How Can I Protect Myself
The best way to protect yourself from HIV is to not have sex and not share needles.
If you decide to have sex, reduce your risk of getting HIV by:
- using a condom every time you have sex
- getting tested for HIV and making sure all partners do too
- reducing the number of sexual partners you have
- getting tested and treated for STDs having an STD increases the risk of HIV infection
Understanding how HIV spreads can help you make safer choices about sex. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about HIV and if you want to get tested.
Do I Have To Tell My Parents If I Want To Get Tested
That depends on where you go to be tested. Some clinics want your parents’ permission before they offer you a test.
Most clinics are confidential. No one else will be told about your test results. You can call a clinic before going there to find out what its policy is on keeping your test confidential.
It’s a good idea, though, to talk with an adult you trust about your concerns. A trusted adult can help you sort through your options. The adult can also help you think about your behavior and what to do about behavior that puts you at risk.
What Happens After You Get Hiv And Aids
First people catch the HIV virus. Most people do not feelanything or have anything after they catch that particular virus.It takes about six months before it shows up on a blood test. Aftera few years a person starts getting thinner and thinner. A personneeds to maintain his or her weight. A person starts gettinginfections more often. It is harder and harder to get overinfections. If there is any possibility that anyone in the vicinityhas tuberculosis, then instead of getting a skin test, a personwith HIV will need an X-Ray to diagnosis it. The constant sicknesssets in and the disease becomes AIDS. Pneumonia comes. Cancercomes. Then comes death.
All this comes as a result of a rather poorly understoodbreakdown of the victim’s immune system. At this time, it’sirreversable but can be held off for a very long time if caughtearly on in it’s cycle.
Recommended Reading: Can Hiv Pass Through Clothes
Symptoms And Stages Of Hiv Infection
FAST FACTS
- There are three stages of HIV infection. The symptoms vary in type and severity from person-to-person.
- Stage 1 after initial infection can feel like flu but not everyone will experience this.
- Stage 2 is when many people start to feel better and may last for 10 years or more. During this time a person may have no symptoms.
- Stage 3 is when a persons immune system is very badly damaged and can no longer fight off serious infections and illnesses.
- The earlier a person is diagnosed with HIV and starts treatment, the better their health will be over time.
- Some people dont get any symptoms during stages 1 and 2, and may not know they have the virus, but they can still pass on HIV.
The signs of HIV infection can vary in type and severity from person-to-person, and some people may not have any symptoms for many years.
The stages below describe how HIV infection progresses in the body if it is left untreated. Without antiretroviral treatment for HIV, the virus replicates in the body and causes more and more damage to the immune system.
However with effective treatment, you can keep the virus under control and stop it from progressing. This is why its important to start treatment as soon as possible after testing positive.
What We Know About Anal Sex

Anal sex is the riskiest type of sex for getting or transmitting HIV. Although receptive anal sex is much riskier for getting HIV than insertive anal sex, its possible for either partnerthe insertive or receptiveto get HIV.
An HIV-negative receptive partners risk of getting HIV is very high because the lining of the rectum is thin. HIV can enter the body through this lining during anal sex from body fluids that carry HIV, including semen or pre-seminal fluid .
More information
On average, an HIV-negative receptive partner has about a 1 in 70 chance of getting HIV every time they have receptive anal sex with a partner who has HIV.
Being the receptive partner for anal sex is about 13 times more risky for getting HIV from a partner with HIV than being the insertive partner.
For women, anal sex is about 17 times more risky for getting HIV from a man with HIV than vaginal sex.
If the partner with HIV takes HIV medicine as prescribed, and gets and keeps an undetectable viral load , you have effectively no risk of getting HIV through sex with that partner.
See how receptive anal sex compares to other sexual activities here.
An HIV-negative insertive partner is also at risk because HIV can enter the body through the opening at the tip of the penis the foreskin if the penis isnt circumcised or small cuts, scratches, or open sores anywhere on the penis. There is some evidence that circumcision decreases a mans risk of getting HIV during sex.
More information
Recommended Reading: What Happens If Your Hiv Positive And Pregnant
Where Can I Find More Resources For A Person Just Diagnosed With Hiv
The following are resources to share with someone with newly diagnosed HIV:
- How to Find HIV Treatment Services, a fact sheet listing HIV-related resources including resources to help find a health care provider and get help paying for HIV medicines, from ClinicalInfo.
- Telling Others, a webpage with information on how to share an HIV diagnosis with others, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The Effects Of Hiv On The Body
Most people are likely familiar with HIV, but they may not know how it can affect the body.
HIV destroys CD4 cells , which are critical to the immune system. CD4 cells are responsible for keeping people healthy and protecting them from common diseases and infections.
As HIV gradually weakens the bodys natural defenses, signs and symptoms will occur.
Find out what happens when the virus enters the body and interrupts its systems.
Once HIV enters the body, it launches a direct attack on the immune system.
How quickly the virus progresses will vary by:
- a persons age
- how quickly theyre diagnosed
The timing of their treatment can make a huge difference as well.
HIV targets the types of cells that would normally fight off an invader such as HIV. As the virus replicates, it damages or destroys the infected CD4 cell and produces more virus to infect more CD4 cells.
Without treatment, this cycle can continue until the immune system is badly compromised, leaving a person at risk for serious illnesses and infections.
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is the final stage of HIV. At this stage, the immune system is severely weakened, and the risk of contracting opportunistic infections is much greater.
However, not everyone with HIV will go on to develop AIDS. The earlier a person receives treatment, the better their outcome will be.
Early on, HIV symptoms may be mild enough to be dismissed.
Don’t Miss: Can Hiv Be Transferred Through Saliva
Who Is At Risk For Hiv Infection
Anyone can get HIV, but certain groups have a higher risk of getting it:
- People who have another sexually transmitted disease . Having an STD can increase your risk of getting or spreading HIV.
- People who inject drugs with shared needles
- Gay and bisexual men, especially those who are Black/African American or Hispanic/Latino American
- People who engage in risky sexual behaviors, such as not using condoms
Side Effects Of Hiv Treatment
People on current HIV treatments may experience mild side effects including:
- tiredness and fatigue
- skin rashes.
If you are on treatment, see your doctor every 3 to 6 months.
Regular blood tests are necessary to make sure your treatment is working and not causing serious side effects. It is recommended that you also get tested for STIs and talk to your doctor about your sexual health and overall wellbeing. Ensure you are having routine screening for cancers and keeping your vaccinations up to date.
Read Also: What Does Hiv Stand For
If I’ve Had Sex That Put Me At Risk How Soon Should I Get Tested
Most experts recommend waiting to be tested until three months after having sex that put you at risk. That’s because it may take that long to develop antibodies that can be found by testing. There are, though, some newer tests that may provide results sooner. Discuss your timing for having tests with your doctor.
It’s important to avoid risky behaviors during that three-month period. If you think you are infected, see a doctor right away. They can help guide you in the testing.
Whats The Difference Between Hiv And Aids
HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. HIV and AIDS are not the same thing. And people with HIV do not always have AIDS.
HIV is the virus thats passed from person to person. Over time, HIV destroys an important kind of the cell in your immune system that helps protect you from infections. When you dont have enough of these CD4 cells, your body cant fight off infections the way it normally can.
AIDS is the disease caused by the damage that HIV does to your immune system. You have AIDS when you get dangerous infections or have a super low number of CD4 cells. AIDS is the most serious stage of HIV, and it leads to death over time.
Without treatment, it usually takes about 10 years for someone with HIV to develop AIDS. Treatment slows down the damage the virus causes and can help people stay healthy for several decades.
Also Check: How To Test For Hiv At Home
What We Know About Less Common Ways That You Can Get Hiv From Syringe Use
The risk for getting or transmitting HIV is very high if an HIV-negative person , other injection equipment with someone who has HIV. Its also possible to get HIV from tattooing or body piercing if the equipment has someone elses blood in it or if the ink is shared. The risk of getting HIV from tattooing or body piercing is higher when the person doing the procedure doesnt have a license. That person may be more likely to use unsafe practices like sharing syringes or ink. There are no known cases in the United States of anyone getting HIV this way.
More Information On average, an HIV-negative person has a 1 in 420 chance of getting HIV from a needlestick if the needle or syringe contains HIV-infected blood.
More InformationThere may be extremely tiny amounts of blood in syringes or works that you may not be able to see, but could still carry HIV. Be aware that HIV can survive in a used syringe for up to 42 days depending on temperature and other factors.
Treatment To Prevent Hiv Infection

Health care workers who are at risk for HIV because of an accidental needle stick or other exposure to body fluids may need medicine to prevent infection.footnote 13
Medicine may also prevent HIV infection in a person who has been raped or was accidentally exposed to the body fluids of a person who may have HIV.footnote 14 This type of treatment is usually started within 72 hours of the exposure.
Studies have shown that treatment with antiretroviral medicine also can reduce the risk of an uninfected person getting infected through sex.footnote 15, footnote 16
Recommended Reading: How Can Hiv Be Contracted
If You Don’t Have A Doctor
Public health units and other organizations may provide free or low-cost, confidential testing and counselling about HIV and high-risk behaviour.
If you don’t have a doctor, contact one of the following for information on HIV testing in your area:
- Your local health unit
- CATIE: 1-800-263-1638 or online at www.catie.ca
What Happens If I Test Positive For Hiv
If your initial test is positive for HIV antibodies, then additional testing is required to confirm that the first one was accurate. Sometimes this involves a second blood test.
When you are first diagnosed you will probably experience strong emotions. During this time, do not try to cope on your own. Seek support by speaking with your doctor, or contact your local community organisation. They have trained peer workers available to help you through the initial stages of a positive diagnosis, but also through your journey of living well with HIV.
Part of testing best practice includes pre- and post-test counselling. Post-test counselling is important, regardless of the outcome. If you test positive, counselling can provide emotional support, further information about living with HIV, and referrals to support services.
If the test is negative, counselling can provide education about HIV and how to reduce your HIV risk in the future. are community organisations that provide support and advocacy for people with HIV. Peer workers are also available to help you navigate living with HIV.
If you have recently been diagnosed with HIV, visit Next Steps for more information.
Recommended Reading: How Long After Sex Should You Get Tested For Hiv
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine every day, exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can protect your health and have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to your sexual partner.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Its important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
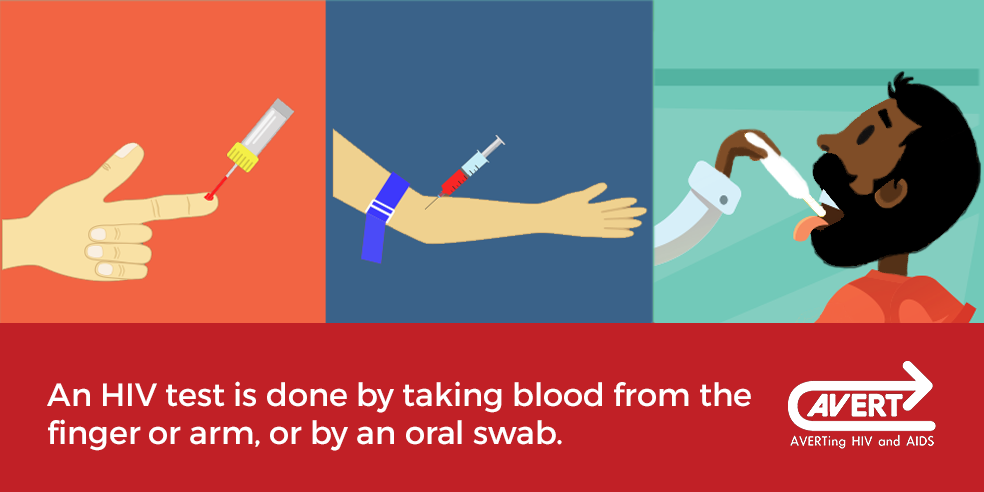
Hiv Is Detected With A Blood Test
Blood tests are the most common and reliable tests for HIV. The virus is detected by taking a sample of your blood either with a conventional blood test or a rapid test .There is a short period of time between exposure to HIV and the ability for tests to detect HIV or its antibodies. This is often referred to as the ‘window period’ between 2 and 12 weeks.
Most tests used in Australia can detect HIV as early as 2 to 4 weeks after infection.
If your blood test shows that HIV or its antibodies are present, you are HIV-positive.
If you have no antibodies in your blood you are HIV-negative. Sometimes negative results might also mean you are in the window period, so you might need a follow-up blood test to make sure.
Recommended Reading: Are There Symptoms Of Hiv
Does Hiv Viral Load Affect Getting Or Transmitting Hiv
Yes. Viral load is the amount of HIV in the blood of someone who has HIV. Taking HIV medicine daily as prescribed can make the viral load very lowso low that a test cant detect it .
People with HIV who take HIV medicine daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex.
HIV medicine is a powerful tool for preventing sexual transmission of HIV. But it works only as long as the HIV-positive partner gets and keeps an undetectable viral load. Not everyone taking HIV medicine has an undetectable viral load. To stay undetectable, people with HIV must take HIV medicine every day as prescribed and visit their healthcare provider regularly to get a viral load test. Learn more.
How Can A Woman Reduce Her Chances Of Contracting Hiv
HIV is transmitted through bodily fluids like blood and semen. Using injection drugs, having unprotected sex and having multiple sex partners increases the chances of acquiring HIV. The only way to be absolutely certain you do not become infected with HIV is to not have sex and not use injection drugs. You also can avoid infection by only having one sex partner as long as your partner does not have HIV and has sex only with you. According to the Centers For Disease Control and Prevention , using a male or female condom every time you have vaginal or anal sex can greatly lower your risk of infection. Using condoms for oral sex will reduce your risk for other STDs as well. It also is important not to douche, since douching removes some of the normal vaginal bacteria that can protect you from infection.
Read Also: What Are The Signs Of Hiv After 3 Months
How Do We Know Treatment As Prevention Works
Large research studies with newer HIV medications have shown that treatment is prevention. These studies monitored thousands of male-female and male-male couples in which one partner has HIV and the other does not over several years. No HIV transmissions were observed when the HIV-positive partner was virally suppressed. This means that if you keep your viral load undetectable, there is effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to someone you have vaginal, anal, or oral sex with. Read about the scientific evidence.
Effects On The Immune System
HIV primarily affects the body by targeting and damaging cells in the immune system. The immune system protects the body against viruses, bacteria, and fungi.
After attaching itself to a type of white blood cell called a CD4 T cell, the virus merges with it. These T cells are an important part of the immune system.
Once inside the CD4 T cell, the virus multiplies. It damages or destroys the cell, then moves on and targets other cells.
A persons CD4 T-cell count is an indication of the health of their immune system.
A healthy CD4 T-cell count is 5001,600 cells/mm3 of blood. If a person does not receive treatment for HIV, their CD4 T-cell count drops over time.
When it drops below 200 cells/mm3, the persons immune system is significantly impaired, making them more susceptible to opportunistic infections.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have Hiv