Hiv Effects On The Circulatory System
Several things make your chances of heart-related problems go up. Because HIV affects your immune system, your body will be inflamed as it tries to fight the infection, like itâs on a constant simmer. This kind of inflammation has been linked to heart disease.
Some drugs you take for HIV can also make heart disease more likely. They can cause insulin resistance, which makes you more likely to get diabetes, and problems breaking down fats. Diabetes, in turn, raises your risk of heart disease. You might need medicines to control your blood sugar and cholesterol.
If you smoke, quit. Eat a variety of vegetables and fruits, plenty of whole grains, and foods with omega-3 fatty acids. Choose lean cuts of meat and low-fat dairy products. Exercise, like taking a brisk walk, for 20 to 30 minutes most days of the week.
If you’re carrying extra weight, losing as little as 5 or 10 pounds could make a big difference.
Hiv Diagnosis And ‘window Period’
You wonât know if you have HIV right after youâre infected. It takes time for your body to make antibodies and for antigens to show up.
The âwindow periodâ is the time between when you might have been exposed to HIV and a test can tell for sure you have it. This varies from person to person and test to test. Your testing counselor can tell you more about the window period for the test youâre taking. Here are some general guidelines:
An antibody test can detect HIV 23 to 90 days after youâre exposed to the virus. The window for a test that uses blood from a vein is faster than one that uses oral fluid or blood from a finger stick.
An antigen/antibody test done in a lab on blood from a vein can detect HIV infection within 18 to 45 days. It takes longer if the testâs done with blood from a finger stick.
A nucleic acid test usually has the shortest window: 10 to 33 days. This test is not generally used to diagnose HIV infection unless you have symptoms and a history that suggest you were infected only a few days ago.
If you have a negative test and werenât exposed to the virus during the window period for that test, you can be certain you didnât have HIV when you were tested.
The CDC recommends that all adults have an HIV test at least once, even if theyâre not at risk. If your risk is higher — for example, you have multiple sex partners or use needles for drugs — you should be tested every year.
Stage : The Asymptomatic Stage
Once a person has been through the acute primary infection stage and seroconversion process, they can often start to feel better. In fact, HIV may not cause any other symptoms for up to 10 or even 15 years .
However, the virus will still be active, infecting new cells and making copies of itself. HIV can still be passed on during this stage. If left untreated, over time, HIV infection will cause severe damage to the immune system.
Read Also: Hiv Causes Hair Loss
How To Identify An Hiv Rash
This article was co-authored by Dale Prokupek, MD. Dale Prokupek, MD is a board-certified Internist and Gastroenterologist who runs a private practice based in Los Angeles, California. Dr. Prokupek is also a staff physician at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and an associate clinical professor of medicine at the Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles . Dr. Prokupek has over 30 years of medical experience and specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the liver, stomach, and colon, including chronic hepatitis C, colon cancer, hemorrhoids, anal condyloma, and digestive diseases related to chronic immune deficiency. He holds a BS in Zoology from the University of Wisconsin Madison and an MD from the Medical College of Wisconsin. He completed an internal medicine residency at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and a gastroenterology fellowship at the UCLA Geffen School of Medicine.There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 89% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 1,885,429 times.
Signs Of Hiv Infection In Children
HIV- infected children may develop a number of signs and symptoms as a result of their HIV infection. However, HIV-infected children may have many years when they have no major health problems and they look, grow and act as other children. After a while the HIV virus may cause certain symptoms. However, some of these signs may also occur in children who have no medical problems at all. Or they may occur in children with other immune system problems.
Some of the more common signs in HIV-infected children include:
- Infections that keep coming back, do not go away or are more severe than in other children
- Swollen glands in more than one area
- White patches in the mouth, on the tongue or in the throat that dont go away
- Repeated fevers
- Slower growth and development than other children the same age
- Diarrhea that continues for several weeks
- Repeated ear infections
- Certain kinds of tumors or cancers
Don’t Miss: Nba Youngboy Aids
Shaming Rarely Works To Shift Behavior
Stigmatizing language can also torpedo attempts at behavior change. We have to be more careful with the terminology in our public health messaging, noted Lynn. Because once someone feels bad about themselves, they are rarely going to be open to hearing anything else you have to say. Thus, trying to shame people into using condoms or wearing masks is rarely successful. Respectfully hearing them out and addressing their concerns is much more likely to persuade them to change.
In academia, language guides published by journals, as well as talks and workshops on the topic, have proliferated over the past five to seven years. Nonetheless, theres a lot more work to be done in this area, said Lynn. I think it would be great if all university departments had a meeting about the terminology used within their discipline. But first, said Lynn, you need to be aware of it. Nobody is going to change anything until they are aware of what they are doing. Next, she suggests, ask, What can we do to change this? Then continue having conversations about inclusive languagechange will take time, but it can happen.
Trying to shame people into certain behaviors, such as getting tested for HIV, seeking mental health care, or getting vaccinated against COVID-19, simply doesnt work. Once you make someone feel bad about who they are or their decisions, they are not going to be open to hearing anymore, said Lynn. Then you are really just talking to the wall. People shut down.
Stages Of The Hiv Lifecycle
Binding and fusion
HIV attaches to a T-helper cell. It then fuses to it and releases its genetic information into the cell.
The types of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called fusion or entry inhibitor drugs because they stop HIV from entering the cell.
Reverse transcription and integration
Once inside the T-helper cell, HIV converts its genetic material into HIV DNA, a process called reverse transcription. The new HIV DNA then enters the nucleus of the host cell and takes control of it.
The types of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called NRTIs , NNRTIs and integrase inhibitor drugs.
Transcription and translation
The infected T-helper cell then produces HIV proteins that are used to produce more HIV particles inside the cell.
Assembly, budding and maturation
The new HIV is put together and then released from the T-helper cell into the bloodstream to infect other cells and so the process begins again.
The type of drugs that stop this stage of the lifecycle are called protease inhibitor drugs.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can Aids Be Dormant
Can Hiv Be Prevented Or Avoided
The best way to prevent HIV is to not have sex with a person who has HIV, or share a needle with a person who has HIV. However, there is also a medicine called PrEP that people can take before coming into contact with HIV that can prevent them from getting an HIV infection.
PrEP stands for pre-exposure prophylaxis. It is for people who are at long-term risk of getting HIV either through sexual activity or by injecting drugs. If youre taking PrEP and come into contact with HIV, the medicine makes it difficult for HIV to develop inside your body.
Other ways to prevent HIV include:
- When you have sex, practice safer sex by using a condom. The best condom is a male latex condom. A female condom is not as effective but does offer some protection.
- Do not share needles and syringes.
- Never let someone elses blood, semen, urine, vaginal fluid, or feces get into your anus, vagina, or mouth.
Stage : Acute Primary Infection
The early symptoms of HIV can feel like having the flu. Around one to four weeks after getting HIV, you may start to experience these flu-like symptoms. These normally dont last long . You may only get some of the symptoms and some people dont have any symptoms at all.
Symptoms can include:
- joint aches and pains
- muscle pain.
These symptoms happen because your body is reacting to the HIV virus. Cells that are infected with HIV are circulating throughout your blood system. In response, your immune system tries to attack the virus by producing HIV antibodies this process is called seroconversion. Timing varies but once you have HIV it can take your body up to a few months to go through the seroconversion process.
Having these symptoms alone does not mean you definitely have HIV. The only way to know if you have HIV is by taking a test. You should always visit your healthcare professional if youre worried about or think youve been at risk of getting HIV, even if you feel well and dont have any symptoms. They can then arrange for you to get tested.
HIV will not always show up in a test at this early stage, and you may need to test again later to confirm your result . Your healthcare professional will talk to you about the timing of your test and answer any concerns. Its important not delay speaking to a healthcare worker if you are worried about HIV.
Also Check: Nba Youngboy Std
Why Do Scientists Look At Recent Samples Of Hiv To Determine The Virus’ Overall Age Wouldn’t It Be Better To Use Older Samples That Haven’t Had As Much Time To Mutate
It would, but scientists don’t have that luxury. Other than the 1959 sample, there are very few preserved specimens of HIV-infected tissue that predate the early ’80s, when the virus was first recognized by health authorities. Researchers still hope there are forgotten samples in African freezers. “There has to be some serum or plasma somewhere, and given modern technology we could fish out the virus,” says Dr. David Ho, director of the Aaron Diamond AIDS Research Center and one of the world’s leading authorities on HIV.
But even if those samples are found someday, they won’t necessarily yield definite answers about the virus’ age, says Korber: “Often, you can’t get anything out of samples like that.” Most African samples are made of blood serum, and serum samples contain viral RNA, which degrades much faster than the DNA found in tissue samples. In fact, says Ho, the 1959 sample, which was sequenced by his laboratory, was kept in a freezer but still didn’t survive the ravages of time. “It was completely dried up,” he says. “We were only able to get small pieces , and we had to stitch them together.”
Activism By Aids Patients And Families
In New York City, Nathan Fain, Larry Kramer, Larry Mass, Paul Popham, Paul Rapoport, and Edmund White officially established the Gay Men’s Health Crisis in 1982.
Also in 1982, Michael Callen and Richard Berkowitz published How to Have Sex in an Epidemic: One Approach. In this short work, they described ways gay men could be sexual and affectionate while dramatically reducing the risk of contracting or spreading HIV. Both authors were themselves gay men living with AIDS. This booklet was one of the first times men were advised to use condoms when having sexual relations with other men.
At the beginning of the AIDS epidemic in the 1980s, there was very little information about the disease. Also, because AIDS affected stigmatized groups, such as LGBTQ, people of low socioeconomic status, there wasn’t much mass media coverage initially when the epidemic started. However, with the rise of activist groups composed of people suffering from AIDS, either directly or through a loved one, more public attention was brought to the epidemic.
Also Check: How Long Does Hiv Stay Dormant
Are There Other Theories About How The Virus Could Have Gotten Into Humans
There are several competing theories, ranging from implausible conspiracies to arguments grounded in extensive research. The best-known of the latter, the “OPV/AIDS” theory, was exhaustively detailed in the 1999 book The River, by author Edward Hooper. As many as a million Africans were given oral polio vaccines between 1957 and 1960. Hooper says witnesses have told him that a few batches of those vaccines were “grown” in chimp cells at a lab in Kisangani, a city in the Democratic Republic of the Congo — and that the chimp cells, and thus the vaccines, could have contained SIVs that jumped into humans. “There are highly significant correlations between the places where this vaccine was administered and the places where ⦠AIDS first appeared on the planet four to 20 years later,” Hooper says.
The majority of HIV researchers subscribe to the bushmeat theory and raise several arguments against the OPV theory. Hahn’s recent research confirming that HIV-1 M and N arose from Pan troglodytes troglodytes chimps in Cameroon presents one problem: The Kisangani lab is in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and it’s home to a different subspecies of chimp than the one that was the source of HIV-1 M and N. However, it is possible that the chimps used in the Kisangani experiments were not from the area. In the spring of 2006, Hooper found a paper indicating that at least one of eight chimps at the Kisangani lab was a Pan troglodytes troglodytes.
Hiv Treatment Side Effects
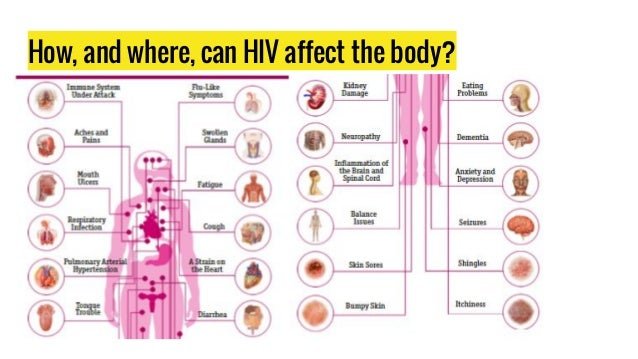
Like all drugs, ART can cause side effects. These vary, depending on the person and type of treatment. Even people taking the same HIV drugs can have different side effects. The most common are:
A hypersensitivity reaction to an HIV drug called abacavir which consists of liver damage or severe skin rashes, can be life-threatening. Call your doctor or get emergency care right away if you think you have a severe reaction to this or any medication you take. Before you start any drug, make sure your doctor explains what side effects to watch out for.
Treatment as prevention: The best way to stay healthy and protect others is to start and stick with treatment. When your viral load is undetectable, you will keep yourself healthy, and thereâs no chance you can pass the virus to your sexual partner.
Also Check: Hiv Screen 4th Generation Wrfx Reactive
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine every day, exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can protect your health and have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to your sexual partner.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Its important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
How Is Hiv Treated
Treatments for HIV typically involve antiretroviral therapy. This isnt a specific regimen, but instead a combination of three or four drugs. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has currently approved nearly 50 different medications to treat HIV.
Antiretroviral therapy works to prevent the virus from copying itself. This maintains immunity levels while slowing the progression of HIV.
Before prescribing medication, a healthcare provider will take the following factors into consideration:
- a persons health history
- the levels of the virus in the blood
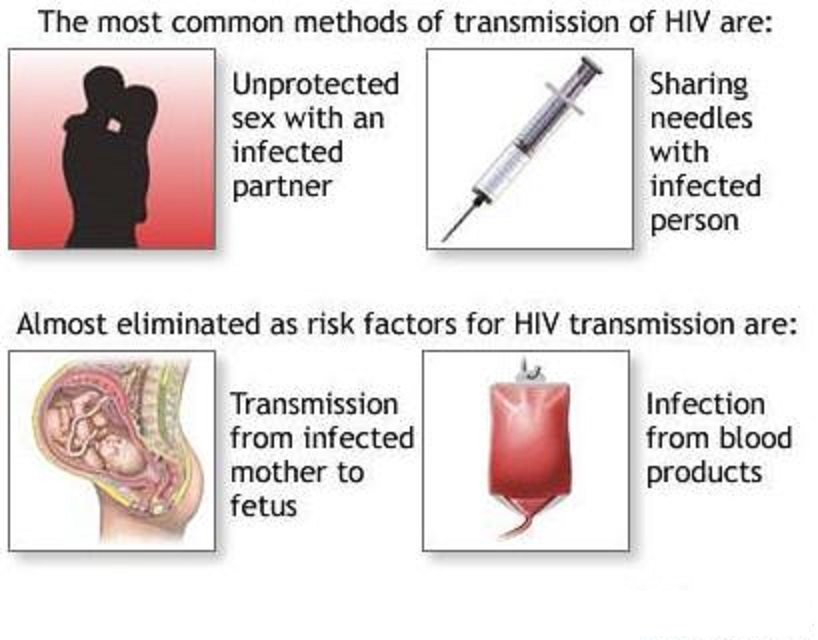
HIV doesnt cause a lot of outward or noticeable symptoms until the disease has progressed. For this reason, its important to understand how HIV is transmitted and the ways to prevent transmission.
HIV can be transmitted by:
- having sex, including oral, vaginal, and anal sex
- sharing needles, including tattoo needles, needles used for body piercing, and needles used for injecting drugs
- coming into contact with body fluids, such as semen, vaginal fluid, blood, and breast milk
HIV is not transmitted by:
- breathing the same air as a person living with HIV
- getting bitten by a mosquito or other biting insect
- hugging, holding hands with, kissing, or touching a person living with HIV
- touching a door handle or toilet seat thats been used by an HIV-positive person
Keeping this in mind, some of the ways a person can prevent HIV include:
Symptoms can take years to appear, which is why its so important to get tested regularly.
You May Like: Do Nba Youngboy Got Herpes
Can Hiv Pass From Mothers To Their Babies
Infection can pass from pregnant women living with HIV to their babies in the womb and during birth. Taking HIV medications during pregnancy and childbirth dramatically lowers the risk of a baby becoming infected with HIV.
After birth, transmission can occur through breast milk. The highest risk may be in the early months after birth. It is recommended that new mothers who are living with HIV formula-feed their babies rather than breast-feed.
If you are a woman living with HIV and you intend to become pregnant, or you find out that you have during your pregnancy, talk to your provider immediately about ways to minimize the chances that your baby will become infected, too.
Recommended Reading: How Does Hiv Affect The Body