Research And Statistics: How Many People Have Hiv/aids
In 2019, close to 37,000 people were diagnosed with HIV in the United States, according to the latest figures available from the CDC. The annual number decreased by approximately 9 percent between 2015 and 2019.
The CDC further estimates that roughly 1.2 million people in the United States were living with HIV at the end of 2019, and that about 13 percent of those individuals were unaware they were HIV-positive.
Anyone can acquire HIV, but the prevalence of HIV is not the same in all communities and varies depending on social and demographic factors.
Hiv Testing And Your Rights
Testing for HIV is voluntary and can only be done with your informed consent, except in exceptional circumstances.
Before you are tested, you will be provided with information about what is involved. what the results might mean for you, and how to prevent HIV transmission in the future. All people who request an HIV test must receive this information from the test provider.
Under Australian and Victorian law, it is unlawful to discriminate against anyone who has HIV. Test results, and details on whether someone has been tested are strictly confidential. It is illegal for any information about a person being tested or a person with HIV to be disclosed without their permission.
Take Time To Process The News
- Receiving an HIV diagnosis can be life changing. You may feel many emotionssadness, hopelessness, or anger.
- Allied health care providers and social service providers can help you work through the early stages of your diagnosis. They are often available at your health care providers office.
- Learn more about what a positive test result means.
Read Also: Does Cookie Johnson Have Hiv
What Happens If The Result Is Positive
The process can vary across the country but, generally speaking, when a test reveals that the individual is HIV positive, the post-test counselling is extensive . Typically, a provider gives a person time to absorb the results, discusses the impact of the positive test result, and provides the opportunity for the person to ask questions. Post-test counselling following a positive diagnosis usually includes support and extensive discussion and comprehensive linkage to other services, including HIV care.
If a rapid point-of-care test indicates a reactive result, the person is informed of the result and, after obtaining informed consent, the counsellor draws a blood sample, which is sent to a laboratory for confirmatory testing. The person is given post-test counselling immediately after receiving a reactive result and again when returning to pick up the result of the confirmatory test one to two weeks later.
Chronic Hiv Infection With Antiretroviral Treatment
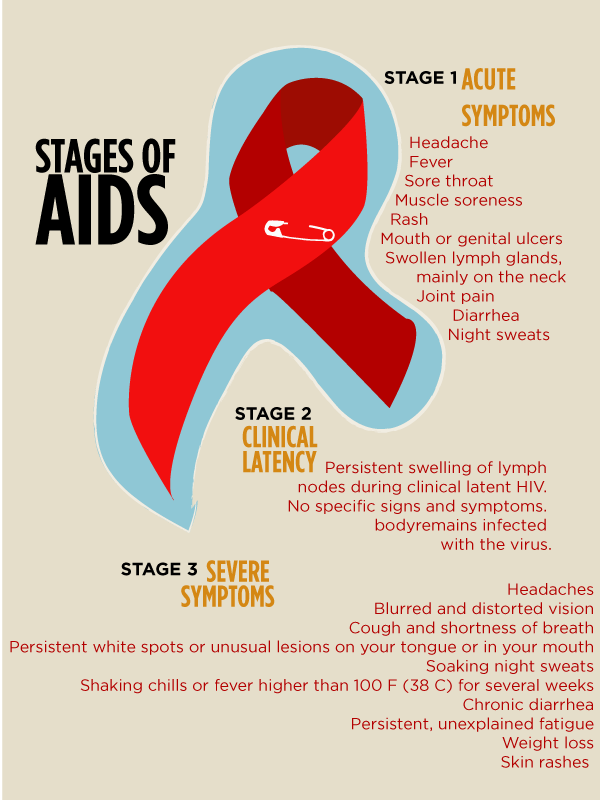
If you take effective HIV treatment, you can live with HIV as a chronic, manageable condition. A chronic health condition is one which continues for a long period of time.
This stage is not included in most descriptions of the stages of infection, which only describe disease progression in the absence of treatment.
However, most people living with HIV who have access to good healthcare are living with HIV as a chronic condition and will continue to do so for the rest of their lives. They are unlikely to fall ill or die as a direct result of HIV.
In order to reach this stage and to remain in it, you need to take HIV treatment and continue to take it, on an ongoing basis. These medications reduce levels of HIV in your body and strengthen the immune system. This usually prevents the symptoms and opportunistic infections described above from occurring.
One of the benefits of effective HIV treatment is that is stops HIV from being passed on. Treatment drastically reduces the amount of HIV in body fluids to the point where there is not enough HIV to transmit the virus to sexual partners.
The chronic infection phase can last for decades. People who start HIV treatment as soon as possible, are able to stick with it and have access to good healthcare are likely to have a similar life expectancy to their peers who dont have HIV.
You May Like: How Many Americans Have Hiv
Hiv Transmission In Australia
In Australia, HIV is commonly transmitted through:
- Unprotected anal or vaginal sex .
- Sharing any needles, syringes, or other injecting equipment.
- From mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding This can occur when the mother doesnt know she is HIV-positive, or is not on effective treatment.
- Tattooing or other procedures that involve unsterile or reused equipment.
- Needle stick injuries.
HIV is not transmitted by:
- kissing, hugging, massaging, mutual masturbation and other body contact
- social interaction
- sharing food, dishes, utensils, drinking glasses
- air, breath, or being coughed or sneezed on
- mosquito, insect or animal bites
- use of communal facilities .
It is perfectly safe to consume food and drinks prepared by someone who is HIV-positive even if theyre not receiving treatment.
People with HIV who are on treatment and achieve and maintain an undetectable HIV viral load cannot transmit HIV sexually.
What’s The Evidence For Specific Management And Treatment Recommendations
Abert, JA, Gallant, JE, Ghanem, KG. âPrimary care guidelines for the management of persons infected with HIV: 2013 update by the HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of Americaâ. . vol. 58. 2014. pp. e1-34.
Bartlett, JG, Gallant, JE, Pham, PA. âAdult HIV/AIDS Treatment: Pocket Guide 2016â.
âCenters for Disease Control and Prevention . Revised recommendations for HIV testing of adults, adolescents, and pregnant women in health-care settingsâ. MMWR. vol. 55. 2006. pp. 1-7.
Cohen, MS, Chen, YQ, McCauley, M. âAntiretroviral treatment of prevention of HIV transmissionâ. . 2016.
Gallant, JE, Daar, ES, Raffi, F. âEfficacy and safety of emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide vs emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate as a backbone for treatment of HIV-1 infection in virologically suppressed adults: randomised, double-blind, active-controlled phase 3 trialâ. . vol. 3. 2016. pp. e158-65.
Gallant, JE. âWhat does the generalist need to know about HIV infectionâ. . vol. 17. 2010. pp. 5-18.
Gallant, JE, Koenig, E, Andrade-Villanueva, J. âCobicistat versus ritonavir as a pharmacoenhancer for atazanavir plus emtricitabine/tenofovir DF in treatment-naïve HIV-1-infected patients: Week 48 resultsâ. . vol. 208. 2013. pp. 32-9.
Gallant, JE, Pham, PA. . 2012.
Lundgren, JD, Babiker, AG, Gordin, F. âInitiation of Antiretroviral Therapy in Early Asymptomatic HIV Infectionâ. N Engl J Med. vol. 373. 2015. pp. 795-807.
Recommended Reading: How Is Hiv Transmitted Through Sex
How Do People Get Hiv
HIV spreads when infected blood or body fluids enter the body. This can happen:
HIV also can pass from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
HIV is NOT spread through:
- pee, poop, spit, throw-up, or sweat
- coughing or sneezing
- sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses
Beware: There Are Other Diseases That Can Mimic Hiv Infection:
-
Although there are other conditions that can cause cellular immunodeficiency with similar clinical manifestations, the sensitivity and specificity of the HIV serology make diagnostic confusion extremely unlikely. Patients who present with manifestations of cellular immunodeficiency should first be tested for HIV. Evaluation for other causes of immunodeficiency is indicated only if there is no laboratory evidence of HIV infection.
Also Check: Can Hiv Be Transmitted Through Eyes
What Is Viral Suppression
Antiretroviral therapy keeps HIV from making copies of itself. When a person living with HIV begins an antiretroviral treatment regimen, their viral load drops. For almost everyone who starts taking their HIV medication daily as prescribed, viral load will drop to an undetectable level in six months or less. Continuing to take HIV medications as directed is imperative to stay undetectable.
If You Already Have Hiv
If you are infected with HIV, you can greatly lower the risk of spreading the infection to your sex partner by starting treatment when your immune system is still healthy.
Experts recommend starting treatment as soon as you know you are infected.footnote 21
Studies have shown that early treatment greatly lowers the risk of spreading HIV to an uninfected partner.footnote 22, footnote 23
Your partner may also be able to take medicine to prevent getting infected.footnote 17 This is called pre-exposure prophylaxis .
Steps to avoid spreading HIV
If you are infected with HIV, you can greatly lower the risk of spreading the infection to your sex partner by starting treatment when your immune system is still healthy.
- Take antiretroviral medicines. Getting treated for HIV can help prevent the spread of HIV to people who are not infected.
- Tell your sex partner or partners about your behaviour and whether you are HIV-positive.
- Follow safer sex practices, such as using condoms.
- Do not donate blood, plasma, semen, body organs, or body tissues.
- Do not share personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or sex toys, that may be contaminated with blood, semen, or vaginal fluids.
Also Check: What Does It Mean When Someone Is Hiv Undetectable
How Much Do Hiv Tests Cost
Unlike rapid tests, blood tests for HIV are covered by Medicare, which means your doctor can order the test free of charge for you.
If you are not eligible for Medicare, you may also be able to claim some of the testing costs through private health insurance. Check with your provider to see if youre eligible.
Letting Partners Know You Have Hiv
If you have just been diagnosed with HIV, it will likely be a difficult time. You might still be struggling to come to terms with diagnosis.
During this time, it is important to let any sexual or injecting partners know they may have been exposed to HIV as soon as you can, so they can be tested and offered PEP if appropriate.
You do not have to do this alone. Your doctor or the Department of Health and Human Services Partner Notification Officers can help you through this process and ensure your identity is not revealed.. Both groups can provide information, support, and guidance for people living with HIV.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Avoid Getting Hiv
How Has Treatment Improved
Antiretroviral medications can help to slow damage caused by HIV infection and prevent it from developing into stage 3 HIV, or AIDS.
A healthcare provider will recommend undergoing antiretroviral therapy. This treatment requires taking three or more antiretroviral medications daily. The combination helps suppress the amount of HIV in the body . Pills that combine multiple medications are available.
The different classes of antiretroviral drugs include:
- non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
- integrase inhibitors
Viral-load suppression allows people with HIV to live healthy lives and decreases their chances of developing stage 3 HIV. The other benefit of an undetectable viral load is that it helps reduce transmission of HIV.
The 2014 European PARTNER study found that the risk of HIV transmission is very small when a person has an undetectable load. This means that the viral load is below 50 copies per milliliter .
This discovery has led to an HIV prevention strategy known as treatment as prevention. It promotes constant and consistent treatment as a way to reduce the spread of the virus.
HIV treatment has evolved tremendously since the onset of the epidemic, and advancements continued to be made. Initial reports from a clinical trial in the United Kingdom and a from the United States showed promising results in experimental HIV treatments that could put the virus into remission and boost immunity.
If You Don’t Have A Doctor
Public health units and other organizations may provide free or low-cost, confidential testing and counselling about HIV and high-risk behaviour.
If you don’t have a doctor, contact one of the following for information on HIV testing in your area:
- Your local health unit
- CATIE: 1-800-263-1638 or online at www.catie.ca
Recommended Reading: When Does Hiv Start Affecting You
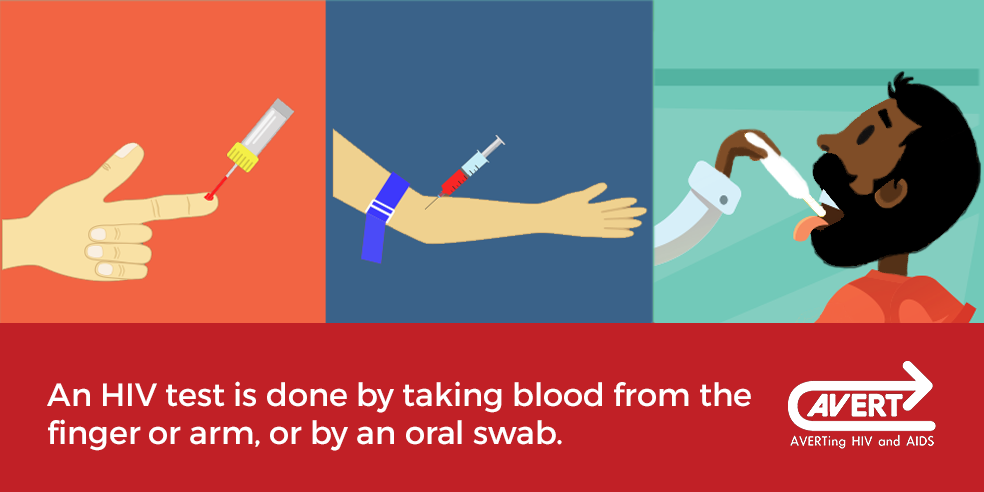
How Is Hiv Diagnosed
Diagnosis of HIV infection during infancy depends on the detection of the virus. Since all infants born to HIV-infected mothers have a positive antibody test at birth because of the passive transfer of the HIV antibody across the placenta, virological testing is used to confirm the diagnosis.
For infants born to HIV-infected mothers, viral diagnostic testing is usually performed within the first 2 days of life, at 1 to 2 months of age, and at 4 to 6 months of age. A diagnosis of HIV infection can be made with two positive virologic tests obtained from different blood samples.
For children over 18 months, adolescents, or adults, diagnosis is made by testing the blood for the presence of HIV antibody.
How Often Do You Need To Get Tested For Hiv
How often you should get tested depends on your personal practices, risk behaviours, and how often you engage in them.
For most people, it is important to have a full sexual health test at least once each year. This testing includes:
- HIV
Even if you always use condoms, it is recommended you get tested annually as condoms dont provide 100% protection against HIV and STIs.
Recommended Reading: Can You Look Up To See If Someone Has Hiv
What Happens If The Result Is Negative
If a standard test reveals that the individual is HIV negative, the provider explains the result, ensures the person understands the result, and discusses any other questions about HIV testing, transmission, or prevention. They may also discuss the need for further safer sex or harm reduction education or other services, provide referral to other community services as appropriate, and discuss opportunities for other testing, such as sexually transmitted infections or hepatitis C, if appropriate.
If a rapid point-of-care test is non-reactive, the person is given the result and post-test counselling as appropriate to their individual needs. This whole process can be completed in one 20-minute visit .
People who test negative but are in the window period, may be advised to test again at an appropriate time to ensure the result is accurate. For those who test HIV negative, but are at continuing high risk for infection, efforts should be made to actively ensure that they are linked to and engaged in enhanced prevention services and risk-reduction counselling. They should also be encouraged to repeat testing as necessary.
Changing Attitudes About Hiv
When someone is diagnosed with HIV, other people may have negative attitudes and beliefs about that person’s behaviour, lifestyle or circumstances in life. These negative associations form what’s called stigma, an experience that can decrease quality of life because it includes:
- judging
Efforts to end stigma will help to:
- prevent new infections
- ensure that people living with HIV receive the care, treatment and support they need
Don’t Miss: Why No Vaccine For Hiv
Reducing Hiv Risks From Chemsex And Drug Use
Some people use drugs such as ice , GHB, ecstasy , ketamine and cocaine) to enhance their sexual experiences . Chemsex can make you lose your inhibitions and be risky if you:
- Inject drugs.
- Forget to take your HIV medications.
- Are taking PreP it can be less effective if it is mixed with other drugs.
Treatment To Prevent Hiv Infection

Health care workers who are at risk for HIV because of an accidental needle stick or other exposure to body fluids may need medicine to prevent infection.footnote 13
Medicine may also prevent HIV infection in a person who has been raped or was accidentally exposed to the body fluids of a person who may have HIV.footnote 14 This type of treatment is usually started within 72 hours of the exposure.
Studies have shown that treatment with antiretroviral medicine also can reduce the risk of an uninfected person getting infected through sex.footnote 15, footnote 16
Don’t Miss: How Long Can Hiv Go Undetected
What Does A Reactive Test Result Mean
A reactive test result is a possible positive result, but means that you will need to go back to test again to confirm this. The healthcare worker will talk you through everything you need to know and help you with any worries that you may have.
You will need to give blood sample, which will then be sent to the lab for testing. At this stage, it’s very important to follow the advice of the healthcare professional.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Is there any sure way to avoid acquiring HIV?
- What is the best treatment for me?
- How can I avoid getting any infections that will make me very sick?
- How can I find support groups in my community?
- What diagnostic tests will you run?
- How often will I need to see my doctor?
- Will there be any side effects to my treatment?
- How does this affect my plans for having a family?
- Is it safe for me to breastfeed my baby?
- Will using a condom keep my sex partners from acquiring HIV?
- Should I follow a special diet?
Read Also: How Long Can You Carry Hiv Without Knowing
When Should This Disease Be Tested For
-
Routine, voluntary HIV testing is recommended by the CDC for all patients 13-64 years of age and by the USPSTF for all patients 15-65 years of age, regardless of perceived risk or health status.
-
HIV testing should be performed in patients with symptoms suggestive of immunosuppression, including unexplained weight loss, chronic diarrhea, fever, chills, sweats, dysphagia or odynophagia, oropharyngeal candidiasis , and more severe or frequent vaginal candidiasis.
-
HIV testing should always be performed in patients with a history of tuberculosis, shingles, sexually transmitted infections, lymphoma, thrombocytopenia, hepatitis B, or hepatitis C, as well as in patients with AIDS-defining opportunistic infections or malignancies.
-
Consider testing for primary HIV infection with HIV serology and viral load in patients presenting with an unexplained mononucleosis-like illness, aseptic meningitis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, mononeuritis multiplex, or facial nerve palsy.
What Does It Mean To Be Durably Undetectable
Taking antiretroviral therapy daily as prescribed to suppress HIV levels leads to an undetectable status. A person is considered to have a durably undetectable viral load if their viral load remains undetectable for at least six months after their first undetectable test result. It is essential to continue to take every pill every day as directed to maintain an undetectable viral load.
You May Like: Can You Get Hiv From Blood Transfusion