Barriers To The Hiv Response In Kenya
Kenya has demonstrated commitment in providing an enabling legal, social and policy environment at the national and county level to reduce barriers to health services for people living HIV. The country established the first HIV tribunal in the world to increase access to justice related to HIV issues.92
Why People Living With Hiv May Have Worse Covid
While several studies have observed worse outcomes in people with HIV, understanding of the reasons for these is incomplete. Possible explanations include:
- HIV-specific factors. It is possible that chronic inflammation in response to HIV infection may raise the risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes. Excess inflammation is most pronounced in individuals who have had a very low CD4 count in the past or with incomplete reconstitution of their immune system. In addition, a low CD4 count may lead to a more severe inflammatory response to SARS-CoV-2.
- Underlying health conditions. If people with HIV have higher rates of underlying health conditions that are risk factors for severe COVID-19, this will affect outcomes. Researchers try to take these into account in their analyses, but studies may not collect enough information on all relevant conditions.
- Social determinants of health. In many places, significant numbers of people with HIV are economically disadvantaged, live in overcrowded housing, work in frontline jobs or belong to ethnic minorities. However, studies do not usually collect data on many of these factors.
Who Is At Greater Risk Of Covid
A large study of risk factors for severe COVID-19, OPENSafely, looked at around 40% of GP patients in England before vaccines were available.
The study found that old age was by far the strongest risk factor. People over 80 were at least 20 times more likely to die from COVID-19 compared to people aged 50-59. People under 40 had a greatly reduced risk compared to the 50-59 age group.
An organ transplant raised the risk of death fourfold. A history of any form of blood cancer including cancer of the bone marrow or lymph nodes in the past five years raised the risk of death threefold. Any neurological condition, severe obesity or uncontrolled diabetes doubled the risk of death. Men were twice as likely to die as women.
Other risk factors such as Black or Asian ethnicity, social deprivation, liver disease, stroke, dementia and kidney disease raised the risk of death by between 50 and 75%, as did a severe respiratory disease other than asthma.
Chronic heart disease, controlled diabetes, a cancer diagnosis other than blood cancer more than one year ago, asthma, lupus, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, moderate obesity and smoking each raised the risk of death slightly.
People who have many of these risk factors are at far greater risk of dying from COVID-19 than people who have few risk factors, regardless of HIV status.
Recommended Reading: Is Undetectable Hiv Contagious
Are Some Regions Of The United States More Impacted By Hiv Than Others
Yes. HIV is largely an urban disease, with most cases occurring in metropolitan areas with 500,000 or more people. The South has the highest number of people living with HIV, but if population size is taken into account, the Northeast has the highest rate of people living with HIV.
*Rates per 100,000 people.
Fasttrack To End Aids: The 909090 Targets
To take the AIDS response forward, UNAIDS has developed a Fast-Track approach to reach a set of time-bound targets by 2020. The targets include 90% of all people living with HIV knowing their HIV status, 90% of people who know their HIV-positive status having access to treatment and 90% of people on treatment having suppressed viral loads. They also include reducing new HIV infections by 75% and achieving zero discrimination.
Also Check: Nba Youngboy Aids
Tuberculosis Among People Living With Hiv
Tuberculosis is the leading HIV-associated opportunistic infection in low- and middle- income countries, and it is a leading cause of death globally among people living with HIV. Death due to tuberculosis still remains high among people living with HIV, however the number of deaths is decreasing. Most of the global mortality due to TB among those with HIV is from cases in Sub-Saharan Africa.
In the charts here we see the number of tuberculosis patients who tested positive for HIV the number receiving antiretroviral therapy and the number of TB-related deaths among those living with HIV.
People who use ART are living longer
ART not only saves lives but also gives a chance for people living with HIV/AIDS to live long lives. Without ART very few infected people survive beyond ten years.3
Today, a person living in a high-income country who started ART in their twenties can expect to live for another 46 years that is well into their 60s.4
While the life expectancy of people living with HIV/AIDS in high-income countries has still not reached the life expectancy of the general population, we are getting closer to this goal.5
ART prevents new HIV infections
There is considerable evidence to show that people who use ART are less likely to transmit HIV to another person.7 ART reduces the number of viral particles present in an HIV-positive individual and therefore, the likelihood of passing the virus to another person decreases.
We need to increase ART coverage
The Global Hiv/aids Epidemic
HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, is one of the worlds most serious public health challenges. But there is a global commitment to stopping new HIV infections and ensuring that everyone with HIV has access to HIV treatment.
According to UNAIDS:
Number of People with HIVThere were approximately 37.7 million people across the globe with HIV in 2020. Of these, 36 million were adults and 1.7 million were children aged 0-14 years. More than half were women and girls.
New HIV InfectionsAn estimated 1.5 million individuals worldwide acquired HIV in 2020, marking a 31% decline in new HIV infections since 2010. Of these new HIV infections:
- 1.3 million were individuals ages 15+
- 160,000 were among children aged 0-14 years
HIV TestingApproximately 84% of people with HIV globally knew their HIV status in 2020. The remaining 16% still need access to HIV testing services. HIV testing is an essential gateway to HIV prevention, treatment, care and support services.
HIV Treatment AccessAs of June 2020, 28.2 million people with HIV were accessing antiretroviral therapy globally. That means 9.5 million people are still waiting. HIV treatment access is key to the global effort to end AIDS as a public health threat. People with HIV who are aware of their status, take ART as prescribed, and get and keep an undetectable viral load can live long, healthy lives and have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners.
Recommended Reading: How Long Can Hiv Go Undetected
Voluntary Medical Male Circumcision
In 2008, Kenya implemented as an HIV prevention measure.61 Since then Kenya has made impressive progress in implementing VMMC programming. In 2015, Kenya was one of only three countries in sub-Saharan Africa to increase VMMC, following a worrying decline in this intervention throughout the rest of the region.62.
By 2016, 92.6% of men in the country were circumcised.63 The next phase of Kenyas VMMC strategy aims to see 95% of men circumcised by 2019 and will focus on infants and adolescents .64
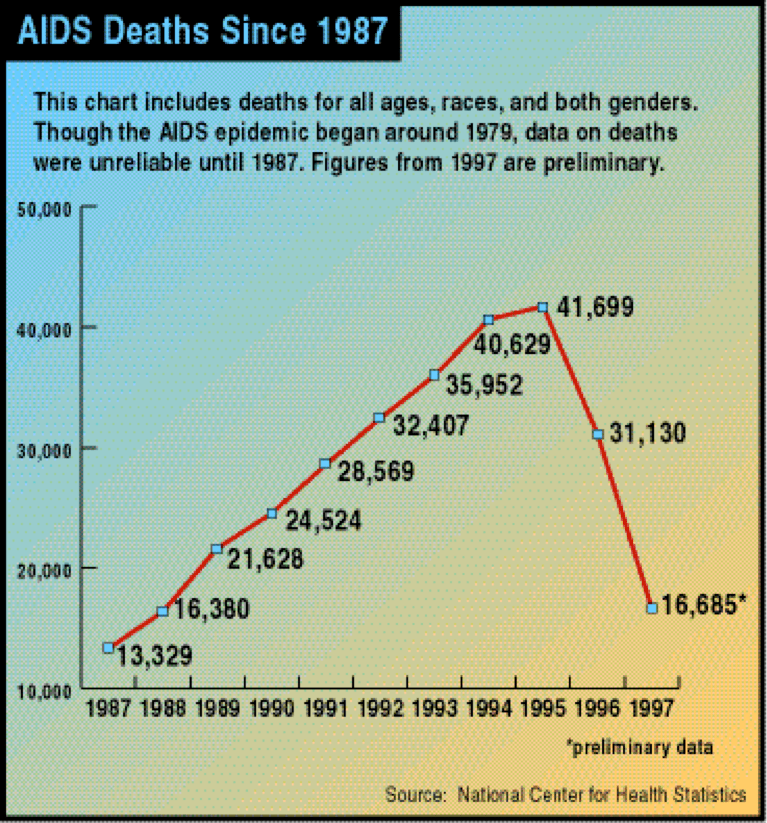
How Many People Die Of Aids Each Year Us
4.3/5people have died of HIVAIDSU.S.HIVpeopleAIDSdie each yearseen here
In 2017, there were 16,350 deaths among adults and adolescents with diagnosed HIV in the United States and 6 dependent areas. These deaths may be due to any cause.
Similarly, how many people die from AIDS every day? AIDS-related DeathsAIDS-related deaths have been reduced by more than 55% since the peak in 2004. In 2018, around 770,000 people died from AIDS-related illnesses worldwide, compared to 1.2 million in 2010 and 1.7 million in 2004.
Beside above, how many people died of AIDS in 2019?
AIDS-related deaths have been reduced by more than 56% since the peak in 2004. In 2018, around 770 000 people died from AIDS-related illnesses worldwide, compared to 1.7 million in 2004 and 1.2 million in 2010.
How many people died of AIDS in the 80s?
Key Facts. The first cases of what would later become known as AIDS were reported in the United States in June of 1981. Today, there are more than 1.1 million people living with HIV and more than 700,000 people with AIDS have died since the beginning of the epidemic.
Also Check: Can You Get Aids Before Hiv
How Many People Have Aids
Approximately 38 million people worldwide are living with AIDS/HIV.
While these numbers might seem huge, it is important to note that today, infection rates have dropped considerably. While this trend continues, it is important to ensure that individuals who are already infected have access to proper healthcare solutions.
Despite this aspect, according to research carried out by UNAIDS, it seems that approximately 38 million people are living with the disease at the moment, which is a worrying HIV statistic.
1.8 million children worldwide are currently infected with HIV.
This grim statistic showcases the number of children who are currently infected with the virus. It is essential to mention that most of these children have been infected by their own mothers during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or childbirth.
As such, we can see one of the main secondary effects associated with the disease the inability to give birth and breastfeed children without putting them at risk of infection.
That said, the first two statistics allow us to give a brief answer to the question of how common is HIV. Luckily, compared to other diseases, HIV is not too widespread, granted that safety precautions can be taken to reduce the chance of infection to practically 0.
Even so, there were times when HIV transmission rates reached worrying highs. Thus, it is essential to counter transmission cases for children, since they have virtually no defense against the disease before being born.
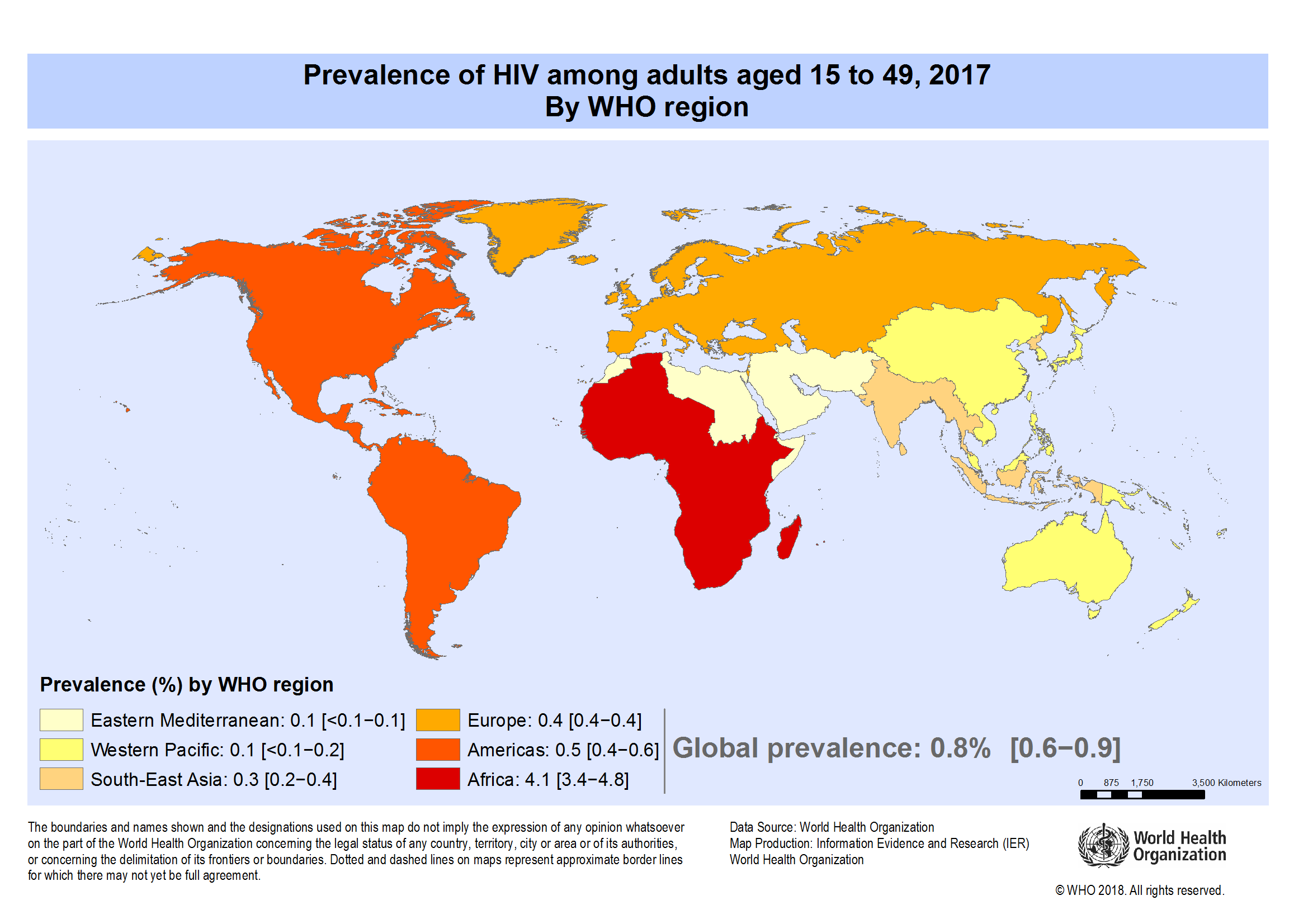
What About Hiv Around The World
HIV disease continues to be a serious health issue for parts of the world. Worldwide, there were about 2.1 million new cases of HIV in 2015. About 36.7 million people are living with HIV around the world, and as of June 2016, 17 million people living with HIV were receiving medicines to treat HIV, called antiretroviral therapy . An estimated 1.1 million people died from AIDS-related illnesses in 2015. Sub-Saharan Africa, which bears the heaviest burden of HIV/AIDS worldwide, accounts for 65% of all new HIV infections. Other regions significantly affected by HIV/AIDS include Asia and the Pacific, Latin America and the Caribbean, and Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
CDC’s Global AIDS websiteexplains what CDC is doing in the global fight against HIV.
Don’t Miss: Jania Has Herpes
Hiv And Aids In Kenya
KEY POINTS
- Kenya has the joint third-largest epidemic in the world, alongside Mozambique and Uganda.
- Kenyas HIV epidemic affects most of its general population, but groups of men who have sex with men, women, sex workers and people who inject drugs are still more vulnerable to infection.
- In recent decades Kenya has been a huge prevention success story in the region. It was one of the first to approve the use of PrEP and has led the way in providing VMMC. As a result new infections have fallen dramatically in recent years.
- In 2018, 69% of adults living with HIV in Kenya were accessing treatment. However treatment coverage among children aged under 15 was lower, at 61%.
- Although awareness of HIV and AIDS is high in Kenya, many people living with HIV face high levels of stigma and discrimination which prevent people accessing HIV services.
Explore this page to find out more about , HIV testing and counselling, HIV prevention programmes, antiretroviral treatment availability, , , funding for HIV, and the way forward for Kenya.
Kenya has the joint third-largest HIV epidemic in the world with 1.6 million people living with HIV in 2018.1In the same year, 25,000 people died from AIDS-related illnesses. While this is still high the death rate has declined steadily from 64,000 in 2010.2
Famous People Who Died From Hiv/aids
For younger Millenials out there, and older people as well, AIDS isnt nearly the scary monster disease that it was for those of us who grew up in the 80s and early 90s. Back then, and for good reason, people were terrified of the disease to the point that people with the condition, despite the fact that it takes a lot of bodily fluid to be transferred from one person to the next, were shunned or isolated because people feared that theyd catch the disease from them. While the work people have done to reduce both the impact of the disease and the stigma surrounding it has been great, its also lowered peoples guards to the point that the disease has actually been on the rebound in recent years. So, with that in mind, lets talk about some of the notable people who died from the disease in the hopes that people remember that while medication has greatly improved, the lifespan of those with either HIV or AIDS, its still a deadly disease. So, wrap it up people!
Don’t Miss: Is Hair Loss A Symptom Of Hiv
Infographic: World Aids Day 2021
Although AIDS-related deaths have declined in recent years, the epidemic still killed 680,000 people in 2020.
2021 40 years since AIDS was discovered in 1981.
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is a chronic and potentially life-threatening condition caused by the human immunodeficiency virus .
HIV attacks the immune system, weakening it to the point where it cannot fight infections.
According to UNAIDS, there were 37.7 million people living with HIV around the world as of 2020.
Some 1.5 million people were infected with HIV in 2020 according to the World Health Organization .
World AIDS Day, commemorated annually on December 1, is dedicated to raising awareness of the AIDS pandemic and mourning those who have died of the disease.
Global HIV/AIDS
HIV/AIDS has killed up to 36.3 million people and infected 79.3 million over the past 40 years.
While deaths have dropped by nearly 50 percent since 2010, some 680,000 people died from AIDS-related illnesses in 2020.
New HIV infections
In 2020, approximately 1.5 million people acquired HIV, with women and girls accounting for about half of new infections. Every week, some 5,000 young women between the ages of 15 and 24 are infected, according to UNAIDS.
More than half of the worlds HIV-positive population live in Eastern and Southern Africa. In 2020, the regions had some 670,000 new infections and 310,000 AIDS-related deaths.
A global breakdown of AIDS cases and deaths is presented in the table below.
- Sex education
How Many Died In The Aids Epidemic
Globally, around 680 000 people will die from AIDS-related illnesses in 2020, compared to only one million in 1999. There were 9 million in the first quarter. The number of people between 3 and 2 million. In 2004, there were 7 million people and in 2005, there were 1 million. A total of 3 million was spent. In 2010, there were 9 million people in the world.
Recommended Reading: Nba Youngboy Truth About Herpes
Delayed Diagnosis And Treatment Leads To Deaths
In MSF-supported hospitals in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Guinea, Malawi and elsewhere, many deaths occur within 48 hours of people being admitted to hospital, explains Dr Gilles Van Cutsem, leader of MSFs HIV/AIDS Working Group. People arrive very ill, often with severe opportunistic infections such as tuberculosis, cryptococcal meningitis, or Kaposi’s sarcoma. When they arrive, sometimes it’s too late to save them. They might not have been diagnosed on time or they failed to get access to a lifesaving treatment.
AIDS-related deaths are primarily driven by delayed diagnosis, treatment interruptions and virologic and immunologic failure among HIV treatment-experienced people. The World Health Organization estimates that more than 30 per cent of people who start HIV treatment worldwide have advanced disease with severe immune suppression, which puts them at a very high risk of contracting opportunistic infections and dying.
HIV/AIDS
Nearly 700,000 people died from HIV-related causes, while 1.5 million people became newly infected with the HIV virus in 2020.
If primary care clinics are not equipped and trained to detect advanced HIV, people at risk will remain undetected and untreated they will deteriorate until they are terminally ill.
Is The World Making Progress In Its Fight Against Hiv/aids
The 1990s saw a substantial increase in the number of people infected with HIV and dying of AIDS.
Between 1996 and 2001 more than 3 million people were infected with HIV ever year. Since then the number of new infections began to decline and in 2017 it was reduced to below 2 million. The lowest number of new infections since 1990.
The number of AIDS-related deaths increased throughout the 1990s and reached a peak in 2005, 2006 when in both years close to 2 million people died. Since then the annual number of deaths from AIDS declined as well and was since halved. 2017 was the first year since the peak in which fewer than 1 million people died from AIDS.
The chart also shows the continuing increase in the number of people living with HIV. The rate of increase has slowed down compared to the 1990s, but the absolute number is at the highest ever with more than 36 million people globally living with HIV.
Don’t Miss: Hiv Screen 4th Generation Wrfx Nonreactive
Tuberculosis And Hiv Co
In 2014, it was estimated that Kenya made up 3.3% of the total number of people living with an HIV/TB coinfection globally.88 Up to 38% of people with tuberculosis in Kenya are co-infected with HIV.89
However, it is reported that 83% of people with a co-infection are being treated for both illnesses. This high figure shows commitment to tackling both public health issues.90 However, efforts to prevent co-infection have been more slow, only 11% of people living with HIV were enrolled on TB preventative therapy in 2016.91