Cancers Common In People With Hiv Infection
Kaposi sarcoma Kaposi Sarcoma Kaposi sarcoma is a skin cancer that causes multiple flat pink, red, or purple patches or bumps on the skin. It is caused by human herpesvirus type 8 infection. One or a few spots may appear… read more , a cancer caused by a sexually transmitted herpesvirus, appears as painless, red to purple, raised patches on the skin. It occurs mainly in men who have sex with men.
Cancers of the immune system . Often, lymph nodes in the neck, under the arms, or in the groin enlarge rapidly and painlessly… read more ) may develop, sometimes first appearing in the brain. When the brain is affected, these cancers can cause weakness of an arm or a leg, headache, confusion, or personality changes.
Having AIDS increases the risk of other cancers. They include cancer of the cervix, anus, testes, and lungs as well as melanoma and other skin cancers. Men who have sex with men are prone to developing cancer of the rectum due to the same human papillomaviruses Human Papillomavirus Infection Human papillomavirus causes warts. Some types of HPV cause skin warts, and other types cause genital warts . Infection with some HPV… read more that cause cancer of the cervix in women.
How It Is Done
The health professional drawing blood will:
- Wrap an elastic band around your upper arm to stop the flow of blood. This makes the veins below the band larger so it is easier to put a needle into the vein.
- Clean the needle site with alcohol.
- Put the needle into the vein. More than one needle stick may be needed.
- Attach a tube to the needle to fill it with blood.
- Remove the band from your arm when enough blood is collected.
- Apply a gauze pad or cotton ball over the needle site as the needle is removed.
- Put pressure on the site and then put on a bandage.
Are All Rna Viruses Retroviruses
All retroviruses are protein-enveloped, positive-stranded RNA viruses that encode a unique enzyme, RT, capable of catalyzing the flow of genetic information from RNA to DNA, counter to that of most biologic systems. Thus, retroviruses have a DNA intermediate in their life cycle that can integrate into the host genome.
Poliovirus, the prototypical picornavirus and causative agent of poliomyelitis, is a nonenveloped virus with a single-stranded RNA genome of positive polarity. The virion consists of an icosahedral protein shell, composed of four capsid proteins , which encapsidates the RNA genome .
You May Like: Nba Youngboy Herpes In My Blood
Challenges Of Latent Hiv Reservoirs
Until scientists are able to clear latent HIV reservoirs, it is unlikely that any vaccine or therapeutic approach will fully eradicate the virus.
There is also the challenge of the immune exhaustion that comes with a long-term HIV infection. This is the gradual loss of the immune systems ability to recognize the virus and launch an appropriate response.
Any type of HIV vaccine, AIDS cure, or other treatment must be created taking immune exhaustion into consideration, finding ways to address and offset the decreasing capabilities of a person’s immune system over time.
Stage : Acute Hiv Infection
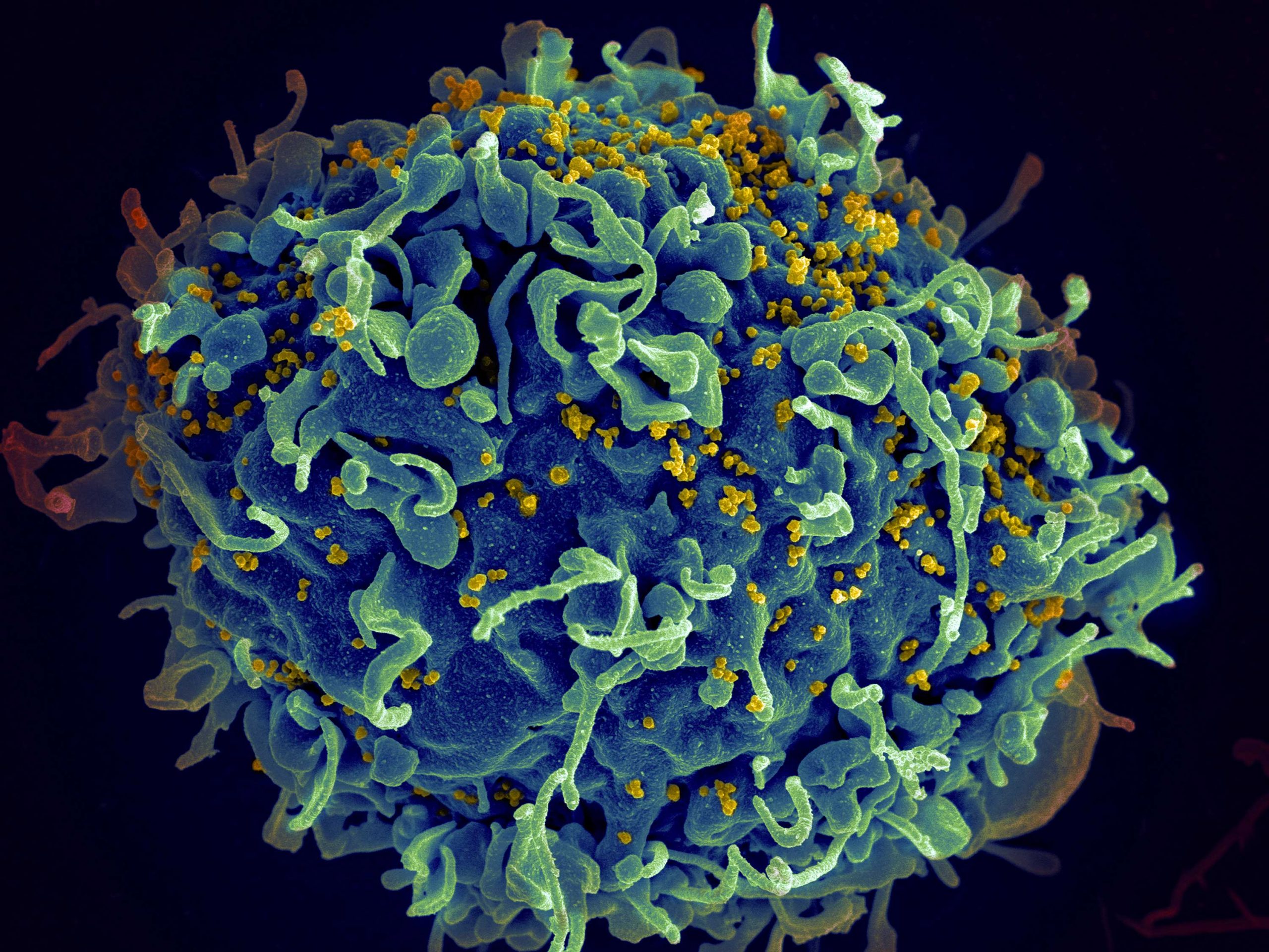
Within the first two to four weeks after HIV infection, about two-thirds of people will experience symptoms that feel like a really bad flu. As the immune system rallies to fight off the virus, fever may develop along with additional symptoms, such as sore throat, swollen glands, mouth sores, rashes, diarrhea, fatigue, headache, and muscle and joint pain.
Read Also: Hiv Stays Alive In Dried Blood
Infection And Infectious Diseases
HIV is able to enter the body via intact mucous membranes, eczematous or injured skin or mucosa and by parenteral inoculation. When transmitted by sexual contact, HIV attaches first to dendritic cells or macrophages/monocytes HIV using CCR-5 as a co-receptor is then preferentially replicated . HIV is taken up by macrophages and replicated as shown for M cells in the mucosa . HIV exposure to blood cells can result in the direct infection of T helper cells and the transmission of R5 and X4 viruses . As mentioned above, 1 HID is equivalent to approximately 500-1,000 HIV particles, with a higher dose required for infection via mucous membranes compared to infection via the bloodstream, e.g. by needle stick injury. The majority of new HIV infections are still transmitted sexually. Another epidemiologically relevant route is parenteral administration of drugs and also snorting of drugs with epistaxis.
Transmission of HIV via blood or transplanted organs, including bone, is possible from about days 5-6 after infection of the donor. Mother-to-child transmission has been demonstrated from the 12th week of gestation, but transmission occurs predominantly in the final trimester and particularly shortly before or during birth . HIV can be transmitted via breast milk .
Who Should Be Tested For Hiv
The CDC recommends that everyone age 13 to 64 get tested for HIV at least once.
People more vulnerable to HIV should get tested more frequently. The CDC defines people in this higher-risk group as those who have:
- Had more than one sex partner in the past year
- Had an HIV-positive partner
- Been diagnosed with or treated for hepatitis or tuberculosis or a sexually transmitted disease in the past year
- Exchanged sex for drugs or money
Don’t Miss: Does Nba Youngboy Still Have Herpes
Whats The Hiv Window Period
As soon as someone contracts HIV, it starts to reproduce in their body. The persons immune system reacts to the antigens by producing antibodies .
The time between exposure to HIV and when it becomes detectable in the blood is called the HIV window period. Most people develop detectable HIV antibodies within 23 to 90 days after transmission.
If a person takes an HIV test during the window period, its likely theyll receive a negative result. However, they can still transmit the virus to others during this time.
If someone thinks they may have been exposed to HIV but tested negative during this time, they should repeat the test in a few months to confirm . And during that time, they need to use condoms or other barrier methods to prevent possibly spreading HIV.
Someone who tests negative during the window might benefit from post-exposure prophylaxis . This is medication taken after an exposure to prevent getting HIV.
PEP needs to be taken as soon as possible after the exposure it should be taken no later than 72 hours after exposure but ideally before then.
Another way to prevent getting HIV is pre-exposure prophylaxis . A combination of HIV drugs taken before potential exposure to HIV, PrEP can lower the risk of contracting or transmitting HIV when taken consistently.
Timing is important when testing for HIV.
How Is Hiv Transmitted Or Spread
The following are the means by which the HIV virus is spread:
-
Vertical transmission. HIV can be spread to babies born to, or breastfed by, mothers infected with the virus.
-
Sexual contact. In adults and adolescents, HIV is spread most commonly by sexual contact with an infected partner. The virus enters the body through the lining of the vagina, vulva, penis, rectum, or abraded or irritated tissues in the lining of the mouth through sexual activity.
-
Blood contamination. HIV may also be spread through contact with infected blood. However, due to the screening of donated blood for evidence of HIV infection, the risk of acquiring HIV from blood transfusions is extremely low.
-
Needles. HIV is frequently spread by sharing needles, syringes, or drug use equipment with someone who is infected with the virus. Transmission from patient to health care worker, or vice-versa, through accidental sticks with contaminated needles or other medical instruments, is rare.
No known cases of HIV/AIDS have been spread by the following:
-
Saliva
-
Malaise
-
Enlarged lymph nodes
An HIV-infected child is usually diagnosed with AIDS when the immune system becomes severely damaged or other types of infections occur. As the immune system deteriorates, complications begin to develop. The following are some common complications, or symptoms, of the onset of AIDS. However, each child may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
Also Check: How Long Can Hiv Be Dormant In Your System
What Behaviors Are The Most Risky For Getting Or Transmitting Hiv
Since there is a fairly high number of people who have HIV and dont know it, you should be tested for HIV so you know your status. Being intoxicated is risky because you are more likely to engage in risky sex if you are drunk or high. In terms of sex acts, anal sex and vaginal intercourse are the most risky behaviors.
Living With Hiv: What To Expect And Tips For Coping
More than 1.2 million people in the United States are living with HIV. Its different for everybody, but with treatment, many can expect to live a long, productive life.
The most important thing is to start antiretroviral treatment as soon as possible. By taking medications exactly as prescribed, people living with HIV can keep their viral load low and their immune system strong.
Its also important to follow up with a healthcare provider regularly.
Other ways people living with HIV can improve their health include:
- Make their health their top priority. Steps to help people living with HIV feel their best include:
- fueling their body with a well-balanced diet
- exercising regularly
- avoiding tobacco and other drugs
- reporting any new symptoms to their healthcare provider right away
Read Also: Nba Youngboy Got Herpes
How Do People Get Hiv
HIV spreads when infected blood or body fluids enter the body. This can happen:
HIV also can pass from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
HIV is NOT spread through:
- pee, poop, spit, throw-up, or sweat
- coughing or sneezing
- sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses
Where Is It Widespread

HIV is spread throught the world, but Sub-Saharan Africa has the greatest number of people who are infected. The World Health Organization and the United Nations’ UNAIDS office estimate that more than a third of adults are infected with HIV in some areas of Africa. There are many case of HIV in South and Southeastern Asia. The numbers of people who have HIV in Eastern Europe are growing because of injection drug use.
There are two main types of the virus: HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-2 is most commonly found in West Africa, although places in other parts of the world are seeing it, too. HIV tests usually look for both kinds.
Don’t Miss: Hiv Screen 4th Generation Wrfx Reactive
Can You Survive Hiv
A person with HIV can live for a long period of time without being diagnosed with HIV. However, if an untreated HIV infection is present, the overall mortality rate is more than 90%. Infections usually last between eight and ten years before they become fatal. It varies from person to person, but it is possible.
Can Hiv Be Prevented
To reduce the risk of getting HIV, people who are sexually active should:
- use a condom every time they have sex
- get tested for HIV and make sure all partners do too
- reduce their number of sexual partners
- get tested and treated for STDs having an STD increases the risk of HIV infection
- consider taking a medicine every day if they are at very high risk of getting infected
For everyone:
- Do not inject drugs or share any kind of needle.
- Do not share razors or other personal objects that may touch blood.
- Do not touch anyone else’s blood from a cut or sore.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take To Show Hiv Symptoms
When Should You Call The Doctor If You Have Hiv Or You Think You Have Been Exposed To Hiv
There is also post-exposure prophylaxis , which is used in emergencies and should be started within 72 hours after the possible exposure. This involves taking antiretroviral therapy after this exposure. ART may be prescribed after sexual assault, or if you think you have been exposed during consensual sex or drug-taking.
If you already know you have HIV, you should follow your healthcare providers instructions on when to call. It is important to treat any type of infection, so call if you have new symptoms or things like a fever, sweating episodes, diarrhea, and so on. Its better to check with your doctor if you have any kind of symptom that worries you.
The main feature of managing AIDS is to continue to take your medicines and to fight back at opportunistic infections at the first sign of them.
Is It Safe For Children With Hiv To Receive Routine Immunizations
-
MMR, or measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine, is safe to give to children with HIV, unless they have a severely weakened immune system.
-
DTaP/Td vaccine is safe to give to infants and children with HIV.
-
Hib and Hep B vaccines are safe to give to children with HIV.
-
Hepatitis A and B vaccines are safe to give to HIV-positive children.
-
VZIG should be considered for known HIV-positive children, depending on their immune status.
-
A yearly influenza vaccine is recommended for children with HIV, as well as any individual living in the same household as a child with HIV. There are two types of influenza vaccine children and adults with HIV should receive the “shot” form of the vaccine–not the nasal spray form, as it contains a live virus. Pneumococcal vaccine can be safely administered to age-appropriate HIV-infected children.
Always consult with your child’s doctor regarding immunizations for an HIV-infected child.
You May Like: Can You Get Aids Before Hiv
Favorite Information On Nutrition For Hiv
If youre living with HIV, nutrition is vital for your long-term health and well-being. The Well Project, a nonprofit that focuses on women with HIV and AIDS, offers resources on how to incorporate the ideal foods for optimal health. Youll find information on how to fight weight and muscle loss, keep your energy levels high, and minimize side effects from HIV medication.
Is There A Vaccine For Hiv
Currently, there are no vaccines to prevent or treat HIV. Research and testing on experimental vaccines are ongoing, but none are close to being approved for general use.
HIV is a complicated virus. It mutates rapidly and is often able to fend off immune system responses. Only a small number of people who have HIV develop broadly neutralizing antibodies, the kind of antibodies that can respond to a range of HIV strains.
The first HIV vaccine efficacy study in 7 years was underway in South Africa in 2016. The experimental vaccine is an updated version of one used in a 2009 trial that took place in Thailand.
A 3.5-year follow-up after vaccination showed the vaccine was 31.2 percent effective in preventing HIV transmission.
The study involves 5,400 men and women from South Africa. In 2016 in South Africa, about contracted HIV. The results of the study are expected in 2021.
Other late-stage, multinational vaccine clinical trials are also currently underway.
Other research into an HIV vaccine is also ongoing.
While theres still no vaccine to prevent HIV, people with HIV can benefit from other vaccines to prevent HIV-related illnesses. Here are the CDC recommendations:
- pneumonia:
Read Also: How Long Does Aids Take To Show
Causes And Risk Factors Of Hiv/aids
HIV is spread by direct contact with certain body fluids from a person with HIV who has a detectable viral load. These fluids are:
- Blood
- Semen and preseminal fluid
- Rectal fluids
- Vaginal fluids
- Breast milk
In the United States, HIV is mostly spread through sex, particularly anal and vaginal intercourse. People can also transmit HIV by sharing used injection equipment, such as syringes and other paraphernalia.
Mothers can spread HIV to babies during pregnancy, birth, and breastfeeding.
Common Questions & Answers
HIV is an abbreviation that stands for human immunodeficiency virus. If you are HIV positive it means that an HIV test has detected the presence of the virus in your body. HIV attacks your body’s immune system.
AIDS is an acronym that stands for the disease caused by HIV, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. It is a late stage of infection in which the HIV virus has actively damaged the immune system.
Recommended Reading: Does Aids Cause Hair Loss
What You Can Do To Reduce Stigma
You can help reduce stigma by being respectful, compassionate and non-judgemental. Model this behaviour for others when you witness stigmatizing behaviours.
When talking about HIV, certain terms can be stigmatizing. Be thoughtful about the words you use when discussing the topic.
Learn more about the facts of HIV. Treatment can lower the amount of virus in a person’s blood to a level that’s too low to be measured on a standard blood test. This means it’s undetectable.
People living with HIV on treatment who maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their sexual partners.
Knowing and sharing these facts widely can help to reduce stigma. Share our Undetectable = Untransmittable infographic to help us raise awareness.
In addition, HIV is not transmitted through:
- healthy, unbroken skin