How To Prevent Hiv From Progressing
The most effective way is to take antiretroviral medication as soon as possible and to do so consistently as prescribed.
Antiretroviral therapy keeps the immune system healthy and reduces the risk of transmitting the virus to virtually zero.
The sooner a person receives a diagnosis, the sooner they can begin treatment. Early treatment can improve the persons outlook and lower the risk of the virus passing on to others.
Howcan I Test For Hiv
It is entirely yourchoice whether you test for HIV on its own, or as part of a screen in combination with othersexually transmitted infections . Testing for several STIs provides amore complete view of your current sexual health.
Better2Know providesvarious HIV tests which can be taken at different times, depending on how longhas passed after your last incident of concern.
Our HIV testingoptions include:
- 28-Day HIV DUO Test this test is extremelyaccurate at 28 days and is recommended by the UKs HIV testing guidelines.
- 28-Day 5th Generation HIVTest thisadvanced test distinguishes between the three markers of HIV and will tell you which you have tested positive for.
- 10-Day HIV RNA PCR Test this test can be taken 10days after an incident of concern, providing the earliest possible indicationof an HIV infection.
- Instant HIV Test available at 26 days, thistest will provide results within 20 minutes at your appointment.
You may decide to testfor HIV as part of a Better2Know screen, in combination with other STIs.Testing for several infections, our screens are designed to provide total peaceof mind surrounding your sexual health.
Our HIV screeningoptions include:
First Stage: Acute Hiv Infection Symptoms
Most people don’t know right away when they’ve been infected with HIV. But they may have symptoms within 2 to 6 weeks after theyâve gotten the virus. This is when your body’s immune system puts up a fight. It’s called acute retroviral syndrome or primary HIV infection.
The symptoms are similar to those of other viral illnesses, and they’re often compared to the flu. They typically last a week or two and then go away. Early signs of HIV include:
- Ulcers in your mouth, esophagus, anus, or genitals
- Headache and other neurological symptoms
If you have symptoms like these and might have come into contact with someone with HIV in the past 2 to 6 weeks, go to a doctor and ask that you get an HIV test. If you donât have symptoms but still think you might have come into contact with the virus, get tested.
Early testing is important for two reasons. First, at this stage, levels of HIV in your blood and bodily fluids are very high. This makes it especially contagious. Second, starting treatment as soon as possible might help boost your immune system and ease your symptoms.
A combination of medications can help fight HIV, keep your immune system healthy, and keep you from spreading the virus. If you take these medications and have healthy habits, your HIV infection probably wonât get worse.
You May Like: How Do They Check For Hiv
The Progression To Aids
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus is the virus that causes the Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome . TYou can have HIV without having AIDS, but you can’t have AIDS without also having HIV. Many people live their entire lives with HIV and don’t get AIDS. This is because we have exceptional treatments, known as antiretroviral therapy or ART, that prolongs both the quantity and quality of life. HIV medicines help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives. HIV medicines also reduce the risk of HIV transmission . Unfortunately, many people with HIV are either diagnosed late in their disease or do not access the lifesaving treatments that are currently available.
- The Human Immunodeficiency Virus is the virus that causes the Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome .
- This is because we have exceptional treatments, known as antiretroviral therapy or ART, that prolongs both the quantity and quality of life.
The 7 Stages Of The Hiv Life Cycle Explained
#1 BindingThis is the very first stage of the HIV Lifecycle. The HIV virus attacks the CD4 cell and attaches Itself to the cell on its surface. It does this by first attaching to the CD4 cells receptor than the CCR5 or the CXCR4 coreceptor.
#2 FusionThe second stage of the HIV life cycle is called fusion and this is done after the virus has effectively attached itself to the CD4 cell. The entire HIV viral envelope will then fuse with the cell which allows it to gain entry into it.
#3 Reverse TranscriptaseThe third stage happens once the HIV virus has entered the CD4 cell. This allows the virus to release an HIV Enzyme or reverse transcriptase enabling it to convert the viruss genetic makeup. It converts its HIV RNA to HIV DNA. This conversion is what allows the HIV Virus to enter the cells nucleus to integrate with it.
#4 IntegrationWhen the HIV virus has successfully entered the CD4 cells nucleus it releases another HIV enzyme known as integrase. This is the enzyme the virus uses to integrate its own DNA into the infected CD4 cells DNA. This is the fourth step in the HIV virus life cycle.
#5 ReplicationThe fifth stage of the HIV life cycle is when the virus starts to form HIV proteins in long chains. `These are the protein chains that the HIV virus uses to replicate itself and spread to other CD4 cells in the body.
You May Like: Do You Have Hiv Forever
Treating Stds And Hiv
Its important to get tested if you think youve been exposed to any STD or to HIV. Getting proper treatment can reduce your risk of serious complications and the chance of spreading it to others. Although the treatments for STDs and HIV are different, theres some overlap.
Treating an STD can help to slow the spread of HIV in your body. But STD treatments wont prevent or stop HIV. Similarly, the antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV wont prevent or cure STDs.
The treatments youll need for an STD depend on which one you have.
STDs caused by bacteria like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis are treated with antibiotics. STDs caused by viruses like human papilloma virus , hepatitis B, and herpes cant be cured, but treatments can reduce your symptoms and your risk of passing them on to others.
HIV is also caused by a virus and cant be cured. But treatments can stop HIV from progressing to AIDS and can greatly reduce the risk of passing the virus on to sexual partners.
In fact, people who take antiretroviral drugs as directed and have an undetectable amount of HIV in their blood effectively have no risk of transmitting the virus to sexual partners.
Viral STDs or HIV cant be cured, but many people living with them still lead full and active lives. When treated, these conditions dont cause symptoms and dont continue to damage your body. The virus will continue to live in your body, but the treatments will keep it from harming you.
Stage Of Progression To Aids Aids Symptoms
As mentioned above, if the infected person is not taking antiretroviral therapy , he or she develops AIDS within about ten years of getting infected, after which the average survival time is 2 to 3 years.
ART will slow down this progression to AIDS for decades. As mentioned above during the clinical latency stage, the AIDS virus and the immune system of the body are in balance and there are hardly any symptoms.
In the stage of AIDS, the AIDS virus has damaged the immune system making the person very vulnerable to infections.
AIDS is said to have developed when the blood count of the CD4 cells of the immune system falls below 200 per micro liter of blood. The normal CD4 count is 500 to 1200 per micro liter of blood or per mm3
The invading microorganisms take the opportunity of the weakened immune system of the infected person and start invading the body.
These infections are, therefore, called opportunistic infections. These infections would normally never bother a person with a healthy immune system.
There are 26 conditions that can occur in a person who has progressed to AIDS and which can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Almost every organ in the body is affected.
People with AIDS have a high risk of developing viral induced cancers which include Kaposis sarcoma, Burkitts lymphoma, primary central nervous system lymphoma, and cervical cancer.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hiv Aids
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine every day, exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can protect your health and have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to your sexual partner.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Its important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
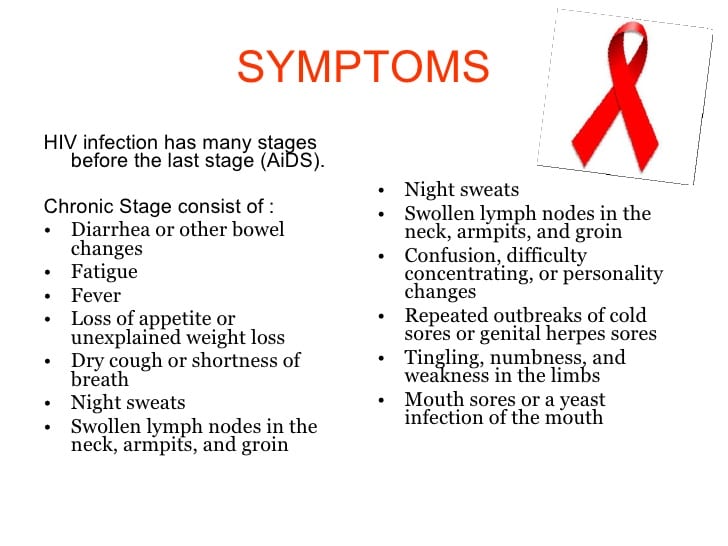
Individual Symptoms Of Hiv Vary From One Person To Another If You Have An Active Sex Life Or Think You May Have Been Exposed To Hiv It Is Important To Get Tested Here Are Some Common Symptoms Of Hiv Many People Experience Severe Flu
This article is also available in Simplified Chinese and Thai.
Symptoms of HIV can vary between individuals however the first signs of infection generally appear within the first 1-2 months. Many, but not all, people will experience severe flu-like symptoms which is your bodys natural response to the virus. This is called the seroconversion period.
Its during this time that its crucial to identify if HIV is the cause, as your viral load is very high which greatly increases the risk of passing it on. And the only way to know for sure is by getting tested.
You May Like: How Is Hiv Test Done
Risks Of Contracting Hiv And Stds
Just as HIV and STDs are spread in the same ways, they can also share some of the same risk factors. A risk factor is anything that makes you more likely to contract a condition or disease.
For HIV and some STDs, risk factors include:
- having unprotected sex of any kind
- sharing injection needles
- sharing tattoo or piercing needles
- having sexual encounters under the influence of drugs or alcohol
The risks of contracting HIV or an STD are also higher among some populations and groups. This can be due to a variety of factors, like:
- lack of access to healthcare
- discrimination faced in accessing healthcare
- population size
47 percent of primary and secondary syphilis were among men who have sex with men. But STDs are common among all Americans. Its important for anyone of any gender or sexuality who has one or more risk factors to get tested and treated.
Lack Of Symptoms In Early Stages
ARS is common once a person has HIV. Still, this isnt the case for everyone. Some people have HIV for years before they know they have it. According to HIV.gov, symptoms of HIV may not appear for a decade or longer. This doesnt mean that cases of HIV without symptoms are less serious. Also, a person who doesnt experience symptoms could still transmit HIV to others.
Symptoms in early HIV tend to appear if the rate of cell destruction is high. Not having symptoms can mean that not as many CD4 cells, a type of white blood cell, are killed early on in the disease. Even though a person has no symptoms, they still have the virus. Thats why regular HIV testing is critical to prevent transmission. Its also important to understand the difference between a CD4 count and a viral load.
Read Also: Does Magic Johnson Still Have Hiv
How Does Chronic Hiv Affect The Body
The chronic HIV stage is known as the latent or asymptomatic stage. During this stage, a person usually wont have as many symptoms as they did during the acute phase. This is because the virus doesnt multiply as quickly.
However, a person can still transmit HIV if the virus is left untreated and they continue to have a detectable viral load. Without treatment, the chronic HIV stage can last for many years before advancing to AIDS.
Advances in antiretroviral treatments have significantly improved the outlook for people living with HIV. With proper treatment, many people who are HIV-positive are able to achieve viral suppression and live long, healthy lives. Learn more about HIV and life expectancy.
A normal CD4 count ranges from approximately 500 to 1,600 cells per cubic millimeter of blood in healthy adults, according to HIV.gov.
A person receives an AIDS diagnosis when they have a CD4 count of fewer than 200 cells/mm3.
A person may also receive an AIDS diagnosis if theyve had an opportunistic infection or another AIDS-defining condition.
People with AIDS are vulnerable to opportunistic infections and common infections that may include tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, and pneumonia.
People with weakened immune systems are also more susceptible to certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma and cervical cancer.
The survival rate for people with AIDS varies depending on treatment and other factors.
The Cdc And Who Staging Criteria
Now as far as the staging is concerned, we have two authorities who stage the infection using different guidelines.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention classifies the severity of the disease according to the CD4 count. CD4 are cells of the bodys immune system and play a critical role in defending the body against diseases.
These cells are neutralized by the HIV virus and their count goes on falling as the disease progresses.
This classification is rarely used in routine clinical management but is used more in clinical and epidemiological research.
In contrast, the World Health Organization classifies HIV disease on the basis of clinical manifestations
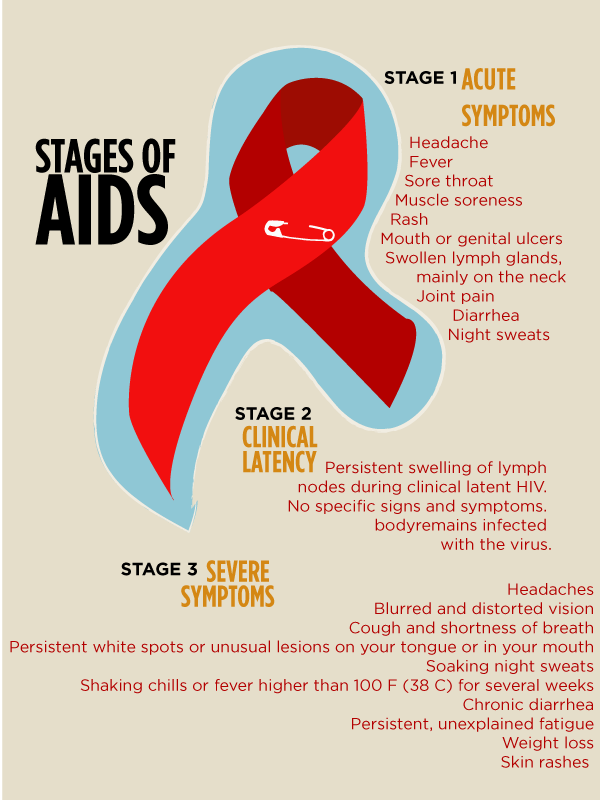
The three clinical stages of HIV are:
- Acute infection stage
- AIDS: Stage when AIDS sets in
Also Check: Can Dried Blood Transmit Hiv
Who Needs Hiv Testing
The CDC advises that routine HIV testing should be provided in all healthcare settings, especially if testing for other sexually transmitted infections at the same time.
People engaging in behaviors that puts them at an increased risk for contracting HIV should be tested at least once a year.
Known risk factors include:
HIV testing is also recommended:
- before a person begins a new sexual relationship
- if a person learns that theyre pregnant
- if a person has symptoms of another sexually transmitted infection
An HIV infection is now considered a manageable health condition, especially if treatment is sought early.
If a person has contracted HIV, early detection and treatment can help:
- improve their frame of mind
- lower their risk of disease progression
- prevent the development of stage 3 HIV, or AIDS
It can also help reduce their risk of transmitting the virus to other people.
The life expectancy of people with an HIV diagnosis who start treatment early is the same as those without the virus. People who know that theyve been exposed to HIV should seek care as soon as possible.
In some cases, if theyre treated within 72 hours, their healthcare provider may prescribe post-exposure prophylaxis .
These emergency medications may help reduce their chances of contracting HIV after theyve been exposed to it.
Not all tests require a blood sample or a visit to a clinic.
This is because it generally takes 3 months for the body to produce a detectable number of antibodies.
How Long Does It Take For Hiv To Infect The Body
On average it takes 2 to 12 weeks after infection for the virus to take hold and for the body to start to mount its defence by developing antibodies. From the point of exposure, if any transmission took place, the person is said to have HIV. 72 hours after any possible exposure, a tablet can be taken that can prevent the onward transmission, if a person thinks they have recently been at risk, they can take the pill to prevent infection.
Read Also: What Happens When Hiv Is Undetectable
What Are The Symptoms Of Hiv
Not everyone will have identical symptoms because it depends on the person and what stage of the disease they are in.
There are three stages of human immunodeficiency virus . Each stage has a unique set of symptoms. These include the following
Stage 1: Acute HIV infection
This stage starts around two to four weeks after getting HIV. The symptoms are similar to those of the flu, which last for a week or two. Symptoms include the following
Stage : Chronic Hiv Infection
After the acute stage has ended and if the person has not received treatment the virus remains active, reproducing at very low levels but continuing to damage immune cells.
At this stage, there are usually no symptoms or very mild ones. This is why doctors sometimes call stage 2 asymptomatic HIV infection or clinical latency. The virus can still pass to others during this stage, even if it causes no symptoms.
Without treatment, this stage can last for 10 years or more before the person develops stage 3 HIV.
However, modern antiretroviral medications can stop the infection from progressing. These drugs greatly reduce the amount of HIV in the body, the viral load, to very low levels.
When the viral load is so low that tests cannot detect it, HIV can no longer damage the immune system or transmit to other people. Some people refer to this as undetectable equals untransmittable or U=U.
A person with stage 2 HIV who takes effective antiretroviral therapy may never develop stage 3 HIV.
Also Check: What Is Prep Hiv Side Effects