stays Alive In Dried Blood
Who Else Should Get Hiv Tests
The CDC recommends that everyone between ages 13 and 64 get tested at least once even if you have no risk factors for HIV. Other people who should get tested at certain times or regularly include:
Pregnant women. HIV can be passed from mother to child in the womb. HIV testing is part of pregnancy care, but you have to agree to do it. If you test positive, antiretroviral therapy can protect your unborn baby from getting HIV. This works extremely well if you start treatment early.
People in a high-risk group. Get tested at least every 12 months if you inject drugs, work in the sex trade, have multiple sex partners, or do anything else that puts you at a higher risk.
If you are a sexually active gay or bisexual man, consider testing every 3 months. This is especially important if you donât know whether or not your partner or partners have HIV. Most infections happen in men who have sex with other men, and many donât know if they have HIV or not.
CDC: âTesting,â âHIV Risk Reduction Tool: The Window Period,â âHIV Risk Reduction Tool: Post-exposure Prophylaxis for Preventing HIV after Exposure,â âAn Opt-Out Approach to HIV Screening,â âHIV and Gay and Bisexual Men.â
NAM AIDSMap : âFalse negative results on HIV tests.â
HIV.gov: âHIV Testing Overview,â âHow Can You Tell If You Have HIV?â
San Francisco AIDS Foundation: âThe Questions about PrEP.â
GMHC: âHIV/AIDS Basics,â âThe GMHC Testing Center.â
Avert: “When to Get Tested for HIV.”