I Prefer Sex Without A Condom So I Don’t Always Use Them Would Prep Still Work To Prevent Hiv If I Don’t Use Condoms
If a person takes the PrEP medication consistently as directed, it provides a high level of protection against HIV. Condoms provide protection against sexually transmitted infections . People who are on the PrEP medication but are not using condoms may be exposed to an STI. It is important to be aware that having an STI can increase a persons chance of getting HIV if exposed to the virus. Some STIs dont have symptoms or symptoms may disappear on their own for periods of time. If you are not using condoms regularly, it would be especially important to have regular testing for STIs and to get treated as soon as possible if you have an STI. Screening for chlamydia and gonorrhea should include swabs of a persons genitals, rectum and mouth. Learning about the signs and symptoms of STIs is helpful in identifying whether you or one of your partners has an STI. Condom use is recommended but choosing to not use condoms routinely should not prevent you from being prescribed PrEP.
Prep And Multiple Sex Partners
The efficacy of PrEP does not appear to be diminished by many of the traditional risk factors associated with infection.
While inconsistent condom use and multiple sex partners, for instance, are known to increase the risk of HIV infection, they might not reduce the effectiveness of PrEP in high-risk individuals.
However, this is not proven and more research is needed.
The case of the person who contracted a wild-type HIV while on PrEP was part of a European PrEP study. The man took the medication as prescribed, which was confirmed through blood tests.
He reported over 90 sex partners and over 100 acts of condomless anal sex during the 12-week trial. While on PrEP, the man was diagnosed twice with rectal gonorrhea and once with rectal chlamydia.
Given his record of taking the medication, some researchers suspect that the medication may have been overwhelmed by very high levels of exposure to HIV or other factors, such as having other STDs when exposed to HIV.
If so, these still-unidentified factors may place others at risk. Until researchers know more, safer sex practices, such as using condoms, should be adhered to if only to provide an additional layer of protection.
This added protection is particularly important if you don’t know whether or not your partners were tested for HIV, or if they have HIV but you’re unsure if they’re being treated with medication.
In addition, PrEP does not protect you against other types of sexually transmitted infections.
How Long Do I Need To Be On Prep
Talk with your doctor about your personal circumstances. There are several reasons that people stop taking PrEP:
- If your risk of getting HIV infections becomes low because of changes that occur in your life.
- You don’t want to take medication every day or often forget to take your medication other ways of protecting yourself from HIV infection may work better for you.
- You have side effects from the medication that are interfering with your life.
- Blood tests show your body is reacting to PrEP medication in unsafe ways. Your doctor may decide there are other options for you.
Talk with your doctor if you are having trouble remembering to take your medication or if you want to stop PrEP.
It is important to make sure that you continue taking PrEP for 28 days after your last potential exposure to HIV before ceasing it.
Don’t Miss: Is Hiv Curable Or Treatable
What Are The Other Possible Side Effects Of Truvada For Prep
Serious side effects of TRUVADA may also include:
- Kidneyproblems, including kidney failure. Your healthcare provider should do blood and urine tests to check your kidneys before and during treatment with TRUVADA. If you develop kidney problems, your healthcare provider may tell you to stop taking TRUVADA.
- Too much lactic acid in your blood , which is a serious but rare medical emergency that can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get these symptoms: weakness or being more tired than usual, unusual muscle pain, being short of breath or fast breathing, stomach pain with nausea and vomiting, cold or blue hands and feet, feel dizzy or lightheaded, or a fast or abnormal heartbeat.
- Severe liver problems, which in rare cases can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get these symptoms: skin or the white part of your eyes turns yellow, dark “tea-colored” urine, light-colored stools, loss of appetite for several days or longer, nausea, or stomach-area pain.
- Bone problems, including bone pain, softening, or thinning, which may lead to fractures. Your healthcare provider may do tests to check your bones.
Common side effects in people taking TRUVADA for PrEP are headache, stomach-area pain, and decreased weight. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effects that bother you or do not go away.
How Effective Is Prep
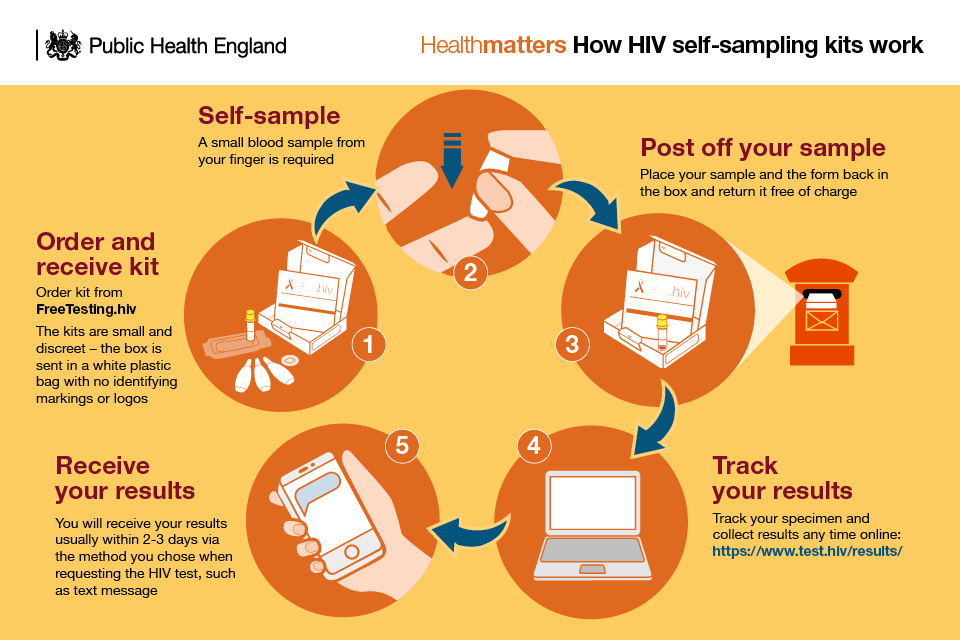
If you use it correctly, PrEP can lower your chances of getting HIV from sex by more than 90%. And using condoms and PrEP together helps you stay even safer. PrEP can also lowers your chances of getting HIV from sharing needles by more than 70%.
Its really important to take PrEP every day. PrEP doesnt work as well if you skip pills. If you dont take it every day, there might not be enough medicine in your body to block HIV.
PrEP doesnt prevent other sexually transmitted infections, like gonorrhea and chlamydia. So use condoms along with PrEP to help you avoid other STDs and give you extra protection against HIV.
You May Like: Can You Get Hiv Through Saliva
Awareness And Demand Generation
Many people who could benefit from PrEP are still unaware of its existence.
One study surveying awareness and acceptability of PrEP among men who have sex with men in Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland found that only one third were aware of PrEP. Men who tested for HIV every six months were most likely to be aware of PrEP.79
A US-based study among adolescent men who have sex with men found that only 16% of survey participants were aware of PrEP, also that those who reported more regular conversations about HIV with the parents were more likely to be aware of PrEP. Among those who were aware of PrEP, more meaningful communication with a parent was associated with adolescents feeling more in control with regard to using PrEP.80
Another US-based study among young black men who have sex with men, one of the most vulnerable groups for HIV in the USA, found awareness and uptake of PrEP to be low, echoing the treatment disparities that this group experienced earlier in the HIV response.81
Similarly, only 39% of men who have sex with men surveyed in Thailand said that they would definitely use PrEP. Those participants who perceived themselves to be at higher risk of HIV were more motivated to take PrEP, whereas younger and less educated participants and those engaging in transactional sex were less likely to take it.82In the UK, around half of men who have sex with men have shown an interest in taking PrEP.83
How Much Does Prep Cost
Most health insurance plans, including Medicaid, cover PrEP. Check with your insurance company to see if PrEP is covered on your plan. You might also be able to get help with other expenses, like copays, coinsurance, and deductibles, though Gilead or patient advocacy groups like the Patient Advocate Foundation.
If you dont have health insurance, you can still get help paying for PrEP. Gilead has a medication assistance program that could make PrEP free for you, depending on your income. Your doctor or nurse will need to submit an application for you to find out if you qualify.
The staff at your local Planned Parenthood health center can also help you apply for health insurance or assistance programs that can make PrEP affordable for you.
Read Also: How Long After Sex Should You Get Tested For Hiv
Sharing Needles And Injecting Equipment
If you inject drugs, this could expose you to HIV and other viruses found in blood, such as hepatitis C.
It’s important not to share needles, syringes, injecting equipment such as spoons and swabs, or the actual drugs or liquids used to dilute them.
Many local authorities and pharmacies offer needle exchange programmes, where used needles can be exchanged for clean ones.
If you’re a heroin user, consider enrolling in a methadone programme. Methadone can be taken as a liquid, so it reduces your risk of getting HIV.
A GP or drug counsellor should be able to advise you about both needle exchange programmes and methadone programmes.
If you’re having a tattoo or piercing, it’s important that a clean, sterilised needle is always used.
Who Should Take Prep
PrEP can be used by people who are HIV negative and at high risk for HIV infection. Canadian guidelines define this as:
- men or transgender women who report condomless sex with men and have any of the following:
- infectious syphilis or rectal bacterial STI in the last year
- use of post-exposure prophylaxis more than once
- a high score on a valid HIV risk assessment tool
The above list includes people who are likely to be at the highest risk of getting HIV. These criteria can be used to identify PrEP candidates but should not be used to deny someone access to PrEP. Other individuals may be at risk for HIV through sex or drug use and could benefit from the use of PrEP. For example, the Canadian PrEP guideline states: When considering PrEP for heterosexual adults on the basis of having multiple or unknown-status partners, practitioners must make decisions on a case-by-case basis, using local epidemiologic data and patient-reported risk behaviours/exposures in the partner.
Don’t Miss: Can Hiv Spread Through Oral
How Effective Is Prep In Preventing Hiv
When taken as directed , Truvada can reduce your risk of contracting HIV through sex by 99 percent. For those hoping to prevent transmission while using IV drug use, PrEP can be 74 percent effective.
Thus far, clinical research on Descovy has shown its equally effective at preventing HIV transmission through sex as Truvada.
PrEP effectiveness depends on consistency, so dont forget to take it daily.
How Hiv Attacks The Body
The human body has no natural means of fighting and getting rid of HIV. HIV targets your immune system directly, aiming at a specific type of white blood cell. White blood cells are immune system cells tasked with shielding the body against infection and disease.
The group of specific white blood cells attacked by HIV are called CD4 cells. Also known as T-cells or helper cells, CD4 cells help coordinate your bodys immune response, organizing protection against harmful invaders. HIV tricks CD4 cells into becoming a safe haven in which the virus can reproduce and spread throughout your body. HIV depends on CD4 cells to survive and thrive. Without helpful CD4 cells, HIV may not stand a chance.
Read Also: Can Hiv Be Cured Early
What Is The Most Important Information I Should Know About Truvada For Prep
Before and while taking TRUVADA for PrEP:
- You must be HIV negative before you start and while taking TRUVADA for PrEP. Do not take TRUVADA to reduce the risk of getting HIV-1 unless you are confirmed to be HIV negative.
- Get tested for HIV-1 immediately before and at least every 3 months while taking TRUVADA.
- If you think you were exposed to HIV-1, tell your healthcare provider right away. They may do more tests to confirm that you are still HIV negative.
TRUVADA can cause serious side effects:
Get Testing And Treatment

If youre an MSM, consider getting tested at least once a year for HIV. People who have sex with multiple partners or partners of unknown HIV status should consider getting tested more frequently, such as every 3 to 6 months.
People who test positive for HIV should follow their doctors recommended treatment plan. Taking antiretroviral medication will lower the risk of complications and help prevent HIV transmission.
It also helps to ask your sexual partners about their testing history and status.
You May Like: Can You Get Hiv From Getting Fingered
Is It Ok To Switch Between Daily Prep And On
On-demand PrEP is only for cis-gender MSM. Other individuals are not eligible for on-demand PrEP because studies have not demonstrated that it is effective for other populations. Before switching from daily PrEP to on-demand PrEP, or vice versa, a cis-gender MSM should consult with their healthcare provider.
Who Should Consider Taking Prep
PrEP is for people who dont have HIV but who are at risk of getting HIV through sex or injection drug use.
Specifically, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that PrEP be considered for people who are HIV negative who have had anal or vaginal sex in the past 6 months and:
- have a sexual partner with HIV , or
- have not consistently used a condom, or
- have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease in the past 6 months.
PrEP is also recommended for people without HIV who inject drugs and:
- have an injection partner with HIV, or
PrEP should also be considered for people without HIV who have been prescribed non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis and:
- report continued risk behavior, or
- have used multiple courses of PEP.
If you think PrEP may be right for you, talk to your health care provider.
Don’t Miss: Where Did Hiv Aids Originated From
What Impact Can Prep Have On The Lgbtq+ Community
Theres something to be said about having full knowledge and control over your own sexual health. If you can take the necessary steps towards having access to the products and services available, it can be freeing in and of itself. The goal is to empower people to have safe sex and to take charge of their health.
Tops Bottoms And Prep: What You Need To Know About Hiv Prevention
Nearly 70% of people living with HIV are homosexual and bisexual men and thankfully the use of PrEP for HIV prevention is increasing among this group. According to a recent study, the number of gay and bisexual males taking PrEP increased by 500% from 2014 to 2017. However, only 35% of gay and bisexual males who were at high-risk of HIV transmission were taking the medication.
It is important that everyone takes the proper precautions to protect themselves from HIV transmission. While some people are at more risk than others due to lifestyle choices or other practices, there is a common misconception that your risk of HIV transmission is higher or lower depending on your sexual orientation or preferred sexual position.
PrEP is designed to help protect any person regardless of sexual orientation from HIV transmission. But, you may be wondering if PrEP could affect you differently or be more or less effective depending on if you are a top, bottom, or vers.
For instance, many tops assume they do not need to take PrEP since they are at a lower risk of contracting HIV than a bottom since they are not penetrated.
So, does PrEP work differently for tops and bottoms?
Well first, lets explain what puts you most at risk for HIV transmission and why you should consider taking PrEP in the first place regardless of sexual orientation.
You May Like: How To Know If You Hiv
What Is Prep And Who Should Consider It
PrEP is a daily pill taken to lower a persons risk for getting HIV. It works best as part of a program of preventive services that includes regular HIV testing.
Global research during the past decade shows that a combination of two antiretroviral medicines is more than 90% effective at preventing HIV. These medicines, emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, are known by the brand name Truvada. Along with other medicines, they are also used to treat HIV.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and many expert guidelines recommend PrEP for those at high risk for HIV, including
- men who have sex with men
- heterosexual men and women who have high-risk exposure
- people who inject drugs
- transgender women.
Currently, 50% of new HIV cases in the US occur among Black and Latino gay and bisexual men. Slightly more than 15% occur among heterosexual women, roughly three-quarters of whom are women of color.
The CDC estimates that 1.1 million people in the US would benefit from PrEP, including 175,000 women and 780,000 people of color. Yet prescriptions for PrEP are sluggish, particularly in populations at increased risk. Since 2012, only 135,000 PrEP prescriptions have been filled in the US. Almost all were for men largely, white men in the Northeast and on the West Coast who have sex with men.