Ways Hiv Is Transmitted
HOW IS HIV PASSED FROM ONE PERSON TO ANOTHER?
Most people get or transmit HIV through one of the following ways:
- Anal sex
- Sharing needles, syringes, or other drug ejection equipment
- Perinatal transmission
Not every exposure to HIV carries the same risk and some activities are riskier than others. Many factors increase or decrease HIV risk. In addition, there are many effective ways you can reduce your risk of getting or transmitting HIV. Read more about HIV prevention.
WHAT BODY FLUIDS TRANSMIT HIV?
Only certain body fluids from a person who has HIV can transmit HIV. These fluids include
- Blood
- Vaginal fluids
- Breast milk
These fluids must come in contact with a mucous membrane or damaged tissue or be directly injected into the bloodstream for transmission to occur. Mucous membranes are found inside the rectum, vagina, penis, and mouth.
SEXUAL ACTIVITIES
Some sexual activities are riskier than others for getting or transmitting HIV. The most common way to get or transmit HIV through sexual activity is from having anal or vaginal sex without using protection . There is extremely low to no chance of getting or transmitting HIV through activities such as oral sex, touching, and kissing.
Anal Sex
Anal sex is when a penis is inserted into an anus. The person inserting the penis is called the insertive partner and the person receiving the penis is called the receptive partner .
Vaginal Sex
Remember!
SHARING NEEDLES, SYRINGES, OR OTHER DRUG INJECTION EQUIPMENT
PERINATAL TRANSMISSION
Can Hiv Pass From Mothers To Their Babies
Infection can pass from pregnant women living with HIV to their babies in the womb and during birth. Taking HIV medications during pregnancy and childbirth dramatically lowers the risk of a baby becoming infected with HIV.
After birth, transmission can occur through breast milk. The highest risk may be in the early months after birth. It is recommended that new mothers who are living with HIV formula-feed their babies rather than breast-feed.
If you are a woman living with HIV and you intend to become pregnant, or you find out that you have during your pregnancy, talk to your provider immediately about ways to minimize the chances that your baby will become infected, too.
Can You Get Hiv From Having Sex With Someone Who Has Aids
If you have sex with someone who has AIDS, not HIV, can you still get HIV? Sarah*
Yes. People who have AIDS are infected with the HIV virus. This means they can pass HIV on to others.
AIDS happens after someone has had HIV for many years. In AIDS, the immune system is severely weakened. When someone gets HIV, that person can spread the infection to other people immediately. And if HIV develops into AIDS, the virus can spread to others.
HIV/AIDS spreads when infected blood or body fluids enter the body. This can happen:
- during sex
- through sharing needles for injecting drugs or tattooing
HIV/AIDS also can pass from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
To reduce your risk of getting HIV/AIDS if you are sexually active:
- Use a condom every time you have sex .
- Get tested for HIV and make sure all partners do too.
- Have fewer sexual partners.
- Get tested and treated for STDs having an STD increases the risk of HIV infection.
- Consider taking a medicine every day if you are at very high risk of getting infected .
It’s also important to:
- not inject drugs or share any kind of needle
- not share razors or other personal objects that may touch blood
- not touch anyone else’s blood from a cut or sore
*Names have been changed to protect user privacy.
Also Check: How Much To Get Hiv Test
Hiv And Maternal Transmission
HIV can be passed from mother to child during pregnancy, delivery, or through breastfeeding. If left untreated throughout these stages, there is a 15-45% chance of an HIV positive mother transmitting the virus to their child . However there are treatment options to prevent this from happening.
If pregnancy occurs and there has been potential HIV exposure, ask a healthcare provider about getting tested for HIV as early as possible. Taking medications called antiretroviral therapy as prescribed can reduce the viral load so that the baby has a very low chance of contracting HIV .
A person with HIV should not breastfeed their child, as breast milk can transmit HIV. Even if a person is taking ART and their viral loads are undetectable, they should still not breastfeed.
Vaginal And Anal Intercourse
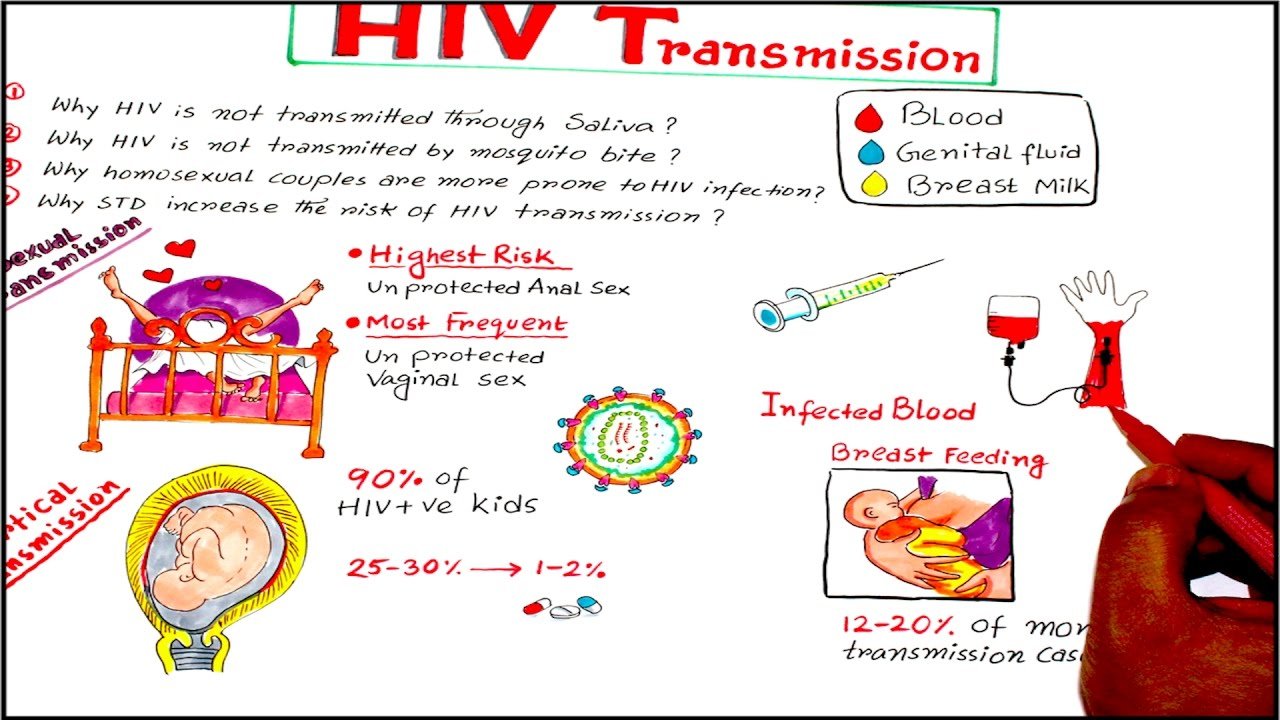
The HI virus can be transmitted through unprotected vaginal sex without a condom. Vaginal fluids, semen, pre-ejaculation fluid and blood are all possible transmitters. Vaginal dryness caused by menstruation, pregnancy, breastfeeding or ageing reduces the safety of intercourse. Sores and sexually transmitted infections increase the risk of HIV infection. A water- or silicone-based lubricant prevents sores and dryness of mucous membranes, prevents the condom from breaking during intercourse and increases pleasure of intercourse.
HIV is most easily transmitted through unprotected anal sex without a condom, because the mucous membrane of the rectum is fragile and can easily develop sores. The HI virus can be found in semen, pre-ejaculation fluid and the rectum wall. Also the tip of the glans and the end of the urethra can chafe. In addition to using a condom, it is important to use enough lubricant while having anal sex. Lubricant reduces the risk of sores and of the condom breaking and thus reduces the risk of catching an HIV infection.
Don’t Miss: Are Hiv And Aids The Same
Blood Transfusions And Transplants
In the early days of the HIV epidemic in the 1980s to early 1990s, there were many people infected with HIV due to tainted blood transfusions. Prior to 1992, there were no screening tools available to ensure that the U.S. blood supply, including clotting factors and plasma, was free of the virus.
That risk has fallen dramatically in recent decades due to advances in detection technologies and the universal screening of blood and tissue donations in the United States and other countries. This not only includes the screening of HIV but other bloodborne infections like hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
Today, the risk of HIV from a blood transfusion in the United States is roughly one in 1.5 million. From 2002 to 2008, only one documented case of HIV transmission from a transfusion was reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
The risk outside of the United States can vary dramatically. In Egypt, for instance, one in four HIV infections is the result of a transfusion. By contrast, in South Africa, the country with the highest HIV incidence in the world, the transmission risk is closer to one of every 76,000 transfusions.
How Is Hiv Transmitted
HIV is transmitted between humans through the exchange of certain types of bodily fluids. Bodily fluids that can transmit HIV include blood, semen, breast milk, and vaginal fluids .
Not all body fluids can transmit HIV. The following cannot transmit HIV:
- Exchanging saliva, like through closed-mouth kissing or sharing drinks/utensils
- Coming in contact with an HIV positive personâs tears, sneezes, or sweat
- Ordinary physical contact, such as hugging, hand shaking, or touching shared objects like cutlery, cups, or toilet seats .
- Air or water
- Pets and insects cannot carry the virus and infect you, because transmission of HIV is only between humans .
While care needs to be taken in some situationsâlike when having sex or when open injuries are presentâthis certainly does not mean that it is unsafe to be around people with HIV. Think of how you interact with the vast majority of peopleâbodily fluids are not exchanged. Harboring discriminatory thoughts only perpetuates a fearful stigma against someone with HIV, which only hurts the person who has it.
HIV is often transmitted through sexual activity and drug use in adults in the United States . Maternal transmissionâfrom mother to childâis how the infection is spread to infants .
Also Check: Can You Get Hiv Without Ejaculation
How Is Hiv Spread Through Blood
You can become infected if you have contact with the blood of someone who has HIV. Blood-borne infection with HIV can occur through:
- sharing injection equipment when using drugs
- getting tattoos or body piercings with unsterilized needles
- accidental needle sticks
- splashing blood in your eyes
HIV is NOT spread by blood passed through insect bites.
If you inject drugs, the best thing to do is to use new or sterilized injection equipment every time. You can also take a daily medication called pre-exposure prophylaxis to lower your risk of HIV. Learn more about PrEP.
How Can You Get Hiv
HIV is found in the following bodily fluids of someone living with the virus:
- blood
- vaginal fluids
- breastmilk.
For you to get HIV, these bodily fluids need to get into your blood through a mucous membrane , via shared injecting equipment, or through broken skin .
There is not enough HIV virus in other bodily fluids, like saliva, sweat or urine, to transmit it from one person to another.
Someone living with HIV who has an undetectable viral load, meaning effective treatment has lowered the amount of virus in their blood to levels where it cannot be detected by a normal blood test, cannot pass on HIV.
A person living with HIV with a detectable viral load can pass the virus to others whether they have symptoms or not.
HIV is most infectious in the first few weeks after infection. At this time many people are unaware of their status.
The main ways you can get HIV are:
Recommended Reading: When Do Signs Of Hiv Show Up
How Is Hiv/aids Transmitted
Sexual contact – HIV is spread most commonly by sexual contact with an infected partner. The virus enters the body through the lining of the vagina, vulva, penis, rectum, or mouth during sexual activity.
Blood contamination – HIV may also be spread through contact with infected blood. However, due to the screening of blood for evidence of HIV infection, the risk of acquiring HIV from blood transfusions is extremely low.
Needles – HIV is frequently spread by sharing needles, syringes, or drug use equipment with someone who is infected with the virus. Transmission from patient to healthcare worker, or vice-versa through accidental sticks with contaminated needles or other medical instruments, is rare.
Mother-infant – HIV also can be spread to babies born to, or breastfed by, mothers infected with the virus.
Learn more about:
How Is Hiv Spread From Person To Person
HIV can only be spread through specific activities. In the United States, the most common ways are:
- Having vaginal or anal sex with someone who has HIV without using a condom or taking medicines to prevent or treat HIV. Anal sex is riskier than vaginal sex.
- Sharing injection drug equipment , such as needles, with someone who has HIV.
Less common ways are:
- From mother to child during pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding. However, the use of HIV medicines and other strategies have helped lower the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV to 1% or less in the United States.
- Getting stuck with an HIV-contaminated needle or other sharp object. This is a risk mainly for health care workers. The risk is very low.
HIV is spread only in extremely rare cases by:
- Having oral sex. But in general, the chance that an HIV-negative person will get HIV from oral sex with an HIV-positive partner is extremely low.
You May Like: Can Hiv Pass Through Clothes
How Is Hiv Spread Through Sex
You can get infected from sexual contact with someone who has HIV. Sexual contact that can transmit HIV includes:
- vaginal sex
- anal sex
- oral sex
If you have sex, the best thing you can do to prevent HIV infection is practice “safer sex” with any partner who is not proven to be HIV negative . To do so, always use protection–this could include using a condom, dental dam, or other latex barrier, and/or PrEP . It is also important to avoid “rough sex” or other activities that might cause bleeding. If you use lube with a condom, make sure it is water-based, not oil-based. Oil-based lube causes latex condoms to break. See more tips for using condoms note that, if used correctly and consistently, condoms also protect against other sexually transmitted infections and against pregnancy.
If you have unprotected sex with someone who is infected, it doesn’t mean that you will be infected, too. But there is always a chance, especially if your partner is not on effective HIV medicines. Using condoms and PrEP reduces your risk.
HIV is NOT spread by:
- hugging or massage
- sex toys you don’t share
- daily living with someone who has HIV
For more information, see Sex and Sexuality in the Daily Living section.
How Is Hiv Not Transmitted

HIV is not transmitted by saliva, tears, sweat, urine or feces. HIV does not survive well outside the human body. It cannot be transmitted through casual contact with a person who has HIV, or through objects such as toilet seats, doorknobs or dishes used by a person who has HIV.
In the past, some people got HIV after receiving a blood transfusion or organ or tissue transplant. However, Canada implemented HIV screening for all blood and tissue donations in 1985.
References
C. Arkelle
You May Like: Could You Have Hiv And Not Know
How To Prevent The Spread Of Hiv
People living with HIV can use the following to prevent transmitting it to others:
- Pre-exposure prophylaxis : This is a daily pill that contains two antivirals called tenofovir and emtricitabine. When a person takes it daily, PrEP can reduce the risk of acquiring HIV through sex by
- of a recent potential HIV exposure.
Strategies To Reduce Risk
As with any other mode of HIV transmission, prevention requires a combination of strategies to more effectively:
- Reduce the infectivity of the HIV-positive partner
- Reduce the susceptibility of the HIV-negative partner
Current evidence has shown that the consistent use of antiretroviral therapy in the HIV-infected partner completely eliminates the risk of HIV transmission when viral activity is suppressed to undetectable levels.
The effectiveness of the strategy known as Treatment as Prevention , is evidenced by the PARTNER1 and PARTNER2 studies in which not a single HIV infection occurred among 1,770 gay and heterosexual mixed-status couples despite engaging condomless anal or vaginal sex.
The studies, which ran from 2010 to 2018, showed unequivocally that undetectable equals untransmittable in a real-world setting.
The use of pre-exposure prophylaxis , whereby the uninfected partner is prescribed a daily dose of the HIV drug Truvada, can also reduce risk. Studies have shown that when taken daily, PrEP reduces the risk of getting HIV from sex by about 99%.
Although these figures may suggest that condoms are no longer needed, neither TasP nor PrEP can prevent other sexually transmitted diseases.
Moreover, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , only 59.8% of Americans with HIV are able to achieve an undetectable viral load. Without complete viral suppression, TasP is rendered useless, placing the uninfected partner at risk.
Recommended Reading: How Do You You Have Hiv
Hiv Transmission Through Sexual Acts
Sexual intercourse with an HIV-infected personTransmission of HIV is primarily through unprotected vaginal or anal intercourse , as well as through oral sex under certain conditions.
How does HIV get into the body during sexual contact? To gain entry into the body of an uninfected person, the HI virus needs to bind or latch onto target cells with specific receptors on its surface. Cells with these special receptors are plentiful in the lining of the genital track and that of the anus.
During unprotected sex with an HIV+ person, the virus binds with the CD4 receptors in the lining of the genital tracks or anal track of the uninfected partner.
Tears in the membrane linings of the genital tracks – especially in the anal-rectal area – also make it easy for the virus to enter the sex partners bloodstream. Because the membrane linings of body cavities – especially in the anal-rectal area, and, to a lesser extent, in the vagina – are very delicate, they can be torn as a result of friction generated during sexual intercourse.
Sexually transmitted infections , such as syphilis, gonorrhoea or herpes, make it very easy for HIV to get into the body. An untreated STI in either partner increases the risk of HIV transmission during unprotected intercourse ten-fold.
Why are women more easily infected by HIV than men?Women are two to four times more likely to get infected with HIV through unprotected vaginal sex than men, due to the following reasons:
Oral Sex With A Vagina
The risk of transmission through oral sex with a vagina is very low because the mouth is an unfriendly environment for HIV. Saliva breaks down the virus, and the mucous membranes in the mouth are more protective than anal or vaginal tissue. The minimal risk of transmission from oral sex with a vagina is only for the person performing the oral sex, as their mouth is in contact with vaginal fluid. However, there is little data documenting HIV transmission via oral sex from an infected vagina to an uninfected person.
Performing oral sex on a vagina during menstruation increases the risk, because blood has more HIV than vaginal fluid.
A person receiving oral sex is generally not at risk as that person is coming into contact only with saliva, which does not transmit HIV. The presence of other sexually transmitted infections can increase the risk of HIV transmission during oral sex.
Also Check: What Is Hiv 1 And 2 Antibody Test