How Is Hiv Diagnosed
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved tests that detect HIV antibodies in urine, fluid from the mouth , or blood. If a test on urine or oral fluid shows that you are infected with HIV, you will probably need a blood test to confirm the results. If you have been exposed to HIV, your immune system will make antibodies to try to destroy the virus. Blood tests can find these antibodies in your blood.
Most doctors use a screening blood test. If the screening is positive , the blood sample is tested again to verify the result. If the second test is positive, a test called a Western blot is performed for further confirmation.
It may take as long as six months for HIV antibodies to show up in a blood sample. If you think you have been exposed to HIV but you test negative for it:
- Get tested again in six months to be sure you are not infected.
- Meanwhile, take steps to prevent the spread of the virus. If you are infected, you can still pass HIV to another person at this time.
Some people are afraid to be tested for HIV. But if there is any chance you could be infected, it is very important to find out. HIV can be treated. Getting early treatment can slow down the virus and help you stay healthy. And you need to know if you are infected so you can prevent spreading the infection to other people.
When To Get Tested
CBCs can provide information on a wide range of conditions and a persons overall health.
A doctor may order one during a routine checkup or if there are signs and symptoms of an underlying problem.
People undergoing treatment for chronic conditions may regularly visit a doctor for a CBC.
Anyone experiencing persistent symptoms should contact a doctor for a checkup.
What Is Being Tested
The complete blood count is a group of tests that evaluate the cells that circulate in blood, including red blood cells , white blood cells , and platelets . The CBC can evaluate your overall health and detect a variety of diseases and conditions, such as infections, anemia and leukemia.
Blood cells are produced and mature primarily in the bone marrow and, under normal circumstances, are released into the bloodstream as needed. The three types of cells evaluated by the CBC include:
Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells, also called erythrocytes, are produced in the bone marrow and released into the bloodstream when they mature. They contain hemoglobin, a protein that transports oxygen throughout the body. The typical lifespan of an RBC is 120 days. Thus, the bone marrow must continually produce new RBCs to replace those that age and degrade or are lost through bleeding. A number of conditions can affect the production of new RBCs and/or their lifespan, in addition to those conditions that may result in significant bleeding.
White Blood Cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes, are cells that exist in the blood, the lymphatic system, and tissues and are an important part of the bodyâs natural defense system. They help protect against infections and also have a role in inflammation, and allergic reactions. There are five different types of WBCs and each has a different function. They include neutrophils, lymphocytes, basophils, eosinophils, and monocytes.
Platelets
Read Also: How Do Anti Hiv Drugs Work
Could A Cbc Blood Test Illude To Hiv
The complete blood count measures the amount of these cells in a sample of your blood. CBCs are especially important for people living with HIV because some HIV drugs and some infections can cause changes in the number of red or white blood cells. Red blood cells Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body.
Is There Anything Else I Should Know
Many different conditions can result in increases or decreases in blood cell populations. Some of these conditions may require treatment, while others may resolve on their own.
Recent blood transfusions affect the results of the CBC.
Normal reference CBC values for babies and children are different from adults. The laboratory will supply the reference intervals for various age groups, and a healthcare practitioner will take these into consideration when interpreting data.
Read Also: How To Treat Hiv Patients
What Is Included In A Cbc
A CBC is typically performed using an automated instrument that measures various parameters, including cell counts and the physical features of some of the cells. A standard CBC includes:
Red blood cell tests:
- Red blood cell count is a count of the actual number of red blood cells in your blood sample.
- Hemoglobin measures the total amount of the oxygen-carrying protein in the blood, which generally reflects the number of red blood cells in the blood.
- Hematocrit measures the percentage of your total blood volume that consists of red blood cells.
- Red blood cell indices provide information on the physical features of the RBCs:
- Mean corpuscular volume is a measurement of the average size of your red blood cells.
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin is a calculated measurement of the average amount of hemoglobin inside your red blood cells.
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration is a calculated measurement of the average concentration of hemoglobin inside your red blood cells.
- Red cell distribution width is a measurement of the variation in the size of your red blood cells.
White blood cell tests:
Platelet tests:
What Are Hiv/aids Symptoms And Signs
- During the first few weeks of HIV infection, mononucleosis-like or flu-like symptoms may occur that include fever, body aches, headache, and rarely a brief rash that may not be noticed. Many people do not have any symptoms at all.
- Around seven or eight years after HIV infection on average, the person may begin to feel unwell. Signs of HIV infection in both men and women include swollen lymph glands, loss of energy, loss of appetite, and loss of weight. The person begins to develop frequent infections, progressing to more unusual infections, as the immune system begins to fail.
- After starting effective treatment for HIV, most people begin to feel much better within a few weeks. Within a few months, immune cells improve and may even normalize.
- It is important to remember that many people can have HIV infection for many years and be infectious to others without knowing it or even being aware that they were ever at risk for HIV. One in six people with HIV infection is aware of it.
Don’t Miss: Can Aids Be Treated Back To Hiv
What Is It Used For
A CD4 count may be used to:
- See how HIV is affecting your immune system. This can help your health care provider find out if you are at higher risk for complications from the disease.
- Diagnose AIDS
- The names HIV and AIDS are both used to describe the same disease. But most people with HIV don’t have AIDS. AIDS is diagnosed when your CD4 count is extremely low.
- AIDS is the most severe form of HIV infection. It badly damages the immune system and can lead to opportunistic infections. These are serious, often life-threatening, conditions that take advantage of very weak immune systems.
You may also need a CD4 count if you’ve had an organ transplant. Organ transplant patients take special medicines to make sure the immune system won’t attack the new organ. For these patients, a low CD4 count is good, and means the medicine is working.
Would A Cbc Show Signs Of Hiv
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
You May Like: Does Hiv Make You Lose Weight
First Things First: Tests To Confirm That Youre Pregnant
All pregnancy tests work by detecting a hormone in your blood or urine thats there only if youre pregnant. This hormone human chorionic gonadotropin is produced when a fertilized egg implants in your uterus.
There are two types of pregnancy tests:
- A urine test can be performed at your doctors office or with a home pregnancy test
- Urine tests can usually tell if youre pregnant about one week after a missed period
If a home pregnancy test shows that youre pregnant, call your doctor right away. He or she can use a more sensitive test along with a pelvic exam to confirm it. Plus, seeing your doctor early in your pregnancy helps you and your baby stay as healthy as possible .
What Does The Test Result Mean
A healthcare practitioner typically evaluates and interprets results from the components of the CBC together. Depending on the purpose of the test, a number of additional or follow-up tests may be ordered for further investigation.
For additional details, see the tables in the section Details on CBC Results below that briefly and generally explain what the result for each component of the CBC may mean.
To see an example of a CBC lab report, see this sample report.
You May Like: How Many People Have Hiv In Atlanta
Why Do Some Blood Tests Require Fasting
Everything you eat and drink contains vitamins, proteins, and other nutrients that can cause the related levels in your blood to temporarily spike or drop.
Fasting for 812 hours helps ensure that blood test results are free from these variables, making your test results as accurate as possible.
Some common tests that may require fasting include:
- cholesterol tests
Results may take anywhere from a few hours to a few days to become available. Heres an overview of how long some common tests may take:
- complete blood count : 24 hours
- basic metabolic panel: 24 hours
- complete metabolic panel: 2472 hours
- lipid panel: 24 hours.
This can depend on the specific lab where you get tested or how many tests you get done at once. If you order multiple tests, you may not get the complete results until all of the tests are completed.
Sometimes a lab will only release results to your doctor, who reviews them and then releases them to you.
What Do The Results Mean

CD4 results are given as a number of cells per cubic millimeter of blood. Below is a list of typical results. Your results may vary depending on your health and even the lab used for testing. If you have questions about your results, talk to your health care provider.
- Normal: 500â1,200 cells per cubic millimeter
- Abnormal: 250â500 cells per cubic millimeter. It means you have a weakened immune system and may be infected with HIV.
- Abnormal: 200 or fewer cells per cubic millimeter. It indicates AIDS and a high risk of life-threatening opportunistic infections.
While there is no cure for HIV, there are different medicines you can take to protect your immune system and can prevent you from getting AIDS. Today, people with HIV are living longer, with a better quality of life than ever before. If you are living with HIV, it’s important to see your health care provider regularly.
You May Like: How Is Hiv Test Done
What Is A Cbc
When you visit a clinic setting for any sort of complaint, the first blood test and the most common investigation of choice is a Complete Blood Count.
CBC or a Complete Blood Count or a Full Blood Count is a test performed for quantitative and qualitative analysis of blood cells present in circulation. A complete blood count also helps one to know what the hemoglobin count of a person is.
Although a complete blood count test may seem very basic, it is often the simplest and most economical test to evaluate the health status of any individual.
Routine Tests During Pregnancy
Certain lab tests are part of routine care during pregnancy. Some of these tests are done with a blood sample. Others use a urine sample or a sample of tissue taken from your vagina, cervix, or rectum. These tests can help find conditions that may increase the risk of complications for you and your fetus. Many problems found by these tests can be treated during pregnancy.
Don’t Miss: What Happens When Hiv Enters The Body
What Do Sti Tests Check For
A quick STI check-up will test for the four most common sexual infections: chlamydia, gonorrhea, HIV and syphilis. Youll need to provide a urine sample or swab sample and also a blood sample. The online STI testing kits are discreet, quick and can be ordered to your home you can get the results quickly too.
Why Do I Need A Cd4 Count
Your health care provider may order a CD4 count when you are first diagnosed with HIV. You will probably be tested again every few months to see if your counts have changed since your first test. If you are being treated for HIV, your health care provider may order regular CD4 counts to see how well your medicines are working.
Your provider may include other tests with your CD4 count, including:
- A CD4-CD8 ratio. CD8 cells are another type of white blood cell in the immune system. CD8 cells kill cancer cells and other invaders. This test compares the numbers of the two cells to get a better idea of immune system function.
- HIV viral load, a test that measures the amount of HIV in your blood.
Read Also: What Is The Best Hiv Early Detection Test
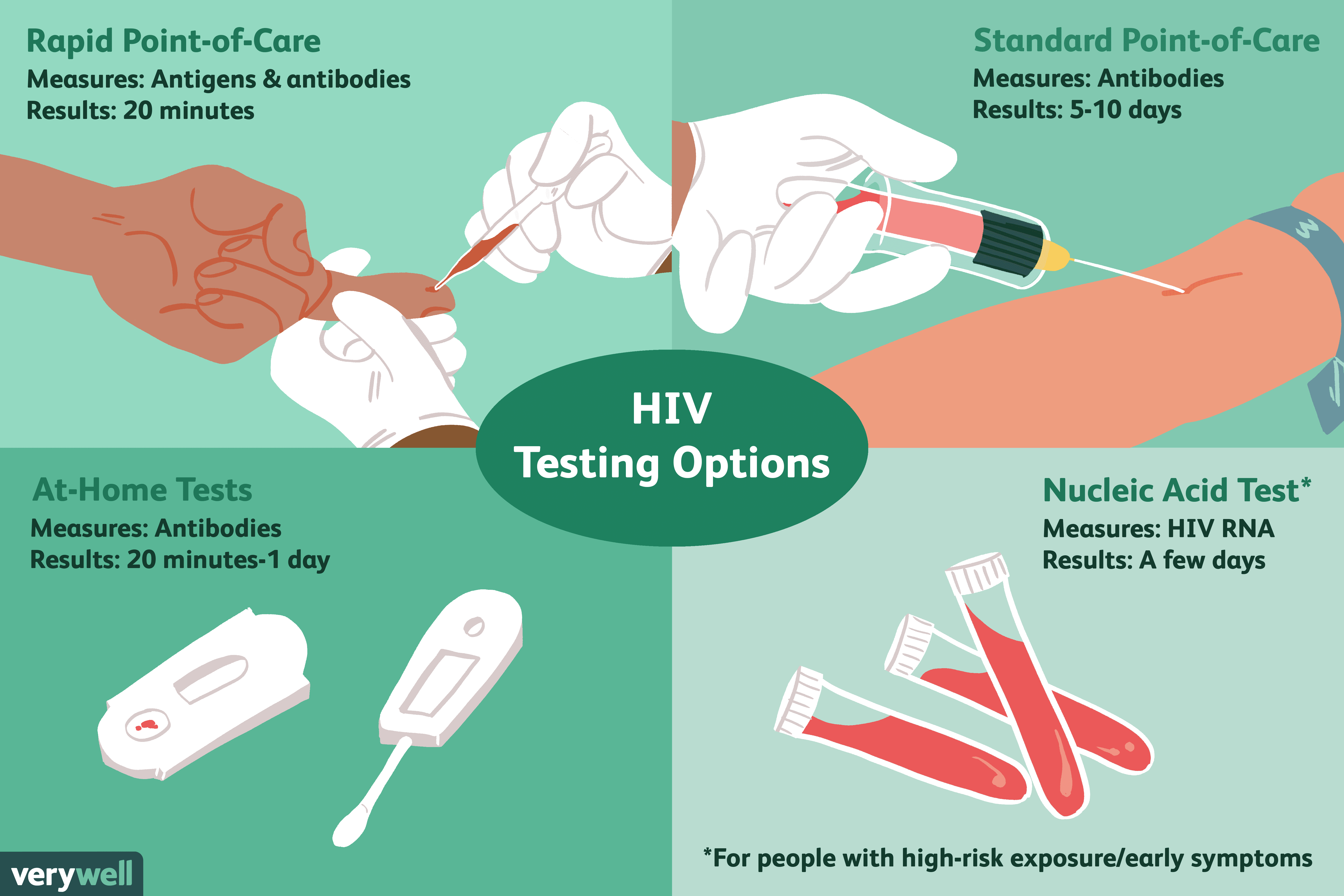
Is Hiv Test Accurate After 3 Weeks
This type of test measures antibodies to HIV. The body can take up to three months to produce these antibodies. Most people will have enough antibodies to test positive within three to 12 weeks after contracting HIV. At 12 weeks, or three months, 97 percent of people have enough antibodies for an accurate test result.
Lab Tests Are Important Tools
Having regular lab tests is necessary to care for your health. If you are living with HIV , you will probably have several such tests done. The complete blood count and blood chemistry tests described below check your overall health, including whether you have side effects from your HIV medications. See our fact sheets on Understanding CD4 Cells and CD4 Cell Tests and Understanding Lab Tests II: Viral Load, Resistance, and Tropism for information on other tests that your health care provider may order.
You May Like: How Is Hiv Not Transmitted
Hiv And Your Complete Blood Count
If you have HIV, your healthcare provider will routinely perform blood tests to evaluate the status of your immune system and the level of viral activity in your body .
In addition to these tests, others will be performed to monitor for side effects or medical issues arising from the infection itself. Central to this is a panel of tests called the complete blood count . The test measures the composition of cells in a sample of blood to flag for changes that fall outside of the “normal” range of values.
By doing so, a CBC can reveal if an infection is developing or if an antiretroviral drug like AZT is causing anemia.
A CBC measures constituent cells in your blood, including white blood cells , red blood cells , and platelets . The test is typically ordered every three to six months but may be ordered more frequently if there is an active infection or illness.
Testing For Birth Defectsexpand All
- What is the first step to screen for birth defects during pregnancy?
Screening for birth defects begins by assessing your risk factors. Early in your pregnancy, your obstetriciangynecologist may give you a list of questions to find out whether you have risk factors. If you do have risk factors, you might want to see a genetic counselor for more detailed information about your risks.
- What factors increase the risk of birth defects?
Most babies with birth defects are born to couples without risk factors. But the risk of birth defects is higher when certain factors are present. Risk factors include
-
having a personal or family history of birth defects
-
belonging to certain ethnic groups
-
being 35 or older
Also Check: What Does The Hiv Virus Look Like
What Is Hiv What Is Aids
HIV is a virus that attacks the immune system, the bodys natural defense system. Without a strong immune system, the body has trouble fighting off disease. Both the virus and the infection it causes are called HIV.
White blood cells are an important part of the immune system. HIV invades and destroys certain white blood cells called CD4+ cells. If too many CD4+ cells are destroyed, the body can no longer defend itself against infection.
The last stage of HIV infection is AIDS . People with AIDS have a low number of CD4+ cells and get infections or cancers that rarely occur in healthy people. These can be deadly.
Having HIV does not mean you have AIDS. Even without treatment, it takes a long time for HIV to progress to AIDSusually 10 to 12 years. If HIV is diagnosed before it becomes AIDS, medicines can slow or stop the damage to the immune system. With treatment, many people with HIV are able to live long and active lives.