Is There Anything Else I Should Know
The HTLV-I/II viruses become inactive in the body after an infection, but they are never totally eradicated. For this reason, a person who has tested positive will not be able to donate blood.
HTLV-II antibodies may show a positive result on a test for HTLV-I antibodies . This means that even though a person has really had an HTLV-II infection, initial testing may show an HTLV-I positive test result.
When To Take A Rapid Hiv Test
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , everyone between 13 and 64 years old should be tested for HIV at least once in their life. People who have sex without condoms, have multiple sexual partners, or share drug equipment are at higher risk for HIV and should be tested more frequently, whether through regular or rapid testing.
If you think youve been exposed to HIV within the past 72 hours, contact your healthcare provider or medical professional about post-exposure prophylaxis, which is medication that can prevent HIV after a possible exposure.
After someone has been infected with the virus it can take about two weeks for HIV antigen to be detectable with current antigen tests, and more than three weeks to produce enough HIV antibodies to be detected by antibody tests. In a very small number of people, the process takes up to several months.
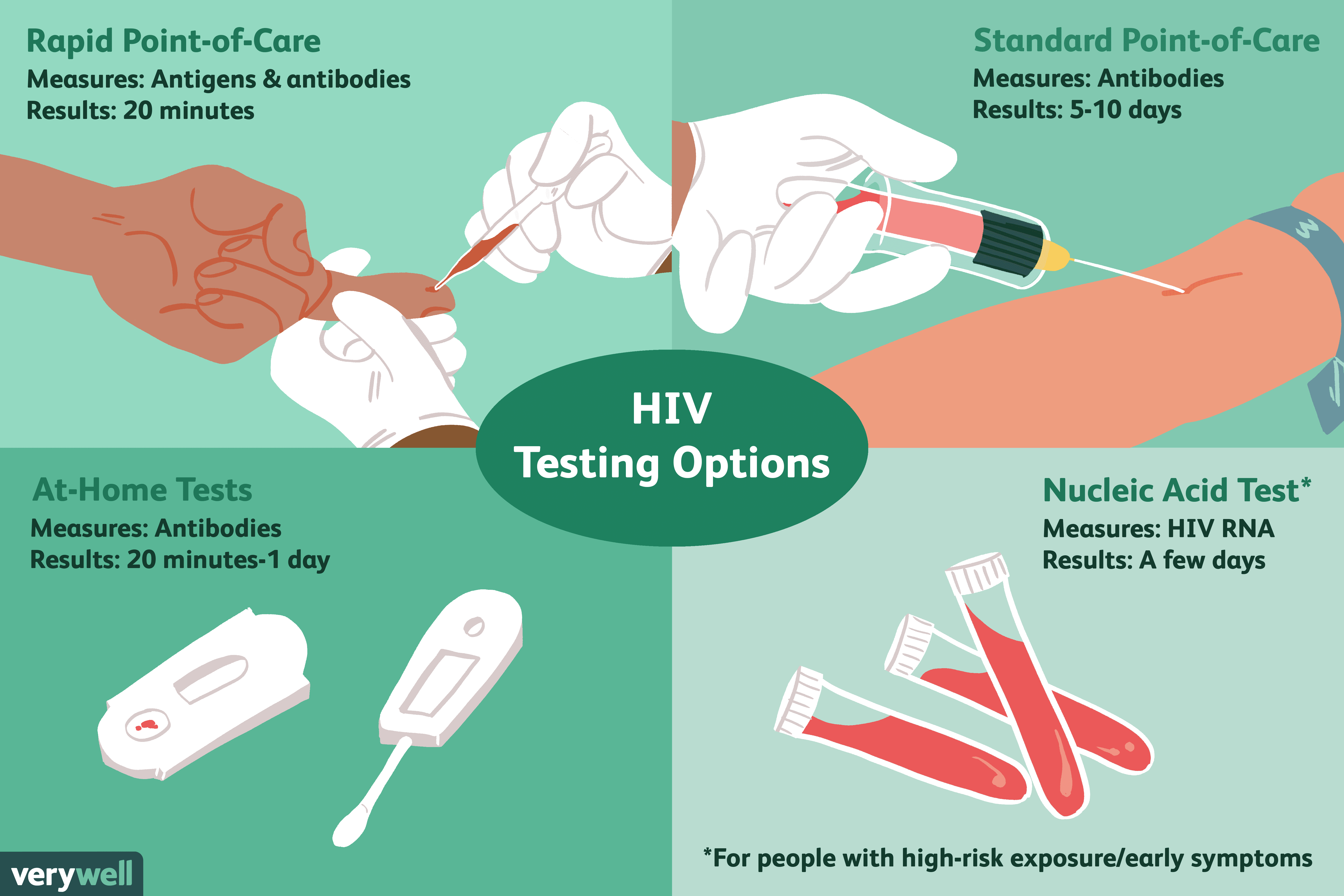
There are different window periods for different types of tests:
- Antigen and antibody tests take blood from a vein, and can detect HIV between 18 and 45 days after exposure
- Antigen and antibody tests done with blood from a finger prick can detect HIV between 18 and 90 days after exposure
- Antibody tests can take 23 to 90 days after an exposure to detect HIV. Most rapid tests and self-tests are antibody tests. In general, antibody tests that use blood from a vein can detect HIV sooner after infection than tests done with blood from a finger prick or with oral fluid
Screening Donor Blood And Cellular Products
Tests selected to screen donor blood and tissue must provide a high degree of confidence that HIV will be detected if present ” rel=”nofollow”> sensitivity is required). A combination of antibody, antigen and nucleic acid tests are used by blood banks in Western countries. The World Health Organization estimated that, as of 2000, inadequate blood screening had resulted in 1 million new HIV infections worldwide.
In the US, the Food and Drug Administration requires that all donated blood be screened for several infectious diseases, including HIV-1 and HIV-2, using a combination of antibody testing and more expeditious nucleic acid testing . These diagnostic tests are combined with careful donor selection. As of 2001, the risk of transfusion-acquired HIV in the US was approximately one in 2.5 million for each transfusion.
You May Like: Nba Youngboy Std
Factors Influencing Health Status And Contact With Health Servicesnote
The Names Htlv And Hiv Look And Sound Similar Are These Diseases Related
They both belong to the same group of viruses known as retroviruses and can be passed through blood and sexual contact, but they are only very remotely related, and HTLV does NOT cause AIDS and does not have the same devastating effects on a persons immune system that HIV does.
HTLV and HIV do, however, share a historical naming convention. HTLV-III was the name given to HIV when it was first identified. The virus was later reclassified and the name was changed to HIV. Since that time, the term HTLV-III has been re-used to designate a different HTLV virus. The newly designated HTLV-III virus, as well as an HTLV-IV virus, have been identified and are being studied, but testing of them is only being done on a research basis.
Recommended Reading: How Long Before Hiv Turns Into Aids
Advice For Coding And Documenting Hiv
National HIV Testing Day is June 27.
Wednesday is National HIV Testing Daya day designated to highlight the importance of testing in detecting, treating, and preventing human immunodeficiency virus infection.
This special day is designed to encourage people to get tested for HIV, know their status, and get linked to care and treatment if they have HIV. This years theme, Doing It My Way, Testing for HIV, reminds us that each person has his or her own reasons why they test for HIV, and their own unique ways of doing so.
About 1.1 million people in the United States have HIV, and one in seven of them dont know it. Many people have HIV for years before they get a diagnosis. For those living with undiagnosed HIV, testing is the first step in maintaining a healthy life and reducing HIV transmission. Thus, awareness of HIV infection through HIV testing is the first step to social services that improve life quality and length of survival.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend to healthcare providers that they:
- Routinely provide HIV testing to all people ages 13 to 64, in accordance with CDC guidelines.
- Screen all teens and adults for HIV risk and test people at high risk at least once a year. This includes some gay and bisexual men who may benefit from more frequent testing .
- Start people on HIV treatment as quickly as possible after diagnosis.
Ask A Laboratory Scientist
This form enables patients to ask specific questions about lab tests. Your questions will be answered by a laboratory scientist as part of a voluntary service provided by one of our partners, American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science. Please allow 2-3 business days for an email response from one of the volunteers on the Consumer Information Response Team.
Recommended Reading: How Long Can Aids Be Dormant
Pretest And Posttest Counseling
Pretest and posttest counseling can be done by nonmedical personnel. Pretest counseling can be completed in person, via prerecorded video, or pamphle,t and takes less than 20 minutes. Counseling protocols and counselor prompt cards are available on the CDC website. A system for posttest referrals needs to be prearranged for patients with positive rapid test results to facilitate follow-up.
If HIV seropositivity is expected, patients whose test results are positive with rapid HIV tests should be told they likely have HIV and need further confirmatory testing. If HIV is not likely, a patient with a positive rapid test result should be counseled that he or she may have HIV but that a confirmatory test is necessary. Patients are expected to be anxious after learning rapid HIV test results.
Patients with a high suspicion for acute HIV infection and a probable false-negative rapid HIV test result should have HIV RNA viral load testing done and should be referred for follow-up HIV ELISA testing. Remember that during acute HIV infection, the ELISA test usually will be negative.
Protect patient confidentiality. Patients may not have informed family members or friends of their risk behaviors or diagnosis.
Consequences Of Antenatal Testing
The primary purpose of AND is to relieve parents of anxiety over inheriting a genetic disease, or giving birth to a child with congenital abnormalities , and this is the major outcome. AND is defined as intended to inform parents of the birth of an affected infant, to allow in utero treatment, or delivery at a special centre for immediate postnatal treatment, or to allow termination of an affected fetus in practice the last of these three has become the most used course of action. Many writers have criticised this attitude as wrong. Among the argument put forward is that wide acceptance of selective abortion diminishes the importance of and the motivation for, research on cures for genetic disorders, whether in utero or after birth to be taken up.
Also Check: Nba Youngboy Truth About Herpes
What Is Encounter Screening
EncounterscreeningScreening
. Correspondingly, what does encounter for screening mean?
Z12 Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasms. Page 1. Z12 Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasms. Screening is the testing for disease or disease precursors in asymptomatic individuals so that early. detection and treatment can be provided for those who test positive for the disease.
One may also ask, what is Encounter for screening for lipoid disorders? Encounter for screening for lipoid disordersZ13. 220 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Correspondingly, what is diagnosis code z13 220?
Z13. 220 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of encounter for screening for lipoid disorders. A ‘billable code‘ is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
How will a coder recognize if a test is a screening or diagnostic test?
A screening test is given to those who have no symptoms of the condition in question. An example would be measurement of cholesterol levels in people who have no symptoms of cardiovascular disease. A diagnostic test is used to confirm a suspected condition once initial testing has revealed its possibility.
Who Should Get An Hiv Test
The CDC recommends that everyone in the United States between the ages of 13 and 64 get tested for HIV at least once.
You should be tested more often — at least once a year — if youâre at higher risk of getting HIV, including if you:
- Have had several sexual partners
- Had unprotected sex with someone who is or could be HIV-positive, including someone whose sexual history you don’t know
- Injected drugs with a needle, syringe, or other device that someone else used first
- Have had or are getting tested for tuberculosis, hepatitis, or any sexually transmitted disease, including syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, or herpes
- Have had sex for drugs or money
- Had sex with someone who has a history of any of these
Also Check: Jania Has Herpes
Aims Of Antenatal Testing
ANS services are based on population screening to identify people with a genetic risk, or a risk of having a child with a congenital or genetic disorder . In the Dutch Health Council report on genetic screening, the major aim is defined as: “To enable people to decide upon a course of action that is acceptable for them” . ANS includes:
1. Screening for sporadic conditions affecting the fetus
2. Family history for genetic risks
3. Population screening for carriers of common recessively inherited diseases.
Different health authorities in different countries have pointed out various aspects of ANS. While the Danish Health Council considers screening as a community-based form of help based on the obligation to help the weak, the Nuffield Council on Bioethics points out that, although the primary aim seems to be to improve the health of persons suffering from genetic disorders, the benefits should include enabling individuals to take account of the information for their own lives, and empowering them as prospective parents to make informed choices about having children .
Although the screening test is not usually in itself diagnostic, it detects a subgroup of those tested who are at higher risk of having the disease or disorder than the original population screened, in many cases it is possible to make diagnoses with considerable accuracy.
Three different types of ANS methods are widely used
– to ensure optimal treatment of affected infants through early diagnosis .
Q& a: Using Codes Z21 And B20 For Hiv Patients

Sharme Brodie, RN, CCDS,answered this question.
Q: I have a question about coding human immunodeficiency virus and HIV-related illnesses. If a physician documents a patient is HIV positive, should the chart be coded to Z21? What about if they document the patient is HIV positive with an HIV-related illnesswould that be coded to B20?
A: You are correct. The ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting, Section I.C.1.a.2.f. says that patients who are HIV positive with any known prior diagnosis of an HIV related illness should be coded to code B20. Only confirmed cases are coded using code B20. HIV is one of three conditions that cannot be coded based on the documented terminology, possible, probable, or suspected, or any other similar terminology.
It is not required that any form of testing be documented, such as a positive serology test. The physicians diagnostic statement that the patient is HIV positive with a prior HIV-related condition is all that is necessary for coding. Once a patient is coded to B20, they will always have B20 coded on their record they will never go back to being coded using the asymptomatic code Z21.
Editors Note: Sharme Brodie, RN, CCDS, CDI education specialist and CDI Boot Camp instructor for HCPro in Middleton, Massachusetts, answered this question. For information, contact her at . For information regarding CDI Boot Camps, .
Don’t Miss: Does Nba Youngboy Really Have Herpes
Initial Evaluation: Physical Examination
A complete physical examination should be performed at the initial encounter, with particular attention given to the oral, integumentary, and lymph node examinations. The key components of the physical examination as outlined in the HIVMA/IDSA Primary Care Guidance include:
- Vital signs and General Appearance: including height and weight, evidence of obesity, wasting, or lipodystrophy
- Skin: rashes, bruising, inflammatory dermatoses, cutaneous lesions, and cutaneous manifestations of systemic disease
- Lymph nodes: generalized or localized lymphadenopathy
- Eye: retinal exudates or cotton wool spots, hemorrhages, pallor, icterus
- Oropharynx: abnormalities of dentition, gingiva, or mucosa including ulcers, candidiasis, and oral hairy leukoplakia
- Cardiovascular: peripheral pulses, auscultation, and presence/absence of edema
- Chest: auscultation for breath sounds, airway movement, and wheezing
- Breast: nodules, nipple discharge
- Genitourinary: ulcers, warts, discharge, and appearance of cervix on gynecologic examination
- Anorectal: ulcers, warts, fissures, hemorrhoids, masses
- Neuropsychiatric: speech problems, gait abnormalities, focal deficits , headaches, seizures, signs of dementia or memory impairments, depression and anxiety inventory, signs of drug or alcohol intoxication
I Found Out I Am Positive For Htlv What Precautions Should I Take To Avoid Infecting Others
You can take several steps to avoid spreading the infection, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention:
- Tell your health care practitioner that you have been infected he or she can speak with you about necessary precautions.
- Do not donate blood, tissues, organs, or sperm.
- If you are a new mother, do not breastfeed.
- Do not share needles or syringes.
- Use condoms to prevent sexual transmission.
You May Like: How Long Can Hiv Be Dormant In Your System
Laboratory Criteria For Hiv Diagnosis
The CDC has established the following laboratory criteria to meet the 2014 case definition for HIV .
Obtaining a CD4 cell count as a surrogate marker to indicate HIV infection and the degree of immunosuppression is not recommended since CD4 counts can markedly decline without HIV in the setting of acute illness, bone marrow suppression, or chronic hepatitis C virus infection.
Medical Coding For Hiv Screening And Diagnosis
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus or HIV is a retrovirus that affects the human immune system and allows people become much more susceptible to infections and diseases. This virus found in body fluids of the infected person is passed from one person to another through sexual contact, prenatal transmission and blood transfusion. Though HIV infection leads to the development of AIDS, it is possible that the patient may get infected with HIV without developing AIDS. In most cases, HIV infection progresses without proper treatment which will eventually develop into AIDS. HIV screening and diagnosis identifies the infection in the early stages, helps to slow down the rate at which the virus replicates and delays the development of AIDS. Proper medical coding of screening procedures on the medical claims is essential on the part of physicians or medical coding companies to ensure accurate documentation and appropriate reimbursement.
HIV Testing, Treatment and Importance of Early Diagnosis
HIV screening and testing guidance continues to evolve depending upon the changes in testing technology and methods to reach patients. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has published the updated federal guidance on HIV screening and testing for physicians, nurses, administrators, clinical coordinators, program managers and laboratory personnel who test specimen.
Reporting HIV Infection on Medical Claims
ICD-9 Codes
- V08: Asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus infection status
Don’t Miss: Does Nba Youngboy Still Have Herpes
When Is It Ordered
HTLV testing may be performed when a person has symptoms or findings that suggest that the person has a condition associated with an HTLV-I or HTLV-II infection, especially when that person also has identified risk factors.
Signs and symptoms of adult T-cell lymphocytic leukemia or lymphoma may include:
- Fever
- Increased number and abnormal immature lymphocytes
- Enlarged lymph nodes
Symptoms of HTLV-Iassociated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis may include:
- Weakness in the lower limbs
- Muscle spasms and contractions
- Urinary, bowel, and sexual dysfunction
Testing may be performed on:
- A mother when her child has been diagnosed with an HTLV infection
- The sexual partner of a person when that person has been diagnosed with an HTLV infection
- A person when he or she has been told that the blood that the person donated was positive for HTLV-I/II
- A person when he or she has risk factors and symptoms that the healthcare practitioner suspects may be linked to an HTLV infection, such as uveitis, dermatitis, or arthritis