Laboratory Hiv Testing Algorithm As Recommended By Cdc/aphl
The CDC and APHL HIV testing algorithm, which was initially published in 2014 and then updated in 2018, allows for more accurate diagnosis of acute HIV-1, more accurate diagnosis of HIV-2, fewer indeterminate results , and faster turnaround time than previous approaches . Because no single test is capable of detecting HIV immediately following infection, some patients with very early HIV infection will escape detection with this test algorithm.
How Can You Prevent Hiv
HIV can be spread by people who don’t know they are infected. To protect yourself and others:
- Practice safe sex. Use a condom every time you have sex until you are sure you and your partner are not infected with HIV.
- Don’t have more than one sex partner at a time. The safest sex is with one partner who has sex only with you.
- Talk to your partner before you have sex the first time. Find out if he or she is at risk for HIV.
- Get tested together and retested 6 months later. Use condoms in the meantime.
- Don’t drink a lot of alcohol or use illegal drugs before sex. You might let down your guard and not practice safe sex.
- Don’t share personal items, such as toothbrushes or razors.
- Never share needles or syringes with anyone.
Sonora Quest Laboratories is committed to the fight against HIV and AIDS, supporting various programs and fund-raising events through The Apothecary Shops, Aunt Ritas Foundation, the Southern Arizona AIDS Foundation, and the Southwest Center for HIV/AIDS. Our expansive HIV test offerings allow us to assist doctors and patients in all stages of the disease.
To learn more about HIV/AIDS, talk with your doctor, go to your local health department, or visit:
How Is Hiv Diagnosed
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved tests that detect HIV antibodies in urine, fluid from the mouth , or blood. If a test on urine or oral fluid shows that you are infected with HIV, you will probably need a blood test to confirm the results. If you have been exposed to HIV, your immune system will make antibodies to try to destroy the virus. Blood tests can find these antibodies in your blood.
Most doctors use a screening blood test. If the screening is positive , the blood sample is tested again to verify the result. If the second test is positive, a test called a Western blot is performed for further confirmation.
It may take as long as six months for HIV antibodies to show up in a blood sample. If you think you have been exposed to HIV but you test negative for it:
- Get tested again in six months to be sure you are not infected.
- Meanwhile, take steps to prevent the spread of the virus. If you are infected, you can still pass HIV to another person at this time.
Some people are afraid to be tested for HIV. But if there is any chance you could be infected, it is very important to find out. HIV can be treated. Getting early treatment can slow down the virus and help you stay healthy. And you need to know if you are infected so you can prevent spreading the infection to other people.
You May Like: Does Nba Youngboy Have Herpes
The Complete Blood Count
The most common laboratory test is the complete blood count . It examines the components of blood, including red and white blood cells and platelets. Most test results are reported as amounts in a sample of blood or as a percentage. Other laboratory tests are discussed in Fact Sheet 122 and Fact Sheet 123.
All blood cells are made in the bone marrow, the center of large bones. Some medications or diseases can damage the bone marrow. This can reduce the numbers of different types of red or white blood cells.
Every laboratory has its own “reference range” or normal values for the results of each test. Most lab reports show the normal range and highlight any test results outside the normal range.
For more information on laboratory test results, see Fact Sheet 120 or Lab Tests online at
Protecting Your Newborn Child

HIV positive women must avoid breastfeeding their infants. CDC recommends that HIV positive women refrain from breastfeeding to avoid postnatal transmission of HIV to their infants through breast milk. HIV positive mothers should also make sure they offered, accept and adhere to anti-retroviral therapy for the infant from birth until the infants HIV status is confirmed negative.
Read Also: Cookie Johnson Hiv
Quick Answers For Clinicians
The length of time after exposure before HIV infection can be detected depends on the type of test used. Nucleic acid amplification testing can identify HIV 10-33 days after infection. Fourth generation antigen/antibody tests can detect HIV 18-45 days after infection. Antibody-only tests require additional time to yield reliable results because the patient must mount an immune response to the HIV infection before antibodies can be detected. NAAT is not generally recommended for initial screening in asymptomatic patients. However, NAAT is recommended in certain cases, such as in patients who present with symptoms of HIV infection with known recent exposure, in infants born to individuals with HIV, and for monitoring of disease .
If a rapid test result is negative in a patient with a possible exposure, testing should be repeated after the window period to confirm the negative result. In general, repeat testing should be considered in high-risk patients if clinically indicated.
The use of preexposure prophylaxis can reduce the accuracy of diagnostic tests, including antibody testing, antigen testing, and nucleic acid amplification testing .
Other Factors Influencing Hiv Transmission Risk
Within each route of transmission, estimates of the risk of transmission vary widely, likely due to the role of behavioural and biological co-factors. Viral load appears to be an important predictor of transmission, regardless of route of transmission. However, the evidence indicates that viral load is not the only determinant, and other co-factors, such as the presence of co-infections, play a role in increasing or decreasing the risk of transmission.
Viral Load
The strongest predictor of sexual transmission of HIV is plasma viral load . A dose-response relationship has been observed, where each ten-fold increase in plasma VL resulted in an increased relative risk of transmission of 2.5 to 2.9 per sexual contact. The concentration of HIV in genital secretions also plays a major role in sexual transmission. While there is a strong correlation between HIV concentrations in plasma and in genital secretions, some studies have found genital tract HIV shedding in 20% to 30% of men and women without detectable plasma viral load. Much of what is known about the impact of viral load on the sexual transmission of HIV is derived from studies of heterosexual populations. Very little is known about the relationship between HIV viral load and rate of transmission through anal intercourse.
Co-infections
Circumcision
Also Check: Does Cookie Johnson Have Hiv Aids
What Is Hiv Testing
HIV testing, also called HIV screening, is the only way to know if you have the virus.
Several types of tests check your blood or other body fluids to see whether you’re infected. Most can’t spot HIV right away, because it takes time for your body to make antibodies or for enough of the virus to grow inside you.
How Soon After Exposure To Hiv Can Tests Detect I Have The Virus
The window of time between exposure to HIV and when a test will show you have the virus varies from person to person and by the type of test:
- Nucleic acid test : The NAT test can detect HIV infection the earliest. It can tell if you have HIV infection 10 to 33 days after exposure.
- Antigen/antibody test: The antigen/antibody test can detect infection 18 to 45 days after exposure when performed by a lab using blood from a vein. If the sample is from a finger prick, the window is 18 to 90 days after exposure.
- Antibody test: Antibody tests can detect infection 23 to 90 days after exposure.
If your initial test is negative, get a second test after the window of time has passed. The second test can confirm your negative result in case you got tested before the infection was active in your body.
Remember, post-exposure prophylaxis can help prevent infection, but you must start it within 72 hours of possible infection. Talk to your healthcare provider about how to start PEP.
Read Also: Hiv Stays Alive In Dried Blood
Staining And Examination Using A Microscope
Doctors sometimes can identify a microorganism simply by looking at it under a microscope.
Most samples are treated with stains. Stains are special dyes that color the microorganisms, causing them to stand out from the background. Some microorganisms have a distinctive size, shape, and stained color that enable doctors to recognize them.
However, many microorganisms look alike and cannot be distinguished using a microscope. Also, there must be enough of them, and they must be large enough to be seen with a microscope. For example, viruses cannot be identified using a microscope because they are too small.
For bacteria, doctors often first use Gram stain . Bacteria are classified as follows:
-
Gram-positive
-
Gram-negative
Doctors can make some treatment decisions based on whether bacteria are gram-positive or gram-negative.
In addition to Gram stain, other stains can be used depending on the microorganisms thought to be present.
Why It Is Done
A test for the human immunodeficiency virus is done to:
- Detect an HIV infection.
- Screen blood, blood products, and organ donors to prevent the spread of HIV.
- Screen pregnant women for HIV infection. Pregnant women who are infected with HIV and receive treatment are less likely to pass the infection on to their babies than are women who do not receive treatment.
- Find out if a baby born to an HIV-positive woman also is infected with HIV. A PCR test is often done in this case because the baby may get antibodies against HIV from the mother and yet not be infected.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend HIV screening as part of routine blood testing.
- As part of regular medical care for people 15 to 65 years old.
- For all pregnant women.
- For people younger than 15 and older than 65 if they have a high risk for HIV, such as for people who engage in high-risk behavior.
You and your doctor can decide if testing is right for you.
This test is not done to determine if a person has AIDS. A diagnosis of AIDS means a person is HIV-positive and other problems are present.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have Hiv
Diagnosis Of Specific Infections
Patients presenting with cervicitis, vulvovaginitis, urethritis, pharyngitis or proctitis
Chlamydia trachomatis
- NAATs and, to a lesser extent, culture and serology are used for diagnostic purposes.
- Culture is the preferred method for medico-legal purposes.
- NAATs may provide valuable adjunctive testing. For such purposes, positive NAAT findings should be confirmed.Footnote 2Footnote 14
- Consult with your local laboratory regarding the availability of such testing and refer to the Medico-legal considerations section for information on confirming positive NAAT test results.
NAAT
- Cervical swabs can also be submitted.
What Happens If The Test Is Positive
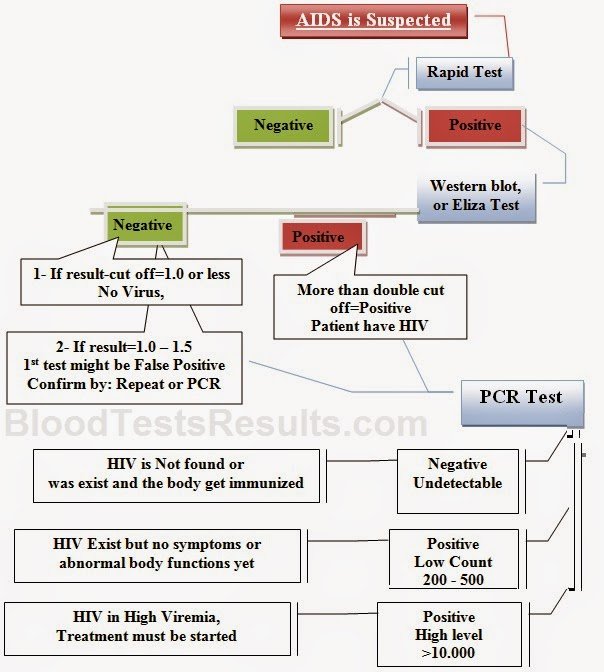
If you receive a positive result, you will want to work with your healthcare provider on a treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will determine how far HIV has progressed and recommend medicines to help you manage it.
You will also want to talk about your diagnosis with your sexual partner. If you and your partner have had unprotected sex, you could have transmitted the virus to them. They should get tested, too.
You May Like: Does Cookie Johnson Have Hiv
Lab Tests And Why They Are Important
As part of your HIV care, your provider will order several laboratory tests. The results of these lab tests, along with your physical exam and other information you provide, will help you and your provider work together to develop the best plan to manage your HIV care so that you can get the virus under control, protect your health, and reduce the chance that you will pass the virus to others.
Your healthcare provider will repeat some of these tests as part of your ongoing HIV care to continue to assess your health and how well your HIV treatment is working.
The lab tests may include:
- CD4 Percentage: This measures how many of your white blood cells are actually CD4 cells. This measurement is more stable than CD4 counts over a long period of time, but, for most people, the CD4 count remains a more reliable measure of how well your immune system is working than the CD4 percentage.Why its important: This measurement is less likely to vary in between blood tests than CD4 counts .
- Complete Blood Count : This is a measure of the concentration of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in a sample of your blood.Why its important: A CBC is one of the most commonly ordered blood tests. It can reveal infections, anemia , and other medical issues.
Topics
Appendix A: Ethical And Professional Considerations
Policy concerning the ethical and professional roles and responsibilities of care providers is informed by the providers’ respective institutional code of ethics as well as the professional colleges under which they are governed.
The following is designed to complement, not supersede, existing codes of conduct or jurisdictional health policies and regulations or any applicable laws and regulations of the jurisdiction.
You May Like: Does Nba Youngboy Have Hiv
How Is Hiv Treated
The standard treatment for HIV is a combination of medicines called Highly Active Anti-Retroviral Therapy . Anti-retroviral medicines slow the rate at which the virus multiplies. Taking these medicines can reduce the amount of virus in your body and help you stay healthy.
It may not be easy to decide the best time to start treatment. There are pros and cons to taking HAART before you have symptoms. Discuss these with your doctor so you understand your choices.
First, to determine the best treatment regimen, your doctor may order an HIV Genotype test. Next, to monitor the HIV infection and its effect on your immune system, or to check on your response to therapy, a doctor may order these tests:
- Viral Load, which shows the amount of virus in your blood.
- CD4+ Cell Count, which shows you how well your immune system is working.
If you have no symptoms and your CD4+ cell count is at a healthy level, you may not need treatment yet. Your doctor will repeat the tests on a regular basis to see how you are doing. If you have symptoms, you should consider starting treatment, whatever your CD4+ count is.
After you start treatment, it is important to take your medicines exactly as directed by your doctor. When treatment doesn’t work, it is often because HIV has become resistant to the medicine. This can happen if you don’t take your medicines correctly. Ask your doctor if you have questions about your treatment.
To stay as healthy as possible during treatment:
Diagnosis Of Infectious Disease
, MD, FACP, Wellington Regional Medical Center
Infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms Types of Infectious Organisms Microorganisms are tiny living creatures, such as bacteria and viruses. Microorganisms are present everywhere. Despite their overwhelming abundance, relatively few of the thousands of species… read more , such as bacteria Overview of Bacteria Bacteria are microscopic, single-celled organisms. They are among the earliest known life forms on earth. There are thousands of different kinds of bacteria, and they live in every conceivable… read more , viruses Overview of Viral Infections A virus is composed of nucleic acid, either DNA or RNA, surrounded by a protein coat. It requires a living cell in which to multiply. A viral infection can lead to a spectrum of symptoms from… read more , fungi Overview of Fungal Infections Fungi are neither plants nor animals. They were once thought to be plants but are now classified as their own kingdom. Some fungi cause infections in people. Because fungal spores are often… read more , and parasites Overview of Parasitic Infections A parasite is an organism that lives on or inside another organism and benefits from the host at the host’s expense. Although this definition actually… read more .
Many different types of laboratory tests can identify microorganisms. Laboratory tests use a sample of blood, urine, sputum, or other fluid or tissue from the body. This sample may be
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Hiv Live On Surfaces
Whats The Hiv Window Period
As soon as someone contracts HIV, it starts to reproduce in their body. The persons immune system reacts to the antigens by producing antibodies .
The time between exposure to HIV and when it becomes detectable in the blood is called the HIV window period. Most people develop detectable HIV antibodies within 23 to 90 days after transmission.
If a person takes an HIV test during the window period, its likely theyll receive a negative result. However, they can still transmit the virus to others during this time.
If someone thinks they may have been exposed to HIV but tested negative during this time, they should repeat the test in a few months to confirm . And during that time, they need to use condoms or other barrier methods to prevent possibly spreading HIV.
Someone who tests negative during the window might benefit from post-exposure prophylaxis . This is medication taken after an exposure to prevent getting HIV.
PEP needs to be taken as soon as possible after the exposure it should be taken no later than 72 hours after exposure but ideally before then.
Another way to prevent getting HIV is pre-exposure prophylaxis . A combination of HIV drugs taken before potential exposure to HIV, PrEP can lower the risk of contracting or transmitting HIV when taken consistently.
Timing is important when testing for HIV.