How Does Hiv Affect The Body
The human immune system involves many types of cells which guard against germs responsible for most diseases. The immune system’s most important guard cells are B-cells and T-cells, which are special white blood cells. B-cells and T-cells cooperate to fight any germ that attacks the human body.
B-cells produce particular proteins, called antibodies, that try to neutralize the invading germ. After a person recovers from an infection, these antibodies continue to circulate in the bloodstream, acting as part of the immune system’s “memory.” Immune system memory explains why a person rarely suffers a second attack from an infectious disease such as measles. If the same germ is encountered again, the antibodies will recognize and neutralize it. T-cells attack the germ directly and try to kill it.
Who Should Be Tested For Hiv
The CDC recommends that everyone age 13 to 64 get tested for HIV at least once.
People more vulnerable to HIV should get tested more frequently. The CDC defines people in this higher-risk group as those who have:
- Had more than one sex partner in the past year
- Had an HIV-positive partner
- Been diagnosed with or treated for hepatitis or tuberculosis or a sexually transmitted disease in the past year
- Exchanged sex for drugs or money
How Are Hiv And Aids Treated
Medicines can help people with HIV stay healthy. They can also prevent HIV from progressing to AIDS.
Health care providers prescribe a combination of different medicines for people with HIV and AIDS. They must be taken exactly as prescribed or they won’t work. These medicines:
- help keep the number of CD4 cells high
- reduce the viral load of HIV
Regular blood tests will check the number of CD4 cells in the body and the viral load.
If an HIV-positive person’s CD4 count gets low, doctors prescribe daily antibiotics. This prevents pneumocystis pneumonia, which happens in people with weakened immune systems.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Has Herpes
Common Questions & Answers
HIV is an abbreviation that stands for human immunodeficiency virus. If you are HIV positive it means that an HIV test has detected the presence of the virus in your body. HIV attacks your body’s immune system.
AIDS is an acronym that stands for the disease caused by HIV, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. It is a late stage of infection in which the HIV virus has actively damaged the immune system.
Quantity Of Hiv Virus In Blood
The amount of HIV virus present in your blood could determine how likely are you to pass this disease to your unborn/newborn baby. Merely being HIV positive doesnt indicate that your child will be HIV positive too. So make sure that you get tested regarding the quantity of virus present in your body.
Don’t Miss: Do Nba Youngboy Have Herpes
Hiv Effects On The Nervous System
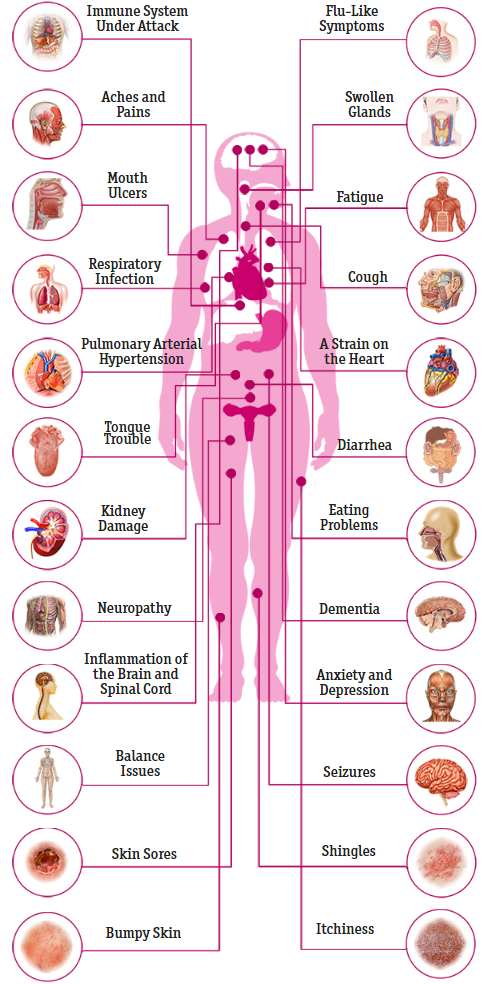
About half of people with AIDS have nerve problems related to the virus. Infection or inflammation can damage your spinal cord or brain and keep your nerve cells from working the way they should. Some medications can also affect your nervous system.
Brain
Inflammation in your brain and spinal cord can lead to confusion and other thinking problems as well as weakness, headaches, seizures, and balance problems.
When AIDS is far along, you might get dementia and have problems remembering things.
Having HIV can also affect your mental health. Many people living with it have depression or anxiety. Mental health professionals and support groups can help you work through your concerns and manage your life with HIV.
Nerves
The opportunistic infection cytomegalovirus can attack your nerves, making it hard for you to control your arms and legs or your bladder.
Itâs common for tiny holes to form in spinal fibers when people with AIDS donât get treatment. This is called vacuolar myelopathy and causes trouble walking.
HIV or the drugs that treat it can also damage nerves all over your body, causing neuropathy. You might have pain, numbness, weakness, burning, stiffness, or tingling.
Antiretroviral therapy to treat HIV can lower your risk of getting these conditions or complications. If a medication is causing the problems, your doctor might switch you to a different one.
Can Hiv Be Transmitted Via Contact With Menstrual Blood
Menstrual blood touching intact skin poses no HIV transmission risk. If it comes into contact with broken skin or is swallowed, then HIV transmission is possible but still unlikely. Due to the effectiveness of HIV treatment, the menstrual blood of someone living with HIV who is adherent to their antiretroviral medication could well have no detectable virus . The small number of case reports documenting HIV transmission via exposure to blood involved a significant amount of blood from the HIV-positive person, as well as open wounds in the other persons skin.
Also Check: Hiv Screen 4th Generation Wrfx Nonreactive
Are Women At Greater Risk Of Hiv During Menstruation
The menstrual bleeding during a period itself does not increase the risk of acquiring HIV. However, hormonal changes during menstrual cycles are believed to place women at greater risk than at other times. The biology of the vagina and cervix mean that women, especially adolescents and older women, are in general more vulnerable to HIV and sexually transmitted infections than men.
A 2015 study in monkeys concluded that immune protection is at its lowest mid-cycle, providing a window of opportunity for infections to enter. In addition, researchers following a group of 37 HIV-negative female sex workers in Nairobi, Kenya found an association between the first stage of the menstrual cycle and factors that could mean increased susceptibility to HIV infection. The authors concluded that a better understanding of the natural hormonal cycle on the vaginal immune environment is required to identify exactly how it influences HIV sexual transmission in women.
Since more research is needed to establish clarity on when women are most at risk, women should always consider using barrier methods such as male and female condoms to provide the best protection from STIs including HIV, regardless of the stage of their menstrual cycle.
Hiv Effects On The Digestive System
More than half of people who have AIDS report digestive symptoms as the virus or an opportunistic infection targets the walls of their intestines. Diarrhea is the most common one. Over time, the virus can change how your digestive tract works and even how it looks.
Liver
Some HIV medications can damage your liver. Many people with HIV also have a form of inflammation called hepatitis.
Limit how much alcohol you drink, and don’t use recreational drugs. Having diabetes, high cholesterol, or triglycerides and being overweight can lead to fatty liver disease, so keep an eye on the carbs, fats, and calories you eat each day.
Talk to your doctor about getting the hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines. Thereâs no vaccine against hepatitis C, but you should get tested for it.
Get regular blood tests to catch any liver problems early.
Mouth
Your mouth might be one of the first places where you notice signs of HIV. Things like dry mouth, fungal infections, gum disease, cold sores, and canker sores can make chewing or swallowing painful. If they go on too long, you might not be able to take your HIV medication or get the nutrients you need.
Good dental habits can help prevent these issues, so brush and floss regularly. See your dentist for checkups, and tell them if youâre having problems. Most mouth conditions tied to HIV are treatable.
Recommended Reading: Does Nba Youngboy Have An Std
Hiv Prevention And Treatment
If a person is HIV positive, there are treatment options to keep them healthy and prevent them from transmitting it. Thankfully, with proper treatment for HIV, people can live long, healthy lives by keeping their viral load under control in Stage 2.
HIV treatment drugs suppress a persons viral load or the number of HIV cells in the body. Doctors will monitor the cell count and when it falls an undetectable range, they are considered to be non-transmittable.
Scientific research has proven that a person cannot transmit HIV to another partner if their viral load is undetectable. This is commonly which stands for undetectable = untransmittable.
Of course, the best way to stop HIV transmission is to understand how to protect yourself and others from exposure. Using condoms and avoiding sharing needles is effective but taking PrEP can provide the greatest protection even if you are accidentally exposed.
PrEP is a medication prescribed by a doctor which can lower the risk of HIV transmission significantly. This drug stops HIV from being able to reproduce in the body. So, it can be taken before exposure and stop HIV transmission.
If a person has knowingly been exposed to HIV and is not currently on PrEP or has missed numerous doses, then they will be prescribed PEP. This is a medication regimen of HIV prevention drugs that must be administered with 72 hours of exposure. This can stop HIV from reproducing and diminish a persons viral load.
How Might I Become Infected With Hiv
HIV is transmitted from an HIV-positive person through infected body fluids such as semen, pre-ejaculate fluid, blood, vaginal secretions or breast milk. HIV can also be transmitted through needles contaminated with HIV-infected blood, including needles used for injecting drugs, tattooing or body piercing. HIV is most often transmitted sexually.
Recommended Reading: Does Aids Cause Hair Loss
How Flu Infiltrates Your Body
The flu virus typically enters your body through your nose via droplets from an infected person who sneezes or coughs near you. If a sick person is standing within six feet of you, theyre close enough to spread germs.
Once in your nose, the virus sets up residence, infecting the cells in your nasal passageways and airways. The virus enters a cell and replicates, making daughter viruses that then go and infect more cells nearby. This continues until more and more of your cells are infected.
Most people who get the flu feel sick for three to five days, but you can feel crummy for longer, Chu says. You can infect someone else a day before your symptoms appear and up to seven days after. Youre most contagious within the first three to four days after you notice symptoms.
Once inside your cells, the virus is able to remain undetected by your immune system, essentially hiding in plain sight for a little while, at least.
How Is Hiv Recognized

Doctors use laboratory tests to confirm HIV infection. The Elisa and Western Blot analyses identify people who have been exposed to HIV. These tests determine if the blood contains particular antibodies that result from contact with the virus. They do not identify who among a group of infected individuals will develop the disease. The presence of antibodies or HIV markers means the person has been infected with HIV but no one can predict when and if they will get AIDS related symptoms.
Doctors diagnose AIDS by blood tests and the presence of specific illnesses such as pneumocystis carinii pneumonia or Kaposi’s sarcoma. These diseases overcome the weakened immune system and are responsible for the high death rate among AIDS patients.
You May Like: Can You Get Aids Before Hiv
How A Weak Immune System Affects Your Skin
For some people with HIV, skin conditions are one of the most obvious signs of infection. Skin conditions can appear in the earliest stage of HIV, but may increase in frequency as the disease progresses.
HIV weakens your immune system, so your body is more likely to develop infection since it cant fight disease effectively. Common skin conditions that people with HIV experience include:
- Bacterial infections
- Inflammatory dermatitis
- Skin cancer
Inflammatory dermatitis can take many forms, and its common for people with HIV. Dermatitis can appear like areas of dry skin or red and itchy patches. Some examples of skin infections that people with HIV may contract include syphilis, oral thrush, and shingles.
Another condition that can develop if you have HIV is lipodystrophy. HIV can cause fat distribution in the body to change, resulting in fat loss around the face or fat buildup between the shoulder blades or elsewhere.
Taking antiretroviral medications for HIV generally helps reduce the number of skin conditions that people with HIV develop. Along with taking medication, getting regular skin exams and seeking treatment for specific skin conditions can help them from getting worse. For patients bothered by fat loss from HIV lipodystrophy, Sculptra® Aesthetic at Z-Roc Dermatology is an injectable filler to fill contours and improve your appearance.
Trust our team for all your skin care needs. Make an appointment at Z-Roc Dermatology online or call our office today.
Who Is At Risk For Hiv Infection
Anyone can get HIV, but certain groups have a higher risk of getting it:
- People who have another sexually transmitted disease . Having an STD can increase your risk of getting or spreading HIV.
- People who inject drugs with shared needles
- Gay and bisexual men, especially those who are Black/African American or Hispanic/Latino American
- People who engage in risky sexual behaviors, such as not using condoms
Read Also: Does Youngboy Really Have Herpes
Hiv Effects On The Circulatory System
Several things make your chances of heart-related problems go up. Because HIV affects your immune system, your body will be inflamed as it tries to fight the infection, like itâs on a constant simmer. This kind of inflammation has been linked to heart disease.
Some drugs you take for HIV can also make heart disease more likely. They can cause insulin resistance, which makes you more likely to get diabetes, and problems breaking down fats. Diabetes, in turn, raises your risk of heart disease. You might need medicines to control your blood sugar and cholesterol.
If you smoke, quit. Eat a variety of vegetables and fruits, plenty of whole grains, and foods with omega-3 fatty acids. Choose lean cuts of meat and low-fat dairy products. Exercise, like taking a brisk walk, for 20 to 30 minutes most days of the week.
If you’re carrying extra weight, losing as little as 5 or 10 pounds could make a big difference.
Does Contraception Increase Womens Risk Of Hiv
Observational research studies in the past had suggested a possible increased risk of HIV for women using progestogen-only injectable contraception, such as DMPA intra-muscular injection, also known as Depo-Provera. A recent large study with a more reliable methodology, conducted in four African countries, however found no significant difference in risk of HIV infection among women using hormonal or non-hormonal long-acting reversible contraceptive methods .
Read Also: Nba Youngboy Herpes Song
What Is Hiv And Aids
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus is a virus that infects the immune system. Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome . AIDS is the most advanced stage of the HIV infection and causes the immune system to become vulnerable to other infections. HIV can also be known as “the AIDS virus.”
The full name for AIDS describes several of the characteristics of the disease.
Acquired indicates that it is not an inherited condition.
Immune Deficiency indicates that the body’s immune system breaks down.
Syndrome indicates that the disease results in a variety of health problems.
It takes on average, 5-10 years for the initial HIV infection to progress to AIDS if not treated. While there is presently no cure or vaccine for HIV, with proper medical care, HIV can be managed and a near-normal lifespan can be expected with early treatment.
Effects On The Immune System
HIV primarily affects the body by targeting and damaging cells in the immune system. The immune system protects the body against viruses, bacteria, and fungi.
After attaching itself to a type of white blood cell called a CD4 T cell, the virus merges with it. These T cells are an important part of the immune system.
Once inside the CD4 T cell, the virus multiplies. It damages or destroys the cell, then moves on and targets other cells.
A persons CD4 T-cell count is an indication of the health of their immune system.
A healthy CD4 T-cell count is 5001,600 cells/mm3 of blood. If a person does not receive treatment for HIV, their CD4 T-cell count drops over time.
When it drops below 200 cells/mm3, the persons immune system is significantly impaired, making them more susceptible to opportunistic infections.
Don’t Miss: How Fast Does Hiv Spread
Do People Living With Hiv Have Other Health Conditions
Yes. Its common for people living with HIV to have other health issues.
Some of these issues may be directly related to HIV or its treatment. Others may be completely unrelated.
These health conditions can mean more doctors visits, lab tests, and medications to keep up with.
Taking HIV medication daily as prescribed, and staying in regular medical care is the best way for people living with HIV to stay healthy.
How Long Does It Take To Develop The Disease
There is no fixed period between the first contact with HIV and the development of the disease. Signs and symptoms resulting from infection with HIV develop in stages. Many infected individuals may have no symptoms for several years. But others may develop symptoms within three years from the time of infection.
Symptoms of HIV infection are fever, swollen lymph glands in the neck and armpits, sweating, aches, fatigue, unexplained weight loss and diarrhea.
Within eight years, about 50 percent of all infected people develop specific conditions categorized as AIDS. These conditions include a lung disease called “pneumocystis carinii pneumonia,” skin tumours called “Kaposi’s sarcoma,” fungal and viral infections such as candidiasis and herpes zoster, and severe diarrhea.
Some AIDS patients also suffer from dementia resulting in problems with memory and thinking. AIDS patients are prone to various infections of the brain, just as they suffer from an unusually high number of cancers, bacterial and viral infections of other parts of the body.
You May Like: Does Nba Youngboy Really Have Herpes