The Global Distribution Of Deaths From Hiv/aids
In some countries HIV/AIDS is the cause of more than a quarter of all deaths
Globally, 1.7% of deaths were caused by HIV/AIDS in 2017.
This share is high, but masks the wide variations in the toll of HIV/AIDS across the world. In some countries, this share was much higher.In the interactive map we see the share of deaths which resulted from HIV/AIDS across the world. Across most regions the share was low: across Europe, for example, it accounted for less than 0.1% of deaths.
But across some countries focused primarily in Southern Sub-Saharan Africa the share is very high. More than 1-in-4 of deaths in South Africa and Botswana were caused by HIV/AIDS in 2017. The share was also very high across Mozambique ; Namibia ; Zambia ; Kenya ; and Congo .
Death rates are high across Sub-Saharan Africa
The large health burden of HIV/AIDS across Sub-Saharan Africa is also reflected in death rates. Death rates measure the number of deaths from HIV/AIDS per 100,000 individuals in a country or region.
In the interactive map we see the distribution of death rates across the world. Most countries have a rate of less than 10 deaths per 100,000 often much lower, below 5 per 100,000. Across Europe the death rate is less than one per 100,000.
Across Sub-Saharan Africa the rates are much higher. Most countries in the South of the region had rates greater than 100 per 100,000. In South Africa and Mozambique, it was over 200 per 100,000.
What Behaviors Are The Most Risky For Getting Or Transmitting Hiv
Since there is a fairly high number of people who have HIV and dont know it, you should be tested for HIV so you know your status. Being intoxicated is risky because you are more likely to engage in risky sex if you are drunk or high. In terms of sex acts, anal sex and vaginal intercourse are the most risky behaviors.
Hiv Is An Infection That Can Lead To Aids
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Its a virus that breaks down certain cells in your immune system . When HIV damages your immune system, its easier to get really sick and even die from infections that your body could normally fight off.
About 1.1 million people in the U.S. are living with HIV, and more than 38,000 new infections happen every year. Most people with HIV dont have any symptoms for many years and feel totally fine, so they might not even know they have it.
Once you have HIV, the virus stays in your body for life. Theres no cure for HIV, but medicines can help you stay healthy. HIV medicine lowers or even stops your chances of spreading the virus to other people. Studies show that using HIV treatment as directed can lower the amount of HIV in your blood so much that it might not even show up on a test when this happens, you cant transmit HIV through sex.Treatment is really important . Without treatment, HIV can lead to AIDS. But with medicine, people with HIV can live long, healthy lives and stop the spread of HIV to others.
Don’t Miss: What Does The Hiv Virus Look Like
Hiv Testing After A Recent Infection
If you are concerned about a possible recent HIV infection, you should take an HIV test. If this test result is non-reactive or negative, it can be repeated in a few weeks to be sure. Not everyone has symptoms after a recent infection and thus testing is the only reliable way to know whether you have HIV.
If you might have been exposed to HIV within the last 72 hours, you and your doctor should also discuss whether post-exposure prophylaxis is appropriate in your case. PEP is taken in order to prevent HIV from taking hold and to remain HIV negative.
The most accurate tests for HIV diagnosis after recent infection are antigen/antibody laboratory tests . An HIV antigen is part of the virus itself and is present in high levels in the blood between HIV infection and seroconversion. During seroconversion, HIV antibodies are produced by the body in response to infection and they persist for life.
Symptomatic seroconversion illness occurs in at least 50%, and possibly as many as 80 or 90%, of infected individuals.
HIV antigen/antibody tests will detect the majority of those infected with HIV within four weeks of infection but can sometimes detect infections as early as ten days afterward. While they are extremely accurate, they require blood to be drawn with a needle and results are not available immediately. These tests tend to be offered in hospital settings or for confirmatory purposes.
Do Condoms Stop Hiv Being Passed On
Yes.Using a condom correctly prevents contact with semen or vaginal secretions , stopping HIV from being passed on. The virus cannot pass through the latex of the condom.
Condoms should only be used with a water-based lubricant;as oil-based lube weakens them.
People with HIV who are on effective treatment and have an undetectable viral load cannot pass on HIV through any of their body fluids.
Its also important to remember that if you have sex without a condom other sexually transmitted infections ;can be passed on.
Sex without a condom can also result in pregnancy if other contraception is not being used.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Treatment For Hiv Aids
What We Know About Hiv Testing
About 1 in 7 people in the United States who have HIV dont know they have it. Getting an HIV test is the only way to know your HIV status. HIV testing is easier, more available, and more accurate than ever. There are three types of HIV tests available in the United States; some can detect HIV sooner than others.
Does Hiv Viral Load Affect Getting Or Transmitting Hiv
Yes.;Viral load is the amount of HIV in the blood of someone who has HIV. Taking HIV medicine daily as prescribed can make the viral load very lowso low that a test cant detect it .
People with HIV who take HIV medicine daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex.
HIV medicine is a powerful tool for preventing sexual transmission of HIV. But it works only as long as the HIV-positive partner gets and keeps an undetectable viral load. Not everyone taking HIV medicine has an undetectable viral load. To stay undetectable, people with HIV must take HIV medicine every day as prescribed and visit their healthcare provider regularly to get a viral load test. Learn more.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Find Out You Have Hiv
Why Do Some People With Hiv Infection Develop Aids
Over time, untreated HIV infection damages the immune system and makes it more difficult to fight infections and cancers.
Before there were effective treatments for HIV infection, all infected people went on to develop AIDS within about 10 years. Today, people with HIV who take effective treatment are unlikely to develop AIDS and will have a near-normal life expectancy. This is because these medicines keep the amount of virus in their blood under control and protect the immune system.
What Should I Do If I Need To Clean Up Blood
HIV does not usually survive long outside of the body, but contact with blood should be avoided.;
Hepatitis C can survive in dried blood at room temperature for several weeks, and hepatitis B can survive in dried blood for around a week outside the body.
To clean up blood that has been spilled, wear rubber gloves and mop up the liquid using bleach and warm water . Use warm, soapy water to clean away blood spilled on someones body.
Put the waste, used gloves and bloodied clothes in a plastic bag, seal and throw away.
Don’t Miss: Is Hiv Curable Or Treatable
Whats The Outlook For Maculopapular Rash
There is a wide range of causes for this type of rash and a wide range of outcomes. Allergic reactions and minor reactions to drugs generally clear up quickly. Most childhood viral and bacterial infections have a known and limited course. Once your doctor diagnoses the cause of the condition, theyll be able to provide an outlook based on your case.
What Can Effective Hiv Treatment Do
HIV medication keeps you healthy so you can live a normal lifespan.
Treatment can also reduce your viral load to undetectable levels so that you wont be able to pass on HIV to anyone else. It can take up to six months from starting treatment to become undetectable, so its important to test and start treatment on time.
You May Like: How To Test For Hiv At Home
Read Also: How Can Hiv Be Contracted
What Is The Treatment For Hiv
ART is recommended for everyone who has HIV. ART prevents HIV from multiplying, which reduces the amount of HIV in the body . Having less HIV in the body protects the immune system and prevents HIV infection from advancing to AIDS. ART cant cure HIV, but HIV medicines help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives.
ART also reduces the risk of HIV transmission. A main goal of ART is to reduce a persons viral load to an undetectable level. An;undetectable viral load;means that the level of HIV in the blood is too low to be detected by a viral load test. People with HIV who maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partner through sex.
What You Can Do To Reduce Stigma

You can help reduce stigma by being respectful, compassionate and non-judgemental. Model this behaviour for others when you witness stigmatizing behaviours.
When talking about HIV, certain terms can be stigmatizing. Be thoughtful about the words you use when discussing the topic.
Learn more about the facts of HIV. Treatment can lower the amount of virus in a person’s blood to a level that’s too low to be measured on a standard blood test. This means it’s undetectable.
People living with HIV on treatment who maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their sexual partners.
Knowing and sharing these facts widely can help to reduce stigma. Share our Undetectable = Untransmittable infographic to help us raise awareness.
In addition, HIV is not transmitted through:
- healthy, unbroken skin
Recommended Reading: How Often Do You Have To Take Hiv Medication
If You Already Have Hiv
If you are infected with HIV, you can greatly lower the risk of spreading the infection to your sex partner by starting treatment when your immune system is still healthy.
Experts recommend starting treatment as soon as you know you are infected.footnote 21
Studies have shown that early treatment greatly lowers the risk of spreading HIV to an uninfected partner.footnote 22, footnote 23
Your partner may also be able to take medicine to prevent getting infected.footnote 17 This is called pre-exposure prophylaxis .
Steps to avoid spreading HIV
If you are infected with HIV, you can greatly lower the risk of spreading the infection to your sex partner by starting treatment when your immune system is still healthy.
- Take antiretroviral medicines. Getting treated for HIV can help prevent the spread of HIV to people who are not infected.
- Tell your sex partner or partners about your behaviour and whether you are HIV-positive.
- Follow safer sex practices, such as using condoms.
- Do not donate blood, plasma, semen, body organs, or body tissues.
- Do not share personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or sex toys, that may be contaminated with blood, semen, or vaginal fluids.
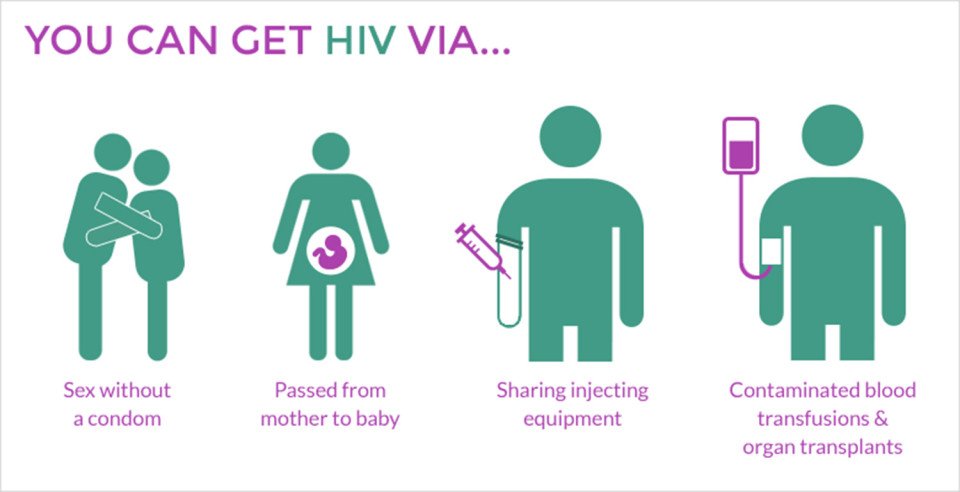
How Is Hiv Transmitted Or Spread
The following are the means by which the HIV virus is spread:
-
Vertical transmission. HIV can be spread to babies born to, or breastfed by, mothers infected with the virus.
-
Sexual contact. In adults and adolescents, HIV is spread most commonly by sexual contact with an infected partner. The virus enters the body through the lining of the vagina, vulva, penis, rectum, or abraded or irritated tissues in the lining of the;mouth through sexual activity.
-
Blood contamination. HIV may also be spread through contact with infected blood. However, due to the screening of donated blood for evidence of HIV infection, the risk of acquiring HIV from blood transfusions is extremely low.
-
Needles. HIV is frequently spread by sharing needles, syringes, or drug use equipment with someone who is infected with the virus. Transmission from patient to health care worker, or vice-versa, through accidental sticks with contaminated needles or other medical instruments, is rare.
No known cases of HIV/AIDS have been spread by the following:
-
Saliva
-
Malaise
-
Enlarged lymph nodes
An HIV-infected child is usually diagnosed with AIDS when the immune system becomes severely damaged or other types of infections occur. As the immune system deteriorates, complications begin to develop. The following are some common complications, or symptoms, of the onset of AIDS. However, each child may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Got Hiv
How Do I Know If I Have Aids
HIV disease becomes AIDS when your immune system is seriously damaged. If you have less than 200 CD4 cells or if your CD4 percentage is less than 14%, you have AIDS. See Fact Sheet 124 for more information on CD4 cells. If you get an opportunistic infection, you have AIDS. There is an official list of these opportunistic infections put out by the Centers for Disease Control . The most common ones are:
- KS , a skin cancer;
- CMV , an infection that usually affects the eyes
- Candida, a fungal infection that can cause thrush or infections in your throat or vagina
AIDS-related diseases also includes serious weight loss, brain tumors, and other health problems. Without treatment, these opportunistic infections can kill you.
The official CDC definition of AIDS is available at AIDS is different in every infected person. Some people die a few months after getting infected, while others live fairly normal lives for many years, even after they officially have AIDS. A few HIV-positive people stay healthy for many years even without taking antiretroviral medications .
When Should I Get Tested For Hiv
If you think you could have HIV, talk to your doctor or sexual health clinic about having a test. Not all people who have HIV will experience a seroconversion illness, so testing is important if you think you might be at risk. Some people at high risk need to be tested regularly.
You should get tested for HIV if:
- you have had unprotected sex with a partner whose HIV status is unknown or who has HIV but does not have a measurable amount of virus in their blood
- you have had unprotected sex with a person from a country that has high rates of HIV infection
- your sexual partner has recently travelled to a country that has high rates of HIV infection and may have had unprotected sex there
- you have had unprotected sex with a sex worker in Africa, Eastern Europe, South East Asia or Papua New Guinea
- you have ever shared injecting equipment
Early diagnosis is important and can improve the long-term course of the illness.
It is a good idea to talk to your doctor or sexual health clinic about other STIs at the same time.
Your information will be kept confidential unless there are major concerns for your safety or the safety of others. HIV is a notifiable disease, which means laboratory staff need to inform the government about new cases, but this information is also confidential.
Also Check: Where Does Hiv Originated From
How Is Hiv Transmitted
HIV is transmitted from an infected person by body fluids such as blood, semen, breast milk, rectal fluids, vaginal fluids or other blood-containing secretions. Transmission occurs when these fluids come in contact with the various mucous membranes of the body, through cuts/openings of the skin, or directly injected into the bloodstream. As a result, anyone who is occupationally exposed to these body fluids risks contracting the disease. Preventive measures include wearing protective clothing, gowns, gloves, masks and goggles to control the spread of HIV among workers who may be at risk.
Unprotected sexual intercourse with infected people poses the single most important risk of infection. HIV can also be passed from one partner into the bloodstream of the other through tiny cuts or scratches.
Intravenous drug abusers may contract HIV if they share needles with infected people. Hemophiliacs requiring frequent transfusions or blood products are at risk due to the possibility of receiving contaminated blood. Since 1985, Canada’s Red Cross has been screening all blood donations for HIV antibodies.
If an individual is struck with a HIV-contaminated needle or sharp object can also pose an opportunity for transmission. Health care workers are at high risk for this type of exposure.
How Hiv Infects The Body
HIV infects;the immune system,;causing progressive damage and eventually making it unable to fight off infections.
The virus attaches itself to immune system cells;called CD4 lymphocyte cells, which protect the body against various bacteria, viruses and other germs.
Once attached, it enters the CD4 cells and uses it;to make thousands of copies of itself. These copies then leave the CD4 cells, killing them in the process.
This process continues until eventually the number of CD4 cells, also called your;CD4 count, drops so low that your immune system stops working.
This process may take up to 10 years, during which time you’ll feel and appear well.;
Page last reviewed: 22 April 2021 Next review due: 22 April 2024
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Contracted Hiv
How Hiv Is Not Spread
The virus doesn’t survive well outside the body. So HIV cannot be spread through casual contact with an infected person, such as by sharing drinking glasses, by casual kissing, or by coming into contact with the person’s sweat or urine.
It is now extremely rare in Canada or the United States for HIV to be transmitted by blood transfusions or organ transplants.