Increased Outbreaks Of Other Sexually Transmitted Infections
For people who already have another sexually transmitted infection , HIV can lead to worsening symptoms.
Human papillomavirus , which causes genital warts, is more active in people who have HIV. HIV can also cause more frequent and more intense outbreaks in people with genital herpes. Their bodies may not respond as well to their herpes treatment, either.
HIV is transmitted through bodily fluids. This can happen through sharing needles during drug use or through sexual intercourse. Key ways to reduce the risk of HIV include the following:
- not sharing needles when using injected drugs
- taking pre-exposure prophylaxis the US Preventive Services Task Force recommends this preventive medication for people with known risk factors for HIV
- not douching after sex it can alter the natural balance of bacteria and yeast in the vagina, making an existing infection worse or increasing the risk of contracting HIV and STDs
- using a condom, properly, if not in a monogamous relationship with an HIV-negative partner
Women without HIV who have HIV-positive partners arent at risk of contracting the virus if their partner uses HIV medications daily and achieves viral suppression, though ongoing use of a condom is recommended.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Trusted Source , HIV-positive people pose effectively no risk of transmitting HIV when their viral load is consistently measured at fewer than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood.
What You Can Do To Reduce Stigma
You can help reduce stigma by being respectful, compassionate and non-judgemental. Model this behaviour for others when you witness stigmatizing behaviours.
When talking about HIV, certain terms can be stigmatizing. Be thoughtful about the words you use when discussing the topic.
Learn more about the facts of HIV. Treatment can lower the amount of virus in a person’s blood to a level that’s too low to be measured on a standard blood test. This means it’s undetectable.
People living with HIV on treatment who maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their sexual partners.
Knowing and sharing these facts widely can help to reduce stigma. Share our Undetectable = Untransmittable infographic to help us raise awareness.
In addition, HIV is not transmitted through:
- healthy, unbroken skin
Symptoms And Stages Of Hiv Infection
FAST FACTS
- There are three stages of HIV infection. The symptoms vary in type and severity from person-to-person.
- Stage 1 after initial infection can feel like flu but not everyone will experience this.
- Stage 2 is when many people start to feel better and may last for 10 years or more. During this time a person may have no symptoms.
- Stage 3 is when a persons immune system is very badly damaged and can no longer fight off serious infections and illnesses.
- The earlier a person is diagnosed with HIV and starts treatment, the better their health will be over time.
- Some people dont get any symptoms during stages 1 and 2, and may not know they have the virus, but they can still pass on HIV.
The signs of HIV infection can vary in type and severity from person-to-person, and some people may not have any symptoms for many years.
The stages below describe how HIV infection progresses in the body if it is left untreated. Without antiretroviral treatment for HIV, the virus replicates in the body and causes more and more damage to the immune system.
However with effective treatment, you can keep the virus under control and stop it from progressing. This is why its important to start treatment as soon as possible after testing positive.
Also Check: Would You Date Someone With Hiv
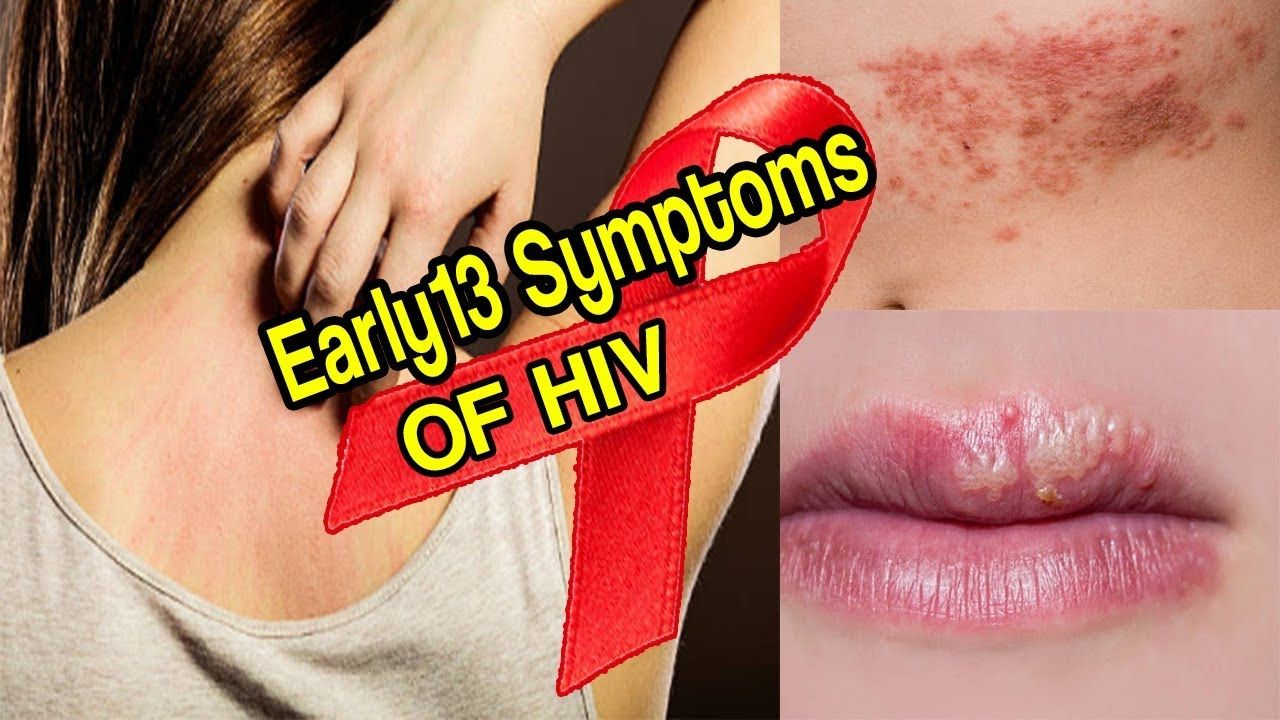
Skin Rashes And Skin Sores
Most people with HIV develop skin problems. Rash is a common symptom of HIV, and many different types of skin rashes are associated with the condition. They may be a symptom of HIV itself or the result of a concurrent infection or condition.
If a rash appears, its a good idea to have a healthcare provider review ones medical history. They can use a complete medical history to determine which diagnostic tests are needed.
Sores, or lesions, may also form on the skin of the mouth, genitals, and anus of people with HIV.
With proper medication, however, skin problems may become less severe.
How Can I Prevent Passing Hiv To Others

A few precautions that you can take to protect yourself from HIV infection are:
- Reduce your number of sexual partners.
- Get your partners tested for HIV
- Have safe sex by using a condom
- Talk to your doctor about pre-exposure prophylaxis which reduces the risk of getting HIV from sex by more than 90%. PrEP is an HIV prevention option for people who dont have HIV but who are at high risk of becoming infected with HIV
- Do not use any form of drugs which you need to inject. Even if you do make sure you use only sterile drug injection equipment
Recommended Reading: Can Your Immune System Fight Off Hiv
Fever And Night Sweats
People with HIV may experience long periods of low-grade fever. A temperature between 99.8°F and 100.8°F is considered a low-grade fever.
The body develops a fever when something is wrong, but the cause isnt always obvious. Because its a low-grade fever, those who are unaware of their HIV-positive status may ignore the symptom.
Sometimes, night sweats that can interfere with sleep may accompany fever.
Women with HIV can experience changes to their menstrual cycle. Their periods may be lighter or heavier than normal, or they may not have a period at all.
HIV-positive women may also have more severe premenstrual symptoms.
Hiv : Causes Symptoms Prevention And Treatment
When Charlie Sheen recently broke the news of his HIV-positive status on American television in 2015, the world sat up and took note.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , more than 1.1 million people are currently HIV infected in the USA, and as many as 15 percent remain unaware of their infection.
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. This virus infiltrates and destroys the CD4 cells, which are a type of T-helper cells or white blood cells that play an important role in the immune system.
These cells navigate the entire body through the bloodstream and are responsible for detecting any cellular anomalies as well as signs of an infection or disease. Thus, they essentially work as foot soldiers in the bodys natural defense system.
As the HIV virus breaks down more and more of CD4 cells over time, the immune system is rendered weak and incapacitated to fight off everyday infections and more serious ailments such as cancer.
Once contracted, the impact of these conditions is also far more amplified and dangerous. In fact, for an HIV victim, even the most minor sickness can end up being fatal if not attended to properly as the damage tends to progressively worsen.
Some research demonstrates that there is a disparity in gender incidence for HIV infection and shows that HIV-1 prevalence among girls and young women is double that among males of the same age.
Contents
You May Like: How Can You Catch Hiv
Early Signs And Symptoms Of Hiv In Men
Early symptoms of HIV in men are often vague and unspecific.
In men, initial HIV symptoms are typically unspecific. Early symptoms are usually bearable and frequently mistaken for flu or another mild condition. People may easily underestimate them or mistake them for minor health conditions.
Men can experience flu-like symptoms some days to weeks after contracting the virus, which may include:
- pain in the joints
- swollen lymph nodes
Men may undervalue initial symptoms and put off seeing a doctor until the symptoms worsen, by which time the infection might have advanced.
The fact that some men do not seek timely treatment may be why the virus affects men more severely than women.
Although scientists and researchers have made significant progress in the prevention and treatment of HIV over the last decades, it remains a serious health problem in most countries around the world.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , in 2016, an estimated 39,782 people were diagnosed with HIV in the U.S.
Although the number of new diagnoses fell by 5 percent between 2011 and 2015, there were still around 1.1 million people in the U.S. living with HIV in 2015.
A higher number of men than women are living with the virus. By the end of 2010,
In 2016, 44 percent of new HIV diagnoses were among African Americans, compared with 26 percent among white people and 25 percent among Hispanics and Latinos.
Who Should Get Tested And How Often
The CDC recommends that people within the age gap of 1364 years should make it a point to get tested at least once in their lifetime. Furthermore, people who are in high-risk populations should exercise greater precaution and get tested often, which is every 36 months.
To be more certain, you must speak with your healthcare provider to get a fair assessment of your risk factors and accordingly determine how often you should get tested for HIV.
Recommended Reading: How Did The First Person Get Hiv
Progressing To Stage 3 Hiv
If a person with HIV does not receive treatment, the condition may eventually progress to stage 3 HIV, also known as AIDS. Thanks to modern medical advances, HIV infection rarely reaches stage 3 in the U.S. nowadays.
Stage 3 HIV is not a specific disease but a syndrome with a wide range of identifiable symptoms. The symptoms can also stem from other illnesses that occur because opportunistic infections take advantage of reduced immune activity.
Symptoms include:
Treatment will depend on the individual and any complications. The persons healthcare team will help them make a suitable plan.
Second Stage: Clinical Latency Symptoms
After your immune system loses the battle with HIV, the flu-like symptoms will go away. But thereâs a lot going on inside your body. Doctors call this the asymptomatic period or chronic HIV infection.
In your body, cells called CD4 T cells coordinate your immune systemâs response. During this stage, untreated HIV will kill CD4 cells and destroy your immune system. Your doctor can check how many of these cells you have with blood tests. Without treatment, the number of CD4 cells will drop, and youâll be more likely to get other infections.
Most people don’t have symptoms they can see or feel. You may not realize that you’re infected and can pass HIV on to others.
If youâre taking ART, you might stay in this phase for decades. You can pass the virus on to other people, but itâs extremely rare if you take your medicines.
Don’t Miss: What To Do If Hiv Positive
Stage : The Asymptomatic Stage
Once a person has been through the acute primary infection stage and seroconversion process, they can often start to feel better. In fact, HIV may not cause any other symptoms for up to 10 or even 15 years .
However, the virus will still be active, infecting new cells and making copies of itself. HIV can still be passed on during this stage. If left untreated, over time, HIV infection will cause severe damage to the immune system.
Hiv Exposure Through Sexual Behavior
- Engaging in intercourse with an HIV-infected person Anal intercourse is the first and vaginal intercourse is the second highest-risk sexual behaviors for HIV transmission.
- Engaging in unprotected intercourse with multiple partners This can lead to other sexually transmitted infections, making you more susceptible to contracting the HIV virus through intercourse.
- Engaging in transactional intercourse This typically involves multiple partners and high-risk sexual behavior.
Read Also: What Does Hiv Stand For
When Do Symptoms Occur
Some people have flu-like symptoms within two to four weeks after infection, but others may not feel sick or not develop symptoms at all until later.
See a healthcare provider if you have symptoms of HIV and think you may have been exposed to HIV. Getting tested for HIV is the only way to know for sure.
In the United States, HIV is spread mainly through having anal or vaginal sex or sharing needles or syringes with an HIV-positive partner. Anal sex is the highest-risk behavior.
You can prevent HIV by using condoms correctly every time you have sex pre-exposure prophylaxis, a prevention method in which the HIV-negative partner takes daily HIV medicine to prevent HIV and treatment as prevention, a method in which the HIV-positive partner takes daily HIV medicine to achieve and maintain an undetectable viral load.
Only antigen/antibody tests or nucleic acid tests can diagnose acute HIV infection. NATs look for actual virus in the blood, and antigen/antibody tests look for HIV antibodies and antigens. Antibodies are produced by your immune system when youre exposed to viruses like HIV, and antigens are foreign substances that cause your immune system to activate.
However, no test can detect HIV immediately after infection. NATs can usually tell if you have an HIV infection 10 to 33 days after exposure, while antigen/antibody tests can tell 18 to 45 days after exposure.
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Mouth ulcers or sores
First Stage: Acute Hiv Infection Symptoms
Most people don’t know right away when they’ve been infected with HIV. But they may have symptoms within 2 to 6 weeks after theyâve gotten the virus. This is when your body’s immune system puts up a fight. It’s called acute retroviral syndrome or primary HIV infection.
The symptoms are similar to those of other viral illnesses, and they’re often compared to the flu. They typically last a week or two and then go away. Early signs of HIV include:
- Ulcers in your mouth, esophagus, anus, or genitals
- Headache and other neurological symptoms
If you have symptoms like these and might have come into contact with someone with HIV in the past 2 to 6 weeks, go to a doctor and ask that you get an HIV test. If you donât have symptoms but still think you might have come into contact with the virus, get tested.
Early testing is important for two reasons. First, at this stage, levels of HIV in your blood and bodily fluids are very high. This makes it especially contagious. Second, starting treatment as soon as possible might help boost your immune system and ease your symptoms.
A combination of medications can help fight HIV, keep your immune system healthy, and keep you from spreading the virus. If you take these medications and have healthy habits, your HIV infection probably wonât get worse.
Read Also: How Are Drugs For Hiv Patients Administered
To 14 Days After Exposure
Known as acute retroviral syndrome, or ARS, the acute stage occurs immediately after being infected, when the immune system has yet to control the virus. During this time, an estimated 40 percent to 90 percent of people will experience mild to moderate flu-like symptoms, whereas the rest wont experience any symptoms at all.
Although these signs typically appear within 7 to 14 days of exposure, they can also crop up as early as 3 days. Around 30 percent of people with ARS will develop a maculopapular rash of pink to red bumps, usually on the upper half of the body. The rash will gradually converge into larger, raised hives.
Other common ARS symptoms include:
- Fever
- Diarrhea
Because I Have Hiv Will I Eventually Get Aids
Though it cannot be said with surety for how long the average person who is HIV positive can live things are changing due to advances in medical science. A person even with full-blown AIDS can live for many years.Majority of the people who are HIV positive will develop AIDS during their life, within a span of 10 years after contracting the virus or more. With early intervention and treatment
These are some of the variables that can determine how long a person who is HIV positive can live:
Read Also: What Is The Body’s Initial Reaction To The Hiv Virus
General Misconceptions About Hiv Transmission
There are several myths regarding the spread of HIV that add to the sense of suspicion that shrouds this condition and contribute to the unjust and unwarranted alienation of its victims. People tend to make assumptions without educating themselves about the facts, and as a result, HIV patients are forced to become social pariahs.
Instead of operating out of the fear of a probable infection, one must get his/her facts straight. Unlike your run-of-the-mill viral infections, the HIV virus, contagious as it may be, does not spread through the following:
- Skin-to-skin contact
- Holding hands, hugging, or kissing an HIV patient
- Sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses with a patient
Hiv Exposure Through Injection Or Infusion
- Sharing drug-injecting equipment with an HIV-infected person can infect you, too.
- Sharing drug preparation equipment with an HIV-infected person can also infect you.
- Healthcare workers are at high risk of accidentally being struck with an HIV-infected needle.
- Using needles or syringes bought from street sellers can infect you with HIV, as these sellers often repackage used needles and syringes and sell them as new items.
- HIV-contaminated blood transfusions or organ and tissue transplants also raise the risk of spreading HIV.
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Hiv And Aids