An Introduction To Global Hiv Statistics
For many years, the Human Immunodeficiency Virus, also known as HIV, has affected millions of people throughout the world. To put things into perspective, HIV represents the leading cause of AIDS, a disease that is characterized by prolonged damage to the immune system, thus making it easier for patients to catch a variety of diseases.
HIV is transmitted via blood and during sex, yet protection methods are luckily available to reduce its spread. Below, readers will get to learn more about the condition through a variety of AIDS statistics.
At the moment, there are numerous misconceptions about HIV and AIDS, but we are here to disperse them. This article is meant to explain better the main facts and statistics associated with the virus. All the data we present here comes from reputable sources.
To kick things off, it is important to mention that a weakened immune system makes treating and catching diseases more difficult. As such, according to WHO HIV statistics and facts, the AIDS/HIV does not represent a direct cause of death but rather weakens the body, thus making it unable to fight infections that wouldnt normally be life-threatening. This leads to the high number of deaths that we are already accustomed to, caused by a variety of associated diseases.
Based on these aspects, this article will list several HIV statistics on a variety of subjects, including, but not limited to, how common HIV is, the demographics of AIDS, transmission rates, and more.
How Have Deaths From Hiv/aids Changed Over Time
Global deaths from HIV/AIDS halved within a decade
The world has made significant progress against HIV/AIDS. Global deaths from AIDS have halved over the past decade.
In the visualization we see the global number of deaths from HIV/AIDS in recent decades this is shown by age group. In the early 2000s 2004 to 2005 global deaths reached their peak at almost 2 million per year.
Driven mostly by the development and availability of antiretroviral therapy , global deaths have halved since then. In 2017, just under one million died from the disease.
You can explore this change for any country or region using the change country toggle on the interactive chart.
HIV/AIDS once accounted for more than 1-in-3 deaths in some countries, but rates are now falling
Global progress on HIV/AIDS has been driven by large improvements in countries which were most affected by the HIV epidemic.
Today the share of deaths remains high: more than 1-in-4 deaths in some countries are caused by HIV/AIDS. But in the past this share was even higher.In the visualization we see the change in the share of deaths from HIV/AIDS over time. From the 1990s through to the early 2000s, it was the cause of greater than 1-in-3 deaths in several countries. In Zimbabwe, it accounted for more than half of annual deaths in the late 1990s.
We see that over the past decade this share has fallen as antiretoviral treatment has become more widely available.
Children living with HIV
New HIV infections of children
Hiv By The Numbers: Facts Statistics And You
Centers for Disease Control reported the first five known cases of complications from HIV in Los Angeles in June 1981. The previously healthy men had contracted pneumonia, and two died. Today, more than a million Americans have the virus.
Being diagnosed with HIV was once a death sentence. Now, a 20-year-old with HIV who begins treatment early can expect to live to their
of people ages 13 and older with HIV dont know they have it.
An estimated 39,782 Americans were newly diagnosed with HIV in 2016. In that same year, 18,160 individuals living with HIV developed stage 3 HIV, or AIDS. This is in striking contrast to the early days of HIV.
According to the American Federation of AIDS Research, by the end of 1992, 250,000 Americans had developed AIDS, and 200,000 of these had died. By 2004, the number of cases of AIDS reported in the United States closed in on 1 million, with deaths totaling more than 500,000.
diagnosed in the United States in 2016, 2,049 men and 7,529 women contracted the virus. Overall, new diagnoses decreased.
When it comes to , 17,528 of those diagnosed in the United States in 2016 were black, 10,345 were white, and 9,766 were Latino.
Americans in the
- New York
- Georgia
AIDS.gov reports that 36.7 million people worldwide are living with HIV, and 35 million have died since 1981. Additionally, the majority of people with HIV live in developing and moderate-income nations, such as those in sub-Saharan Africa.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take To Become Undetectable Hiv
Impact On Young People
- Teens and young adults continue to be at risk, with those under 35 accounting for 57% of new HIV diagnoses in 2019 .51 Most young people are infected sexually.52
- Among young people, gay and bisexual men and minorities have been particularly affected.53
- Perinatal HIV transmission, from an HIV-infected mother to her baby, has declined significantly in the U.S., largely due to increased testing efforts among pregnant women and ART which can prevent mother-to-child transmission.54,55,56
- A recent survey of young adults found that HIV remains a concern for young people, especially for young people of color.57
Tuberculosis Among People Living With Hiv
Tuberculosis is the leading HIV-associated opportunistic infection in low- and middle- income countries, and it is a leading cause of death globally among people living with HIV. Death due to tuberculosis still remains high among people living with HIV, however the number of deaths is decreasing. Most of the global mortality due to TB among those with HIV is from cases in Sub-Saharan Africa.
In the charts here we see the number of tuberculosis patients who tested positive for HIV the number receiving antiretroviral therapy and the number of TB-related deaths among those living with HIV.
People who use ART are living longer
ART not only saves lives but also gives a chance for people living with HIV/AIDS to live long lives. Without ART very few infected people survive beyond ten years.3
Today, a person living in a high-income country who started ART in their twenties can expect to live for another 46 years that is well into their 60s.4
While the life expectancy of people living with HIV/AIDS in high-income countries has still not reached the life expectancy of the general population, we are getting closer to this goal.5
ART prevents new HIV infections
There is considerable evidence to show that people who use ART are less likely to transmit HIV to another person.7 ART reduces the number of viral particles present in an HIV-positive individual and therefore, the likelihood of passing the virus to another person decreases.
We need to increase ART coverage
Don’t Miss: Lil Wayne Hiv Rumors
Men Who Have Sex With Men
Men who have sex with men account for 70% of all new HIV infections in the United States. According to the CDC, there were approximately 8,000 deaths among gay and bisexual men diagnosed with HIV in 2018.
In addition to physiological vulnerabilities to infection , high rates of homophobia and stigmatization drive many MSM to avoid HIV testing, treatment, and care. These factors translate to a higher rate of HIV mortality.
According to a 2011 study in the American Journal of Public Health, MSM with HIV are about 160 times more likely to die from an AIDS-related complication than men who exclusively engage in penile-vaginal sex.
If You Are Admitted To Hospital With Covid
The clinical management of COVID-19 in people with HIV is the same as for people who do not have HIV.
BHIVA advises that it is a good idea to tell the healthcare team looking after you in hospital that you are living with HIV so that they can do tests to rule out other lung infections that may occur in people with HIV. Keep a list of the HIV medications you are taking so that they can be prescribed as soon as possible if you are admitted.
CD4 cell counts can fall during COVID-19, so doctors should remember to give opportunistic infection prophylaxis if the CD4 cell count falls below 200.
Further guidance on what to do if you are admitted to hospital with COVID-19 is published on the BHIVA website.
Read Also: Does Aids Cause Hair Loss
In 2019 It Was Estimated That There Are 105200 People Living With Hiv In The Uk
- 94% of these people are diagnosed, and therefore know that they have HIV. This means that around 1 in 16 people living with HIV in the UK do not know that they have the virus.
- 98% of people diagnosed with HIV in the UK are on treatment, and 97% of those on treatment are virally suppressed which means they cant pass the virus on. Of all the people living with HIV in the UK, 89% are virally suppressed.
Historical Data For Selected Countries
HIV/AIDS in World from 2001 to 2014 adult prevalence rate data from CIA World Factbook
| HIV in World in 2014 |
|---|
| Region/Country |
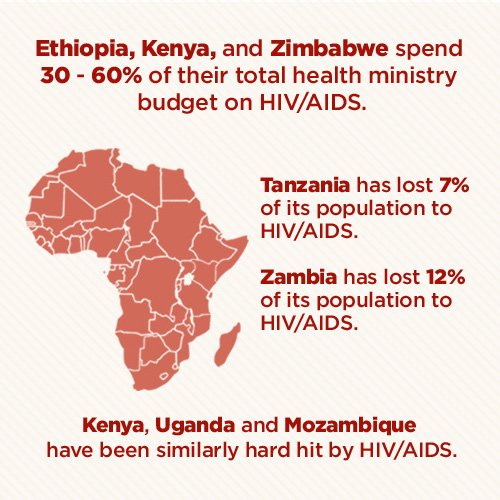
The pandemic is not homogeneous within regions, with some countries more afflicted than others. Even at the country level, there are wide variations in infection levels between different areas. The number of people infected with HIV continues to rise in most parts of the world, despite the implementation of prevention strategies, Sub-Saharan Africa being by far the worst-affected region, with an estimated 22.9 million at the end of 2010, 68% of the global total.
South and South East Asia have an estimated 12% of the global total. The rate of new infections has fallen slightly since 2005 after a more rapid decline between 1997 and 2005. Annual AIDS deaths have been continually declining since 2005 as antiretroviral therapy has become more widely available.
Don’t Miss: Does Nba Youngboy Have Aids
Who Is At Greater Risk Of Covid
A large study of risk factors for severe COVID-19, OPENSafely, looked at around 40% of GP patients in England before vaccines were available.
The study found that old age was by far the strongest risk factor. People over 80 were at least 20 times more likely to die from COVID-19 compared to people aged 50-59. People under 40 had a greatly reduced risk compared to the 50-59 age group.
An organ transplant raised the risk of death fourfold. A history of any form of blood cancer including cancer of the bone marrow or lymph nodes in the past five years raised the risk of death threefold. Any neurological condition, severe obesity or uncontrolled diabetes doubled the risk of death. Men were twice as likely to die as women.
Other risk factors such as Black or Asian ethnicity, social deprivation, liver disease, stroke, dementia and kidney disease raised the risk of death by between 50 and 75%, as did a severe respiratory disease other than asthma.
Chronic heart disease, controlled diabetes, a cancer diagnosis other than blood cancer more than one year ago, asthma, lupus, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, moderate obesity and smoking each raised the risk of death slightly.
People who have many of these risk factors are at far greater risk of dying from COVID-19 than people who have few risk factors, regardless of HIV status.
Aids Research And Society
In June 2001, the United Nations held a Special General Assembly to intensify international action to fight the HIV/AIDS pandemic as a global health issue, and to mobilize the resources needed towards this aim, labelling the situation a “global crisis”.
Regarding the social effects of the HIV/AIDS pandemic, some sociologists suggest that AIDS has caused a “profound re-medicalisation of sexuality“.
There has been extensive research done with HIV since 2001 in the United States, The National Institutes of Health which is an agency funded by the U.S department of Health and Human Services has substantially improved the health, treatment, and lives of many individuals across the nation. The human immunodeficiency virus is generally the precursor to AIDS. To this day there is no cure for this virus However, treatment, education programs, proper medical care, and support have been made available.
NIH, is coordinated by the Office of AIDS Research and this research carried out by nearly all the NIH Institutes and Centers, in both at NIH and at NIH-funded institutions worldwide. The NIH HIV/AIDS Research Program, represents the world’s largest public investment in AIDS research. Other agencies like the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases have also made substantial efforts to provide the latest and newest research and treatment available.
- Heterosexual men accounted for 8% of new HIV diagnoses.
- Heterosexual women accounted for 16% of new HIV diagnoses.
Don’t Miss: Hiv Causes Hair Loss
How Many People Have Died From Aids
Roughly 690,000 people died indirectly of AIDS in 2019.
This statistic is important because it showcases that AIDS does not represent a direct cause of death. Its rather the deficient immune system that is the main culprit, granted that a weak immune system is no longer capable of fighting disease and infection.
According to UNAIDS, an error margin must be taken into account. Hence, the real numbers are situated between 500,000 and 970,000.
Are People With Hiv At Higher Risk Of Severe Covid

The largest studies looking at the risk of severe illness have reached differing conclusions about the risk for people with HIV of being admitted to hospital or suffering severe illness due to COVID-19.
A global study conducted by the World Health Organization in 268,412 people in 37 countries, including just over 15,000 people living with HIV found that people with HIV were 13% more likely to be admitted to hospital with severe or critical COVID-19 after controlling for age, gender and co-morbidities.
In the United States, the National COVID Cohort Collaborative analysed COVID-19 cases up to February 2021 and found that people with HIV were at 32% higher risk of being admitted to hospital with COVID-19 and 86% higher risk of requiring mechanical ventilation.
Similarly, a US study which matched people with HIV admitted to hospital with COVID-19 to people without HIV by sex, race, body mass and underlying conditions found that people with HIV were 70% more likely to require in-patient care.
However, a study of COVID-19 admissions in major UK hospitals up to 31 May 2020 found that HIV status did not affect a personâs chances of improvement after admission, when the analysis controlled for severity of illness at admission, frailty, pre-existing conditions, age and ethnicity. Nor were people with HIV at greater risk of requiring mechanical ventilation.
There are no data on âlong COVIDâ in people with HIV.
Don’t Miss: Does Youngboy Really Have Herpes
Eastern Europe And Central Asia
There is growing concern about a rapidly growing epidemic in Eastern Europe and Central Asia, where an estimated 1.233.7 million people were infected as of December 2011, though the adult prevalence rate is low . The rate of HIV infections began to grow rapidly from the mid-1990s, due to social and economic collapse, increased levels of intravenous drug use and increased numbers of sex workers. By 2010 the number of reported cases in Russia was over 450,000 according to the World Health Organization, up from 15,000 in 1995 and 190,000 in 2002 some estimates claim the real number is up to eight times higher, well over 2 million.
Ukraine and Estonia also have growing numbers of infected people, with estimates of 240,000 and 7,400 respectively in 2018. Also, transmission of HIV is increasing through sexual contact and drug use among the young . Indeed, over 84% of current AIDS cases in this region occur in non-drug-using heterosexuals less than 26 years of age.
In most countries of Western Europe, AIDS cases have fallen to levels not seen since the original outbreak many attribute this trend to aggressive educational campaigns, screening of blood transfusions and increased use of condoms. Also, the death rate from AIDS in Western Europe has fallen sharply, as new AIDS therapies have proven to be an effective means of suppressing HIV.
Global Hiv & Aids Statistics Fact Sheet
GLOBAL HIV STATISTICS
- 28.2 million people were accessing antiretroviral therapy as of 30 June 2021.
- 37.7 million people globally were living with HIV in 2020.
- 1.5 million people became newly infected with HIV in 2020.
- 680 000 people died from AIDS-related illnesses in 2020.
- 79.3 million people have become infected with HIV since the start of the epidemic.
- 36.3 million people have died from AIDS-related illnesses since the start of the epidemic.
People living with HIV
- In 2020, there were 37.7 million people living with HIV.
- 36.0 million adults.
- 1.7 million children .
- 53% of all people living with HIV were women and girls.
People living with HIV accessing antiretroviral therapy
- As of 30 June 2021, 28.2 million people were accessing antiretroviral therapy, up from 7.8 million in 2010.
- In 2020, 73% of all people living with HIV were accessing treatment.
- 74% of adults aged 15 years and older living with HIV had access to treatment, as did 54% of children aged 014 years.
- 79% of female adults aged 15 years and older had access to treatment however, just 68% of male adults aged 15 years and older had access.
New HIV infections
AIDS-related deaths
COVID-19 and HIV
Key populations
Recommended Reading: Does Nba Youngboy Has Herpes