What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Hiv
No two people with HIV will have the same symptoms, and some may not have any at all. But the infection can cause some common changes over time.
In the first few weeks: These first, flu-like symptoms happen because your body is reacting to HIV. Your immune system is trying to fight it off. The symptoms at this stage can include:
- Rash
- Aches and pains in muscles and joints
Keep in mind that even if you have these symptoms, that doesnât automatically mean you are HIV-positive. Many different illnesses can cause these problems. Talk to a doctor or an HIV testing facility if you think you might be infected.
At this early stage of HIV infection, itâs important to know that you may not get accurate results from an HIV test. It can take 3-12 weeks for enough signs of the virus to show up on routine tests for the infection, which measure antibodies against HIV. A new kind of screening, called a nucleic acid test, can detect the virus itself during this early stage, but itâs expensive and not usually used for routine HIV testing.
Let the testing site or your doctor know if you think you might be recently infected. Also, be sure to use a condom every time you have sex, and take other steps to prevent spreading the virus.
After years with untreated HIV, youâre likely to get infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi that your body is no longer strong enough to fight off. They can be a sign that your infection has gone from HIV to AIDS. You might have:
Show Sources
Aids Is The Final Stage
Controlling HIV with medications is crucial to both maintaining quality of life and helping prevent progression of the disease. Stage 3 HIV, also known as AIDS, develops when HIV has significantly weakened the immune system.
According to the CDC National Prevention Information Network, CD4 levels give one indication that HIV has progressed to its final stage. CD4 levels decreasing below 200 cells per cubic millimeter of blood is considered a sign of AIDS. A normal range is considered 500 to 1,600 cells/mm3.
AIDS can be diagnosed with a blood test to measure CD4. Sometimes its also determined simply by a persons overall health. In particular, an infection thats rare in people who dont have HIV may indicate AIDS. Symptoms of AIDS include:
- persistent high fevers of over 100°F
- pneumonia
AIDS is the final stage of HIV. According to AIDSinfo, it takes at least 10 years without treatment for most people with HIV to develop AIDS.
At that point, the body is susceptible to a wide range of infections and cant effectively fight them off. Medical intervention is necessary to treat AIDS-related illnesses or complications that can otherwise be fatal. Without treatments, the CDC estimates the average survival rate to be three years once AIDS is diagnosed. Depending on the severity of their condition, a persons outlook may be significantly shorter.
Stage : The Asymptomatic Stage
Once a person has been through the acute primary infection stage and seroconversion process, they can often start to feel better. In fact, HIV may not cause any other symptoms for up to 10 or even 15 years .
However, the virus will still be active, infecting new cells and making copies of itself. HIV can still be passed on during this stage. If left untreated, over time, HIV infection will cause severe damage to the immune system.
Read Also: How Long Does Hiv Last
Can Hiv Symptoms Show Up The Day After Sex
No, HIV has no symptoms in the days immediately following exposure or infection.
So if you had sex yesterday and today you are feeling under the weather, you can rest assured that this is nothing to do with having picked up HIV yesterday. If your health is poor today, you should investigate the real reason for that — it is likely to be something totally different from HIV.
And if you think you took a risk in the sex you had yesterday, then looking out for symptoms either today or in the coming weeks is a completely unreliable way to infer your HIV status. Many people don’t have any symptoms soon after HIV infection or don’t notice them. Taking an HIV test is the only way to know.
When people do have symptoms soon after HIV infection, this typically occurs in the first few weeks after infection and not during the first week. This is known as acute retroviral syndrome or primary HIV infection.
At this time and for a duration of up to two weeks, some individuals have symptoms including sore throat, muscle and joint aches and pains, rashes, chills, night sweats, headaches, feeling generally unwell, mouth ulcers, weight loss, tiredness and swollen glands.
It’s important to remember that there are many other infections that can cause similar symptoms, including influenza and mononucleosis.
Following this short period, most people have no symptoms for several years.
How To Tell If Symptoms Are Hiv
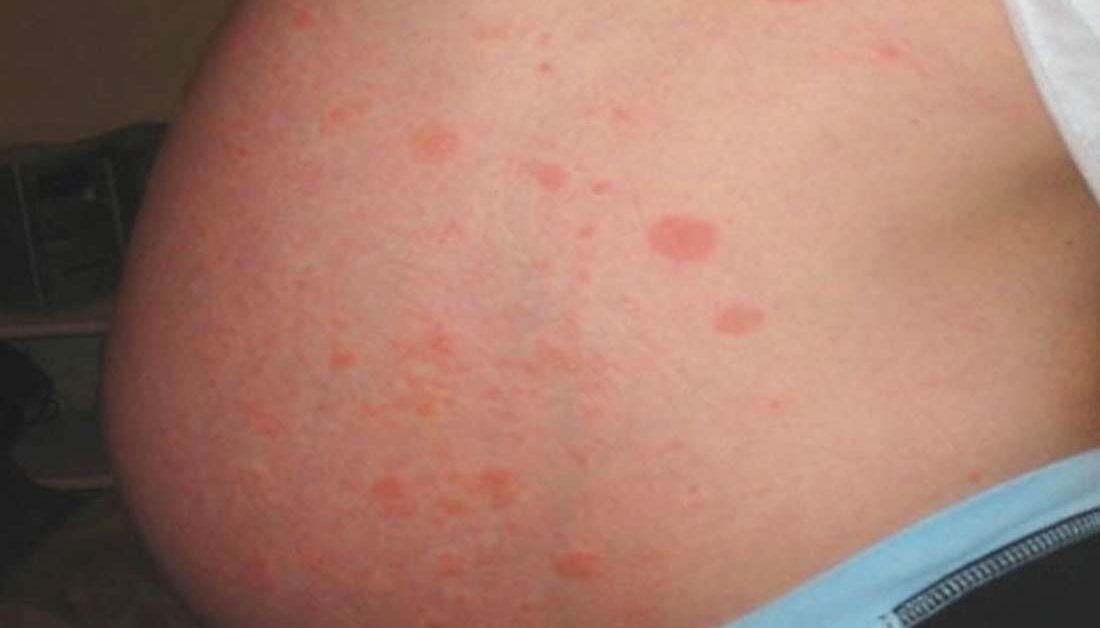
There are three types of HIV tests:
- An NAT involves drawing blood from a vein. It can tell if you have HIV or how much virus is present in your blood. While an NAT can detect HIV sooner than other types of tests, this test is very expensive and not routinely used for screening individuals unless they recently had a high-risk exposure, or a possible exposure and have early symptoms of HIV infection. This test takes several days for results to come back.
- An antigen/antibody test is recommended for testing done in labs and is now common in the United States. It involves drawing blood from a vein, and results take several days to come back. There is also a rapid antigen/antibody test available that is done with a finger prick and takes 30 minutes or less to get results.
- HIV antibody tests only look for antibodies to HIV in your blood or oral fluid. In general, antibody tests that use blood from a vein can detect HIV sooner after infection than tests done with blood from a finger prick or with oral fluid. Antibody tests can detect an HIV infection 23 to 90 days after exposure. Most rapid tests and the only currently approved HIV self-test are antibody tests. They take 20 minutes or less to provide results.
Keep in mind, any positive result would necessitate a second test to confirm it. The only test that would not require a second confirmatory test is the NAT.
You May Like: Can Hiv Be Transmitted Through Eyes
Donor History Questionnaire And Donor Interview
According to the haemotherapy guidelines, the state of health and pre-existing relevant diseases have to be assessed by using a donor history questionnaire and a confidential interview. This can help to identify and defer persons whose donation could represent a health risk to themselves or could be associated with the risk of transmitting a disease to others. For further queries and explanations a physician has to be available. The medical history should cover all issues of the donor selection criteria of the haemotherapy guidelines. These constitute a legally binding basis for decision-making in selecting donors. Since 2015 an updated standardised donor history questionnaire is available , and its application is recommended by Vote 41 of the German Advisory Committee Blood .
Perinatally HIV-infected children who since birth have been effectively treated with antiviral drugs for years may be antibody-negative due to early suppression of HIV replication and could theoretically become potential blood donors. They may have no measurable viral load in plasma but HIV DNA in their blood cells . By declaration of the HIV infection and/or disclosure of the continuous use of anti-retroviral drugs they are excluded from donating blood.
Symptoms And Stages Of Hiv Infection
FAST FACTS
- There are three stages of HIV infection. The symptoms vary in type and severity from person-to-person.
- Stage 1 after initial infection can feel like flu but not everyone will experience this.
- Stage 2 is when many people start to feel better and may last for 10 years or more. During this time a person may have no symptoms.
- Stage 3 is when a persons immune system is very badly damaged and can no longer fight off serious infections and illnesses.
- The earlier a person is diagnosed with HIV and starts treatment, the better their health will be over time.
- Some people dont get any symptoms during stages 1 and 2, and may not know they have the virus, but they can still pass on HIV.
The signs of HIV infection can vary in type and severity from person-to-person, and some people may not have any symptoms for many years.
The stages below describe how HIV infection progresses in the body if it is left untreated. Without antiretroviral treatment for HIV, the virus replicates in the body and causes more and more damage to the immune system.
However with effective treatment, you can keep the virus under control and stop it from progressing. This is why its important to start treatment as soon as possible after testing positive.
Also Check: Hiv Causes Hair Loss
Causes And Stages Of Acute Hiv Infection
HIV is caused by a retrovirus which attacks the bodyâs immune system, specifically CD4 blood cells which are responsible for fighting infections. During acute HIV infection, the HIV retrovirus destroys a lot of CD4 cells as it replicates. This can cause some people to fall ill with flu-like symptoms.
Acute HIV infection is the first stage of HIV infection. It is followed by two further stages:
Clinical latency, also known as asymptomatic HIV infection or chronic HIV infection. The HIV retrovirus continues to replicate within the body, but at low levels. The infected person may not experience any HIV-related symptoms, but can still transmit the virus to other people. Without treatment, this stage can last around 10 years. Towards the end of this phase, the personâs CD4 count starts to decrease and they may start to show symptoms.
AIDS is the final stage of HIV infection. Without treatment, a person can expect to develop AIDS after approximately 10 years. During this stage, a personâs immune system is badly damaged and they are susceptible to severe illnesses such as chronic cryptosporidiosis, lymphoma and pneumonia. Without treatment, a person with AIDS will typically only live around three years.
Treatment can slow the progression of HIV infection, often by decades.
A Timeline Of Hiv Symptoms
What is HIV?
HIV is a virus that compromises the immune system. Theres currently no cure for it, but there are treatments available to reduce its effects on peoples lives.
In the majority of cases, once HIV infection takes hold, the virus stays in the body for life. However, unlike what may occur with infections by other types of viruses, HIV symptoms dont suddenly appear and peak overnight.
If left untreated, the disease progresses over time through three stages, each with its own set of possible symptoms and complications some severe.
Regular antiretroviral treatment can reduce HIV to undetectable levels in the blood. At undetectable levels, the virus wont progress to the later stages of HIV infection. In addition, the virus cant be transmitted to a partner during sex.
Read Also: How Long Can Hiv Lay Dormant
What Are The 3 Stages Of Hiv When Does Hiv Infection Transition To Aids
There are 3 stages of HIV infection.
- Stage 1: Flu-like symptoms after initial HIV infection
- Stage 2: Clinically latency may last for 10 or more years in some individuals
- Stage 3: After HIV reactivation and/or HIVs progressive attack on the immune system, the damaged immune system has a reduced or an inability to protect the individual from serious infections and other illnesses. This stage is termed AIDS. In this stage, lab testing reveals high viral loads and CD4 counts < 200 cells/mm3.
Needle And Syringe Programs
Needle and syringe programs provide clean needles or syringes to people who inject drugs, reducing the risk of the transmission of HIV and other blood-borne diseases such as hepatitis B and hepatitis C. This is sometimes referred to as needle exchange.
The types of NSP outlet vary, from participating pharmacies to vending machines. Find an NSP in your state or territory:
You can also find a local needle and syringe program using the healthdirect Service Finder. Select By name and type needle into the search bar.
Read Also: How Long Does Hiv
Early Signs And Symptoms Of Hiv
Some people experience flu-like symptoms at the start of an HIV infection. These early HIV symptoms usually develop within 2-4 weeks in an infected person and may last anywhere from a few days to a few weeks. This early stage of the infection is known as an acute HIV infection.
Possible early symptoms include:
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Mouth ulcers
Itâs worth keeping in mind that such early symptoms can also be caused by other health conditionsânot just HIV. In short, if youâre experiencing these symptoms, it doesnât necessarily mean that you have HIVâwhich is why STI testing and consulting with your healthcare provider can be helpful next steps to take.
Is There A Period When The Virus Isnt Transmittable

HIV is transmittable soon after its introduced into the body. During this phase, the bloodstream contains higher levels of HIV, which makes it easy to transmit it to others.
Since not everyone has early symptoms of HIV, getting tested is the only way to know if the virus has been contracted. An early diagnosis also allows an HIV-positive person to begin treatment. Proper treatment can eliminate their risk of transmitting the virus to their sexual partners.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Aids Take To Show
Acute Hiv Infection Faqs
Q: When does acute HIV infection occur?A: Acute HIV infection is the first stage of HIV infection. Some people may feel ill with flu-like symptoms two to four weeks after being infected with HIV, while other people who have contracted HIV develop no symptoms at all.
Q: How long do acute HIV infection symptoms last?A: The symptoms of acute HIV infection, which can include flu-like symptoms, swollen lymph glands and mouth ulcers, generally last a few weeks. See the section on Symptoms of acute HIV infection.
Q: How is acute HIV infection treated?A: Acute HIV infection should be treated with antiretroviral drugs as soon as possible after diagnosis. Antiretroviral therapy can help slow the progression of HIV by decades.
Definition Of Exclusion Criteria
Blood donor eligibility is regulated by the Guidelines on the Collection of Blood and Blood Components and on Use of Blood Products . Criteria are defined for the permanent or temporary deferral from donation with respect to the transmission of HIV. Permanently deferred from donation are the following:
-
Persons with a confirmed HIV infection.
-
Persons with non-prescribed IV or IM drug use.
-
Persons whose sexual behaviour puts them at high risk of acquiring severe infectious diseases like HBV, HCV or HIV that can be transmitted by blood:
-
heterosexual persons with high-risk sexual behaviour, i.e. sexual contacts with multiple sex partners,
-
men who have sexual contacts with men
-
male and female sex workers.
Temporary deferral from donating blood is valid for persons:
-
who entered Germany from a country or a region, where they had been continuously resident for more than 6 months, with a comparatively high prevalence of HBV, HCV, HIV or HTLV-1/-2 infections,
-
who had sexual contacts with persons belonging to a group with an enhanced risk of infection with HBV, HCV, HIV and/or HTLV-1/-2 ,
-
with tattoos or body piercing.
Also Check: How Long Can Hiv Be Dormant In Your System
Donor Information And Counselling
Recommendations on how to inform a donor with positive HIV test results are given in the vote on look-back procedures of the Arbeitskreis Blut . HIV-infected donors should be informed in person and in writing by the blood establishment. HIV-infected donors should be counselled and referred to a general practitioner or a specialised centre for further care. The counselling should include information about the HIV transmission routes and the possibility of antiretroviral therapy . The information given should also include the fact that they are no longer suitable as a blood, plasma or organ donor in Germany.
In South Africa, the possibility of exceptions in cases of kidney transplantation to HIV-infected recipients is suggested .
Clarification of the possible origin of the donor’s infection is of epidemiologic interest. Efforts should be made in the donor interview to identify the route and the cause of infection, especially in order to prevent further transmission of the HIV infection. Such data are also required for the anonymous reporting of HIV diagnoses according to the German Transfusion Act and IfSG. A template provided by the Robert Koch Institute with a standardized questionnaire simplifies clarification and supports a nationwide standardised registration system of HIV transmission modes in the donor population.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Aids
Having an infection with the HIV virus does not automatically mean that the patient has AIDS. As the HIV virus infects more and more CD4 cells and makes more copies of itself, the patients immune system gets overwhelmed and begins to falter. When the immune system breaks down due to HIV infection, opportunistic infections like fungal infections, pneumonias, and cancers can occur. When this level of HIV infection occurs, it is called AIDS .
Some of the signs and symptoms of progression of HIV to AIDS are:
Recommended Reading: Average Hiv Life Expectancy
Stage : Acute Primary Infection
The early symptoms of HIV can feel like having the flu. Around one to four weeks after getting HIV, you may start to experience these flu-like symptoms. These normally dont last long . You may only get some of the symptoms and some people dont have any symptoms at all.
Symptoms can include:
- joint aches and pains
- muscle pain.
These symptoms happen because your body is reacting to the HIV virus. Cells that are infected with HIV are circulating throughout your blood system. In response, your immune system tries to attack the virus by producing HIV antibodies this process is called seroconversion. Timing varies but once you have HIV it can take your body up to a few months to go through the seroconversion process.
Having these symptoms alone does not mean you definitely have HIV. The only way to know if you have HIV is by taking a test. You should always visit your healthcare professional if youre worried about or think youve been at risk of getting HIV, even if you feel well and dont have any symptoms. They can then arrange for you to get tested.
HIV will not always show up in a test at this early stage, and you may need to test again later to confirm your result . Your healthcare professional will talk to you about the timing of your test and answer any concerns. Its important not delay speaking to a healthcare worker if you are worried about HIV.