Us Response To The Global Epidemic
The U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief is the U.S. Governments response to the global HIV/AIDS epidemic and represents the largest commitment by any nation to address a single disease in history. Through PEPFAR, the U.S. has supported a world safer and more secure from infectious disease threats. It has demonstrably strengthened the global capacity to prevent, detect, and respond to new and existing riskswhich ultimately enhances global health security and protects Americas borders. Among other global results, PEPFAR provided HIV testing services for nearly 50 million people in Fiscal Year 2020 and, as of September 30, 2020, supported lifesaving ART for nearly 18.2 million men, women, and children.
In addition, the National Institutes of Health represents the largest public investment in HIV/AIDS research in the world. NIH is engaged in research around the globe to understand, diagnose, treat, and prevent HIV infection and its many associated conditions, and to find a cure.
Hiv Doesnt Always Progress To Stage 3
HIV is a virus, and AIDS is the condition the virus may cause. An HIV infection doesnt necessarily progress to stage 3. In fact, many people with HIV live for years without developing AIDS. Thanks to advances in treatment, a person living with HIV can expect to live a near-normal life span.
While a person can have an HIV infection without having AIDS, anyone diagnosed with AIDS has already contracted HIV. Because there is no cure, the HIV infection never goes away, even if AIDS never develops.
The Future Of Hiv In South Africa
South Africa has made great strides in tackling its HIV epidemic in recent years and now has the biggest HIV treatment programme in the world. Moreover, these efforts are now largely funded from South Africa’s own resources.
HIV prevention initiatives are having a particularly significant impact on mother-to-child transmission rates, which are falling dramatically. New HIV infections overall have fallen by half in the last decade, however there are still too many. For certain population groups, such as transgender women, a lack of data is hampering HIV prevention efforts. In addition, the criminalisation of at-risk groups such as sex workers, and widespread gender inequity particularly gender-based violence continues to fuel transmission.
While the short term financing of South Africa’s HIV epidemic is secure, in the longer term, the government needs to explore other strategies in order to sustain and expand its progress.
Also Check: How Do Antiviral Drugs Treat Hiv
Countries With The Highest Rates Of Hiv/aids
Human Immunodeficiency Virus is a virus that weakens the human immune system, sometimes leading to AIDS. If detected early, HIV can be managed to prevent it from progressing to the final stage of AIDS. HIV attacks CD4 cells exposing the infected person to opportunistic infections. Proper diagnosis, treatment, and medical care are essential factors to effective management and control of AIDS which has no permanent cure. While HIV is majorly a sexually transmitted disease, the virus can be transmitted through blood transfusion and during birth or breastfeeding, as well as through a few other means.
Funding For Hiv In South Africa
South Africa largely funds its HIV programmes domestically, only receiving 12% of its HIV funding from external sources in 2018.126
South Africas National Strategic HIV, STI and TB Plan 2017-2022 is predicted to cost 207 billion rand in total. In light of this, in 2017 the South African government increased its budget allocation for HIV and AIDS, despite general budget reductions across the health sector.127
Still the South African National AIDS Council has predicted there will be some funding gaps. However, it is unclear how severe these will be, especially since there is a level of uncertainty around the availability of international funding for HIV and AIDS in the coming years.128
An encouraging sign came with the announcement from the US Presidents Emergency for AIDS Relief that it will be providing 10 billion rand in funding for 2019/2020, an increase from 2018 and 2017 funding levels.129
Treatment and care make up the biggest proportion of the costs, outlined in the NSP. In recent years South Africa has been working hard to negotiate better prices for ARVs, having previously been paying more than most other low- and middle-income countries despite having the worlds largest procurement programme.130 In September 2017 UNAIDS announced a breakthrough pricing agreement, which will allow the single pill regime of Dolutegravir to be sold at around $75 per person per year in south Africa and 90 other low- and middle-income countries.131
Recommended Reading: What Borough Has The Highest Hiv Rate
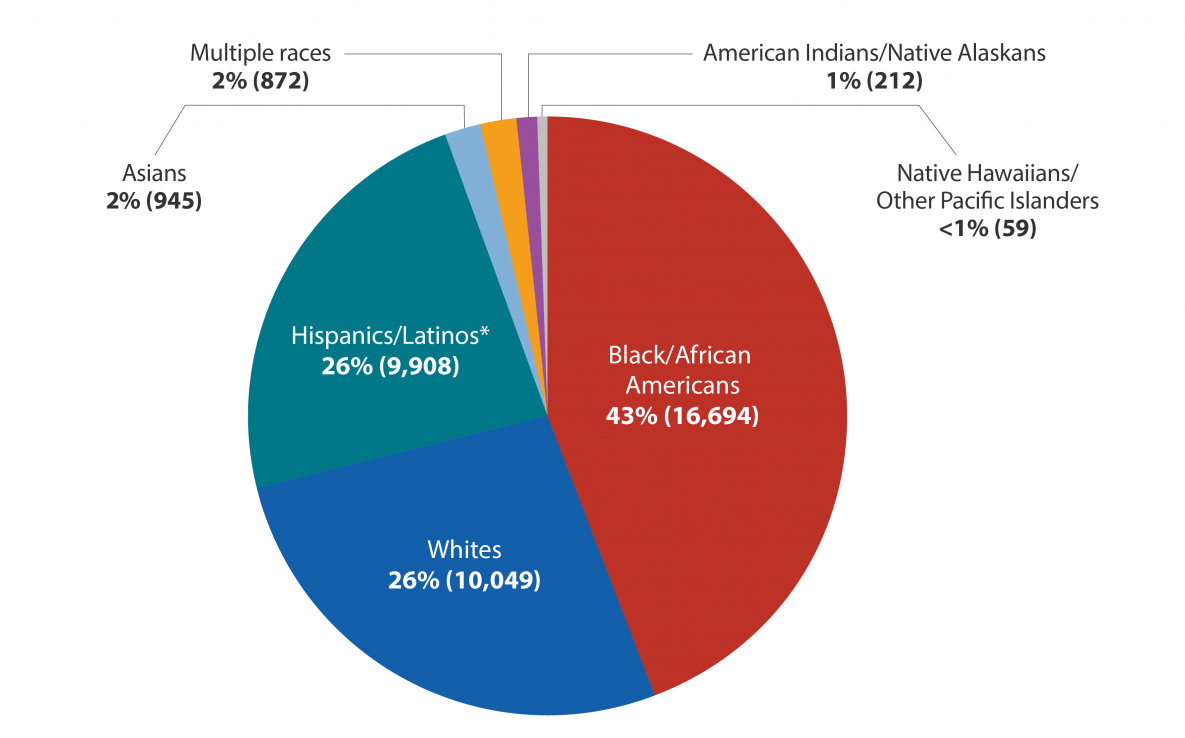
Hiv Deaths In The United States
In the United States, no less than 675,000 Americans have died since the first cases were diagnosed back in 1981. In 2018, approximately 1.2 million Americans were estimated to be living with the disease. From 2014 to 2018, HIV diagnoses decreased by about 7%, but that number varied depending on the region.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , there were 15,820 deaths in people with HIV in the United States in 2018.That’s a significant decrease from the over 50,000 deaths reported at the height of the epidemic in 1995.
Despite the advances, there remains a clear disparity in the populations affected by the disease in the United State. Among some the key risk factors affecting mortality rates are geography, sexuality, and race.
Hiv Diagnoses In Canada
How many people are newly diagnosed with HIV in Canada each year?
There were 2,122 HIV diagnoses in Canada in 2019. This represents a 4% increase over the past 5 years .
Among new HIV diagnoses in 2019 where sex was known , 30.2% were in females and 69.8% were in males.
Among the HIV diagnoses in adults where the likely exposure is known , 39.7% were in gbMSM, 28.3% were from heterosexual sex and 21.5% were in PWID in 2019.
Among females, 38.4% of HIV diagnoses were in women who injected drugs and 48.0% were from heterosexual sex in 2019.
Among males, 56.2% were in gbMSM, 4.8% were among gbMSM who also injected drugs, 14.6% were in men who injected drugs and 20.0% were from heterosexual sex in 2019.
Just over a quarter of all HIV diagnoses in males were in male youth in 2019. Just under a quarter of all HIV diagnoses in females were in female youth in 2019
Where are HIV diagnoses rates the highest?
There are four provinces with HIV diagnoses rates above the national average of 5.6 per 100,000 people in 2019:
- Saskatchewan
- Manitoba
- the territories
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know You Have Hiv Aids
Civil Society’s Role In South Africa
In March 2015 an estimated 136,453 civil society organisations were working in the South African HIV response. In 2017 a new civil society forum was created to provide a platform for civil society and government to work together in the HIV response. 116
One of the most visible civil societies is the Treatment Action Campaign , formed in 1998. TAC has been a driving force in the South African response, promoting access to HIV treatment and care for all South Africans. TACs first major success came in 2002, with the Constitutional Court ruling that the South African government must provide ARVs to prevent mother-to child-transmission.117 The organisation is currently campaigning to improve and strengthen the healthcare system.118
Funding is a major issue facing many civil society organisations. Drops in external funding are making civil society organisations more dependent on financing from the government. While domestic funding is a more sustainable model, the shift has increased competition amongst organisations, and is seen by some as undermining their ability to challenge government policy in their work.119
Condom Use And Distribution
In the most recent NSP, the South African National AIDs Council aimed to increase the number of male condoms distributed annually to 850 million by 2018.83 However, between 2016/17 and 2017/18 the number of male condoms distributed by the government decreased by more than 220 million.84
South Africas female condom programme is also one of the biggest and most established in the world, with over 26 million female condoms distributed in 2016.85 By 2022, the South African National AIDS Council hopes to increase this to 40 million.86
In regards to condom use, South Africas 2017 national HIV impact survey found around 56% of adults with two or more sexual partners in the last year reported using a condom the last time they had sex. Men and women aged between 25 and 49 had similar levels of condom use, at around 53%. Among young people , 68% of young men with multiple partners reported using a condom the last time they had sex, compared to 47% of young women. In contrast, only 33% of older adults with multiple partners used condoms at last sex.87
Challenges remain in ensuring that condom programmes are able to serve all groups, particularly those with higher HIV risk. The new strategy will expand condom distribution, making them available at non-traditional outlets such as hair salons, petrol stations, shops, hotels, truck stops and brothels as well as secondary schools and non-traditional community settings.88
Also Check: How To Take Hiv Test At Home
How To Prevent Hiv From Advancing To Aids
AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV. The best way to avoid AIDS is to start antiretroviral therapy as soon as possible. Taken every day as prescribed, these drugs will keep you healthy and make your viral level so low, it canât be detected. Sticking to the right treatment can keep AIDS at bay for years and decades. It also practically eliminates the chances that youâll pass HIV to your sexual partners and others. Many HIV-positive people live normal life spans.
Hiv And Aids In South Africa
KEY POINTS
- South Africa has the biggest HIV epidemic in the world, with 7.7 million people living with HIV.
- HIV prevalence among the general population is high at 20.4%. Prevalence is even higher among men who have sex with men, transgender women, sex workers and people who inject drugs.
- South Africa has made huge improvements in getting people to test for HIV in recent years. It has now met the first of the 90-90-90 targets, with 90% of people living with HIV aware of their status in 2018.
- The country has the worlds largest ART programme, which has undergone further expansion with the implementation of test and treat guidelines.
- South Africa was the first country in sub-Saharan Africa to fully approve PrEP, which is now being made available to people at high risk of infection.
Explore this page to find out more about , , , , , , and .
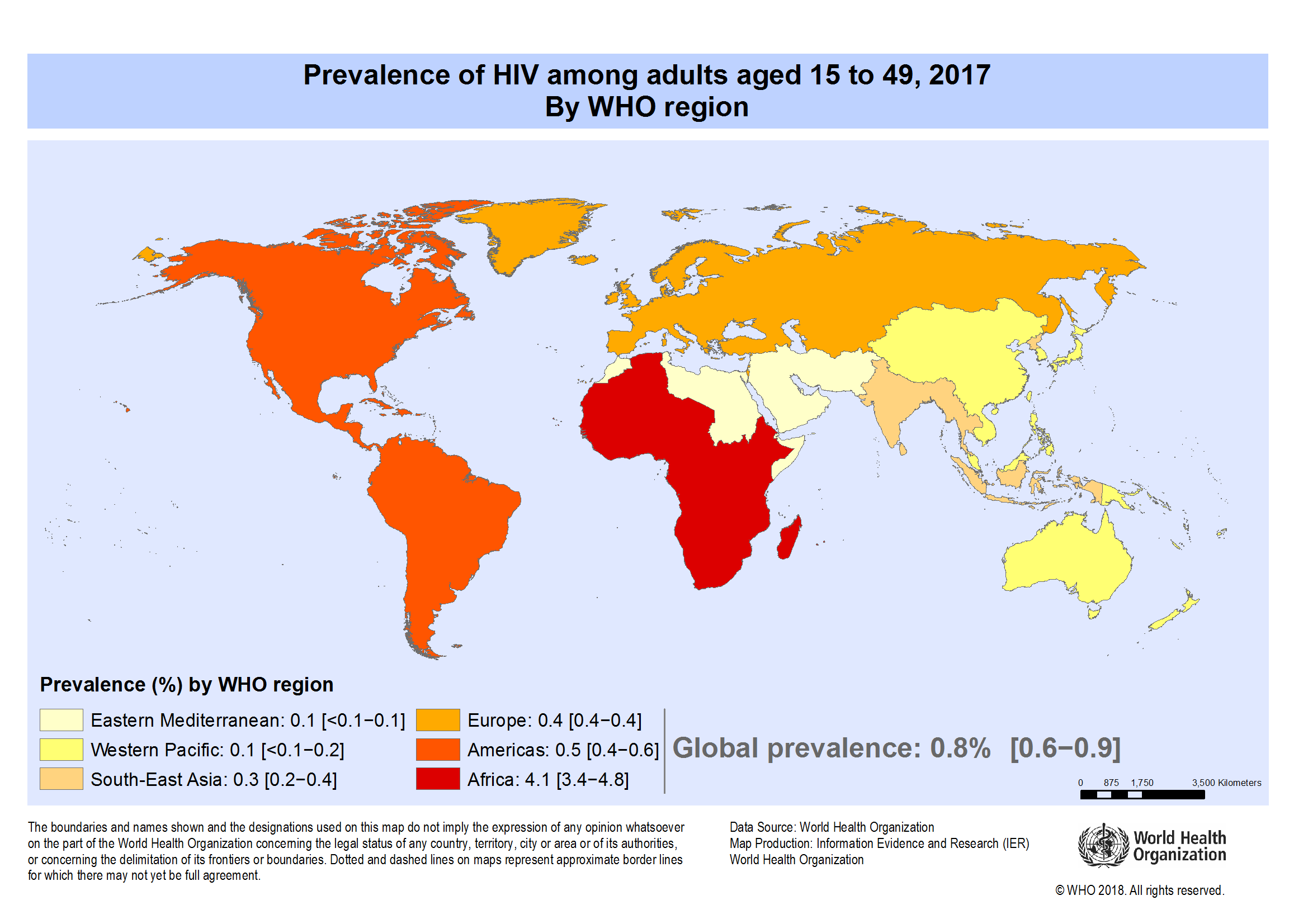
South Africa has the biggest and most high-profile HIV epidemic in the world, with an estimated 7.7 million people living with HIV in 2018.1
South Africa accounts for a third of all new HIV infections in southern Africa.2 In 2018, there were 240,000 new HIV infections and 71,000 South Africans died from AIDS-related illnesses.3
HIV prevalence remains high, with 20.4% of people living with HIV.7 However prevalence varies markedly between regions, ranging from 12.6% in Western Cape to 27% in KwaZulu-Natal.8
You May Like: How Many People Die From Hiv Each Year
Changing Attitudes About Hiv
When someone is diagnosed with HIV, other people may have negative attitudes and beliefs about that person’s behaviour, lifestyle or circumstances in life. These negative associations form what’s called stigma, an experience that can decrease quality of life because it includes:
- judging
Efforts to end stigma will help to:
- prevent new infections
- ensure that people living with HIV receive the care, treatment and support they need
Hiv Infection Can Be Diagnosed By A Simple Test
On HIV transmission, the immune system produces antibodies against the virus. A blood or saliva test can detect those antibodies to determine if the virus is present. It can take several weeks after transmission for the HIV antibody test to come back positive.
Another test looks for antigens, which are proteins produced by the virus, and antibodies. This test can detect HIV just days after infection.
Both tests are accurate and easy to administer.
Read Also: When Did Hiv Start In The Us
What You Can Do To Reduce Stigma
You can help reduce stigma by being respectful, compassionate and non-judgemental. Model this behaviour for others when you witness stigmatizing behaviours.
When talking about HIV, certain terms can be stigmatizing. Be thoughtful about the words you use when discussing the topic.
Learn more about the facts of HIV. Treatment can lower the amount of virus in a person’s blood to a level that’s too low to be measured on a standard blood test. This means it’s undetectable.
People living with HIV on treatment who maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their sexual partners.
Knowing and sharing these facts widely can help to reduce stigma. Share our Undetectable = Untransmittable infographic to help us raise awareness.
In addition, HIV is not transmitted through:
- healthy, unbroken skin
Treatment And Life Expectancy
If HIV develops into stage 3 HIV, life expectancy drops significantly. Its difficult to repair damage to the immune system at this point. Infections and other conditions, such as certain cancers, resulting from severe immune system impairment are common. However, with successful antiretroviral therapy and some immune system recovery, many people with stage 3 HIV live long lives.
With todays treatments for HIV infection, people can live with HIV and never have AIDS develop. Its also important to note that successful antiretroviral treatment and a sustained undetectable viral load greatly lowers the risk of transmitting the virus to a partner.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hiv Without Having Sex
Hiv Vs Aids: Whats The Difference
Overview
It can be easy to confuse HIV and AIDS. They are different diagnoses, but they do go hand-in-hand: HIV is a virus that can lead to a condition called AIDS, also known as stage 3 HIV.
At one time, a diagnosis of HIV or AIDS was considered a death sentence. Thanks to research and the development of new treatments, people with HIV at any stage today are living long, productive lives. An HIV-positive person who adheres to regular antiretroviral treatment can expect to live a near-normal life span.
Hiv And Aids Diagnosis
HIV tests check your blood or fluid from your mouth for antibodies that your body makes in response to the virus. You can take them at a doctorâs office, a community health center, a hospital, or at home.
When you have HIV, your doctor will keep an eye on how much of the virus is in your system. You might hear them call it your âviral load.â Two things will tell them if your infection has become AIDS:
- Your CD4 count. A person with a healthy immune system has 500 to 1,600 CD4 cells in a cubic millimeter of their blood. A person with AIDS has fewer than 200. This number is called your âCD4 count.â
- AIDS-defining infections. These are also called opportunistic infections. These generally happen in people who have a CD4 count below 200. Viruses, bacteria, or fungi that donât usually make healthy people sick can cause these infections in someone with HIV or AIDS.
How long it takes HIV to become AIDS is different for everyone. If you donât get treatment, it might take 10 to 15 years. With treatment, you may never have AIDS.
Read Also: What Does Hiv Do To The Human Body
How Common Is Hiv In The Uk
The most recent estimate suggests there were 105,200 people living with HIV in the UK in 2019. Of these, around 6,600 are undiagnosed so do not know they are HIV positive.
London continues to have the highest rates of HIV in the country: 36% of new diagnoses in 2019 were in London residents and 38% of people seen for HIV care were living in London.
Anyone can get HIV but people from some groups or parts of the world are more likely to be affected. In particular, men who have sex with men and black African people are disproportionately affected.
Of the 4,139 people diagnosed with HIV in the UK in 2019, 41% were gay or bisexual men.
Of the 1,559 heterosexual people diagnosed with HIV in 2019, 37% were black African men and women.
In 2017, the overall mortality rate for people aged 15-59 who were diagnosed early was, for the first time, equal to that of the general population for the same age group.
Aids Diagnosis Is More Complicated
AIDS is late stage HIV infection. Healthcare providers look for a few factors to determine if HIV latency has progressed to stage 3 HIV.
Because HIV destroys immune cells called CD4 cells, one way healthcare providers diagnose AIDS is to do a count of those cells. A person without HIV can have anywhere from 500 to 1,200 CD4 cells. When the cells have dropped to 200, a person with HIV is considered to have stage 3 HIV.
Another factor signaling that stage 3 HIV has developed is the presence of opportunistic infections. Opportunistic infections are diseases caused by viruses, fungi, or bacteria that would not make a person with an undamaged immune system sick.
You May Like: Can Hiv Be Spread By Saliva
Is Canada Reaching The Global 90
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS and the World Health Organization have established a global health sector strategy on HIV to help eliminate AIDS as a public health threat by 2030. Canada has endorsed this strategy. The strategy can be encapsulated in the phrase 90-90-90 and consists of the following targets for the year 2020:
- 90% of people with HIV know their infection status
- 90% of people diagnosed with HIV receive HIV treatment
- 90% of people taking treatment have an undetectable viral load
Canada is approaching the 90% goal for awareness of HIV status and the 90% goal for treatment and has surpassed the 90% goal for achieving viral suppression. Of the estimated 62,050 people with HIV in Canada in 2018, an estimated:
- 87% were diagnosed and aware they had HIV
- 85% of those who were diagnosed were on treatment
- 94% of those on treatment had achieved viral suppression
This means that 70% of all Canadians with HIV had achieved viral suppression in 2018. If all 90-90-90 measures had been reached, 73% of all Canadians with HIV would have achieved viral suppression.