Spread To The Western Hemisphere
Further isolated occurrences of this infection may have been emerging as early as 1966. The virus eventually entered gay male communities in large United States cities, where a combination of casual, multi-partner sexual activity and relatively high transmission rates associated with anal intercourse allowed it to spread explosively enough to finally be noticed.
Because of the long incubation period of HIV before symptoms of AIDS appear, and because of the initially low incidence, HIV was not noticed at first. By the time the first reported cases of AIDS were found in large United States cities, the prevalence of HIV infection in some communities had passed 5%. Worldwide, HIV infection has spread from urban to rural areas, and has appeared in regions such as China and India.
Unresolved Questions About Hiv Origins And Emergence
The discovery of the main HIV/SIV phylogenetic relationships permits explaining broad HIV biogeography: the early centres of the HIV-1 groups were in Central Africa, where the primate reservoirs of the related SIVcpz and SIVgor viruses exist similarly, the HIV-2 groups had their centres in West Africa, where sooty mangabeys, which harbour the related SIVsmm virus, exist. However, these relationships do not explain more detailed patterns of biogeography, such as why epidemic HIV-2 groups only evolved in the Ivory Coast, which is one of only six countries harbouring the sooty mangabey. It is also unclear why the SIVcpz endemic in the chimpanzee subspecies Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii did not spawn an epidemic HIV-1 strain to humans, while the Democratic Republic of Congo was the main centre of HIV-1 group M, a virus descended from SIVcpz strains of a subspecies that does not exist in this country. It is clear that the several HIV-1 and HIV-2 strains descend from SIVcpz, SIVgor, and SIVsmm viruses, and that bushmeat practice provides the most plausible cause of cross-species transfer to humans. However, some loose ends remain.
It is not yet explained why only four HIV groups spread considerably in human populations, despite bushmeat practices being widespread in Central and West Africa, and the resulting human SIV infections being common.
The Status Of The Hiv/aids Epidemic In Sub
Senior Fellow, Futures Group International
Focus Area
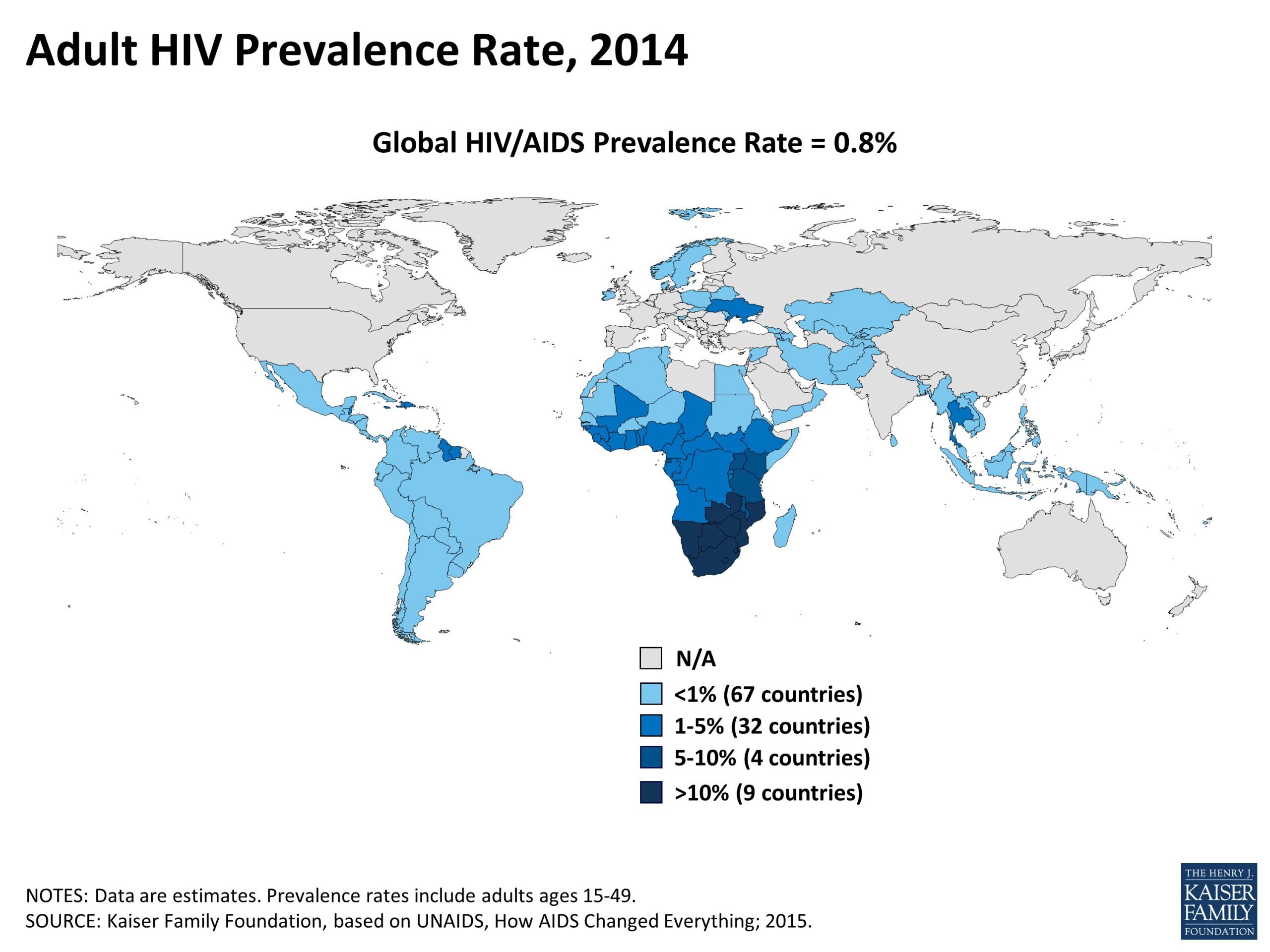
Despite the fact that sub-Saharan Africa contains only about 11 percent of the Earths population, the region is the worlds epicenter of HIV/AIDS. The numbers are daunting. Adult HIV prevalence is 1.2 percent worldwide , but it is 9.0 percent in sub-Saharan Africa. UNAIDS estimates that at the end of 2001, there were 40 million people living with HIV/AIDS, 28.5 million of them from sub-Saharan African. Five million adults and children became newly infected with HIV in 2001, 3.5 million of them from sub-Saharan Africa. Three million people died from AIDS-related causes in 2001, and 2.2 million of these deaths were among sub-Saharan Africans.2
AIDS is now the leading cause of death in sub-Saharan Africa. Life expectancy at birth has plummeted in many African countries, wiping out the gains made since independence. The combination of high birth rates and high AIDS mortality among adults, including many parents, has meant that more than 90 percent of children who have been orphaned as a consequence of the HIV/AIDS epidemic are in this region.2
According to UNAIDS, all the worst affected countries are contiguous to one another in the lower part of the continent. These include South Africa, Lesotho, Swaziland, Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Botswana, Lesotho, Swaziland, and Zimbabwe have prevalence rates above 30 percent.4
| Total Adults and Children |
|---|
| 20.1 |
References
Recommended Reading: Can Someone Get Hiv From Oral
Where We Are Now: 2000
Since 2000, additional factors have begun contribute to the the global spread of HIV. Heroin addiction in Asia has been on the rise, which brought with it dirty needles and the risk of new infections. India suffered with over 2 million diagnoses alone, in spite of the government’s refusal to admit the epidemic had adversely affected the nation.
The WHO released its comprehensive report examining HIV and AIDS in all of its 25-year history in 2010. This report had good news for developed nations: by 2008, the U.S. domestic HIV infection rate was considered effectively stable, and has remained so to this day. The report also demonstrated that while insistent public awareness campaigns about safe sex and other methods of transmission had slowed the rate of HIV infection in developed countries, there was much to be done elsewhere.
Global Education and Aid Efforts
Under President Bush, the U.S. committed funds to help African countries, but the funds were mismanaged and the spread of HIV continued unabated. Of the 4.1 million cases in sub-Saharan Africa then, only 1% received the available drugs. This led to the WHO’s declaration of the failure to treat the 6 million AIDS patients living in developing nations as a global public health emergency.
HIV Denialism Disrupts Aid
By the time Mbeki was recalled from the presidency in 2008 and one year before the FDA approved its 100th HIV/AIDs drug, an estimated 16.9% of South Africans aged 15-49 were HIV positive.
Hiv/aids Is One Of The Worlds Most Fatal Infectious Disease
Almost 1 million people die from HIV/AIDS each year in some countries its the leading cause of death
HIV/AIDS is one of the worlds most fatal infectious diseases particularly across Sub-Saharan Africa, where the disease has had a massive impact on health outcomes and life expectancy in recent decades.
The Global Burden of Disease is a major global study on the causes of death and disease published in the medical journal The Lancet.1 These estimates of the annual number of deaths by cause are shown here. This chart is shown for the global total, but can be explored for any country or region using the change country toggle.
In the chart we see that, globally, it is the second most fatal infectious disease.
According to the Global Burden of Disease study, almost one million people died from HIV/AIDS in 2017. To put this into context: this was just over 50% higher than the number of deaths from malaria in 2017.
Its one of the largest killers globally but for some countries particularly across Sub-Saharan Africa, its the leading cause of death. If we look at the breakdown for South Africa, Botswana or Mozambique which you can do on the interactive chart we see that HIV/AIDS tops the list. For countries in Southern Sub-Saharan Africa, deaths from HIV/AIDS are more than 50% higher than deaths from heart disease, and more than twice that of cancer deaths.
Don’t Miss: How Would I Know If I Have Hiv
Pathogenicity Of Siv In Non
In most non-human primate species, natural SIV infection does not cause a fatal disease . Comparison of the gene sequence of SIV with HIV should, therefore, provide information about the factors necessary to cause disease in humans. The factors that determine the virulence of HIV as compared to most SIVs are only now being elucidated. Non-human SIVs contain a nef gene that down-regulates CD3, CD4, and MHC class I expression most non-human SIVs, therefore, do not induce immunodeficiency the HIV-1nef gene, however, has lost its ability to down-regulate CD3, which results in the immune activation and apoptosis that is characteristic of chronic HIV infection.
In addition, a long-term survey of chimpanzees naturally infected with SIVcpz in Gombe, Tanzania found that, contrary to the previous paradigm, chimpanzees with SIVcpz infection do experience an increased mortality, and also suffer from a human AIDS-like illness. SIV pathogenicity in wild animals could exist in other chimpanzee subspecies and other primate species as well, and stay unrecognized by lack of relevant long term studies.
Where Did Aids Come From
Scientists have traced the origin of HIV back to chimpanzees and simian immunodeficiency virus , an HIV-like virus that attacks the immune system of monkeys and apes.
In 1999, researchers identified a strain of chimpanzee SIV called SIVcpz, which was nearly identical to HIV. Chimps, the scientist later discovered, hunt and eat two smaller species of monkeysred-capped mangabeys and greater spot-nosed monkeysthat carry and infect the chimps with two strains of SIV. These two strains likely combined to form SIVcpz, which can spread between chimpanzees and humans.
SIVcpz likely jumped to humans when hunters in Africa ate infected chimps, or the chimps infected blood got into the cuts or wounds of hunters. Researchers believe the first transmission of SIV to HIV in humans that then led to the global pandemic occurred in 1920 in Kinshasa, the capital and largest city in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
The virus spread may have spread from Kinshasa along infrastructure routes via migrants and the sex trade.
In the 1960s, HIV spread from Africa to Haiti and the Caribbean when Haitian professionals in the colonial Democratic Republic of Congo returned home. The virus then moved from the Caribbean to New York City around 1970 and then to San Francisco later in the decade.
International travel from the United States helped the virus spread across the rest of the globe.
READ MORE: Pandemics That Changed History: A Timeline
You May Like: When Will Hiv Be Cured
Where Did Hiv Come From A Look At The Origins Of The Pandemic Of Our Time
A chimpanzees virus has killed 35 million humans.
That virus, commonly known as HIV, is the defining pandemic of our time. More than 35 million people have been killed by the virus to date. But the virus itself didnt get its start in humans.
HIV/AIDS is, like the vast majority of emerging viruses infecting people, zoonotic in nature. The AIDS crisis, as we generally think of it, began in the 1980s. First as a mysterious illness primarily infecting gay men in urban areas in the United States. But thats not really the beginning. Before the diseases first mention in 1982 in the New York Times, people had been dying of AIDS for at least a decade, though probably not much longer. In Africa, HIVthe virus that causes AIDShad jumped from chimpanzees to humans sometime early in the 20th century.
To date, the earliest known case of HIV-1 infection in human blood is from a sample taken in 1959 from a man whod died in Kinshasa in what was then the Belgian Congo.
Its this fact which keeps me awake at night. Imagine, for a moment, that the HIV virus in that 1959 sample had been studied and identified. If, in the 1950s, the scientific community realized the potential harm this new virus could unleash. What could we have done? What therapies could we have developed before it became one of the deadliest pandemics in human history? Would we have a cure by now?
That work takes several forms, including:
The Worlds Largest Hiv Epidemic In Crisis: Hiv In South Africa
In some communities of KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa, 60 percent of women have HIV. Nearly 4,500 South Africans are newly infected every week one-third are adolescent girls/young women ages 15-24. These are staggering figures, by any stretch of the imagination. Yet, the HIV epidemic is not being treated like a crisis. In February, we traveled to South Africa, to understand what is happening in these areas with hyper-endemic HIV epidemics, where prevalence rates exceed 15 percent among adults. We were alarmed by the complacency toward the rate of new infections at all levels and the absence of an emergency response, especially for young people.
This is no time for business as usual from South Africa or its partners, including the U.S. government through the U.S. Presidents Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief . The epidemic is exacerbated by its concentration in 15-49-year-olds, those of reproductive and working age who are the backbone of South Africa. Without aggressive action to reduce the rate of new infections in young people, HIV will continue to take a tremendous toll on the country for years and generations to come. Collective action is needed to push beyond the complacency and internal barriers to implement policies and interventions that directly target HIV prevention and treatment for young people. PEPFAR should ensure its programs support those efforts.
Read Also: Does Prep Protect Against Hiv
Countries With The Highest Rates Of Hiv/aids
Human Immunodeficiency Virus is a virus that weakens the human immune system, sometimes leading to AIDS. If detected early, HIV can be managed to prevent it from progressing to the final stage of AIDS. HIV attacks CD4 cells exposing the infected person to opportunistic infections. Proper diagnosis, treatment, and medical care are essential factors to effective management and control of AIDS which has no permanent cure. While HIV is majorly a sexually transmitted disease, the virus can be transmitted through blood transfusion and during birth or breastfeeding, as well as through a few other means.
Origin And Epidemic Emergence
Several of the theories of HIV origin accept the established knowledge of the HIV/SIV phylogenetic relationships, and also accept that bushmeat practice was the most likely cause of the initial transfer to humans. All of them propose that the simultaneous epidemic emergences of four HIV groups in the late 19th-early 20th century, and the lack of previous known emergences, are explained by new factor that appeared in the relevant African regions in that timeframe. These new factor would have acted either to increase human exposures to SIV, to help it to adapt to the human organism by mutation , or to cause an initial burst of transmissions crossing an epidemiological threshold, and therefore increasing the probability of continued spread.
Genetic studies of the virus suggested in 2008 that the most recent common ancestor of the HIV-1 M group dates back to the Belgian Congo city of Léopoldville , circa 1910. Proponents of this dating link the HIV epidemic with the emergence of colonialism and growth of large colonial African cities, leading to social changes, including a higher degree of non-monogamous sexual activity, the spread of prostitution, and the concomitant high frequency of genital ulcer diseases in nascent colonial cities.
Social changes and urbanization
Colonialism in Africa
This theory was later dubbed “Heart of Darkness” by Jim Moore, alluding to the book of the same title written by Joseph Conrad, the main focus of which is colonial abuses in equatorial Africa.
You May Like: Who Was Hiv Patient 0
Hiv Rates By Country 2022
HIV, or human immunodeficiency virus, is a disease that weakens a persons immune system by attacking CD4 cells, which help the body fight off infection. If HIV advances, it can lead to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS, a terminal condition. HIV spreads through certain body fluids, most often during unprotected sex, pregnancy and childbirth, transfusion of contaminated blood, or shared use of hypodermic needles. The human body cannot completely eliminate HIV. Therefore, once the virus is contracted, the individual will remain HIV-positive for life. However, HIV can be controlled and its progression slowed significantly by treatment with antiretroviral therapy medicines. HIV rates vary drastically between countries, particularly in Africa, the continent from which the virus is believed to have originated.
Canadian Flight Attendant Theory

A Canadian airline steward named Gaëtan Dugas was referred to as “Case 057” and later “Patient O” with the alphabet letter “O” standing for “outside Southern California”, in an early AIDS study by Dr. William Darrow of the Centers for Disease Control. Because of this, many people had considered Dugas to be responsible for taking HIV to North America. However, HIV reached New York City around 1971 while Dugas did not start work at Air Canada until 1974. In Randy Shilts‘ 1987 book And the Band Played On , Dugas is referred to as AIDS’s Patient Zero instead of “Patient O”, but neither the book nor the movie states that he had been the first to bring the virus to North America. He was incorrectly called “Patient Zero” because at least 40 of the 248 people known to be infected by HIV in 1983 had had sex with him, or with a person who had sexual intercourse with Dugas.
Don’t Miss: Can You Donate Blood If You Have Hiv
The Cultural Response To Hiv
Public response was negative in the early years of the epidemic.
In 1983, Dr. Joseph Sonnabend in New York was threatened with eviction for treating people with HIV, leading to the first AIDS discrimination lawsuit.
Bathhouses across the country closed due to sexual activity and the associated risk. Some schools also barred children with HIV from attending.
U.S. blood banks started screening for HIV in 1985, and men who had sex with men were banned from donating blood . first lifted some of its restrictions in December 2015. The FDA loosened its restrictions again in 2020, motivated by the blood shortage caused by COVID-19.)
In 1987, the United States placed a travel ban on visitors and immigrants with HIV.
The United States government resisted funding needle exchange programs due to the War on Drugs. NEPs were shown to be effective at reducing HIV transmission.
In 1997, researchers calculated that this resistance accounted for .
The number of avoidable transmissions may be even higher.
A 2005 study looked at people in New York City who used injectable drugs and had been admitted to a drug detoxification program. The researchers concluded that the legalization of syringe exchange programs helped reduce HIV prevalence among this group from 50 percent in 1990 to 17 percent in 2002.
Although Strides Have Been Made In The Hiv Response Children Are Still Affected By The Epidemic
Of the estimated 38.4 million people living with HIV worldwide in 2021, 2.73 million were children aged 019. Each day in 2021, approximately 850 children became infected with HIV and approximately 301 children died from AIDS related causes, mostly because of inadequate access to HIV prevention, care and treatment services.
As of 2021, roughly 14.9 million children under the age of 18 had lost one or both parents to AIDS-related causes. Millions more have been affected by the epidemic, through a heightened risk of poverty, homelessness, school dropout, discrimination and loss of opportunities, as well as COVID-19. These hardships include prolonged illness and death. Of the estimated 650,000 people who died of AIDS-related illnesses in 2021, 110,000 of them were children under 20 years of age.
Global trends
In 2021, around 160,000 children aged 09 were newly infected with HIV, bringing the total number of children aged 09 living with HIV to 1.02 million . Nearly 86 per cent of these children live in sub-Saharan Africa. One bright spot on the global horizon is the rapid decline of approximately 52 per cent in new HIV infections among children aged 09 since 2010 due to stepped-up efforts to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV. However, the number of new HIV infections among adolescents has declined at a slower rate of about 40 per cent.
Geographic disparity
Read Also: What Happens If You Get Hiv