How To Recognize And Treat Acute Hiv Syndrome
BARBARA LEE PERLMUTTER, M.D., PH.D., JORDAN B. GLASER, M.D., and SAMWEL O. OYUGI, M.D., Staten Island University Hospital, Staten Island, New York
Am Fam Physician. 1999 Aug 1 60:535-542.
See related patient information handout on acute HIV syndrome, written by the authors of this article.
See related editorials on pages 407 and 411.
The diagnosis of acute human immunodeficiency virus syndrome requires a high index of suspicion and proper laboratory testing. Patients with the syndrome may have fever, fatigue, rash, pharyngitis or other symptoms. Primary HIV infection should be considered in any patient with possible HIV exposure who presents with fever of unknown cause. The diagnosis is based on a positive HIV-1 RNA level in the absence of a positive enzyme-linked immunosorbent antibody assay and confirmatory Western blot antibody test for HIV. Early diagnosis permits patient education as well as treatment that may delay disease progression. Triple-combination antiretroviral therapy should be started immediately and continued indefinitely. Compliance with medication regimens is essential to maximize benefit and discourage the development of viral resistance.
Frequency of Symptoms and Findings Associated with Acute HIV Infection
| Symptoms or findings |
|---|
HIV = human immunodeficiency virus.
Adapted with permission from Kahn JO, Walker BD. Acute human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. N Engl J Med 1998 339:339.
| Symptoms or findings |
|---|
Dhhs Guidelines For Antiretroviral Agents
Current Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in HIV-1Infected Adults and Adolescents, published by US Department of Health and Human Services, recommend starting antiretroviral therapy for all individuals when infection is diagnosed, regardless of stage of infection, as long as barriers to therapy do not exist. Considerations are as follows:
-
The goal of treatment should be the suppression of plasma HIV RNA to below detectable levels
-
Testing for plasma HIV RNA levels and CD4 count and toxicity monitoring should be performed
-
If therapy is initiated before drug-resistance test results are available, a ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitorbased regimen should be used, because clinically significant resistance to protease inhibitors is less common than resistance to non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase and integrase inhibitors in antiretroviral therapynaive persons who harbor drug-resistant virus.
Benefits And Risks Of Treatment
Even though treatment of acute primary HIV infection may seem difficult, compelling reports indicate that the administration of potent antiretroviral therapy can result in a rapid and sustained decline in the viral load to below the limit of detection within three months.12,13 Furthermore, studies of CD4 and CD8 lymphocyte dynamics show restoration of the normal ratio, reflecting recovery of the immune system.14 In one investigation of HIV-1specific cell-mediated immune responsiveness, treatment of acute HIV infection resulted in the restoration of virus-specific immunity with control of viremia in six of six persons studied.15
Early institution of antiretroviral therapy has the advantage of keeping the viral load low by reducing replication and the appearance of resistant HIV phenotypes. It also may prevent immune depletion because of increased immune stimulation resulting from the strong antigenicity of HIV during primary infection.16 This allows for a more favorable initial immune response to HIV.
HIV Infection Without Treatment
FIGURE 1.
Adapted with permission from Fauci AS, Pantaleo G, Stanley S, Weissman D. Immunopathogenic mechanisms of HIV infection. Ann Intern Med 1996 124:65463.
HIV Infection Without Treatment
FIGURE 1.
Adapted with permission from Fauci AS, Pantaleo G, Stanley S, Weissman D. Immunopathogenic mechanisms of HIV infection. Ann Intern Med 1996 124:65463.
Recommended Reading: Does Hiv Make You Age Faster
Dos And Donts For Hiv
HIV-positive women who are expecting to give birth can avert the risk of transmitting the infection to their babies by following a doctor-prescribed treatment and certain precautionary measures.
- The efficacy and success rate of the currently available treatment plan designed for this purpose is such that it reduces the risk of mother-to-fetus transmission to less than 1 percent, even in the case of normal delivery. Conversely, in the absence of this safeguard, the mother is 25 percent likely to pass on the virus to her baby.
- Moreover, some women might have to opt for a cesarean delivery regardless, due to certain unrelated reasons. It is best to enlist the advice of the more informed practitioners at your HIV clinic.
- Also, the mothers milk is another medium through which the virus can be passed on to the baby therefore, breastfeeding in most cases is not recommended in HIV-positive mothers.
Resources:
Can Hiv/aids Be Prevented
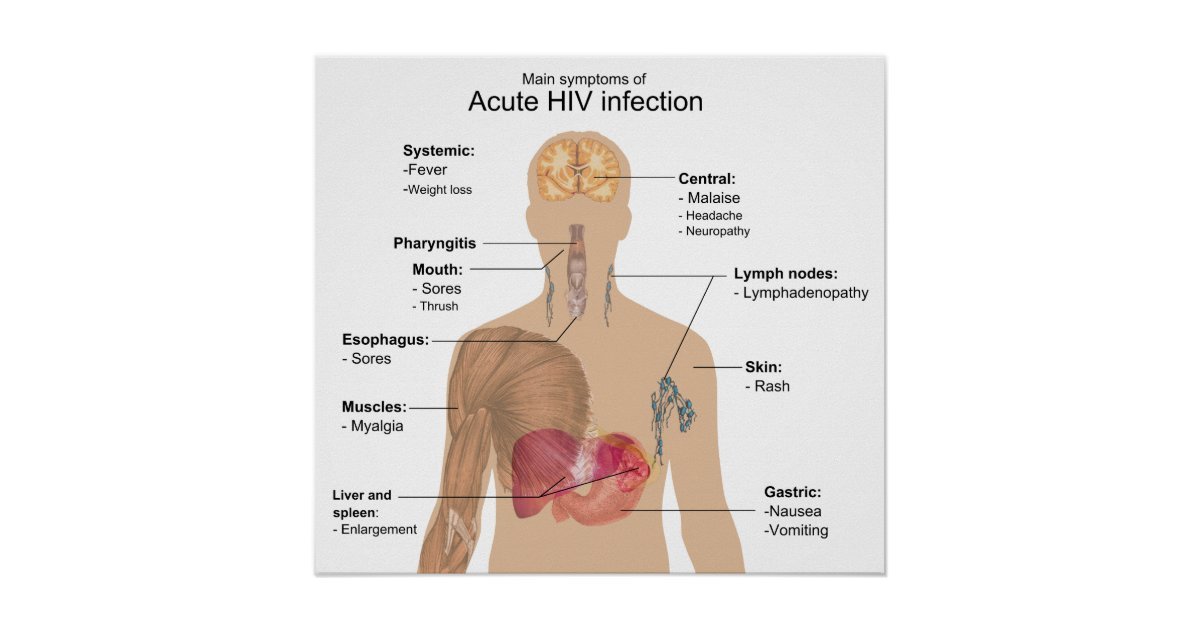
![1 Main symptoms of acute HIV infection [138] 1 Main symptoms of acute HIV infection [138]](https://www.hivtalk.net/wp-content/uploads/1-main-symptoms-of-acute-hiv-infection-138-download.jpeg)
You can reduce the risk of spreading HIV by
- Getting tested for HIV
- Choosing less risky sexual behaviors. This includes limiting the number of sexual partners you have and using latex condoms every time you have sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
- Getting tested and treated for sexually transmitted diseases
- Not injecting drugs
- Talking to your health care provider about medicines to prevent HIV:
- PrEP is for people who don’t already have HIV but are at very high risk of getting it. PrEP is daily medicine that can reduce this risk.
- PEP is for people who have possibly been exposed to HIV. It is only for emergency situations. PEP must be started within 72 hours after a possible exposure to HIV.
NIH: National Institutes of Health
You May Like: Why Is There No Cure For Hiv
How Is An Hiv Test Performed
Before taking an HIV test:
- Ask the clinic what privacy rules it follows.
- Ask your healthcare provider any questions you have about HIV, AIDS, or the HIV test.
To do the HIV test, a small sample of blood is taken from your arm. The blood is sent to a lab and tested for HIV.
Home testing is available. The sample can be obtained via oral secretions , or a blood sample from a finger-stick test strip that is then mailed to a laboratory for screening. Positive results must be confirmed by your doctor before a diagnosis of HIV infection can be established.
Some clinics perform HIV tests without ever taking your name . You must go back to the clinic to get your results. A positive test means you have HIV. A negative test means no signs of HIV were found in your blood.
If your test comes back positive, your healthcare provider is likely to recommend other tests to assess your health. These may include a complete blood count , along with:
- Viral hepatitis screening.
Diarrhea Vomiting And Nausea
Many people with an early HIV infection develop nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and lack of appetite. This can be caused by fungal, bacterial, viral and parasitic infections, which overwhelm an already-compromised immune system. In some cases, these symptoms can also be a side effect to HIV medication.
Read Also: What Is Hiv 1 And 2 Antibody Test
Stage : Acute Primary Infection
The early symptoms of HIV can feel like having the flu. Around one to four weeks after getting HIV, you may start to experience these flu-like symptoms. These normally dont last long . You may only get some of the symptoms and some people dont have any symptoms at all.
Symptoms can include:
- joint aches and pains
- muscle pain.
These symptoms happen because your body is reacting to the HIV virus. Cells that are infected with HIV are circulating throughout your blood system. In response, your immune system tries to attack the virus by producing HIV antibodies this process is called seroconversion. Timing varies but once you have HIV it can take your body up to a few months to go through the seroconversion process.
Having these symptoms alone does not mean you definitely have HIV. The only way to know if you have HIV is by taking a test. You should always visit your healthcare professional if youre worried about or think youve been at risk of getting HIV, even if you feel well and dont have any symptoms. They can then arrange for you to get tested.
HIV will not always show up in a test at this early stage, and you may need to test again later to confirm your result . Your healthcare professional will talk to you about the timing of your test and answer any concerns. Its important not delay speaking to a healthcare worker if you are worried about HIV.
How Long Do Hiv Symptoms Last
This initial onset stage called Acute Retroviral Syndrome starts anywhere from a few weeks to 3 months after infection and can last up to 4 weeks. Due to the ambiguous nature of the symptoms experienced during the ARS stage of infection, HIV is often able to cause serious damage to the immune system before being medically diagnosed.
It should be noted that not every HIV patient experiences the Acute Retroviral Syndrome stage. Reports vary in numbers but generally fall between 50-80% of the population of those infected with HIV experiencing ARS symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Where Does Hiv Come From
What Exactly Is A Retrovirus
A retrovirus is known as retro mainly because it transcribes its actual genetic system in reverse. In the majority of existing creatures, a cells natural substance is encoded from DNA to RNA. A retrovirus is different because it works in the reverse path, by using its RNA coding to generate DNA within an affected cell. Once this happens, the recently generated DNA is entered into the host cells nucleus, essentially hijacking its original equipment so as to generate several replicates of by itself, each one able to infecting as well as destroying a lot of different other host cell count. HIV preferentially targets white blood cells known as helper T-cells Main among these are generally CD4 T-cells, whose task is to activate the bodys defense system.
How Do We Know Treatment As Prevention Works
Large research studies with newer HIV medications have shown that treatment is prevention. These studies monitored thousands of male-female and male-male couples in which one partner has HIV and the other does not over several years. No HIV transmissions were observed when the HIV-positive partner was virally suppressed. This means that if you keep your viral load undetectable, there is effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to someone you have vaginal, anal, or oral sex with. Read about the scientific evidence.
Also Check: How Much Is Hiv Medicine
First Stage: Acute Hiv Infection Symptoms
Most people don’t know right away when they’ve been infected with HIV. But they may have symptoms within 2 to 6 weeks after theyâve gotten the virus. This is when your body’s immune system puts up a fight. It’s called acute retroviral syndrome or primary HIV infection.
The symptoms are similar to those of other viral illnesses, and they’re often compared to the flu. They typically last a week or two and then go away. Early signs of HIV include:
- Ulcers in your mouth, esophagus, anus, or genitals
- Headache and other neurological symptoms
If you have symptoms like these and might have come into contact with someone with HIV in the past 2 to 6 weeks, go to a doctor and ask that you get an HIV test. If you donât have symptoms but still think you might have come into contact with the virus, get tested.
Early testing is important for two reasons. First, at this stage, levels of HIV in your blood and bodily fluids are very high. This makes it especially contagious. Second, starting treatment as soon as possible might help boost your immune system and ease your symptoms.
A combination of medications can help fight HIV, keep your immune system healthy, and keep you from spreading the virus. If you take these medications and have healthy habits, your HIV infection probably wonât get worse.
Hiv Symptoms Every Woman Needs To Know
Human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, attacks the bodys infection-fighting immune system. Without treatment, HIV can lead to AIDS . At the start of the AIDS epidemic in the 1980s, people who were infected with HIV quickly progressed to serious disease. But todays treatments help lower the amount of virus in the bloodso people who are HIV-positive can live healthier, longer lives and not necessarily progress to AIDS.
More than one million people in the US live with HIV, and scarily, one in seven of them dont know they have it. HIV symptoms can be hard to detect. Within a month or two of HIV entering the body, 40% to 90% of people experience flu-like symptoms known as acute retroviral syndrome . But sometimes HIV symptoms don’t appear for yearsor even a decadeafter infection.
RELATED: What Is HIV?
“In the early stages of HIV infection, the most common symptoms are none,” Michael Horberg, MD, director of HIV/AIDS for Kaiser Permanente, in Oakland, California, tells Health. As many as one in five people in the United States with HIV doesn’t know they have it, according to the Centers for Disease Control . That’s why it’s so important to get tested, especially if you currently have or have had unprotected sex with more than one partner or use intravenous drugs.
HIV symptoms for women and for men are often the same here are 16 of the most common signs.
You May Like: What Does The Hiv Virus Attack
Neck And Salivary Gland Disease
Most HIV-infected patients will present with a neck mass during their illness. The differential diagnosis includes neoplasms, infections, HIV lymphadenopathy and parotid disease. Idiopathic follicular hyperplasia is the most common cause but multiple conditions may co-exist. Persistent generalised lymphadenopathy should be differentiated from more serious conditions. A sketchy history and a low yield from microbiological and histological testing often complicate the diagnostic process. A thorough history, an examination, a CD4 count, fine needle aspiration and open biopsies might be needed in the work-up of a suspicious lesion. An infectious or a malignant lesion should be suspected if it is larger than 2 â 3 cm, asymmetric, unilateral, deep and painful. Tender lymphadenopathy is usually infectious while non-tender nodes tend to be malignant. A low CD4 count tends to be associated with infectious or malignant causes of the lymphadenopathy, but a CD4 > 500 is usually associated with PGL. Infectious causes of the lymphadenitis, such as mycobacteria , Pneumocystis, EBV, toxoplasmosis and cat scratch disease, should be excluded.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hiv/aids
The first signs of HIV infection may be flu-like symptoms:
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Mouth ulcers
These symptoms may come and go within two to four weeks. This stage is called acute HIV infection.
If the infection is not treated, it becomes chronic HIV infection. Often, there are no symptoms during this stage. If it is not treated, eventually the virus will weaken your body’s immune system. Then the infection will progress to AIDS. This is the late stage of HIV infection. With AIDS, your immune system is badly damaged. You can get more and more severe infections. These are known as opportunistic infections .
Some people may not feel sick during the earlier stages of HIV infection. So the only way to know for sure whether you have HIV is to get tested.
Also Check: Does Planned Parenthood Do Free Hiv Testing
Hiv Treatment As Prevention
Treatment as prevention refers to taking HIV medication to prevent the sexual transmission of HIV. It is one of the highly effective options for preventing HIV transmission. People living with HIV who take HIV medication daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners.
TasP works when a person living with HIV takes HIV medication exactly as prescribed and has regular follow-up care, including regular viral load tests to ensure their viral load stays undetectable.
Keep Taking Your Hiv Medication To Stay Undetectable
HIV is still in your body when your viral load is suppressed, even when it is undetectable. So, you need to keep taking your HIV medication daily as prescribed. When your viral load stays undetectable, you have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex. If you stop taking HIV medication, your viral load will quickly go back up.
If you have stopped taking your HIV medication or are having trouble taking all the doses as prescribed, talk to your health care provider as soon as possible. Your provider can help you get back on track and discuss the best strategies to prevent transmitting HIV through sex while you get your viral load undetectable again.
Don’t Miss: How Long For Hiv To Show Up On Test
Individual Symptoms Of Hiv Vary From One Person To Another If You Have An Active Sex Life Or Think You May Have Been Exposed To Hiv It Is Important To Get Tested Here Are Some Common Symptoms Of Hiv Many People Experience Severe Flu
This article is also available in Simplified Chinese and Thai.
Symptoms of HIV can vary between individuals however the first signs of infection generally appear within the first 1-2 months. Many, but not all, people will experience severe flu-like symptoms which is your bodys natural response to the virus. This is called the seroconversion period.
Its during this time that its crucial to identify if HIV is the cause, as your viral load is very high which greatly increases the risk of passing it on. And the only way to know for sure is by getting tested.
Stage : The Asymptomatic Stage
Once a person has been through the acute primary infection stage and seroconversion process, they can often start to feel better. In fact, HIV may not cause any other symptoms for up to 10 or even 15 years .
However, the virus will still be active, infecting new cells and making copies of itself. HIV can still be passed on during this stage. If left untreated, over time, HIV infection will cause severe damage to the immune system.
You May Like: Do You Have To Tell Someone You Have Hiv