We Know That Men Who Have Sex With Men In Illinois Are At Higher Risk For Hiv What About Women Who Have Sex With Women
It is not a personâs gender, sexual orientation, race or class that puts them at risk for HIV. People are at risk for HIV when they practice risky behaviors. Women who identify as lesbian or gay can be at risk for HIV by practicing any of the behaviors that place women at risk. Lesbian women have become infected with HIV by using injection drugs or having unprotected sex with male or female partners who are already infected with HIV. Women who have sex with other women should follow guidelines in this fact sheet to protect themselves, and can call the Illinois AIDS/HIV/STD Hotline at 800-243-AIDS for specific information.
If You Think You Might Have Hiv
The first step if you suspect you might be HIV-positive is to get an HIV test. If you test positive, getting started on medication is essential for your health, and may also help your rash.
If your rash is potentially caused by a new HIV medication, stop taking it and contact your doctor right away so they can determine next steps.
Other Symptoms To Watch For
Since an HIV rash signals a problem with the bodys immune system, many people will experience other symptoms along with a skin rash. These symptoms may include:
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fever
- Flu-like symptoms, such as the chills, achy muscles, and a general feeling of illness
If your rash is especially large or causes swelling, you might also experience issues with mobility or getting around.
You May Like: What Is Hiv 1 And 2 Antibody Test
How Do People Get Hiv
HIV spreads when infected blood or body fluids enter the body. This can happen:
HIV also can pass from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
HIV is NOT spread through:
- pee, poop, spit, throw-up, or sweat
- coughing or sneezing
- sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses
What Are The Symptoms Of Later Hiv

As HIV weakens someones immune system, they may experience signs of other illnesses:
- weight loss
- an increase in herpes or cold sore outbreaks
- swollen glands in the groin, neck or armpit
- long-lasting diarrhoea
- tiredness.
But remember: people who dont have HIV can also get any of these they can be the signs of other illnesses.
A weakened immune system may leave someone more open to serious infections such as:
- tuberculosis
Recommended Reading: Is Undetectable Hiv Contagious
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthDepartment of Health and Human ServicesBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
Can Hiv Be Prevented
To reduce the risk of getting HIV, people who are sexually active should:
- use a condom every time they have sex
- get tested for HIV and make sure all partners do too
- reduce their number of sexual partners
- get tested and treated for STDs having an STD increases the risk of HIV infection
- consider taking a medicine every day if they are at very high risk of getting infected
For everyone:
- Do not inject drugs or share any kind of needle.
- Do not share razors or other personal objects that may touch blood.
- Do not touch anyone else’s blood from a cut or sore.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have An Std
Acute Hiv Infection Rash
A rash is one of the earliest symptoms of HIV. It develops during acute HIV infection, which occurs just after contracting the virus. A rash is just one of the many possible symptoms of acute HIV infection, which include:
- Fever
- Swollen tonsils or mouth ulcers
- Diarrhea
These symptoms may begin a few days after being exposed to HIV, but they typically become most noticeable about two to four weeks after infection occurs. They can last anywhere from a few days to several weeks or months.
An acute HIV infection rash and other symptoms of this stage of infection can easily be confused for other ailments or conditions, like the flu or a cold. As a result, many people dont realize that they have HIV.
If you experience an unexplained rash and you have potentially been exposed to the virus, get tested for HIV as soon as possible. Be extra cautious about having safe sex since if you do have an acute HIV infection the viral load is very high during this stage, and youre more likely to pass the virus on to your partners. If youve been taking PrEP and find out you have HIV, you need to stop taking it right away to avoid other health complications.
Hiv/aids And Skin Conditions
Skin conditions are common in people with HIV/AIDS. Many, including Kaposi sarcoma, thrush, and herpes, are caused by germs that take advantage of a weakened immune system. That’s why they are called “opportunistic” infections. Others, like photodermatitis, may be linked to inflammation caused by an overactive immune system as it revives during antiretroviral drug therapy or due to the drugs themselves.
Here are some of the more common skin conditions related to HIV/AIDS.
Don’t Miss: Does Hiv Cause Hair Loss
Taking Care Of Yourself When Living With Hiv
FAST FACTS
Starting antiretroviral treatment as soon as possible, and sustaining it as part of your everyday routine, is the best way of ensuring that your immune system stays strong.
Exercising regularly, eating well, getting enough rest and quality sleep are all vital to maintaining your health.
Your mental wellbeing is just as important as your physical health. Talking about your concerns with family, friends or a support group can really help.
Having HIV doesnt have to stop you living a healthy life in the way that you choose to do. With the right treatment and care, you can expect to live as long as someone who doesnt have HIV. Find out how you can look after yourself and stay healthy.
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine every day, exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can protect your health and have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to your sexual partner.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Its important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
Also Check: Can You Get Hiv From Dried Blood
What Does Aids Look Like
Human Immunodeficiency Virus, or HIV, is a virus that results in Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome, AIDS. HIV compromises the recipients capacity to deal with cancer and infections. When HIV advances, it becomes AIDS. Patients are considered to have AIDS when their CD4 T-cell total falls below 200. People with Kaposis sarcoma, skin cancer, or a lung disease, pneumocystis pneumonia, can also have AIDS as these diseases are common to people with AIDS.
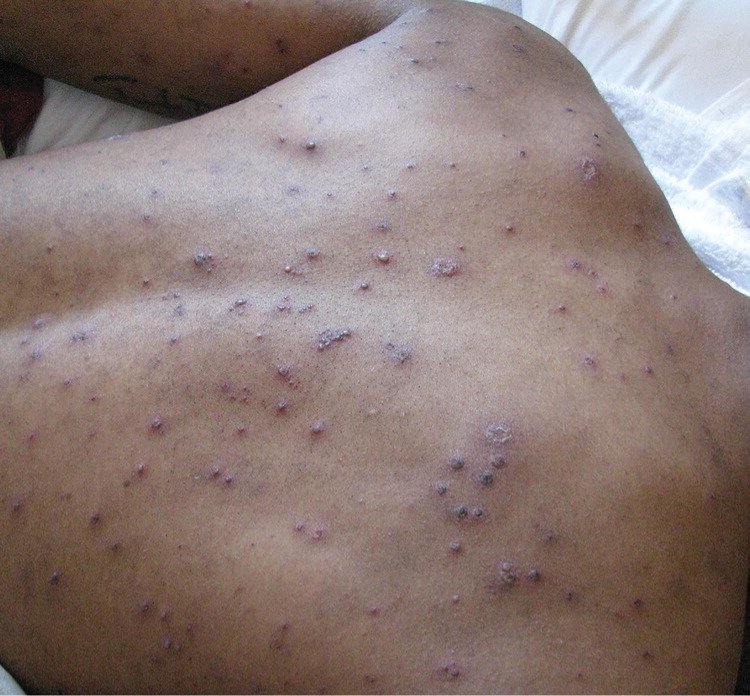
Hiv Rash: What Does It Look Like And How Is It Treated
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Heres our process.
Rash as an early symptom of HIV
A rash is a symptom of HIV that usually occurs within the first two months after contracting the virus. Like other initial symptoms of HIV, its easy to mistake this rash for a symptom of another viral infection. Therefore, its important to learn how to identify this rash and how to treat it.
Recommended Reading: How Long Can Hiv Go Undetected
Rashes Caused By Reactions To Medication
Another possible cause of a rash that develops when someone has HIV is a reaction to a medication. In fact, a rash is one of the most common side effects of antiretroviral medications used to treat HIV.
Rashes that develop due to HIV medications are usually not serious. Monitor the rash for several days to see if it goes away without treatment. If it does not, you may need to switch to a different type of medication or be tested for other possible causes of rash, such as a bacterial infection.
While most of the rashes that develop from taking ARV meds are harmless, its very important to be aware of a condition called Stevens-Johnson Syndrome . This is a rare but potentially fatal skin rash that may develop when taking certain HIV medications. The symptoms of SJS include:
- Fever, headache, and other flu-like symptoms
- Painful, itchy skin
- A skin rash consisting of red, blistered spots
- Peeling skin that develops into painful sores
- Blisters in and around the mouth, nose, eyes, genitals, or mucous membranes
If you experience symptoms of SJS, seek immediate medical care by visiting an emergency room or calling 911.
Of course, other medications besides HIV meds have the potential to cause a reaction like a rash. If you start taking any new medications, be sure to watch for the development of rashes or other unusual symptoms. In addition, you should work closely with your doctor to make sure any medications you take will not interfere with your HIV treatment.
Newly Diagnosed With Hiv
What does an HIV diagnosis mean?
- If you receive an HIV diagnosis, it means that you have HIV.
- Unlike some other viruses, the human body cant get rid of HIV completely. Once you have HIV, you have it for life.
- But with proper medical care, HIV can be controlled. People with HIV who get effective HIV treatment can live long, healthy lives and protect their partners.
What should I do if I just got diagnosed with HIV?
Also Check: Does Cookie Johnson Have Hiv
How Is Hiv Diagnosed
Diagnosis of HIV infection during infancy depends on the detection of the virus. Since all infants born to HIV-infected mothers have a positive antibody test at birth because of the passive transfer of the HIV antibody across the placenta, virological testing is used to confirm the diagnosis.
For infants born to HIV-infected mothers, viral diagnostic testing is usually performed within the first 2 days of life, at 1 to 2 months of age, and at 4 to 6 months of age. A diagnosis of HIV infection can be made with two positive virologic tests obtained from different blood samples.
For children over 18 months, adolescents, or adults, diagnosis is made by testing the blood for the presence of HIV antibody.
What Else Can I Do To Take Care Of Myself
Many of the things we do to take care of ourselves are common sense, such as eating well, exercising and getting plenty of rest and sleep.
However, if youre living with HIV, checking in with your healthcare professional regularly is also important. They should monitor you for other health conditions, which you may experience more as you age, and adjust your treatment as needed.
Teeth and mouth complaints are more common among people living with HIV. Regular brushing, flossing and seeing your dentist can lower the risk of cavities and mouth infections.
You May Like: Does Nba Youngboy Have Herpies
What Is An Hiv Rash
Those who suffer from HIV infection , have a low immunity due to the decrease in their immune cells in the blood. When the immunity is low, a host of various organisms such as bacteria, virus, fungus and parasites can invade the body to cause diseases.
Human immunodeficiency virus itself may cause rash. Medications that are used in various infective stages can also be a cause of the rash in an HIV patient.
However, in many cases, rashes can be one among the first of the signs that appear in an HIV infected person . So it is important to be evaluated by your doctor.
What Research Is Being Done
Within the Federal government, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke , a component of the National Institutes of Health , supports research on the neurological consequences of HIV and AIDS. NINDS works closely with its sister agencies, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and the National Institute of Mental Health , to fund research related to HIV and AIDS. The Office of AIDS Research coordinates AIDS research across NIH.
NINDS conducts research into how the weakened immune systems of individuals with AIDS lead to neurological illnesses. NINDS investigators are studying the JC virus, which can reproduce in the brains of people with impaired immune systems and cause progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy . In one small NINDS study, the anti-cancer drug pembrolizumab showed promise in slowing or stopping the progression of PML. Additional research is needed to confirm results, which could lead to new investigations that help revolutionize treatment for similar chronic infections in immune compromised individuals.
Many individuals whose infection is successfully suppressed with cART experience a reactivation of the virus upon stopping treatment. Researchers are studying how a reservoir of inactive HIV is maintained in the brain. This research is a first step toward developing a means to render the virus permanently dormant or even to rid the brain of all traces of the virus.
Also Check: Does Hiv Cause Hair Loss
Skin Conditions Related To Hiv/aids
What does AIDS look like? The skin conditions listed below may give you something to look out for. A common condition is Kaposis sarcoma, or KS. Someone could have one of these conditions but not necessarily have HIV/AIDS.
1. Thrush
This infection is a form of yeast infection called candida. Its symptoms include lesions on the tongue and inner cheek of the mouth. They can also spread to the gums, tonsils, tongue or roof of the mouth. The creamy white lesions are similar looking to cottage cheese. They may be painful and bleed if scraped while brushing your teeth. For those with HIV, candida can spread to the lungs, esophagus or liver due to the weakened immune system.
2. Kaposi’s Sarcoma
This type of cancer is actually a type of herpes and is common in those who have HIV/AIDS. It affects the mucous membranes and appears as purple lesions on the skin. With a patients compromised immune system, it can easily take over additional parts of the body and select internal organs.
3. Oral Hairy Leukoplakia
An infection that develops as a result of the Epstein-Barr virus, symptoms here are white lesions that appear on the lower portion and sides of the tongue. It is usually found to be one of the beginning signs of HIV/AIDS.
4. Molluscum Contagiosum
5. Herpes
6. Shingles
7. Psoriasis
8. Seborrheic Dermatitis
The Most Common Symptoms Of Seroconversion Are:

- sore throat
- fever
- rash over the body.
Seroconversion is a sign that the immune system is reacting to the presence of the virus in the body. Its also the point at which the body produces antibodies to HIV. Once seroconversion has happened, an HIV test will detect antibodies and give a positive result.
Seroconversion illness happens to most people shortly after infection. It can be severe enough to put someone in hospital or so mild that its mistaken for something like flu although a blocked or runny nose is not usually a symptom.
If you do have HIV, your body fluids are highly infectious during the early weeks and months after transmission. However, once youre on effective treatment and your viral load becomes undetectable you cannot pass on HIV.
It can take up to six months from starting treatment to become undetectable.
You May Like: Does Cookie Johnson Have Hiv
The Complete Blood Count
The most common laboratory test is the complete blood count . It examines the components of blood, including red and white blood cells and platelets. Most test results are reported as amounts in a sample of blood or as a percentage. Other laboratory tests are discussed in Fact Sheet 122 and Fact Sheet 123.
All blood cells are made in the bone marrow, the center of large bones. Some medications or diseases can damage the bone marrow. This can reduce the numbers of different types of red or white blood cells.
Every laboratory has its own “reference range” or normal values for the results of each test. Most lab reports show the normal range and highlight any test results outside the normal range.
For more information on laboratory test results, see Fact Sheet 120 or Lab Tests online at
How Are Hiv And Aids Treated
Medicines can help people with HIV stay healthy. They can also prevent HIV from progressing to AIDS.
Health care providers prescribe a combination of different medicines for people with HIV and AIDS. They must be taken exactly as prescribed or they won’t work. These medicines:
- help keep the number of CD4 cells high
- reduce the viral load of HIV
Regular blood tests will check the number of CD4 cells in the body and the viral load.
If an HIV-positive person’s CD4 count gets low, doctors prescribe daily antibiotics. This prevents pneumocystis pneumonia, which happens in people with weakened immune systems.
Don’t Miss: Does Cookie Johnson Have Aids