How Is Transmission In The Workplace Prevented
The Centers for Disease Control recommend using routine practices to protect workers at risk from HIV exposure. This approach stresses that all situations involving contact with blood and certain other body fluids present a risk. Routine practices outline the use of barriers to prevent workplace exposure to HIV and other viruses. These barriers include the use of:
- engineering controls such as retractable needles
- safe work practices and administrative controls
- protective equipment such as gloves, gowns or aprons, masks, and protective eye wear.
CLOSE ALL
What Conditions Are Considered To Be Opportunistic
Some of the most common of these OIs/cancers among HIV-positive people include:
Cancer: The types of cancers that are you are more likely to get if you have AIDs include lymphoma, Kaposis sarcoma, invasive cervical cancer, anal cancer, liver cancer, and cancers of the mouth, throat and lungs.
Candidiasis : This condition is caused by Candida fungus. It can happen in the skin, nails and mucous membranes throughout the body, such as the mouth or the vagina. The cases can be troublesome, but thrush is especially dangerous when it affects the esophagus or parts of the respiratory system .
Pneumonia: This respiratory condition is most commonly caused by _Pneumocystis jirovecii and the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae._
Salmonella: This infection is spread through contaminated food and water. It causes diarrhea, vomiting and nausea.
Toxoplasmosis: This disease is caused by a parasites that live in cats and rodents and other warm-blooded animals. The infection is spread through the feces. Toxoplasmosis can cause severe problems in the lungs, heart, brain and other organs. If you have a cat, wear gloves to change the litter and be thorough in washing your hands.
Impossible Routes Of Hiv Transmission
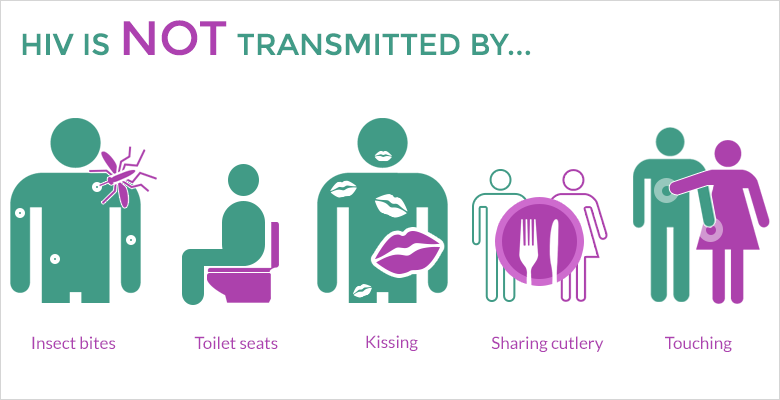
HIV transmission through the following activities is biologically implausible and there have been no documented cases.
There is no risk of HIV being passed on through: coughing, sneezing or spitting kissing, hugging or shaking hands sharing cutlery, plates or cups breathing the same air using the same lavatory mosquito or animal bites.
Also Check: How Is Hiv Transmitted Through Sex
How Do New Hiv Infections Happen
HIV can be passed on to another person through infected blood, semen, vaginal and anal fluids, and breast milk. In the UK, HIV is most commonly transmitted through unprotected anal or vaginal sex or by the sharing of infected needles or other drug-injecting equipment.
HIV cannot live for more than a few minutes outside the human body, so getting HIV is difficult unless you have unprotected sex or share drug-injecting equipment.
It is important to be aware that if someone is on effective medication and the level of virus in their blood has been undetectable for at least 6 months, then they cannot pass on the virus to others.
Mother-to-baby transmission in pregnancy is extremely uncommon in the UK, as doctors work with pregnant women to reduce the risk of this happening.
Many myths continue from the early days of HIV and it is important to be aware that you cannot get HIV through day-to-day contact such as shaking hands or hugging. HIV cannot be transmitted through saliva, including kissing, spitting, or even sharing plates, cups or cutlery. Nor can HIV be passed on though urine or faeces, so you cannot get HIV from a toilet seat!
Tattoos And Body Piercings
- There are no known cases in the United States of anyone getting HIV this way.
- However, it is possible to get HIV from tattooing or body piercing if the equipment used for these procedures has someone elses blood in it or if the ink is shared. This is more likely to happen when the person doing the procedure is unlicensed because of the potential for unsanitary practices such as sharing needles or ink.
- If you get a tattoo or a body piercing, be sure that the person doing the procedure is properly licensed and that they use only new or sterilized needles, ink, and other supplies.
You May Like: How To Cure Hiv Aids
Sequence Analysis Of The Hiv
In one subject from Group B with viral load 18,231 copies/ml in blood, HIV-1 env was PCR detected in all three samples collected concurrently: serum, urine and feces. The PCR products corresponding to the C2-V5 region of HIV-1 env gp120 from all three compartments were cloned and sequenced to determine the viral diversity. A phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method as implemented in Mega 4.0. The validity of the branching orders was estimated with 1000 replicates. Reference strains were obtained from the Los Alamos HIV database by using similar blast search. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that all the sequences belong to HIV-1 subtype B. Blood-, fecal- and urine- derived sequences formed a tightly clustered group of sequences respectively. However, the sequence analysis also showed a distributed pattern of viral variants among blood, feces and urine, indicating that distinct HIV-1 quasispecies existed in different part of tissues within the subject .
Phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1 gp120 C2-V5 sequences from blood plasma, urine and feces. Black triangles: sequences from blood Black circles: sequences from urine Black square: sequences from feces.
Evaluation Of The Sensitivity Of The Pcr Detection Of Hiv
To test the sensitivity of amplifying HIV-1 DNA, 200 mg of normal donor fecal sample was mixed with different concentrations of HIV-1 positive 8E5 cells. Nucleic acid was isolated using NUCLISENS nucleic acid isolation kit. For every DNA sample, the human beta-globin gene was PCR amplified to ensure that the isolated DNA was amplifiable and contained the comparable amount of human DNA. Subsequently, a nested PCR reaction was performed to detect HIV-1 DNA from the isolated DNA using HIV-1 env specific primers. HIV-1 DNA was detected from the DNA isolated from normal donor feces mixed with 8E5 cells and the detection limit was as low as 2.5 copies/reaction .
To test the sensitivity of amplifying HIV-1 RNA, 200 mg of normal donor feces were mixed with a series of different concentrations of HIV-1 positive plasma and nucleic acid was isolated as before followed by RT nested PCR with HIV-1 env specific RT and PCR primers. As a human RNA input control in each sample, cDNA was synthesized by random hexamer followed by nested PCR amplification using human beta-actin mRNA specific primers. HIV-1 RNA was detected from normal feces mixed with HIV-1 positive plasma and the detection limit was as low as 40 copies/reaction .
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hiv From Having Sex One Time
Are Women More Likely To Get Hiv
Yes. Biologically speaking, a woman is more vulnerable to heterosexual transmission of the disease because the genitalia are easily exposed to seminal fluids.
Gender inequality has great influence on the spread of HIV/AIDS among women. In some cultures, many women and girls are often put in situations where they engage in non-consensual sex or have sex for money.
In the U.S., minority communities have been hit the hardest by HIV. African American and Hispanic women together represent less than 25% of all U.S. women, yet they account for more than 78% of AIDS cases reported among women in the country.
Can You Get Hiv Through Oral Sex
The risk of HIV from oral sex is very small unless you or your partner have large open sores on the genital area or bleeding gums/sores in your mouth.
There is only a slightly increased risk if a woman being given oral sex is HIV-positive and is menstruating. However, you can always use a dental dam to eliminate these risks.
Also Check: What Does Hiv Do To The Human Body
When Should You Call The Doctor If You Have Hiv Or You Think You Have Been Exposed To Hiv
There is also post-exposure prophylaxis , which is used in emergencies and should be started within 72 hours after the possible exposure. This involves taking antiretroviral therapy after this exposure. ART may be prescribed after sexual assault, or if you think you have been exposed during consensual sex or drug-taking.
If you already know you have HIV, you should follow your healthcare providers instructions on when to call. It is important to treat any type of infection, so call if you have new symptoms or things like a fever, sweating episodes, diarrhea, and so on. Its better to check with your doctor if you have any kind of symptom that worries you.
The main feature of managing AIDS is to continue to take your medicines and to fight back at opportunistic infections at the first sign of them.
Emergency Hiv Pills: Pep
72 hours should speak with a healthcare provider about PEP. This medication may be able to stop the infection, especially if a person takes it as soon as possible after the potential exposure.
A person takes PEP for 28 days, and a doctor monitors the person for HIV afterward. PEP is not 100% effective, so it is important to use prevention techniques, such as barrier protection and safe injection practices, including while taking PEP.
Don’t Miss: How Much Does Hiv Treatment Cost Per Year
How Do You Get Or Transmit Hiv
You can only get HIV by coming into direct contact with certain body fluids from a person with HIV who has a detectable viral load. These fluids are:
- Blood
- Semen and pre-seminal fluid
- Rectal fluids
- Vaginal fluids
- Breast milk
For transmission to occur, the HIV in these fluids must get into the bloodstream of an HIV-negative person through a mucous membrane open cuts or sores or by direct injection.
People with HIV who take HIV medicine daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners.
Should I Get Vaccines If I Have Hiv/aids

Check with your healthcare provider. Certain vaccines are generally recommended, including:
- Influenza vaccine.
- Human papillomavirus vaccine if you are age 26 or younger.
- Meningococcal series of shots.
- Pneumonia vaccine.
- Tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis vaccine, with a repeat every 10 years of the tetanus/diphtheria vaccine.
You should probably avoid live vaccines, such as the ones for chickenpox and measles, mumps and rubella . This is true especially if your CD4 numbers are 200 or lower. Make sure you discuss vaccine questions with your healthcare provider.
HIV can affect how well the vaccine works. It can also make your viral load increase for a time because your immune system is stimulated by the vaccine.
Read Also: How Can You Prevent The Spread Of Hiv
Early Symptoms Of Hiv
Some people with HIV have no symptoms for months or even years after contracting the virus. Partly because of this, 1 in 7 people with HIV in the U.S. do not know that they have it.
While a person with no symptoms may be unlikely to seek care, there is still a high risk of transmission. For this reason, experts recommend regular testing, so that everyone is aware of their HIV status.
Meanwhile, around 80% of people with HIV develop flu-like symptoms around 26 weeks after contracting the infection. These symptoms are collectively called acute retroviral syndrome.
Early symptoms of HIV may include:
- white spots on the tongue or mouth
- shortness of breath, or dyspnea
- swollen glands lasting for weeks
- diarrhea, which is usually persistent or chronic
- a fever of over 100°F that lasts for weeks
- continuous fatigue
- unintentional weight loss
A person with AIDS has a significantly increased risk of developing a life threatening illness. Without treatment, people with AIDS typically live for around 3 years after the diagnosis.However, by taking other medications alongside HIV treatment, a person with AIDS can control, prevent, and treat serious complications.
When a person with HIV takes effective treatment, the infection may never progress to stage 3. Treatment can also help a person recover some lost immune function, which will help ward off severe infections.
- candidiasis of the bronchi, trachea, esophagus, and lungs
- coccidioidomycosis
- recurrent Salmonella septicemia
- toxoplasmosis
How Can I Know If I Have Hiv
The only way to know if you have HIV is to take an HIV test. Many medical groups recommend routine voluntary HIV screening of all patients aged 18 to 75 years of age as a normal part of medical care. The reason for this is that nearly one out of seven people infected with HIV are not aware that they have the infection.
Don’t Miss: Can Hiv Be Spread By Saliva
Detection Of Fecal Occult Blood From The Fecal Samples
To detect the possible blood content in the fecal samples, an occult blood test was performed in all fecal specimens as described in Materials and Methods section. As shown in Table , fecal blood was detected in 7 out of 39 fecal specimens: 2 from Group A, 1 from Group B, 3 from Group C and 1 from Group D. The fecal occult blood test was negative for the fecal samples which were positive for HIV-1 RNA or DNA. One of the five CD4 mRNA positive fecal specimens was positive for occult blood and the remaining samples were negative.
Means And Requirements For Hiv Transmission
People may become infected with HIV if they engage in specific risk behaviors or if they are exposed through needlestick injuries . Other blood contact with mucous membranes or non-intact skin provides a possible, but not probable, chance of transmission.
HIV is transmitted through:
- Unprotected anal, vaginal, and oral intercourse
- Sharing needles or other injection equipment
- A mother passing the virus to her baby either before or during birth
- An infected woman breastfeeding her infant
- Accidental needlestick injuries, or infected body fluid coming into contact with the broken skin or mucous membranes of another person
- A transfusion prior to 1986 of HIV-infected blood or blood products
In extremely rare cases, HIV can be transmitted by sharing razors or toothbrushes, if infected blood from one person was deposited on the toothbrush or razor and the blood entered the bloodstream of another person.
The transmission of HIV depends upon:
- The availability of the infectious agent in sufficient quantity
- The viability of the infectious agent
- The virulence of the infectious agent
- The ability of the infectious agent to reach the bloodstream, mucous membranes, or broken skin of a potential host
One of the predictors of the infectious level of an HIV-positive person is viral load, which is how much HIV is present in the bloodstream. Studies show a clear connection between higher viral load in the blood and increased transmissibility of HIV.
Test Your Learning
Answer: d
Blood Transfusions
Recommended Reading: Can You Detect Hiv In Urine
Does Hiv Viral Load Affect Getting Or Transmitting Hiv
Yes. Viral load is the amount of HIV in the blood of someone who has HIV. Taking HIV medicine daily as prescribed can make the viral load very lowso low that a test cant detect it .
People with HIV who take HIV medicine daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex.
HIV medicine is a powerful tool for preventing sexual transmission of HIV. But it works only as long as the HIV-positive partner gets and keeps an undetectable viral load. Not everyone taking HIV medicine has an undetectable viral load. To stay undetectable, people with HIV must take HIV medicine every day as prescribed and visit their healthcare provider regularly to get a viral load test. Learn more.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hiv
Some people get flu-like symptoms a month or two after they have been infected. This is called the acute stage. These symptoms often go away within a week to a month.
You can have HIV for many years before feeling ill. This is called clinical latency or the chronic stage.
AIDS is the most severe stage of HIV infection. In this stage, the immune system has been weakened by the HIV virus and is less able to fight off infections. Opportunistic infections are infections that could generally be fought off by a healthy immune system. In order to be diagnosed with AIDS, you have to have fewer than 200 CD4 cells per cubic millimeter of blood , OR you must have developed what are called opportunistic infections or certain cancers. You can develop AIDS even if your CD4 count is not 200 or lower.
Read Also: How Many Pills Do Hiv Patients Take Daily
How Do People Get Hiv
You can get HIV when body fluids from an infected person enter your bloodstream. Body fluids are blood, semen, vaginal fluids, fluids from the anus, and breast milk.
The virus can enter the blood through linings in the mouth, anus, or sex organs , or through broken skin. Both men and women can spread HIV.
You can have HIV and feel okay and still give the virus to others. Pregnant women with HIV can also give the virus to their babies.
The most common ways that people get HIV are having sex with an infected person and sharing a needle to take drugs.
You cannot get HIV from:
- Touching or hugging someone who has HIV/AIDS.
- Public bathrooms or swimming pools.
- Sharing cups, utensils, or telephones with someone who has HIV/AIDS.
- Bug bites.
- Donating blood.
Hiv Transmission In Households

Although HIV has been transmitted between family members in a household setting, this type of transmission is very rare. These transmissions are believed to have resulted from contact between skin or mucous membranes and infected blood. To prevent even such rare occurrences, precautions should be taken in all settings, including the home, to prevent exposures to the blood of persons who are HIV infected, at risk for HIV infection, or whose infection and risk status are unknown. For example:
- Gloves should be worn during contact with blood or other body fluids that could possibly contain visible blood, such as urine, feces, or vomit
- Cuts, sores, or breaks on both the care givers and patients exposed skin should be covered with bandages
- Hands and other parts of the body should be washed immediately after contact with blood or other body fluids, and surfaces soiled with blood should be disinfected appropriately
- Practices that increase the likelihood of blood contact, such as sharing of razors and toothbrushes, should be avoided
- Needles and other sharp instruments should be used only when medically necessary and handled according to recommendations for health-care settings
- Dispose of needles in puncture-proof containers
Don’t Miss: How Much Is Hiv Test